LING 316 - Learning Sound Patterns
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What makes each language unique?
Each language has its own set of sounds (phonemes) and rule for combining them
Like Lego sets → each language has different shaped blocks and different building instruction
What is the “melodic system” of a language?
The tune of speech → tone, stress, length, etc.
Think of English stressing syllables like a drum beat vs. Chinese using tones like musical notes
What sounds does a fetus hear in the womb?
Mostly muffled background noises → mother’s heartbeat, blood flow, digestion, and some external sounds
Like hearing a concert through a wall → muffled, but still rhythmic
How well can a fetus recognize speech sounds?
About 30% of speech sounds are recognizable in the womb
What did Minai et al. (2017) test?
Whether fetuses in the third trimester can tell languages apart based on rhythm
What is the Rhythm-Based Language Discrimination Hypothesis?
Babies can distinguish language if their rhythms are very different
Like telling rap from opera → you don’t need to understand the words, the beat gives it away
How did they measure fetal processing (Minai 2017)?
Faster hear = more processing/attention
Heart speed measured by “inter-beat interval (IBI)”
What languages did they use and why (Minai 2017)?
English (stress-timed) vs. Japanese (mora-timed)
English has strong beats like drumming → Japanese has a steady and even rhythm like a ticking clock
How did they control for differences in speaker voice (Minai 2017)?
One bilingual speaker read both English and Japanese passages
How were the sounds played to the fetus (Minai 2017)?
Through a plastic cone and tubing placed 1 cm above the mother’s abdomen near the baby’s head
Mothers wore headphone so they didn’t react
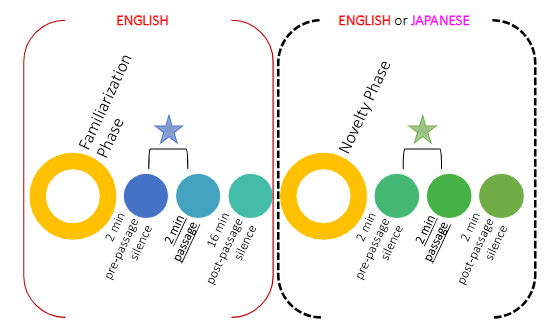
What was the procedure (Minai 2017)?
Familiarization phase → fetus hears English
Novelty phase → fetus hears either English again or Japanese (2 conditions)
Researchers compared IBI changes
What did they find (Minai 2017)?
Fetuses reacted when the language changed from English to Japanese
Shows fetuses can discriminate based on rhythm → not just sound content
What does this suggest about language learning (Minai 2017)?
Babies’ brains are already tuning into their native language properties before birth
Like downloading the “demo version” of your first language in the womb
Who were the babies tested in Mehler et al. (1988)?
4-day-old infants with French-speaking mothers
What method did they use (Mehler 1988)?
High-Amplitude Sucking Procedure (HAS) → pacifier test
When babies are interested → they suck harder/faster on the pacifier
How does HAS work?
Baby has a pacifier with a sensor
Sucking rate shows attention/interest
High Sucking = high interest
What are the phases of HAS?
Conditioning → baby learns that sucking makes a sound play
Habituation → baby hears the same sound repeatedly → gets bored → sucking slows
Testing → New sound is played
If sucking rate goes back up → baby noticed the change
If it stays low → baby didn’t notice a difference
Like Netflix auto play → if a new show comes on and you perk up, you noticed the change
What was Experiment 1 (Mehler 1988)?
French and Russian spoken by a bilingual speaker
4 Conditions:
French → French
French → Russian
Russian → Russian
Russian → French
What were the results of Experiment 1 (Mehler 1988)?
Babies noticed when the language switched (French to Russian - vice versa)
How was Experiment 7 different (Mehler 1988)?
Same as Exp 1 but speech was filtered at 400 Hz → mimics muffled womb hearing
What did the results of Exp 7 shows (Mehler 1988)?
Same outcome → babies still noticed the language switch
Even through the “womb filter” newborns could tell French and Russian apart