Lecture 5: Integrated Cardiovascular Regulation
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
The systemic __ is maintained at a relative constant 75-100 mmHg via intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms.
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
The regulation of MAP is important for determining __ and __, particularly to the heart and brain.
capillary filtration pressures; regional blood flows
MAP - CVP =
CO x SVR
(delta P = Q x R)
Arterial pressure is a major factor determining __.
myocardial oxygen requirements
inc in arterial pressure = inc afterload = inc in workload for heart to overcome = more oxygen required
Abnormally high __ pressures from hypertension lead to degenerative changes in __, resulting in serious and often fatal results.
transmural; arteries
transmural pressure = pressure difference from inside to outside of a vessel wall
__ is normally in the 2-8 mmHg range.
CVP/atrial pressure
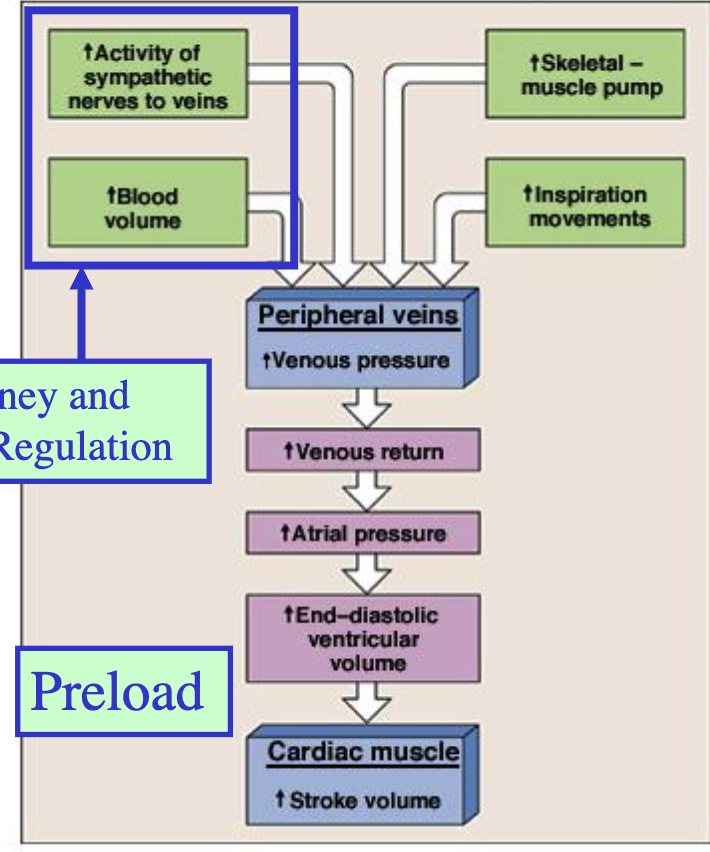
Increase in __ (4) will ultimately increase venous pressure, venous return, EDV, and stroke volume.
skeletal muscle pump
inspiration movements
activity of sympathetic nerves to veins
blood volume
When there is a decrease in blood volume, reflexes like the __ will try to compensate for __ changes, while __ changes are regulated by the kidney and hormonal mechanisms.
baroreceptor; rapid; slower
Baroreceptors effectively __ short term changes in arterial pressure.
buffer
What is the short-term mechanism for changes in blood pressure?
baroreceptors
What is the short-term mechanism for changes in the chemical composition of blood?
chemoreceptors
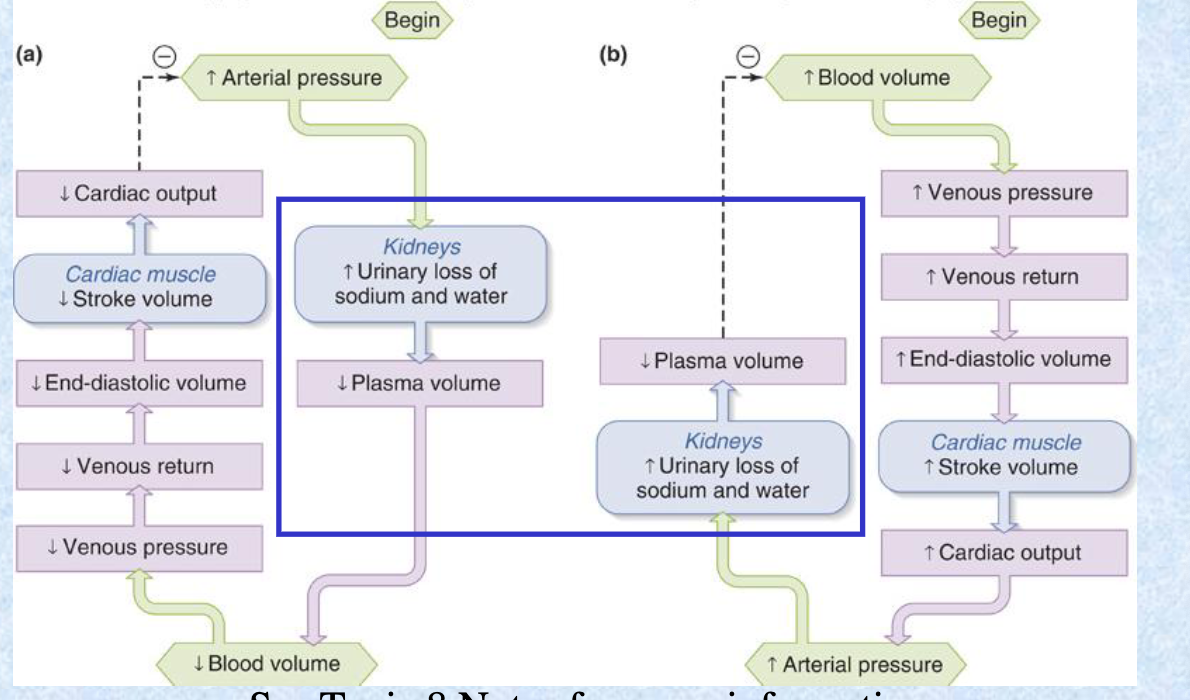
The long-term regulation of blood pressure is mainly a function of the __, which regulate plasma volume by adjustments of: (2).
kidneys; water and salt excretion
this mechanism modulates preload to the heart via changes in blood volume
As a result of __ arterial pressure, an increased urinary loss of sodium and water in the kidneys will __ plasma volume and thus blood volume.
increased; decrease
Long-term regulation of __ is related to the renin-angiotensin system and the kidney.
MAP
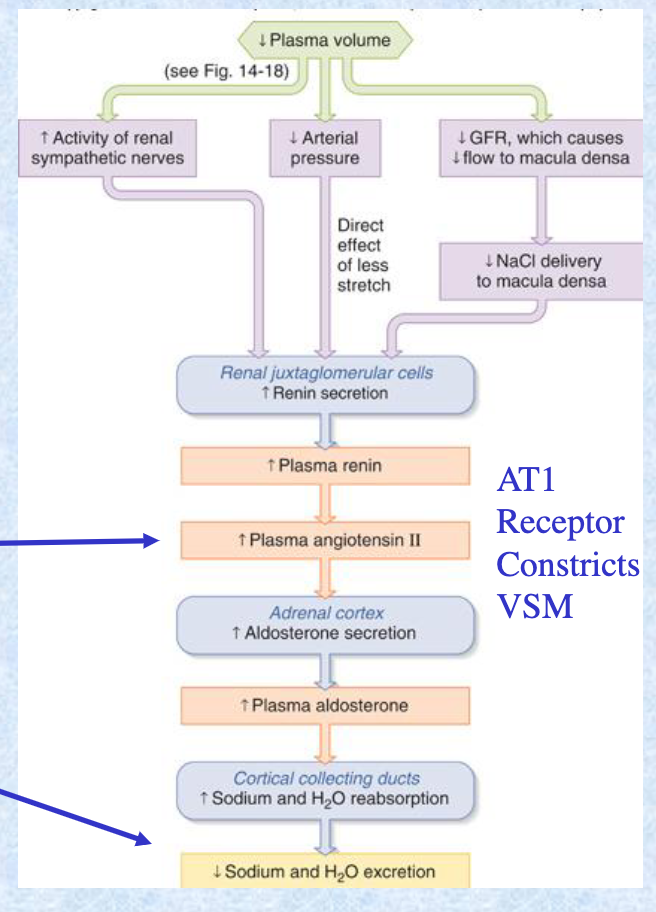
Pressure within the afferent arteriole normally __ renin release.
inhibits
afferent arteriole brings blood to kidney
Na flux through the distal tubule, sensed by macula densa cells, __ renin release.
inhibit
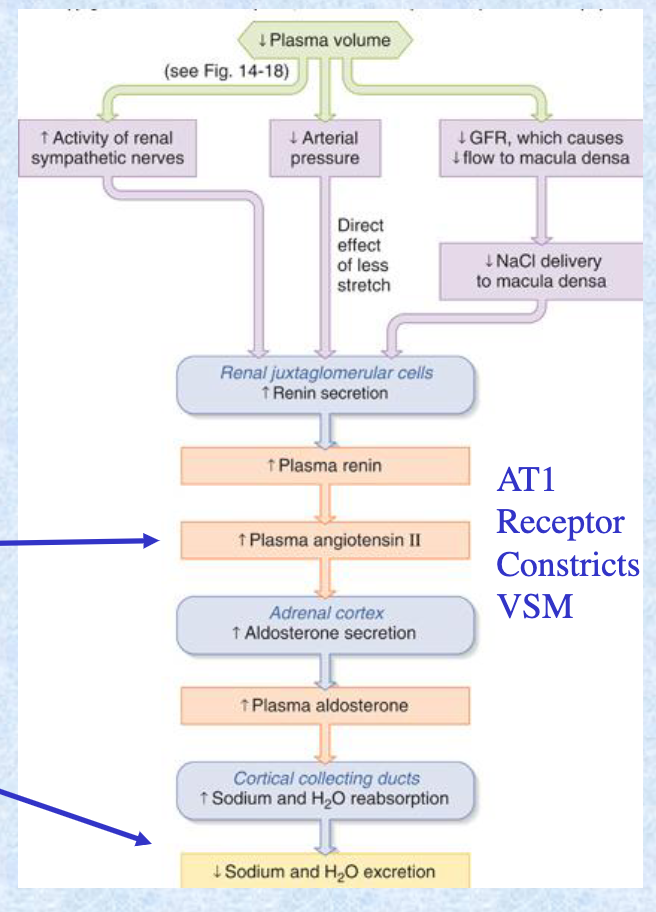
Discharge of sympathetic nerve fibers acting on granular cells __ renin release. Once released, renin acts on plasma angiotensinogen to form __ which is converted to __ by __.
stimulate; angiotensin I; angiotensin II; ACE
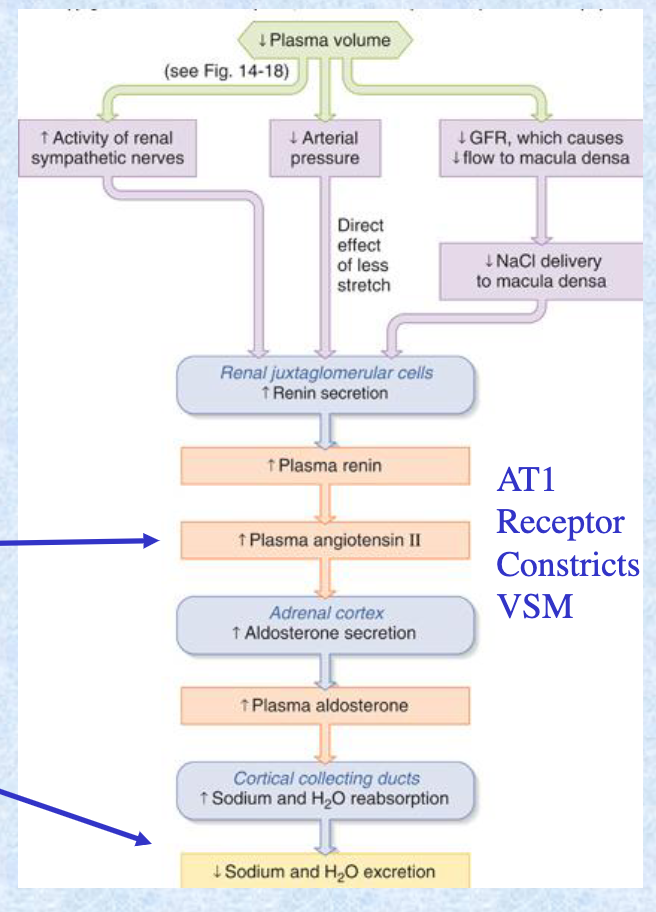
How does angiotensin II affect MAP?
Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone secretion —> increases Na reabsorption —> increases fluid retention —> increases blood volume —> inc in blood volume & peripheral resistance = inc in arterial blood pressure
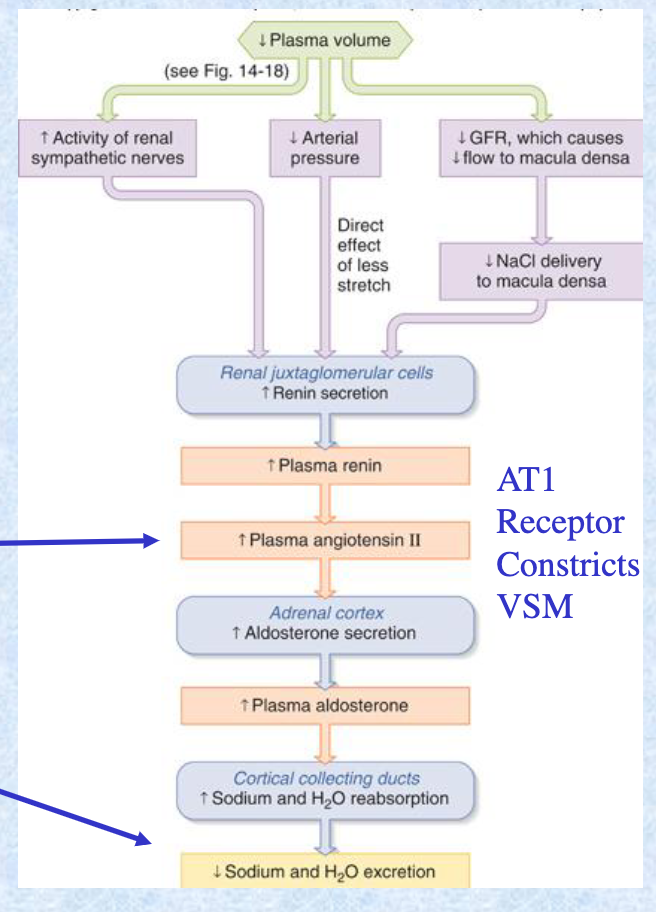
ACE inhibitor drugs __ MAP.
reduce
Pathological increases in renin can lead to __.
hypertension
What are the 4 effects of angiotensin II?
direct vasoconstriction
enhanced peripheral nor-adrenergic transmission
increased sympathetic discharge
release of catecholamines from adrenal medulla
ANF/ANP are secreted by atrial cells in the heart when they are __ by an increased __.
stretched; blood volume
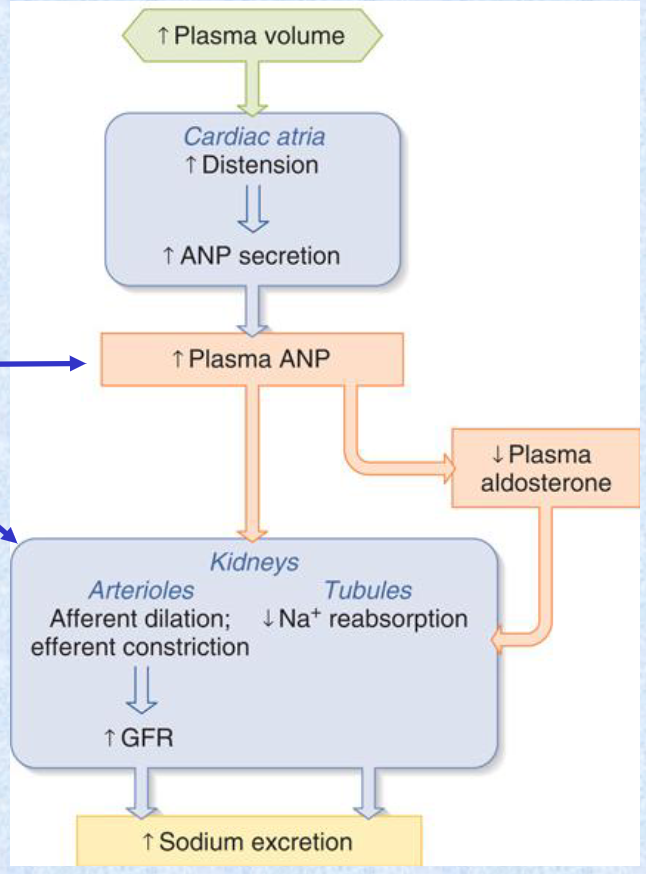
ANF/ANP bind to NPR receptors to __ vascular smooth muscle (VSM) arterioles and increase capillary flow. In the kidney, this reduces Na+ reabsorption thus increases Na+ __ which ultimately __.
dilate; excretion; lowers blood pressure
Vasopressin can be released from the pituitary to __ water retention and thus __.
increase; blood volume
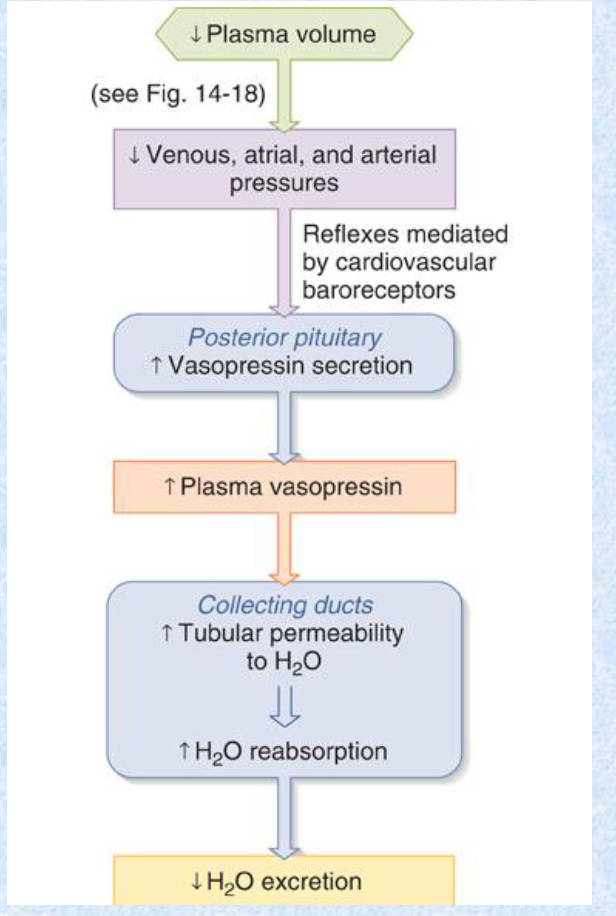
The baroreceptor reflex and hormones in the VSM both contribute to __ regulation.
water volume
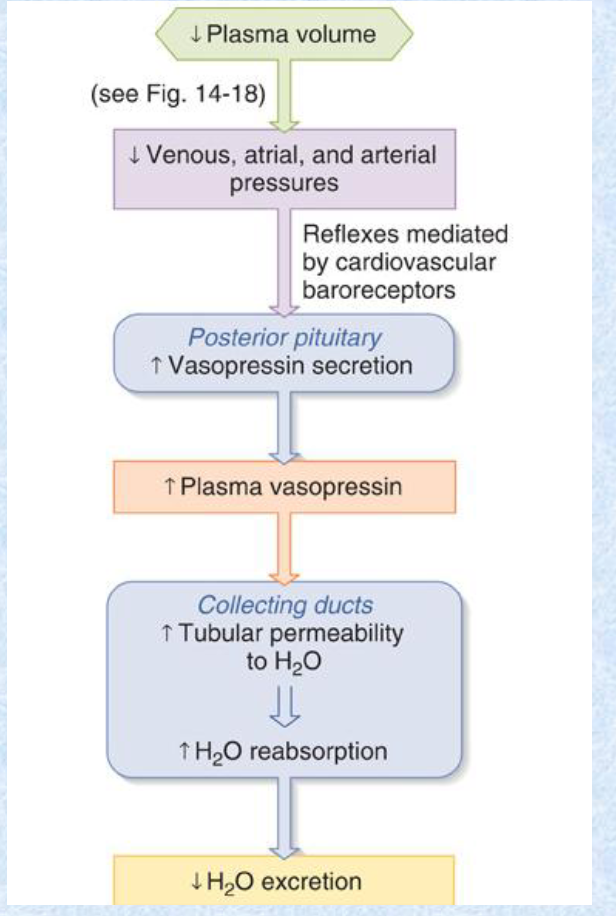
ADH/vasopressin constricts VSM via the __ receptor. This increases water retention to maintain __.
V1; MAP
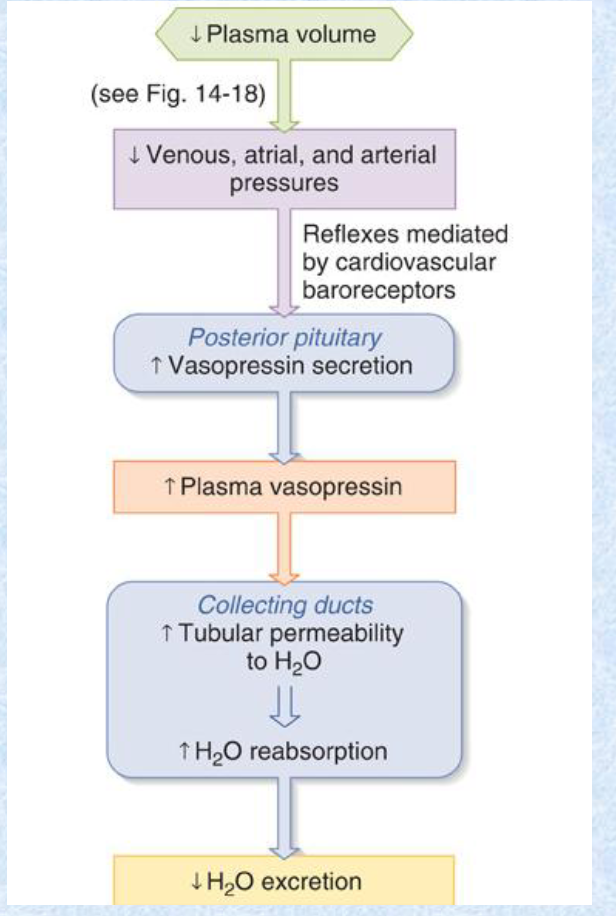
Angiotensin and ADH bind to __ receptors, whereas ANF/ANP binds to NPR, which is a __ receptor.
contraction activator; contraction inhibitor
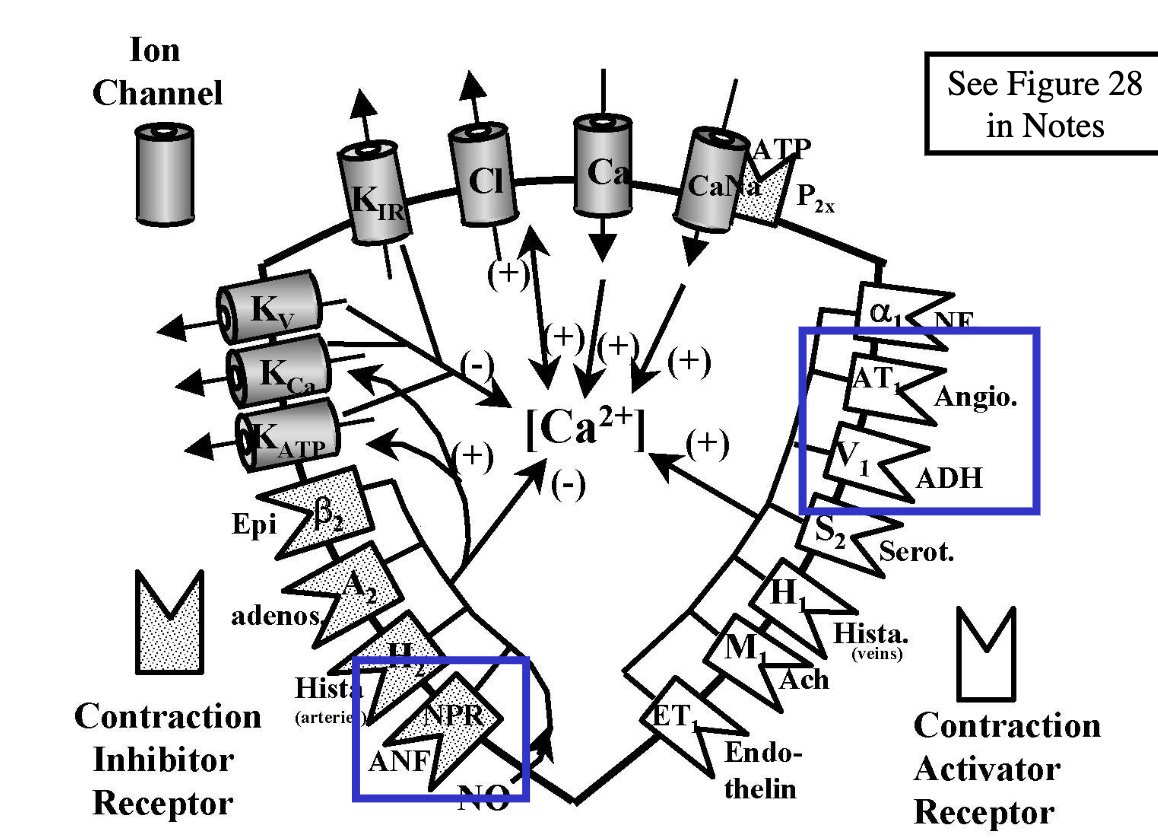
Sympathetic release of __ and __ can ultimately alter vascular smooth muscle’s arteriolar radius (vasoconstrict/vasodilate).
epinephrine, NE
Alpha receptors are more sensitive to __, while beta receptors are more sensitive to __.
NE; epinephrine
At physiological levels, epinephrine __ VSM via the __ receptors.
vasodilates; beta2
At pharmacological levels, epinephrine __ VSM via the __ receptors, which overwhelms the vasodilation from __ sites.
vasoconstricts; alpha1; beta2
Application of epinephrine at pharmacological levels is a common dental practice to reduce __.
gum bleeding
The arterial __ reflex senses increased arterial pressure and starts firing to ultimately __ sympathetic outflow to heart, arterioles, and veins, and __ parasympathetic outflow to the heart.
baroreceptor; decrease; increase
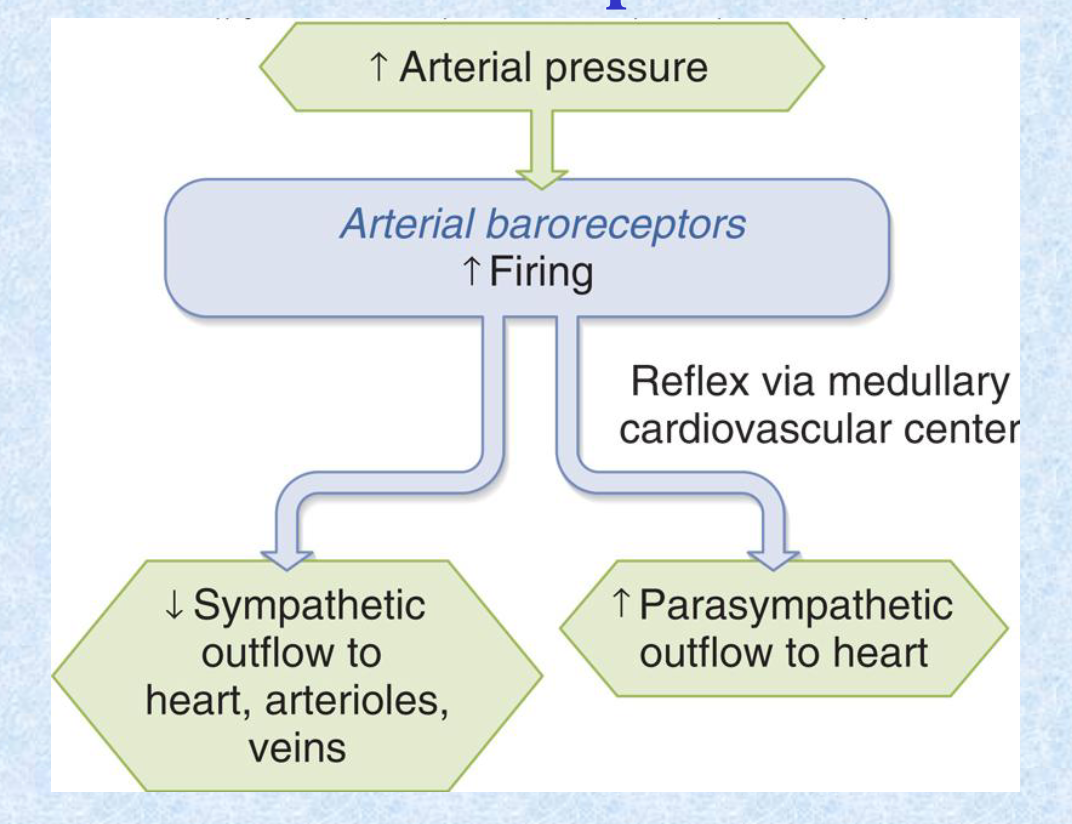
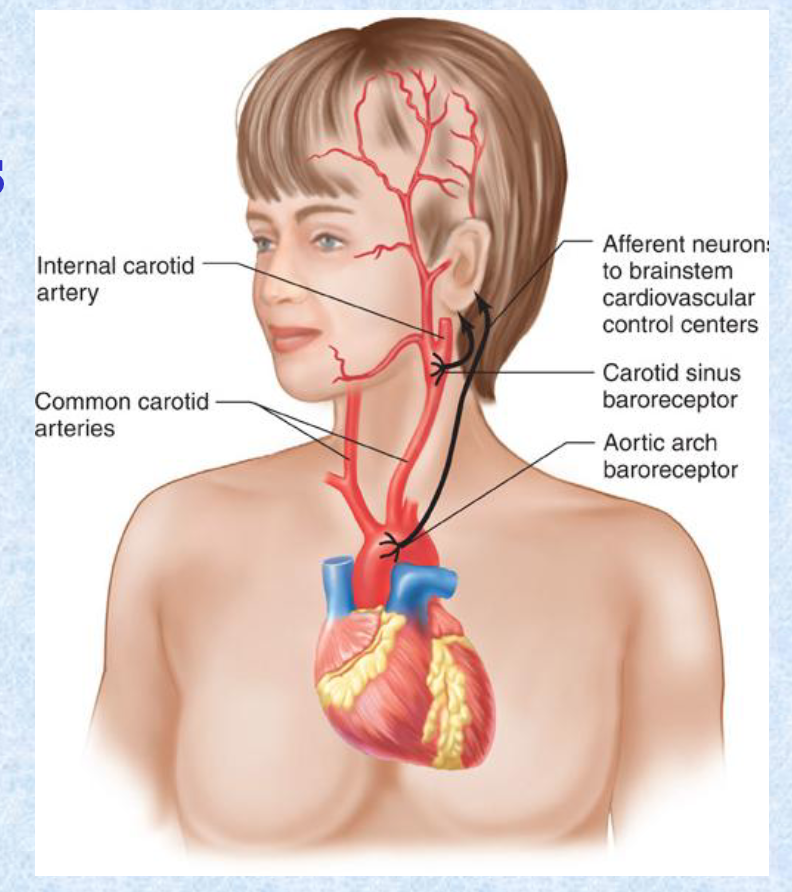
Barorecptors are located in the: (2).
carotid sinus
aortic arch
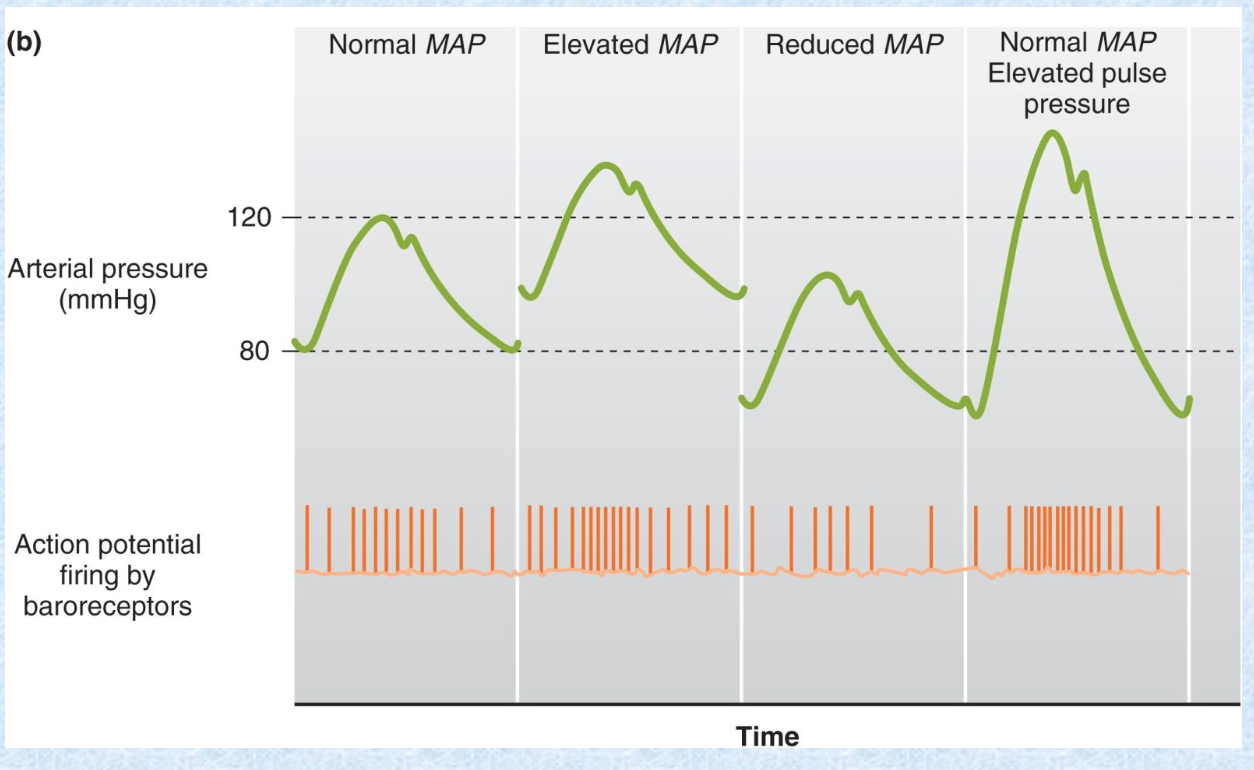
An increase in __ (2) will increase the AP firing by baroreceptors.
MAP or elevated pulse pressure
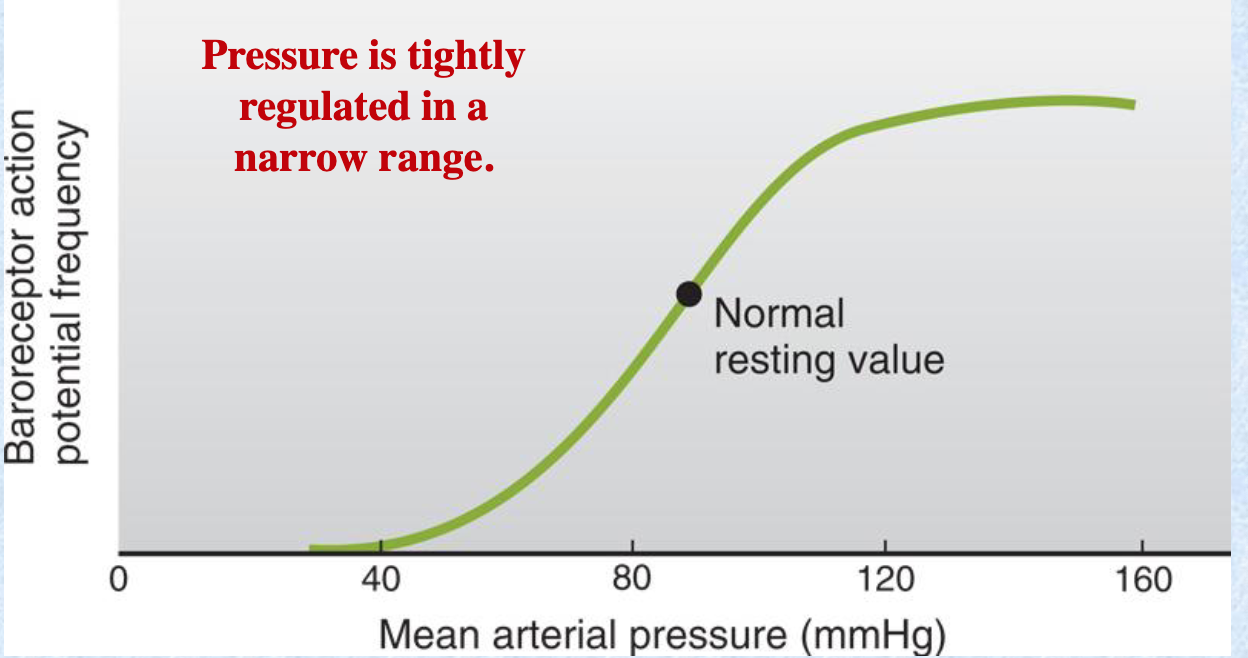
Pressure is tightly regulated in a __ range.
narrow
At a certain high MAP value, baroreceptor AP frequency starts to plateau
When there is a hemorrhage, what mechanisms does the baroreceptor affect? (4)
chronotropic regulation
contractility
preload
afterload
When there is a mild volume loss, what 3 mechanisms occur to restore blood volume?
stimulation of efferent sympathetic fibers —> peripheral vasoconstriction
stimulation of renin secretion by kidney —> inc angiotensin II and aldosterone
antidiuretic hormone release
these prevent a decrease in arterial BP & restore lost blood volume by decreasing urinary water and sodium loss. heart rate isn’t affected
More severe/rapid levels of hemorrhage are associated with a decrease in __. This will trigger arterial baroreceptors, which increase: (2)
arterial blood pressure; heart rate & peripheral vascular resistance
As hemorrhage becomes more severe, __ sets in and reflex __ leads to peripheral vascular insufficiency.
hypotension; vasoconstriction
Receptors sensitive to chemical composition of blood are located in: (2)
carotid body
aortic body
arterial chemoreceptors = peripheral chemoreceptors, not central chemoreceptors
Arterial/peripheral chemoreceptors are more sensitive to arterial __ compared to __ & __.
P_O2; P_CO2; H+
Central chemoreceptors are most sensitive to __.
P_CO2
The main function of all chemoreceptors is to regulate __, but they also induce related __ changes, such as: (4).
ventilation; cardiovascular
vascular resistance
heart rate
cardiac output
blood pressure
Chemoreceptor stimulation causes widespread __, __ arterial pressure, and __ (bc of increased sympathetic efferent discharge).
vasoconstriction; increased; tachycardia
Blood pressure is normally maintained at __ levels via the rapid baroreceptor and chemoreceptor ANS reflexes.
constant
Baroreceptors are sensitive to vascular __, which is a function of __.
stretch; pressure
Baroreceptors are sensitive to both the: (2). With changes in these, the ANS can alter: (4)
mean pressure
rate of any change in pressure
heart rate, contractility, preload, vascular resistance
Local control falls into what 2 general categories?
active hyperemia
flow autoregulation
Arterioles that control the flow into an organ usually lie __ that organ. Thus, interstitial concentrations of __ or __ concentrations in that organ can influence blood flow by vasoconstricting or vasodilating local vessels.
within; metabolites; O2/CO2/H+/K+/NO
Metabolites & O2/CO2/H+/K+ can enter the circulation and elicit more global ANS mediated responses via the __.
metaboreflex
Endothelial cells modulate __ & __ for vasodilation, and __ for vasoconstriction.
NO; prostacyclin; endothelin
Prostaglandins, histamines, bradykinin, adenosine, and other substances released during injury can elicit __.
vasodilation
some of these work directly or in conjunction with endothelial cells
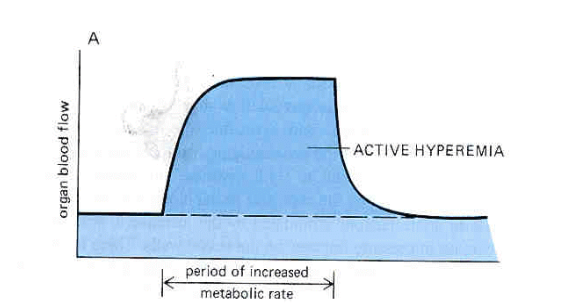
Explain what this graph is showing.
In organs with highly variable metabolic rates, the flow patterns closely follow the tissue’s metabolic rate.
in skeletal muscle, flow increases within seconds upon onset of exercise and returns to ocntrol at end of exercise = active hyperemia / high flow
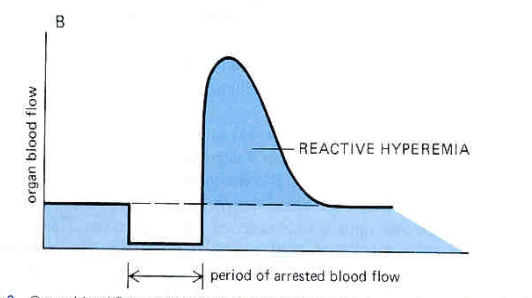
Explain what this graph is showing.
temporary restriction to flow —> higher than normal BP occurs transiently following removal of restriction = reactive hyperemia (= myogenic response to reduced transmural pressure & accumulation of metabolites/CO2)
What is autoregulation?
organs keep blood flow constant despite variations in arterial pressure
occurs except when displaying active or reactive hyperemia
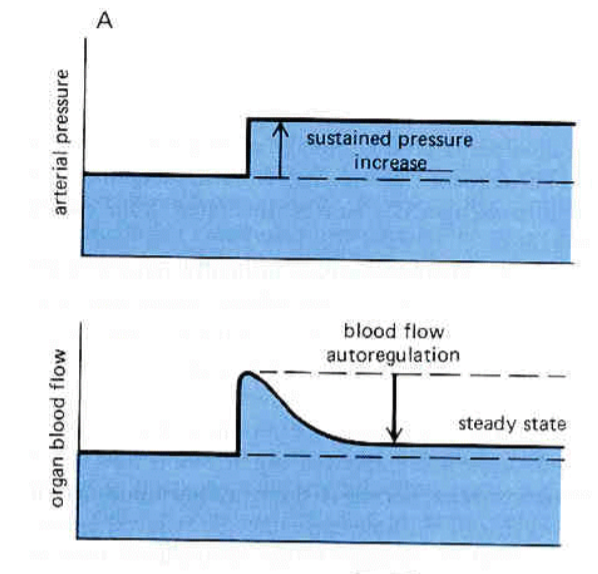
What does this graph show about autoregulation?
in presence of sustained increase in pressure, organ blood flow initially goes up, then drops back down to close to original level (autoregulation).
Flow rate changes from pressure changes will __ or __ metabolites —> fostering a new steady state.
wash out; retain
Direct vessel stretch or reduction from pressure changes will induce __ modulation of smooth muscle contraction.
myogenic
What factors modulate the blood flow via arterial smooth muscle? (3)
hormonal: vasoconstrictors (NE, angiotensin II, ADH, epinephrine @ high doses); vasodilators (ANF, histamine, epinephrine @ physiological levels)
neural: baroreceptors, chemoreceptors
local: metabolites, O2/CO2, myogenic response, osmolarity, local NO
Among the many hormones and factors released, the __ and __ impact the CV system the most, and sometimes can be detrimental.
catecholamines; cortisol
Cortisol affects vascular smooth muscle by enhancing the __ of vascular smooth muscle to __ stimuli (NE).
reactivity; vasoconstricting
Stress activates __ stimulation of the adrenal medulla to secrete catecholamines (primarily __).
sympathetic; epinephrine
Epinephrine [increases/decreases] skeletal muscle fatigue, [increases/decreases] cardiac contractility (thus [increasing/decreasing] cardiac output), and shunts __ from visceral organs to skeletal muscle by constricting visceral blood and vasodilating skeletal muscle blood vessels.
decreases; increases; increasing; blood
decreases skeletal muscle fatigue —> allows muscles to remain active for longer periods (fight or flight)
What are the adaptive advantages of chronic stress?
none: has deleterious effects on physiological processes
can eventually lead to atherosclerosis, arrhythmias, HTN, heart failure
What is a useful function of stress (not chronic)?
increases total peripheral vascular resistance and thus decreases probability of developing hypotension during moderate stress