Equations and Inequalities
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
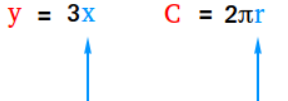
The values that are fed into formula, or equation to initiate calculations
Input
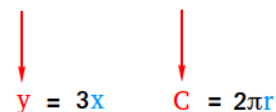
The result of an operation, calculated by applying the order of operations to an input in an equation.
Output
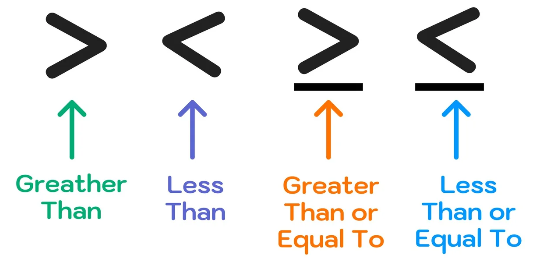
A mathematical statement that compares two expressions and shows that one is greater than, less than, or not equal to the other, often using symbols like <, >, ≤, or ≥.
Inequality

Operations that reverse the effect of the original operation.
Inverse

Pairs of mathematical operations that cancel each other out, such as addition and subtraction or multiplication and division.
Inverse Operations
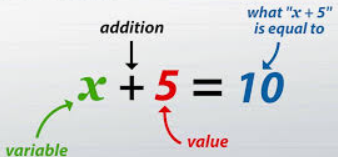
Mathematical statements that assert the equality of two expressions, typically containing variables and constants.
Equations
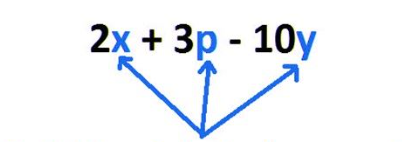
A symbol, typically a letter, that represents an unknown or changing quantity.
Variable
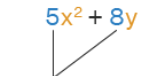
The number, or value, that is multiplied by a variable in a term.
Coefficient
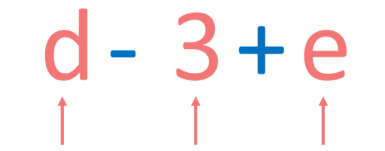
An individual number, variable, or a product of numbers and variables within an algebraic expression that are separated by addition or subtraction signs.
Term
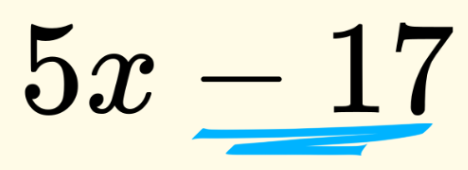
A number, or value, that stands alone in an expression.
Constant
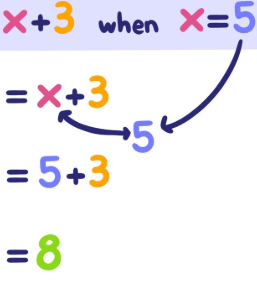
The process of replacing a variable or expression with another, often numerical, value.
Substitution
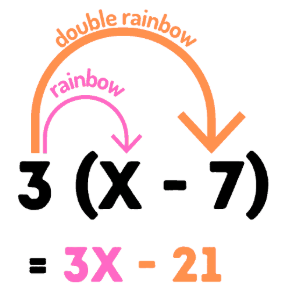
A concept in mathematics that multiplies all values on the inside by the value of the outside of parentheses.
Distributive Property
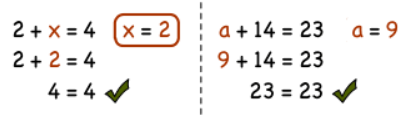
A value in mathematics that makes an equation true.
Solution

To rewrite an algebraic expression by applying the distributive property.
Expand Form