ap bio u5
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
chromosome
tightly coiled package of DNA molecules and associated proteins
gene
carries info for protein making (determines organism traits)
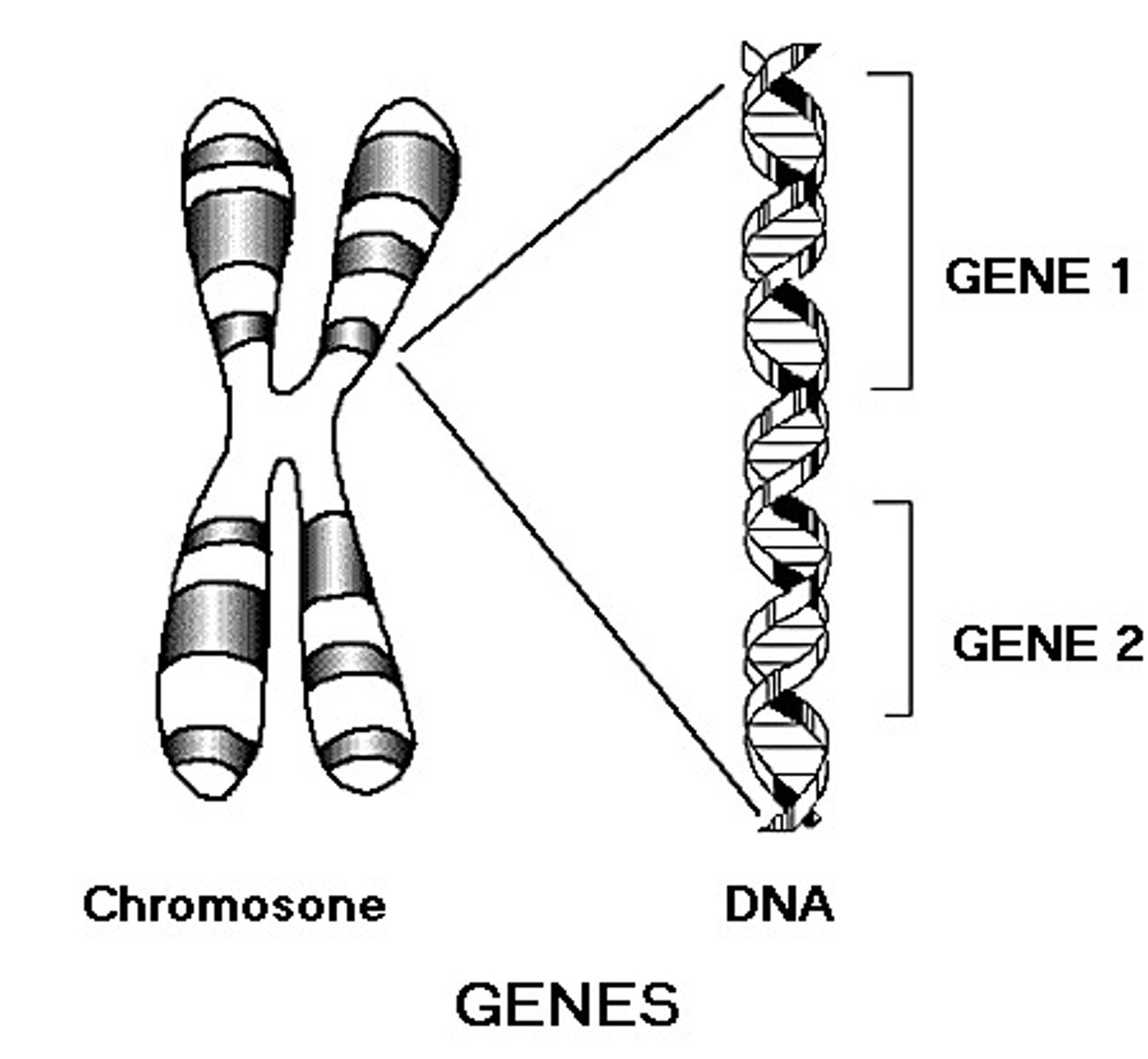
allele
different forms of a gene
genotype
set of genes that an organism carries
phenotype
physical/visible traits of an organism
asexual reproduction + result
a single parent reproduces by itself
*results in genetically identical offspring
sexual reproduction + result
two parents combine their genetic material to produce a new organism
*results in genetically different offspring
*MORE ENERGETICALY EXPENSIVE
haploid
one copy of each chromosome (no homologous pairs)
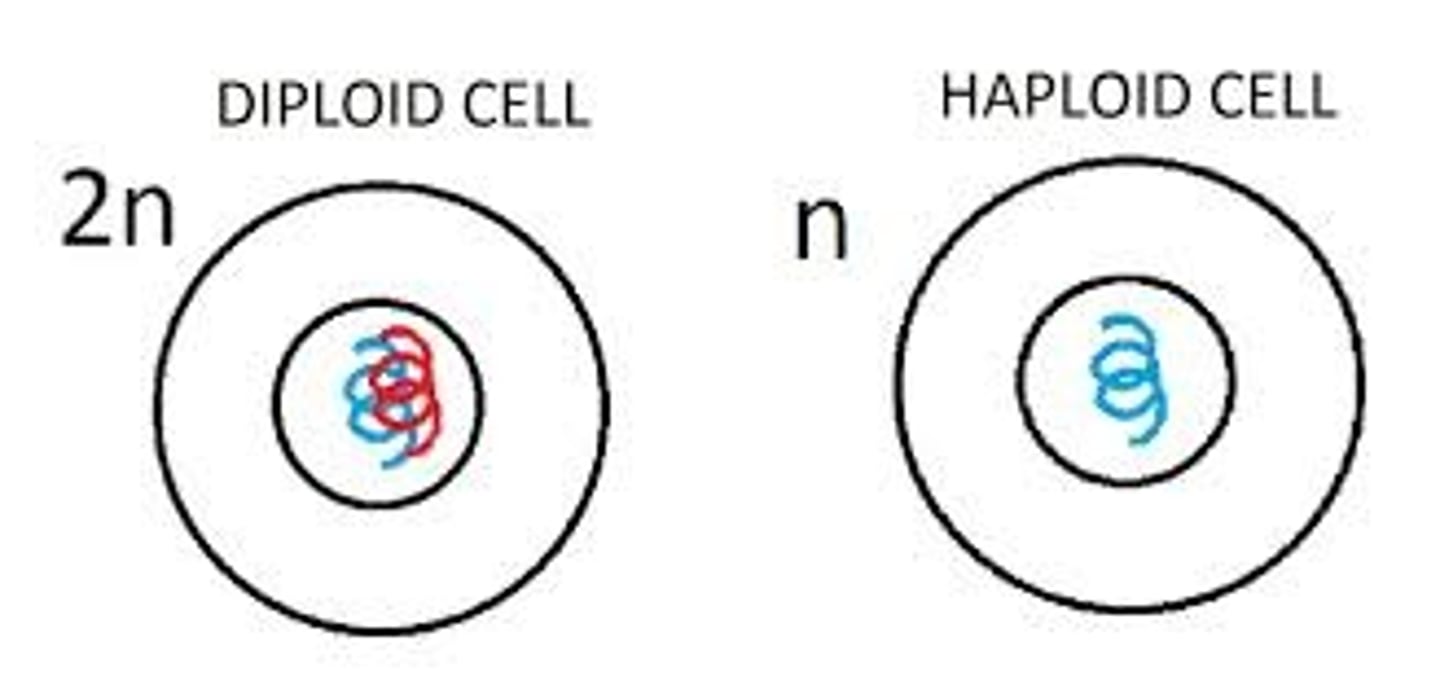
diploid
two copies of each chromosome (homologous pairs)
gametes
haploid sex cells (egg cells in females and sperm in males)
zygote
fertilized egg that results from fusion of male and female gametes
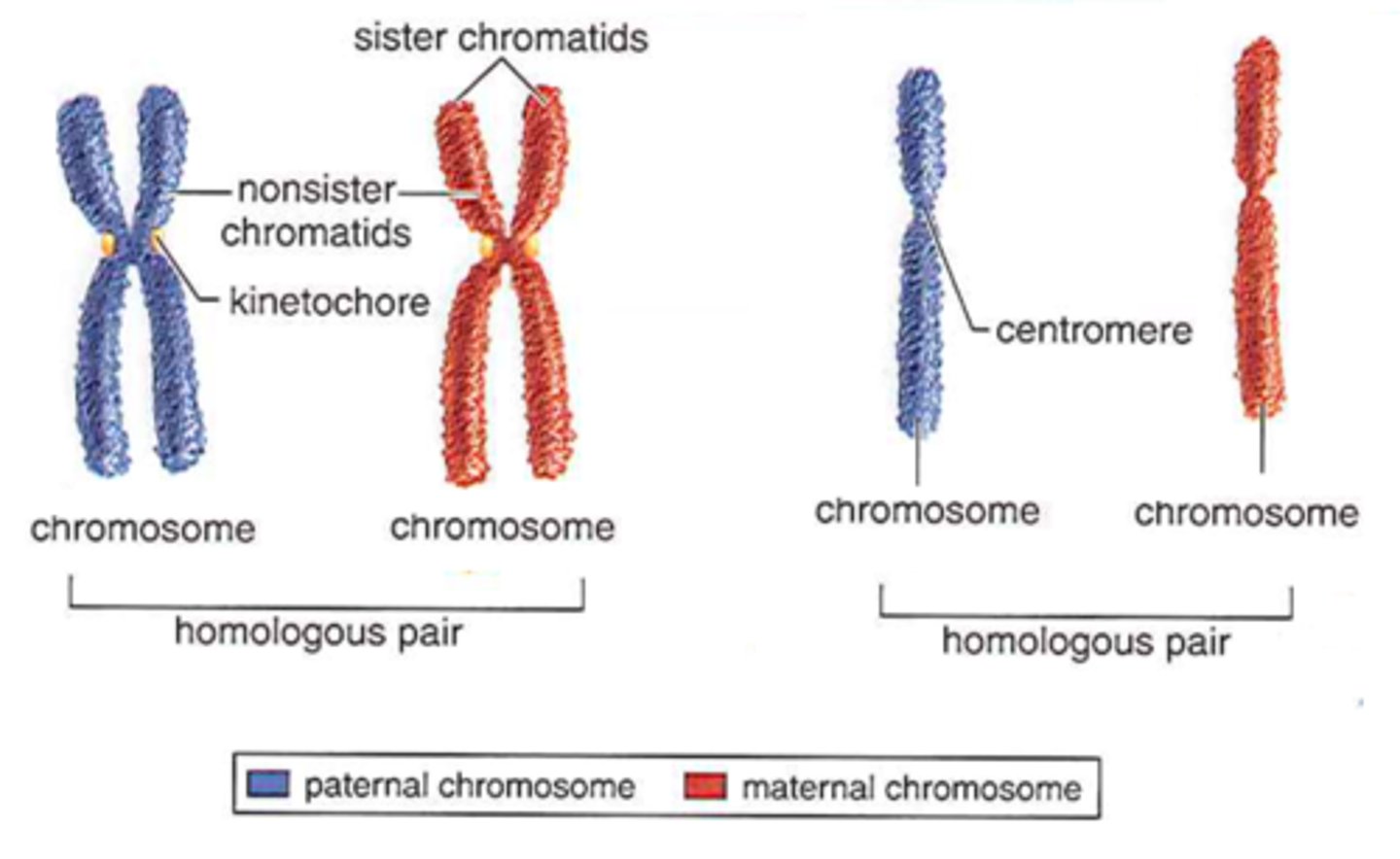
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes that are similar in size and shape + carry the same genes
meiosis
purpose: create gametes (sperm & egg cells) for reproduction
1 diploid parent cell => 4 haploid daughter cells
meiosis results in daughter cells w how many chromosomes?
half the # of chromosomes of the parent cell
prophase I
synapsis: homologous chromosomes stick side-by-side
crossing-over/recombination: chiasma forms & segments are exchanged btwn non-sister chromatids

metaphase I
chromosome pairs RANDOMLY align at center (with spindles attached)
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes move to opposite sides of cell (SISTER CHROMATIDS STAY TGT)
autosomes
any chromosome that isnt a sex chromosome
(22 pairs of chromosomes)
telophase I and cytokinesis
nuclear membrane forms & separates into 2 cells
meiosis II
separate sister chromatids
prophase II
nuclear envelope breaks & chromosomes condense
metaphase II
chromosomes align @ center (single file)
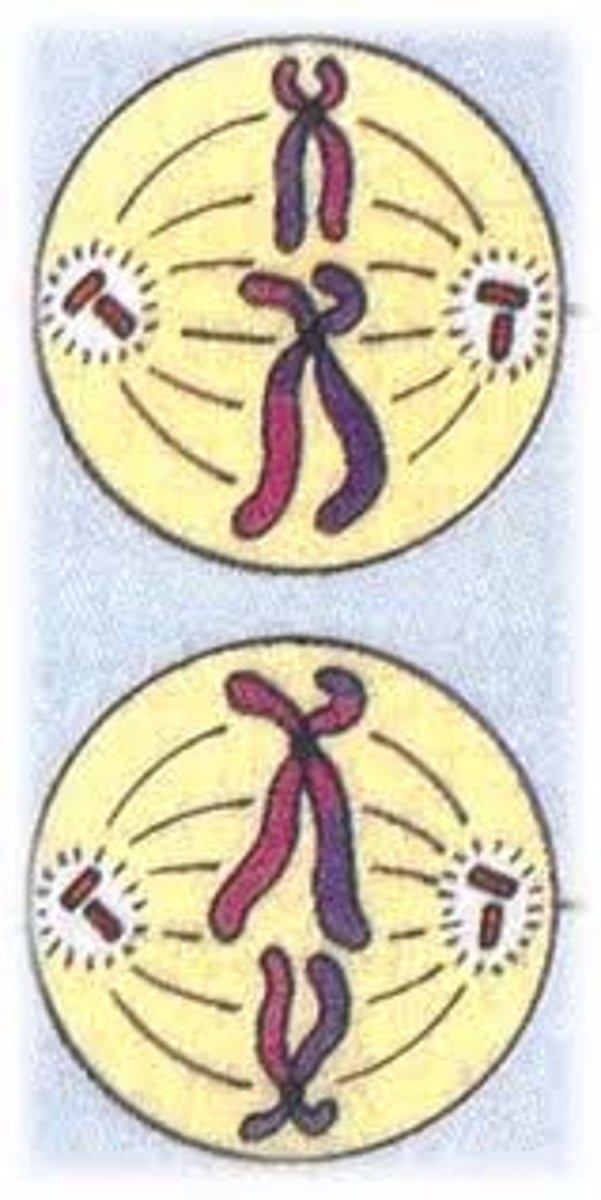
anaphase II
sister chromatids separates
telophase II
nuclear membrane forms
=> FOUR HAPLOID CELLS PRODUCED
mitosis vs meiosis (5 diffs)
MITOSIS: occurs in body cells
MEIOSIS: occurs in sex cells
MITOSIS: produces identical cells
MEIOSIS: produces sex cells (eggs/sperm)
MITOSIS: diploid cell => diploid cell
MEIOSIS: diploid cell => haploid cell
MITOSIS: 1 cell => 2 cells
MEIOSIS: 1 cell => 4 cells
MITOSIS: 1 division
MEIOSIS: 2 divisions
recombination frequency =
map distance btwn genes on the same chromosome
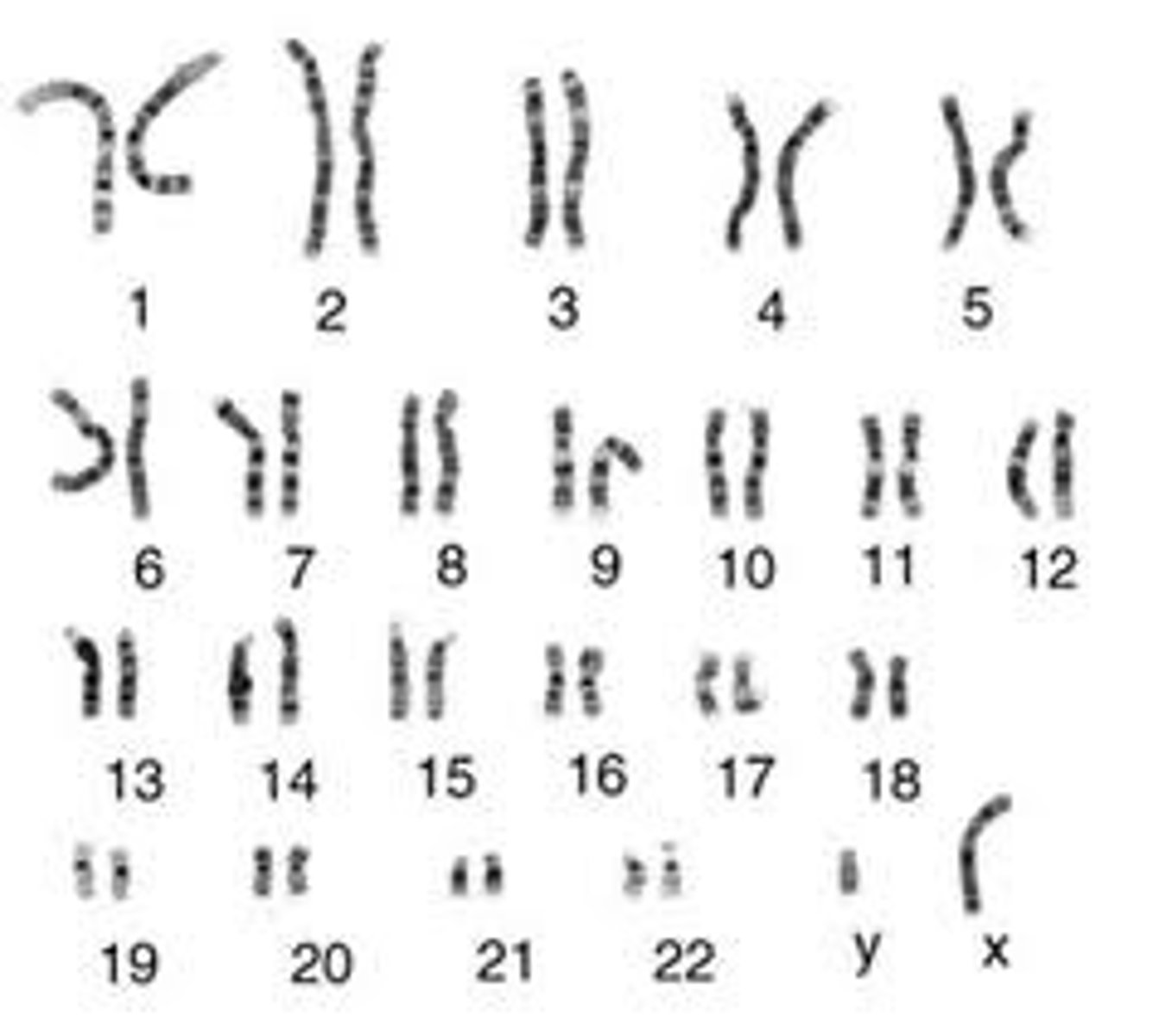
karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape
epistasis
when one gene modifies the expression of another gene
linked genes
physically located near each other in the same chromosome
*inheritance patterns for the linked genes are usually matched, but depends on genetic distance btwn the two genes
sex-linked genes
genes that are located in only one of the two sex chromosomes
x linked: located in only the x chromosome
y linked: located in only the y chromosome
inheritance of X-linked vs Y-linked traits
X linked:
*depends on whether or male/female carries the allele
Y linked:
*females cannot inherit the allele or transmit the allele
*all sons of affected fathers will be affected
maternal inheritance + examples?
organelles are transferred from mother to offspring
(eg. mitochondria and chloroplast)
incomplete dominance
BLENDING (neither is dominant)
red + white = pink
codominance
BOTH traits are expressed
type A + type B = type AB
phenotypic plasticity
ability of genotype to produce diff phenotypes in response to the environment
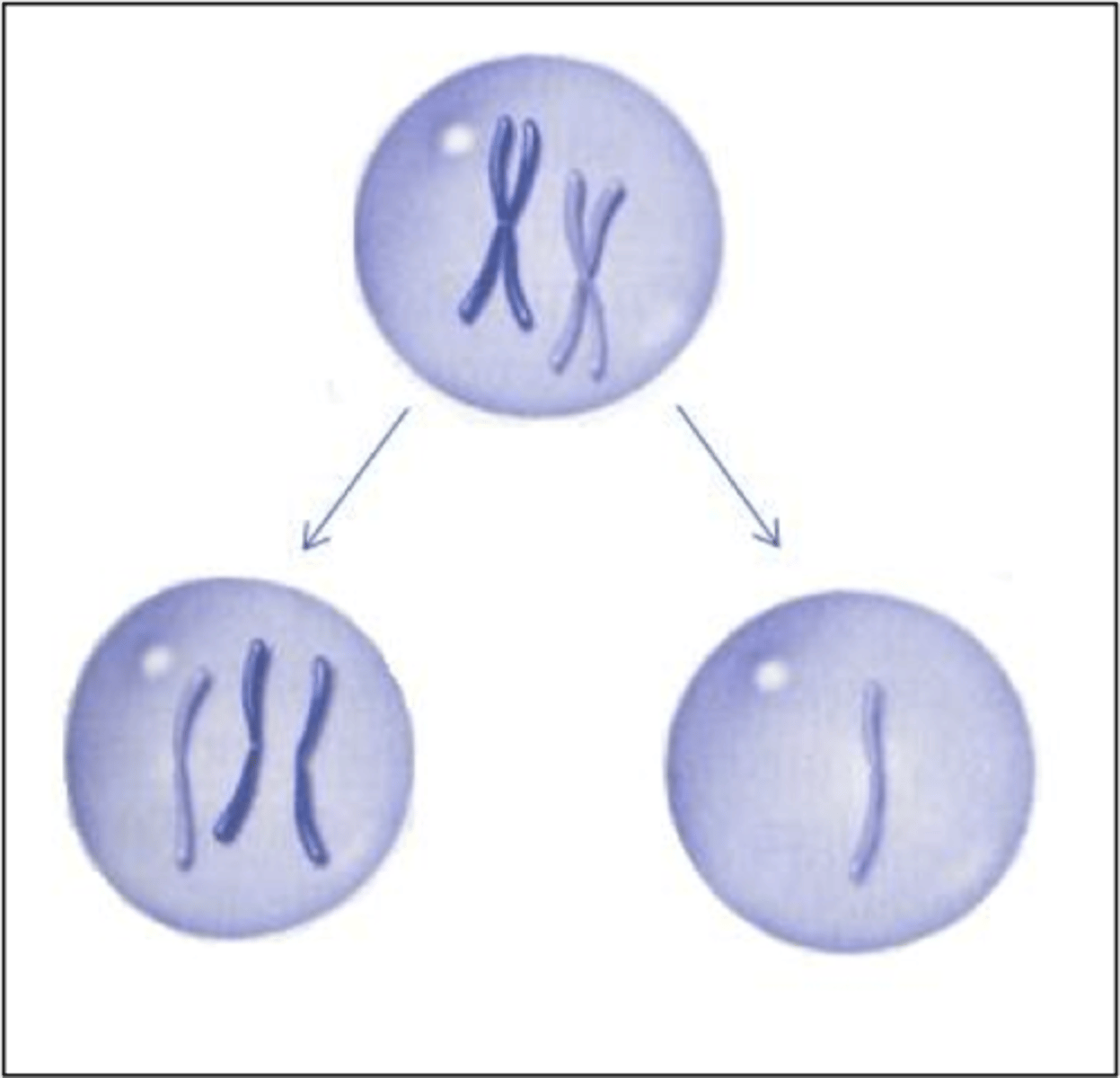
nondisjunction + where it can occur
chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis
(anaphase I or II)
translocation
segment(s) of a chromosome break and are lost or reattached to another chromosome
law of dominance
a dominant allele will express itself over a recessive allele
monohybrid cross
a cross in which only one characteristic is tracked
2x2 cross
law of segregation
pairs of alleles for a trait separate when gametes are formed
dihybrid cross (ratio?)
tracks the inheritance of two traits (each has 2 alleles)
4x4 punnett square
9:3:3:1 RATIO
AA : Aa : aA: aa
law of independent assortment
each member of a pair of homologous chromosomes separates independently of the members of other pairs so the results are RANDOM
polygenic inheritance
the combined effects of several alleles lead to continuous variation
mutations
change in DNA sequence (NOT caused by environ conditions)