bio unit 1 test review
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1 Biology Flashcard Terms - Cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
cell theory
all living things composed of cell(s)
cells preform all life processes (function)
all cells come from pre-existing cells
homeostasis
a balanced state in an organism’s body - must maintain
synthesis
make complex compounds from simple substances
inorganic molecules
water, carbon dioxide, oxygen
nitrogen
most common gas, needed to make proteins and nucleic acids
organic compounds
complex molecules called polymers
always has carbon and hydrogen
synthesized from monomers
carbohydrates
polymers = polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen)
monomers = monosaccharides (glucose)
functions: provide energy for cell
lipids
polymers = fats and oils
monomers = fatty acids
functions: hydrophobic, insulation, form parts of cell membrane, form hormones
proteins
polymers = polypeptides (2 or more make protein)
monomers = amino acids
functions: color chemical reactions, form cell structures, form body parts (ex: enzymes, membranes, proteins, antibodies, neurotransmitters, most hormones)
nucleic acids
monomers = nucleotides
polymers = DNA + RNA
function: genetic code, control traits
passive transport
no energy used to move molecules through membrane
move from high to low concentration
simple diffusion - substances go through lipid bilayer
facilitated diffusion - membrane proteins transport substances in and out, specific protein shapes determines what can pass (ex:lock and key model)
osmosis - diffusion of H20 though cell membrane
hypertonic - water leaves cell, cell shrinks
hypotonic - water enters cell, cell swells
active transport
energy is used to move molecules through membrane
substances move from low to high
protein pumps force substances through the membrane
large particle transport
energy is used to change shape of membrane to let large particles through membrane
endocytosis - membrane surrounds particle and engulfs it into cell
exocytosis - vesicle joins with membrane and expels particle out of cell
cellular respiration
convert energy in food into usable form (atp)
occurs usually in the mitochondria
waste product is carbon dioxide + water
aerobic
word equation : glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy stored in ATP
chemical equation : C6H12O6 + O2 = CO2 + H2O + 38 ATP
Opposite reaction as photosynthesis
cellular respiration steps
glycolysis happens in cytoplasm - glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid, some energy is released
kreb cycle - happens in mitochondria. glucose is broken down into waste products carbon dioxide and water, all energy is released
ATP cycle - happens in mitochondria, some energy is grabbed by a phosphate and stored in ATP - some energy is released as heat
fermentation
when human run low on oxygen muscle cells must do anaerobic respiration
cellular respiration like but anaerobic (no oxygen) and produces less ATP
waste product: lactic acid
yeast do fermentation making alcohol and carbon dioxide as wastes
photosynthesis
process in which the sun’s energy is stored int he chemical bonds of sugar
happens in cells with chloroplasts
converts light energy from sun into stored chemical energy into glucose
word equation: carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
chemical equation: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O = C6H12O6 + 6 O2
waste product: oxygen
benefits: provides food for all plants/animals, provides oxygen for cellular respiration, removes carbon dioxide from atmosphere
Opposite reaction as cellular respiration
chloroplast
cell organelle containing chlorophyll that preforms photosynthesis
stomata
pores or tiny opening under a leaf - lets oxygen, water, and carbon dioxide in and out
guard cells
open and close the stomata to prevent plant from dying out
xylem and phloem
tubes transport water (xylem) and food (phloem) through plant
prokaryotic cell
no nucleus
few organelles
simple, single celled organisms (bacteria + archaea)
eukaryotic cell
has nucleus + many organelles
complex cells, multicellular organisms (protists, fungi, animal, plant)
nucleus
controls cell
holds DNA, genes
cytoplasm
holds cell contents
helps transport materials
mitochondria
carries out cellular respiration
give cell usable energy in the form of ATP (powerhouse of the cell)
ribosome
makes proteins by joking amino acids (protein synthesis)
vacuole
stores food/water/wasste
food vacuoles with lysosomes digest large molecules
waste vacuoles excrete waste out of cell membrane
plant cells have large water vacuoles
cell wall
gives shape, structure and protection
found in plant cells
cell membrane
seperates cell interior from outer enviroment
made of two layers of phospholipids plus proteins embedded int he lipid bilayers
controls what enters an leaves the cell using membrane proteins - the membrane is selectively permable
function includes regulation and homeostasis
cilia
short hair like projects from cell membrane (beat like oars to move cell)
flagella
long whip like projections from cell membranes (moves like a propeller to move cell)
Energy pyramid
shows that energy is used up with each step in a food chain
only about 10% energy is passed from one level to the next
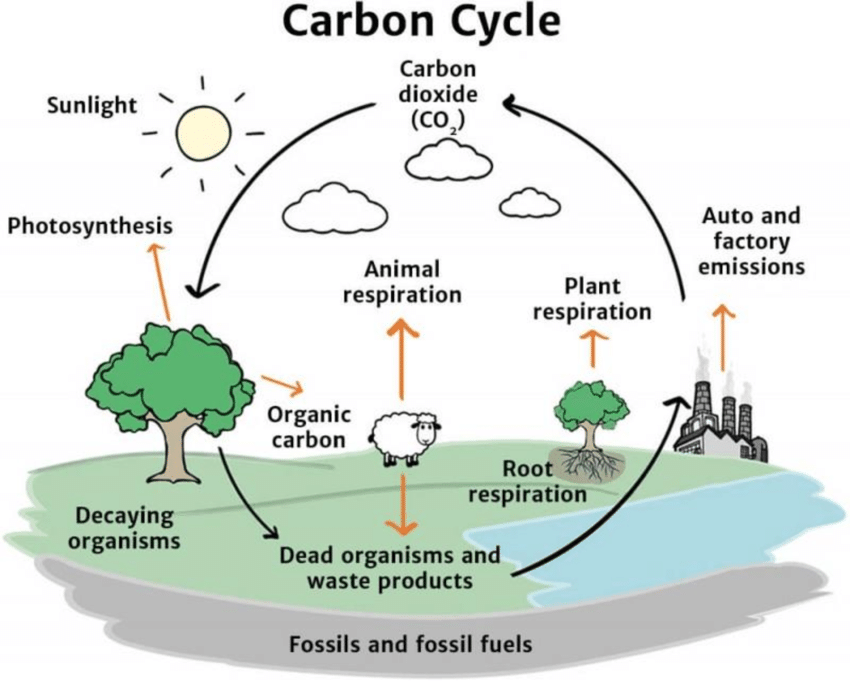
carbon cycle
during photosynthesis plants take in CO2 and release O2 into the air
during cellular respiration CO2 is released as waste
during the process of decay decomposers release CO2
this carbon is used to make glucose (C6H12O6)
water cycle
plants take in H2O, used for photosynthesis
water evaporates from lakes and oceans, rises and cools in atmosphere then returns to earth as precipitation (rain and snow)
nitrogen cycle
bacteria in soil that are decomposers convert N2 from the air into nitrates that plants use as fertilizer
the nitrogen is then used to form organic compoundsr
t or f
plants do photosynthesis, animals do cellular respiration
f
all organisms including plants use cellular respiration to get their energy as ATP
t or f
cellular respiration is breathing
f
breathing is not cellular respiration - breathing exchanges the gases involved in cellular respiration. you inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide when you breath
t or f
we need oxygen to breathe - all living things need oxygen, all living things breathe
f
breathing is used to get oxygen used for cellular respiration - without oxygen you have no cellular respiration, no ATP, no energy
anaerobic organisms (such as yeast and some bacteria) do not always need oxygen and do not breathe
t or f
photosynthesis and cellular respiration make energy
f
the sun makes energy - photosynthesis and cellular respiration convert the light energy into stored chemical energy
t or f
energy is recycled in ecosystems
f
energy is never recycled - only carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, and nitrogen are recycled