Comprehensive Business Types, Structures, and Models Overview
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Business
An organized group of people involved in professional, commercial, or industrial activities.
Profit
Selling a product or service to gain something in return; monetary rewards that create incentives for those involved in the business.
Value in Business
Economic benefits a company receives from consumers in exchange for what they sell.
Value
Money.
Industry
Group of businesses that are classified based on their main business activities.
NAICS
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) is used to classify businesses for data about the U.S economy by Federal statistical agencies.
SIC
The Standard Industrial Classification code used to identify the primary business of an entity assigned by the U.S government.
For Profit
Businesses focused on gaining a financial advantage or benefit; considered the most common type of business model.
Profitable Business
A business that financially makes more money than what they spent in operations at the end of a period.
Nonprofit
Businesses that focus primarily on pursuing a charitable, religious, artistic, education, or scientific purpose; do not seek to financially benefit from operations.
Nonprofit Organizations
Organizations that benefit by making changes in the community through their chosen efforts in education or welfare.
Government
Legal entities that act on the behalf of a country's government while providing commercial activities.
B2G
When 'For profit' businesses pursue government agencies through a Request for Proposal (RFP) where a project is announced and funded by qualified contractors.
Small Business
A small business is typically family or independently owned, profit oriented, and focused on a particular niche industry.
Medium Business
A medium business can be family owned, privately held, or sole proprietorships that sits between a small business and a large enterprise.
Large Enterprise
A large business (enterprise) is the 'poster-child' or most dominant brand that holds great influence in their respective industries.
Large Enterprise Definition
Defined as consisting of over 2,000 employees, dozens of operating locations, access to a wide range of resources, and a defined structure with different departments (HR & Public Relations, Marketing, Finance, Sales, etc...).
Large Enterprise Representation
Represent 3% of businesses in the United States (200,000) and account for a third of the private sector gross domestic product & jobs in the U.S.
SBA
The Small Business Administration is a popular lender in the United States and provides aid to exclusively small businesses through loans, contracts, and counseling.
SBA Functions
Strengthens the national economy and preserves free enterprise, utilizes the 'Size Standards Tool' and the 'Table of Size Standards' to calculate if a business is in the qualification range.
Retail
Businesses that sell goods and services to consumers; typically in smaller quantities for personal usage.
Retail Channels
Use multiple channels including but not limited to brick-and-mortar storefronts, direct mail, and online/websites.
Services
Businesses that provide services that are not tangible items including haircuts, plumbing & utilities, hospitality, healthcare, and cleaning.
Manufacturing
Businesses that focus on using raw materials to produce finished items that are sold to other companies or businesses.
Manufacturing Processes
Use human labor, machines, tools, processes, chemical, and technology.
Distribution
Delivering products and services from the manufacturer to the consumer; a company who distributes is considered a 'distribution channel'.
Distribution Channels
Can consist of manufacturer -> distributor -> retailer -> consumer.
Franchising
A marketing concept that focuses on expanding a business by licensing to others.
Franchisees
Buys into the franchise; benefits include gaining the rights to sell the service, brand, and processes.
Franchisor
Sells the rights for the franchise; benefits include charging the franchisee for the rights to the product or service.
Multilevel Marketing
Companies hire people as distributors to generate sales and expand company reach; they are needed to sell products and recruit others.
Multilevel Marketing Hierarchy
Fall under a hierarchy; pass on some profits to those above them.
Network Marketing
Companies hire individuals that will become part of a larger network while selling products and services.
Network Marketing Structure
Are NOT a part of any hierarchy.
Business Model
Highlights questions about the company and is the totality of the story told about the business; includes the process of generating to delivering.
Subscription Business
Consumers pay a subscription fee to enjoy a product or service.
Bundling
Goods and services are sold together at a discounted rate than being bought separate; generates demand and is more attractive to consumers.
Fremium
Basic services are offered for free and the premium services are offered for a charge.
Leasing
Companies offer businesses and consumers the offer to rent equipment instead of buying them; often charger lower & (without interest) more affordable prices.
Crowdsourcing
Businesses are able to receive knowledge, ideas, and work by breaking up a large project into smaller pieces that individuals online can work on.
Advertising-Supported Revenue
Businesses are able to provide content for free to users while selling ads to generate revenue.
Low Cost
Businesses are able provide a product or service at the lowest possible cost to pass on savings.
Peer-to-Peer
Businesses act as an intermediary for exchanges between goods & services and consumers.
Business Structure
Legal road map that guides the business for life, unless changed by the owners over time; must chosen before registering a business with a state & the government.
Legal Names
Used to register the business with the government.
Trade Names
Used for advertising and sales purposes (called 'the brand').
Sole Proprietorship
Easiest to set up for a business with low cost formation, extra tax deductions, and are easily dissolvable without paperwork.
Partnership
Two or more individuals join a legal agreement to form a for-profit business structure.
Limited Partnership (LP)
One partner has unlimited legal responsibilities while the rest have limited responsibility (less control over the business).
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Every owner has limited liability, considered the more beneficial option.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Owners, partners, and shareholders are able to form a business while protecting personal assets; still must conduct activities in a responsible manner.
Corporations
Any size company that is its own legal entity with its own rights, separate from the owners.
C Corporation
Corporation structures that can have unlimited investors (individuals or other entities) and are taxed as separate legal entities.
Double Taxation
Corporation pays taxes and shareholders pay taxes on dividends.
S Corporation
Corporation structure that is limited to 100 shareholders (U.S. citizens and residents) and avoid double taxation.
Pass-Through Taxation
Profits are divided and taxed at the shareholder level.
B Corporation
For-profit businesses that aim to balance profit with a purpose; focus on making a positive impact on society and the environment.
Cooperatives
Owned by the people they serve called members who vote on the cooperative's mission, business course, and profit sharing.
Business Functions
Processes and activities carried out to support operations and generate income.
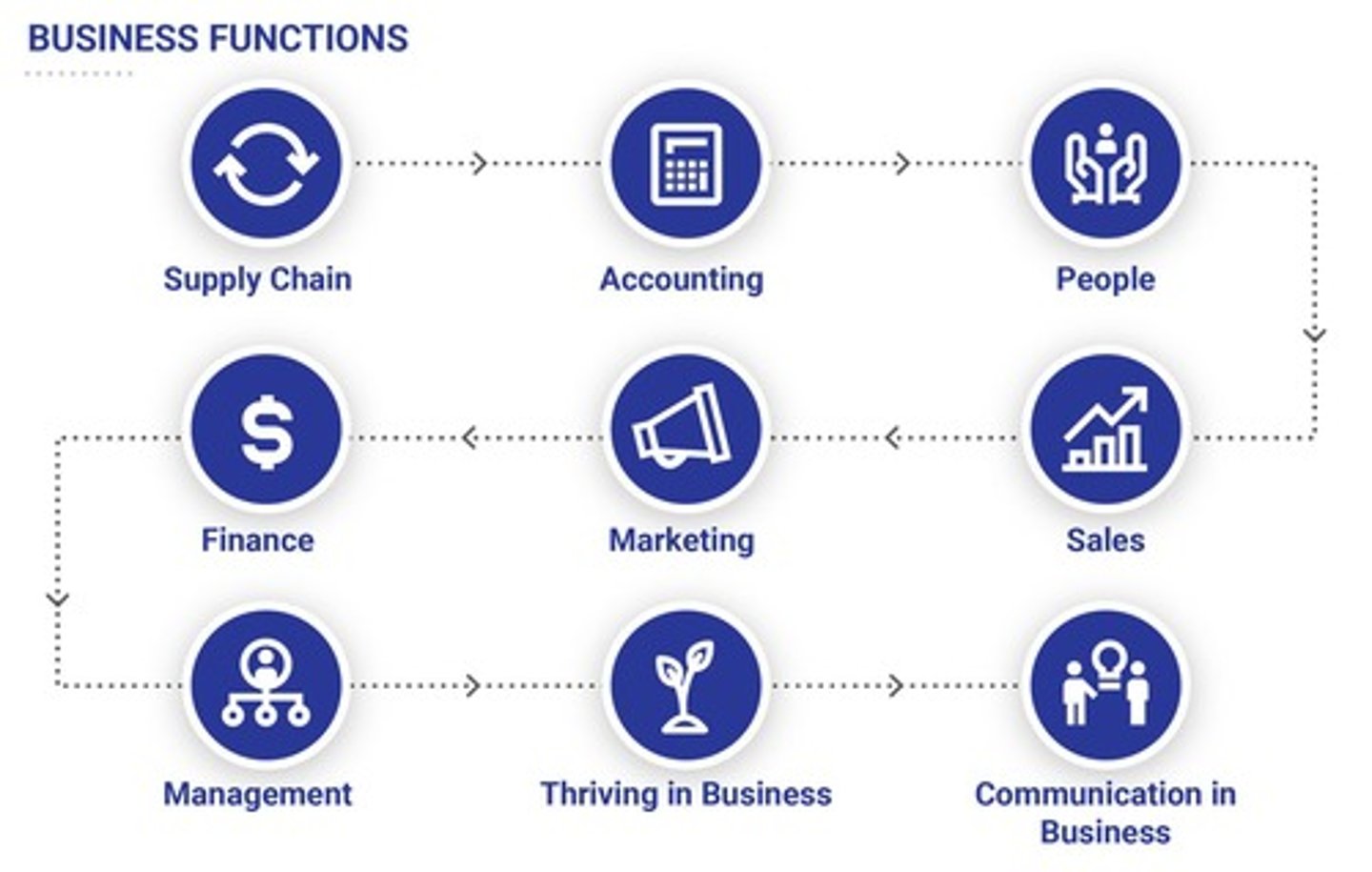
Supply Chain
Network between a business and its suppliers to distribute products.
Accounting
Financial system centered around collecting and analyzing financial information and overseeing monetary transactions.
Human Resources
The people who support a business by hiring, training, retaining, and promoting employees.
Negative Aspects of Business
Not paying taxes, Breaking Laws, Diminishing local pride, Abusing natural resources, Contaminating the environment, Engaging in questionable business practices.
Entrepreneurial Disadvantages
Takes time to become well established, Must work long hours, Healthcare is expense, and as such many entrepreneurs go without it.
Finance
Manages the planning and control of a business' financial resources to promote efficient operations.
Marketing
Supports a business by selecting who products will be aimed towards and how they will be served.
Sales
Focuses on the transactions of an exchanged product or service; oversees the business prospecting.
Management
Process of planning, decision making, organizing, leading, and motivating the people, financial, physical, and informational resources of a business to reach its goals.
Thriving in Business
Taking care of self matters that redefine success, failure, resilience, emotions, and focus on adaptability & ethics.
Communicating in Business
Focuses on learning to communicate, establishing support, and influencing people positively.
Market Based Business Statement
Explains what a business does along with their purpose, who they serve, what they do differently or better than others, and what their values & culture are.
Stakeholders
Any individual or party with an interest in the business and the outcome of its actions.
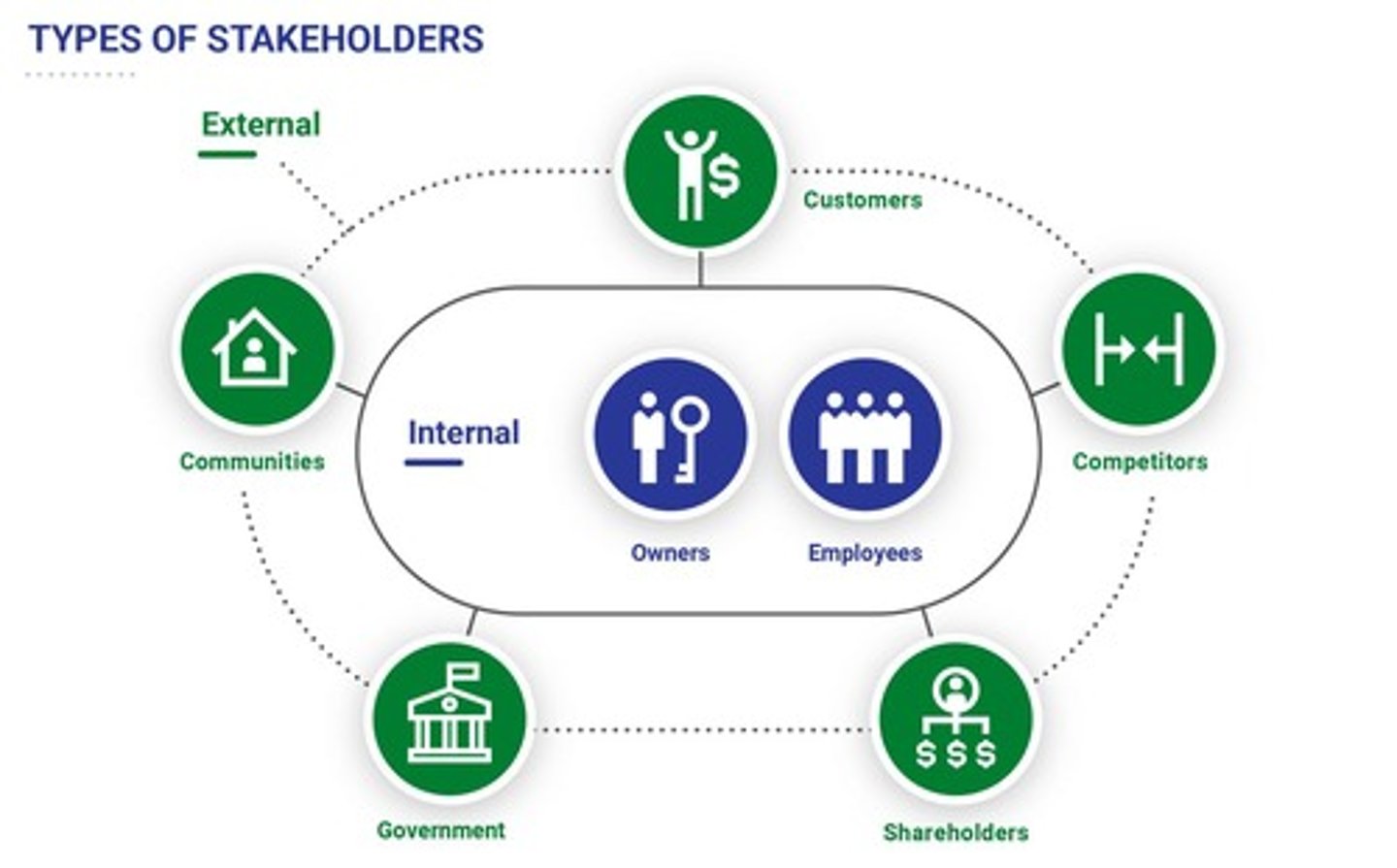
Employees
Individuals hired by the business to perform specific duties and contribute their time and expertise for the opportunity of promotions.
Owners
Founders who have personal & financial goals invested in the business' success along with legal ownership.
Customers
Individuals who buy what the business offers, allowing them to exist.
Competitors
Rivals of a business that offers the same or similar products & services.
Shareholders
Individuals who invest in a business by owning stock, therefore representing part of the business.
Communities
Groups who share similar value, interests, and characteristics; impact business public opinions, operations, and sales.
Artificial Intelligence
Technology that processes characteristics of humans with the ability to reason, discover meaning, and learn from experience.
Conduct Market Research
Step 1 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Write a Business Plan
Step 2 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Find Funding
Step 3 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Select a Location
Step 4 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Pick a Legal Structure
Step 5 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Select a Business Name
Step 6 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Register the Business
Step 7 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Obtain Federal and State Tax IDs
Step 8 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Apply for Licenses and Permits
Step 9 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.
Open a Business Bank Account
Step 10 in the 10 Steps to Beginning Opening a Business.