30: Type IV Hypersensitivity
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
another name for type IV Hypersensitivity
delayed-type hypersensitivity / T cell mediated
cells involved in type IV hypersens
CD4+ T cells, CD8+ CTL
whats the diff between type IV and the other hypersensitivities
it is t cell mediated, others are antibody mediated
delayed hypersens rxns occur from interactions between
antigen, APCs, t cells, macrophages
are Abs as important in type IV
no, cell-mediated instead
whys type IV called delayed hypersens
due to delayed appearance of response and symptoms
whats the goal of type IV mechanism
elimination of intracellular pathogens and if not eliminated, tissue destruction and granuloma formation occurs
describe the basic mechanism of type IV soluble antigen
APC presents tissue antigen
signals CD4 T cell and cytokines
leads to inflammation and tissue injury via neutrophil enzymes
describe the basic mechanism of type IV cell associated antigen
cell associated antigen presented to CD* CTLs resulting in cell death and tissue injury
clinical presentation of type IV rxns
induration, hard, raised lesions
erythema and vesicles, reddened skin and fluid filled vesicles
clinical examples of type IV hypersens
tuberculin reaction, contact dermatitis, stevens johnson syndrome
explain tuberculin reaction
after tuberculin is injected, its taken up by langerhans cells and migrate to lymph node. Here they are presented to memory T cells that generate Th1 effector cells who accumulate antigen around the antigen deposit with t cells.
in human and mice, tuberculin rxn tend to be predominated by
A/B t cells
sheep and cattle, tuberculin rxn tend to be predominated by
y WC1 T cells predominate
t or f: there are no B cells in the tuberculosis lesion
t
symptoms of tuberculosis
bad cough for 3 weeks, chest pain, coughing up blood, weakness, losing weight, no appetite, chills and fever, sweating at night
what is used to identify those suffering from TB
mycobacterial extract
symptoms of t-reaction
red hard swelling at injection site, starts after 12-24 hr, greatest intensity at 24-72 hrs. severe- tissue destruction and necrosis. lesions infiltrated w lymphocytes and macrophages.
human tuberculosis
mycobacterium tuberculosis
bovine tuberculosis
mycobacterium bovis (ZOONOTIC)
dog tuberculosis
mycobacterium canis
how does bovine TB spread
aerosol inhalation, ingestion of unpasteurized milk
wheres bovine tb occur
africa, asia, M.E
describe single intradermal TB test for cattle
-routine
-simple
-prone to false positives poor sensitivity
describe comparative TB test for cattle
-used when avain TB/johne’s disease is prev
-more specific than SID
-more complex than SID
describe short thermal TB test for cattle
-postpartum animals/infected animals
-high efficiency, time consuming
-anaphylaxis risk
describe stormont TB test for cattle
-postpartum/adv cases
-very sens and accurate
-3 visits req and may sensitize an animal
other skin tests for infectious diseases with cell immunity occurs
brucellin
mallein for glanders
histoplasmin
coccidioidin
toxoplasmosin
how long does allergic contact dermatitis occur after infection
48-72 hours
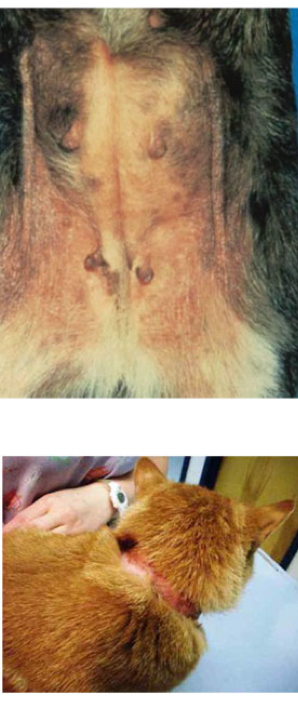
whats allergic contact derm
reactive chemical on skin triggers rxn by binding to PRRs like TLR4
describe the pathogenesis of allergic contact derm
-bind to skin proteins and act as hapten carriers to be recognized by skin macrophages (langerhans cells)
-present antigen to t cell in lymph node
-t cells produce IFN-Y and IL17 and activated cytotoxic t cells
-kill altered cells and see itching/sloughing of skin
how can allergic contact derm rxn get stronger
re-exposure over time
soruces of contact allergens in animals
insecticides, wood preserves, floor waxes, carpet dyes, paints, house plants, metals
how is allergic contact dermatitis diagnosed
-patch testing
-closed: suspected allergens attached to skin for 48-72 hrs and a pos rxn is erythema and vesiculation
open- solution of allergen is applied to skin and examined for 5 days
optimal therapy for allergic contact derm
identification and avoidance bc sensitization therapy not effective
steroids for acute and antibiotics for secondary
name the dermatitis: hairless areas, reactive chemicals, delayed response
allergic contact derm
name the dermatitis: mononuclear cell infiltration, vesiculation pathology.
allergic contact derm
name the dermatitis: hyperemia, urticaria, pruritus, face/nose/eyes/feet
atopic derm
name the dermatitis: foods/pollen/fleas, dx w intradermal testing w immediate response
atopic derm
name the dermatitis: mast cell and eosinophilic infiltration, edema. tx w steroids/antihistamine/hyposensitization
atopic derm
atopic derm is _____, type IV hypersens is_____
type I vs type IV
what kind of rxn is stevens johnson syndrome
mucocutaneous rxn
describe what stevens johnson syndrome is
t cell mediated hypersens to drugs (14 days after) usually antibiotics,sulfa drugs,NDAIDS
symptoms of steven johnson syndrome human
rash that blisters into vesicles, shed large areas of epidermis and develop skin ulcers (skin, lips, mouth, eyes, genitals)
symptoms of stevens johnson syndrome in dogs
dyspnea, fever, vomiting, weight loss. sloughing of skin over the nasal planum, footpads, oral/nasal/pharyngeal/conjunctival and preputial musosa
how do skin ulcers from stevens johnson syndrome occur
keratinocyte apoptosis. due to drugs/their metabolites binding to epidermal cells and triggering CD95L expression leading to CTL destruction
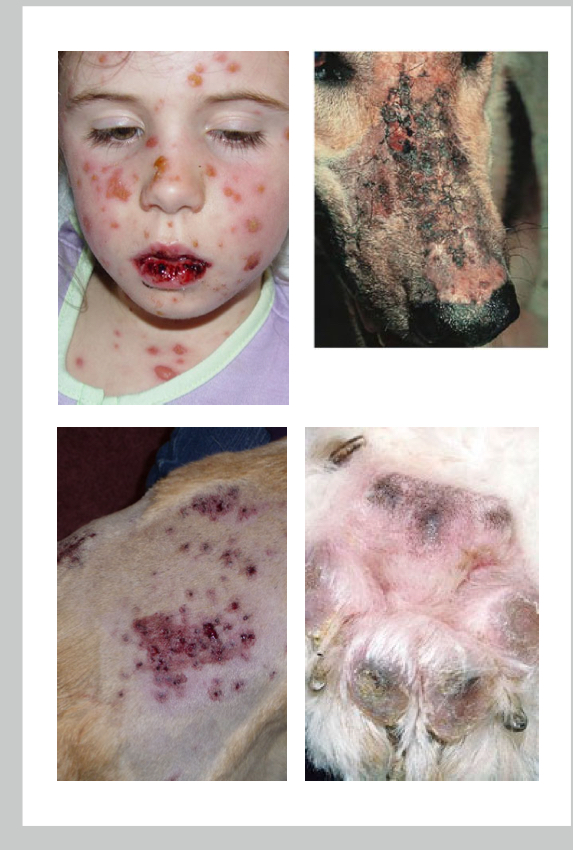
why is CD95L so bad for stevens johnson syndrome
triggers keratinocyte apoptosis leading to skin necrosis
summarize type IV
delayed
summarize III
immune complex
summarize II
antibody
summarize I
allergy/anaphylaxis
delayed hypersens rxns are mainly mediated by
t cells and macrophages
what is the slow developing inflamm response that occurs when reactive chemicals bind to skin cells and trigger t cell responses
allergic contact dermatitis