APHUG 1-3
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
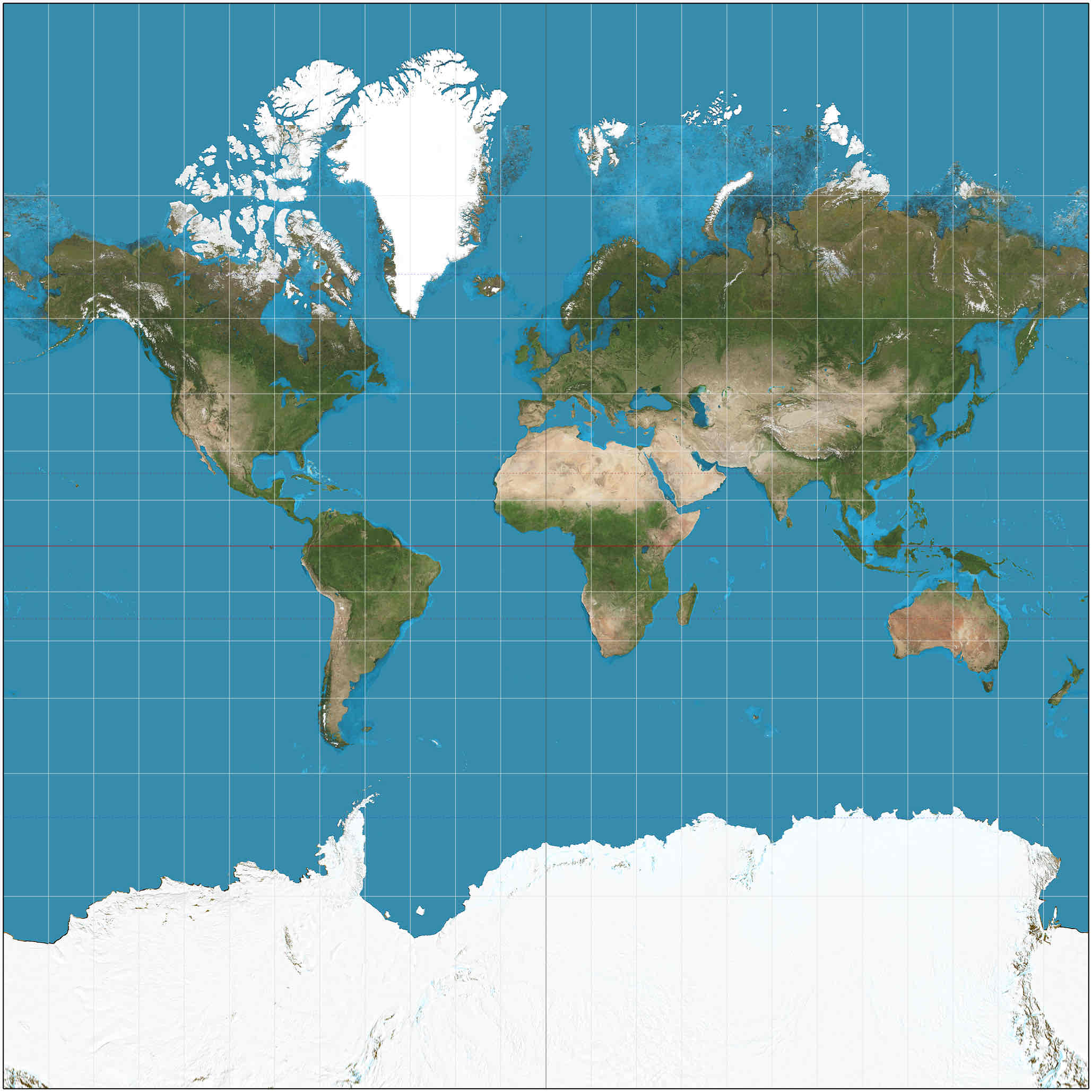
Mercator Projection
Distorts size and shape but is good for navigation
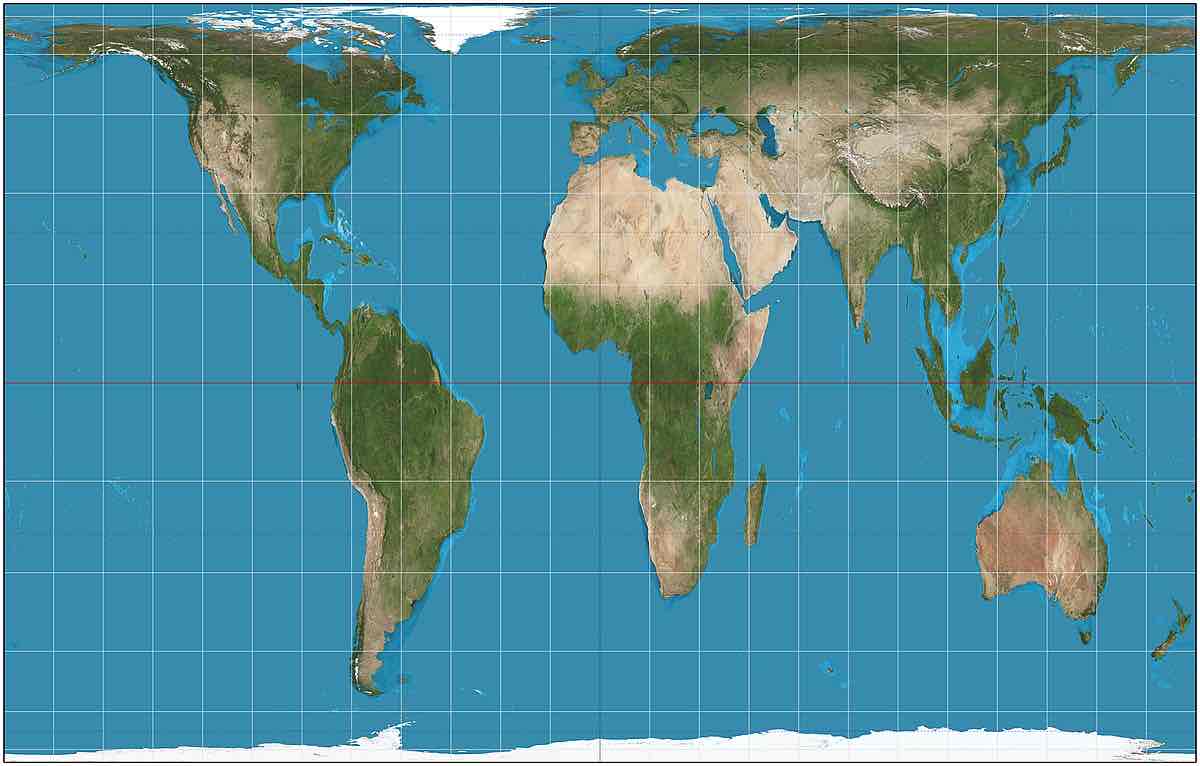
Gall-Peters Projection
Distorts shape and lines but is good for size
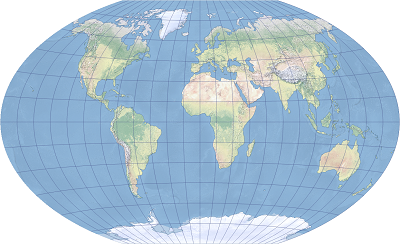
Winkel Tripel Projection
This map is the reference map, compromising on everything
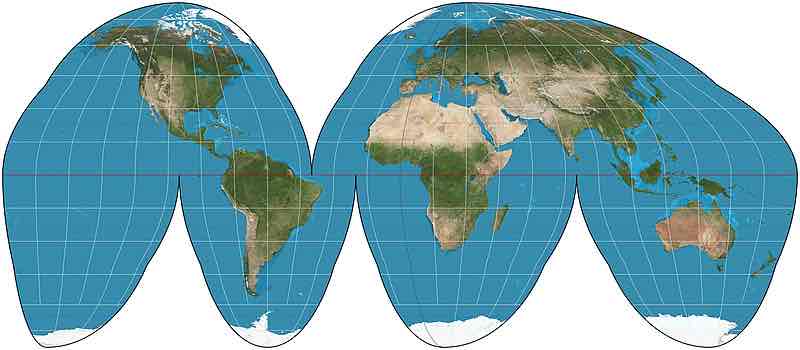
Goode Homolosine Projection
Distorts distance and cuts oceans but is good for size
Site
The physical character of a place
Absolute location
The exact position of a place on the earth's surface.
Relative location
The position of a place in relation to another place
Assimilation
One culture's features are altered to resemble another group
Acculturation
Changes experienced by both groups but the cultural features remain
Syncretism
Combining two groups to form a new culture
Diffusion
The process by which a feature spreads
Relocation diffusion
People move & take their ideas/items with them
Expansion diffusion
Ideas/cultural traits spread without physical movement
Hierarchical diffusion
The spread of an idea from nodes of authority or power to other places
Contagious diffusion
A rapid widespread diffusion of a characteristic throughout the population
Stimulus diffusion
A spread of a principle even if the characteristic does not spread (McDonalds)
Hearth
A place from where an innovation originates
Physiological Density
population per unit of arable land
Agricultural density
Farmers per amount of arable land
TFR (total fertility rate)
How many children are predicted a woman will have in her child bearing years
CDR (Crude Death Rate)
The share of population that dies per year
Describe demographic transition in stage 1 & give an example
High births, high deaths, low but growing population
Describe demographic transition in stage 2 & give example
High births, high but decreasing deaths, growing population
Describe demographic transition in stage 4 & give example
Decreasing then stable birth rates at low, stable low death rates, increasing to stable population (still growing)
Dependency ratio
How many people are dependent on their economy
Developed countries compared to undeveloped countries & example of each & where they are roughly on demographic transition model
Developed countries have many more industrial aid healthcare benefits than undeveloped countries
What are some pronatalist policies
Education & healthcare discounts or benefits
What are some antinatalist policies
Giving women more opportunities for education & jobs
What is the China one-child population
Could only have one child, people would get punished for more. Policy was dropped in 2015
Why have birth rates been declining in developed countries
Women have more education and job opportunities
Why have birth rates not decreased in undeveloped countries
Women are expected to have more than one child, and usually do not have any other opportunities
Give definitions of transnational & internal migration
Transnational migration: When you cross political borders
Internal migration: Moving to a different region in that country
What are all of Ravenstein's laws of migration
-Young
-Looking for jobs
-Man
-Chain Migration
Remittances
Workers sending money to people in the country the emigrated from
What is the difference between immigration and emigration
Emigration refers to someone moving out of a place while immigration refers to someone moving to a place
Refugee
Someone who was forced to migrate from fears
Internally displaced person
Similar to a refugee but does not cross borders
Asylum seeker
Someone who migrates to a different country hoping to be seen as a refugee
Centripetal force
Brings people together
Centrifugal force
Pulls people apart
Habit
Repetative action from one person
Taboos
Norms that are crucial
What are the 4 largest religions
Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism
Environmental determinism
Humans can alter their environment
Possibilism
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment.