Hematopoietic Function
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
hematopoiesis
the process of forming blood
5L needed
plasma
liquid of dissolved protein
transport medium for proteins
maintains colloid osmotic pressure and electrolyte/fluid balance
leukocytes
white blood cells involved in the inflammatory response
erythrocytes
red blood cells carry oxygen and transport carbon dioxide out of tissues
contain HBG that bind to oxygen
hemoglobin
carries oxygen
hematocrit
how much blood volume consists of erythrocytes
thromboplastin
a substance released by damaged cells which signals HELP
create a sticky surface and stimulate coagulation
plasmin
dissolves clots once healing has occurred
thrombocytes
platelets
when does hemtopoiesis begin
during early embryonic development only to deliver oxygen to developing organs
where does hematopoiesis occur in adults
primarily in the bone marrow along with the spleen and liver
what does the lymph system do
produces lymphocytes
liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and thymus produce monocytes
what influences the rate of hematopoiesis
the body’s needs and demands to replace old blood cells
erythropoiesis
formation of RBCs in response to hypoxia or ischemia
what is used for erythropoiesis formation
precursor/stem cells, vitamin B12, folic acid, and iron (for heme)
hypoxia
oxygen is needed so the body will make erythrocytes to deliver more oxygen to organs
infection
inflammatory response activated
WBC are made to fight infection
homeostasis
stopping blood flow in case of injury or clotting disorders
3 steps to homeostasis
vasospasm/vasoconstriction - restricts blood flow to injury
formation of platelet plug - prevents blood from flowing out
coagulation/clotting (fibrin mesh) - liquid to mesh
coagulation cascade
a complex interaction involving 12+ clotting factors
initiated with 20s of injury, may take several minutes to complete
heparin
given to pt to prevent and thin clotting damage
thromboxanes
cause platelets to swell, grow filaments, and clump
VW Factor
secreted by vessels
sticky to promote coagulation & platelet aggregation
thymus
site of t cell maturation
bone marrow
site of hematopoiesis
spleen
filters the blood of damaged/aged RBC
leukocytes normal range
5,000 - 10,000 cells/mL of blood
leukocytosis
increased WBC levels
*active infection
leukocytopenia
decreased WBC
*immune deficiency
neutrophils
first leukocytes to arrive at an infection cite phagocytize microorganisms to prevent infection from spreading
*create pus

neutropenia
condition where the concentration of neutrophils reaches <1,500 cells/mL
causes of neutropenia
increased usage of neutrophils (active infection)
suppression, reduced production, or death of neutrophils
congenital conditions
neutropenia manifestations
infections & ulcerations
fever
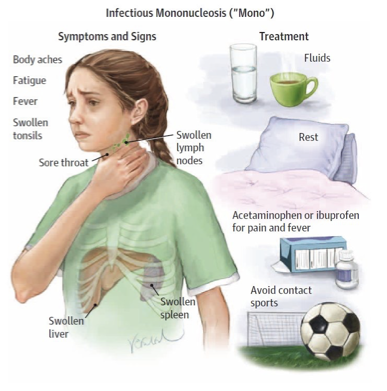
infectious mononucleosis
Mono aka kissing disease
spread by oral transmission
most prevalent in adolescents & young adults
causes of mono
epstein-barr virus in herpes family
infects B cells by killing them or incorporating into its genome
mono manifestations
onset after 4-8 wk incubation
anorexia, malaise, and chills
can lead to leukocytosis,, fever, sore throat, lymphopathy
acute phase 2-3wks
make take 2-3 months to revover
lymphomas
cancers affecting the lymphatic system
hodginks lymphoma
less common = better prognosis
solid tumors containing reed-Sternberg cells often originating in lymph nodes and upper body
B cell only
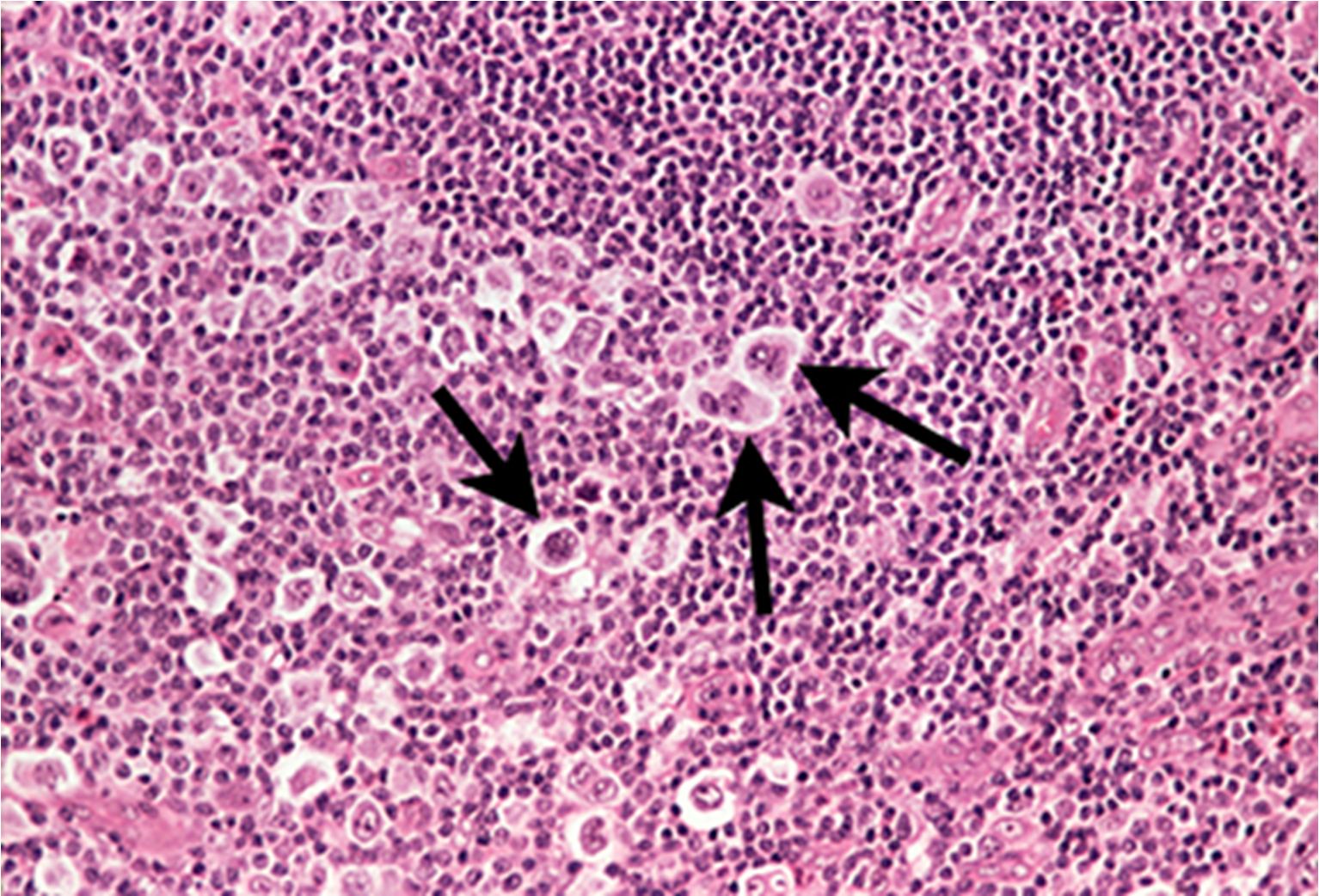
hodgkins lymphoma treatment
most curable with chemo, radiation, surgery
hodgkins manifestations
painless enlarged node, night sweats, pruritis, splenomegaly
only a single group of lymph nodes
non-hodgkin lymphoma
the BAD one
more common 90% = poor prognosis
resembles hodgkins
NO reed sternberg cells
B or T cells
difference of non-hodgkins
metastasize in an unorganized manner
metastasis is often present at diagnosis
difficult to treat, poor prognosis
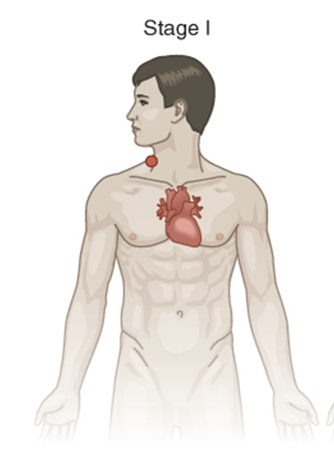
stage 1 lymphoma
found in lymph node group or only 1 part of a tissue or an organ
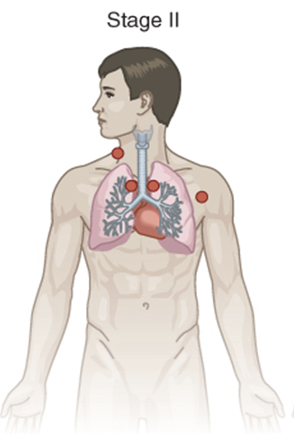
stage 2 lymphoma
cells are in at least 2 lymph groups on the same side of the diaphragm
OR are in one part of a tissue or organ on the lymph nodes near that organ, still on the same side of diaphragm
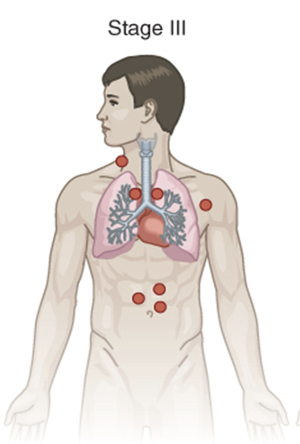
stage 3 lymphoma
cells are in the lymph nodes above and below the diaphragm
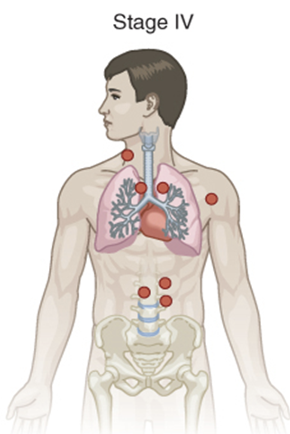
stage 4 lymphoma
cells are found in several parts of one or more organs and tissues and in distant lymph nodes
leukocytes normal count
4,000-11,000 cells/mL
leukemias
cancel of the leukocytes
2nd most common blood cancer
most common childhood cancer
leukemia pathology
they abnormally proliferate and crowd normal blood cells
risk facts of leukemia
mutagens
smoking
chemo
immunodeficiencies
men > women
white >
acute leukemia
less differentiated
good prognosis
chronic leukemia
more differentiated
okay prognosis
chronic leukemia
responds poorly to therapy
myeloid leukemia
improved prognosis by allogenic bone marrow transplant
manifestations of leukemias
leukopenia/anemia/thrombocytopenia
lymphadenpathy
joing swelling, bone pain, WL, anorexia
hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
CNS dysfunction
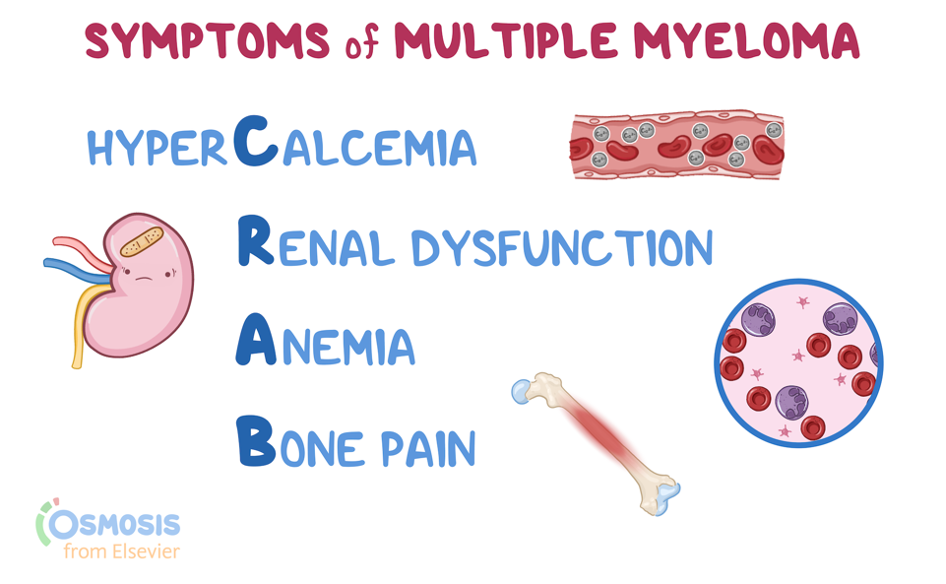
multiple myeloma
cancer of the plasma cells
3rd most common blood cancer in the US
non curable
excessive number of abnormal plasma cells in the bone marrow which cause Bence Jones protein excretion in uring
symptoms CRAB
hypercalcemia
renal dysfunction
anemia
bone pain
RBC normal cound
4.2-5.9 million cells/mcL
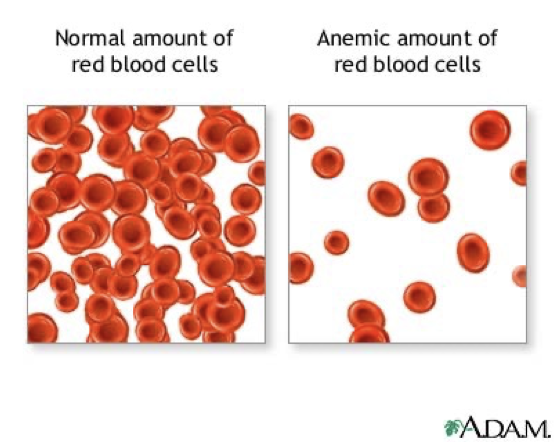
anemia
RBC disease
decreased number of RBC, reduction of HBG, or abnormal HBG
decreases oxygen-carrying capacity creating hypoxia
anemia manifestations
weakness, fatigue, pallor, syncope, dyspnea, tachycardia
iron-deficiency anemia
most widespread most commonly seen in women of childbearing age
iron manifestations
cyanotic sclera
brittle nails
decreased appetite
headache
irritability
stomatitis
pica
delayed healing
pernicious anemia
vitamin B12 deficiency usually caused by a lack of intrinsic factor
leads to decreased maturation, cell division, & protential neruologic complications
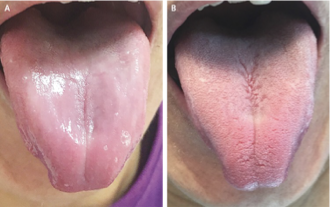
pernicious anemia manifestations
bleeding gums, diarrhea, impaired smell, loss of deep tendon reflexes, anorexia, personality or memory changes, positive Babinski’s sign, stomatitis, paresthesia, unsteady gait
pernicious anemia treatment
B12 injections, not PO bc body cant absorb
aplastic anemia
bone marrow fails to make enough RBC
potentially insidious, sudden, & severe onset
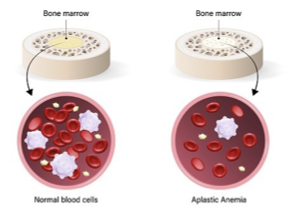
causes of aplastic anemia
idiopathic, autoimmune, medical, viral, or genetic
aplastic anemia manifestations
anemia, leukocytopenia, thrombocytopenia symptoms
hemolytic anemia
results from excessive RBC destruction (hemolysis)
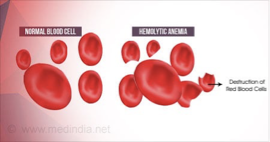
causes of hemolytic anemia
idiopathic, autoimmune, genetic, infections, blood transfussion reactions, blood incompatibility
types of hemolytic anemia
sickle cell, thalassemia, erythroblastosis fetalis
sickle cell anemia
a codominant disorder
hemoglobin S causes RBC to carry less oxygen and clog vessels leading to hypoxia & tissue ischemia
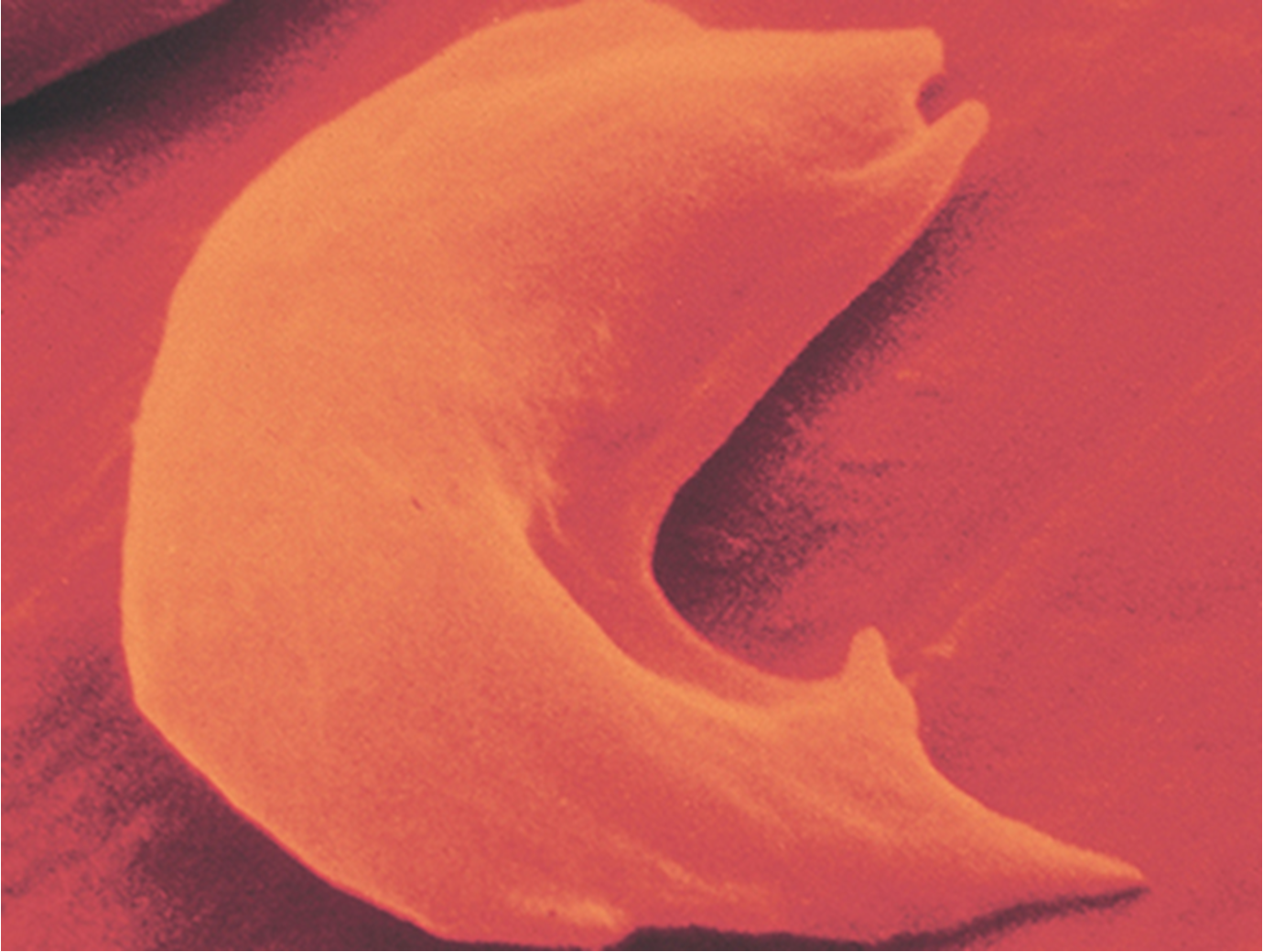

heterozygous sickle cell
less than half of RBC are sickled
homozygous for sickle cell
almost all erythrocytes are sickled
manifestations of sickle cells
around 4months
Sickle cell crisis: painful episodes of ischemia & necrosis
sickle cell triggers
dehydrations, stress, high altitudes, fever, extreme temperatures
thalassemia
autosomal dominant inheritance
abnormal HBG due to lack of either alpha or beta globin (make up HBG)
most common in mediterranean/asian/indian/african
major issues with thalassemia
hypercoagulability
ineffective erythropoiesis
hemolysis
thalassemia manifestations
abortion, growth and developmental delays, fatigues, dyspnea, heart failure, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, bone deformity, jaundice
polycythemia vera
abnormally high RBC and BV and viscocity leading to ischemia and necrosis
complications of polycythemia vera
thrombosis, hypertension, heart failure, hemorrhage, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, acute myeloblastic leukemia
clinical manifestations of polycythemia vera
cyanotic/plethoric skin, hypertension, tachycardia, dyspnea, headaches, vision impairment
normal platelet count
150,000 - 350,000 cells/mL
thrombocytosis
increased platelet level
increases risk of thrombus formation
thrombocytopenia
decreased platelet levels
increased risk of bleeding & infection
hemophilia A
X-linked recessive bleeding disorder caused by deficiency or abnormality of clotting factor VIII
von willebrand disease
most common herditary bleeding disorder
decreased platelet adhession and aggregation
VWD manifestations
bleeding
indications of bleeding
most common in women due to menstruation and childbirth
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
life threatening complication that occurs from many conditions springing from and inappropriate immune response
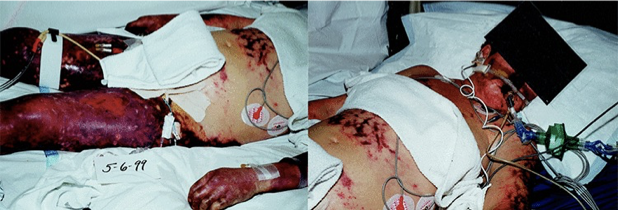
DIC manifestations
tissue ischemia
abnormal and massive bleeding
complications of DIC
shock
multisystem organ failure
immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
hypocoagulation due to autoimmune destruction of platelets
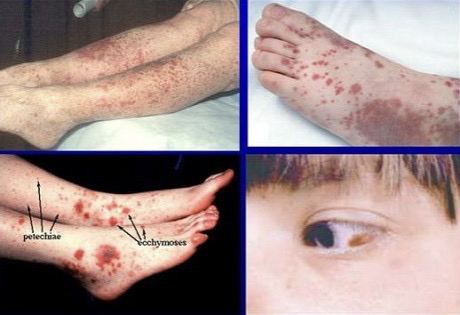
causes of ITP
idiopathic, autoimmune disease, live vaccine immunization, immunodeficiency disorders, viral infections
manifestations of ITP
bleeding
indications of bleeding
treatment of ITP
glucocorticoid steroids, immunoglobulins, plasmapheresis, platelet pheresis
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
caused by a deficiency in the enzyme that cleaves VWF leading to hypercoagulation that depleted platelet levels
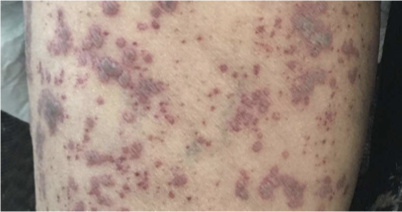
causes of TTO
idiopathic, hereditary, bone marrow transplant, cancer, medication, pregnancy, HIV
manifestations of TTP
purpura, consciousness changes, confusion, fatigue, fever, headache, tachycardia, pallor, dyspnea with exertion, speech changes, weakness, and jaundice
