Psychedelics, Thalamus, and Neuroplasticity Insights
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What receptor is essential for the effects of psychedelics?
5HT2A receptor.
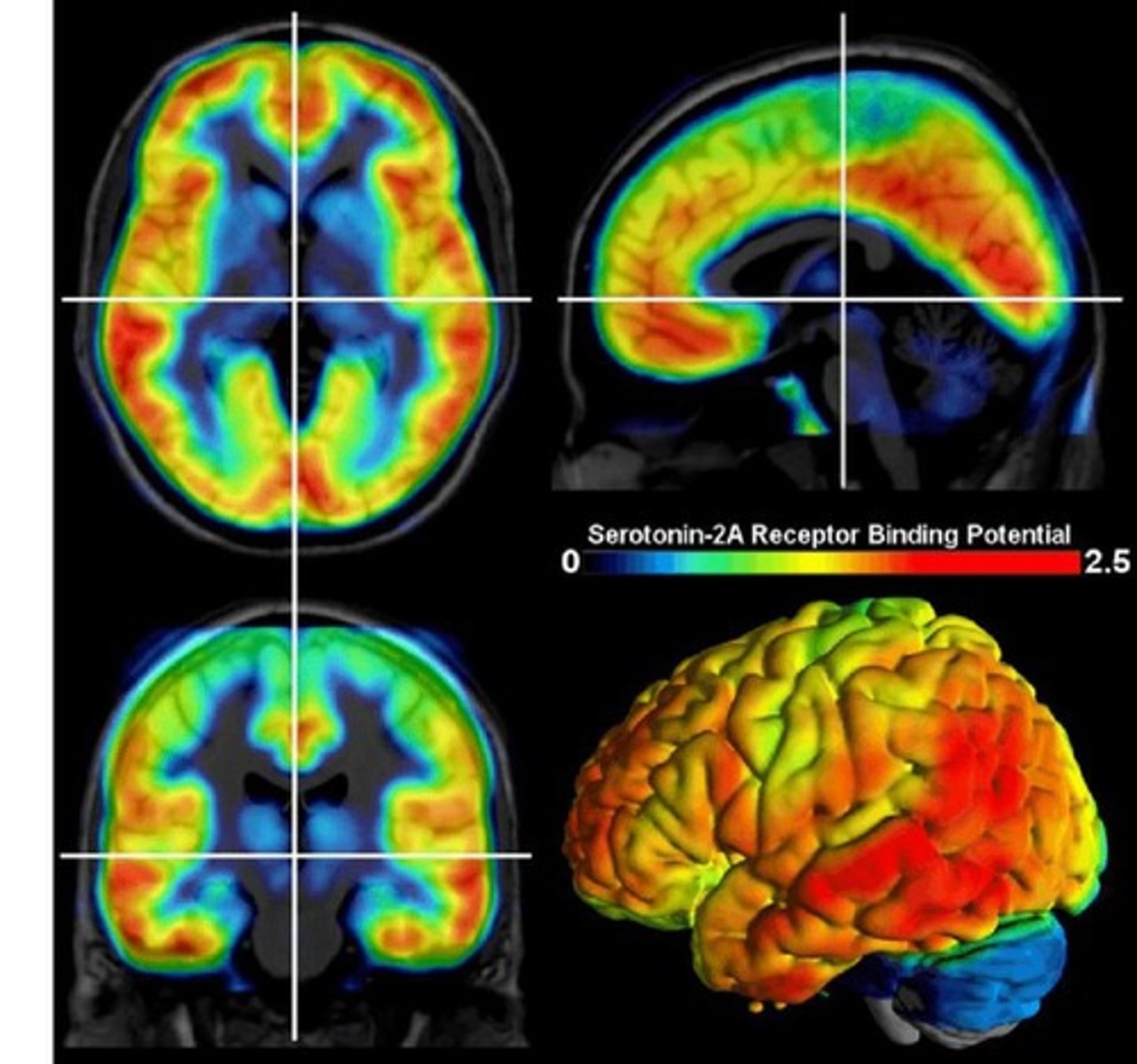
How do psychedelics promote cortical plasticity?
Through activation of the 5HT2A receptor.
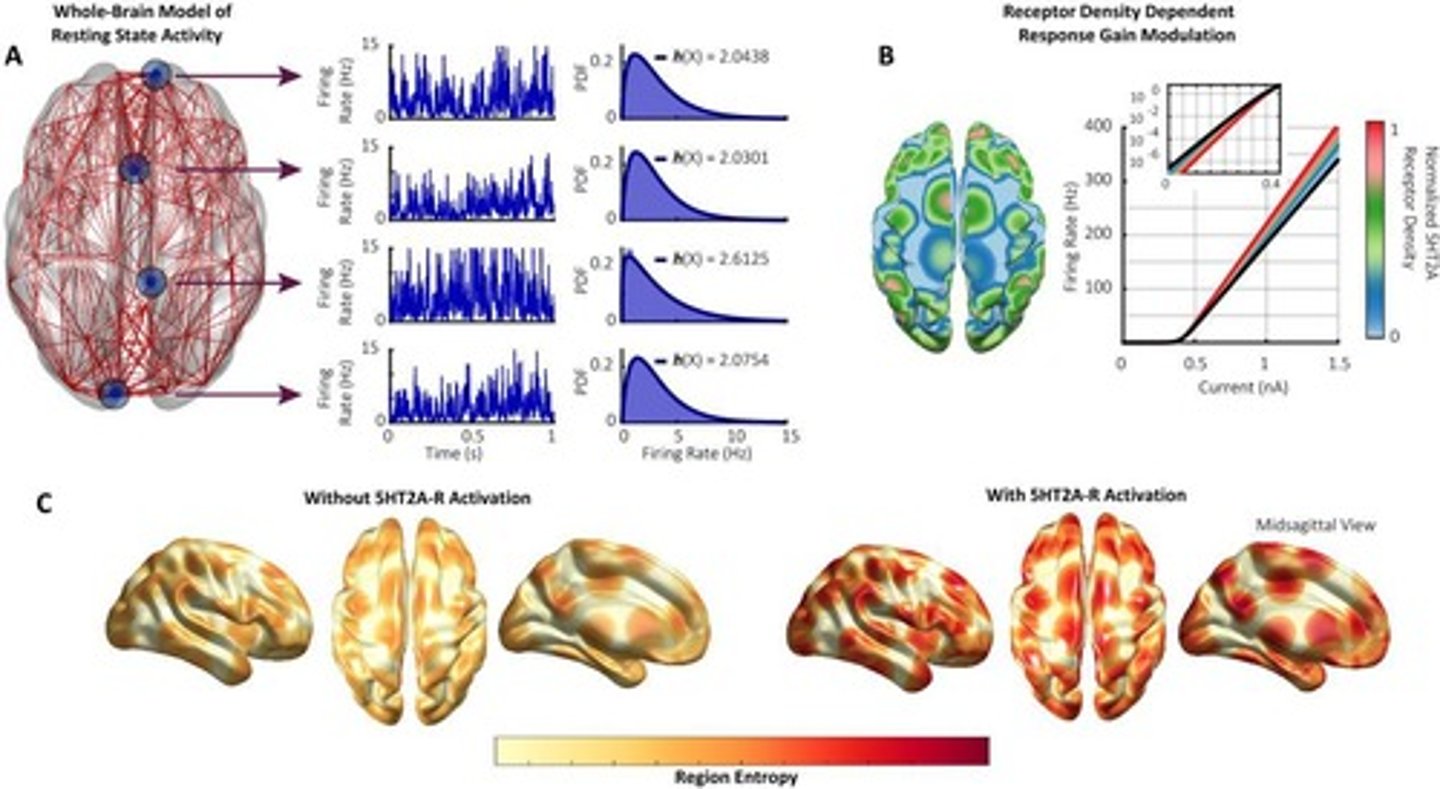
What changes occur in brain networks due to psychedelics?
Brain networks become more connected, promoting neuroplasticity and disrupting normal brain patterns.
What significant experience can psilocybin occasion according to Roland Griffiths?
Mystical-type experiences with substantial personal meaning and spiritual significance.
What percentage of patients reported psilocybin as the most revelatory spiritual experience of their life?
80% of patients.
What did the octopus study reveal about MDMA and sociability?
Octopi given MDMA spent more time interacting with each other compared to control octopi.

What critical period is important for social reward learning in mice?
Mice form positive associations with socializing only during a critical period in adolescence.
What effect did psychedelics have on adult mice that were singly housed during adolescence?
They were able to form positive social bonds that lasted for months after treatment with psychedelics.
What pathways were enhanced in mice after psychedelic treatment?
Oxytocin pathways.
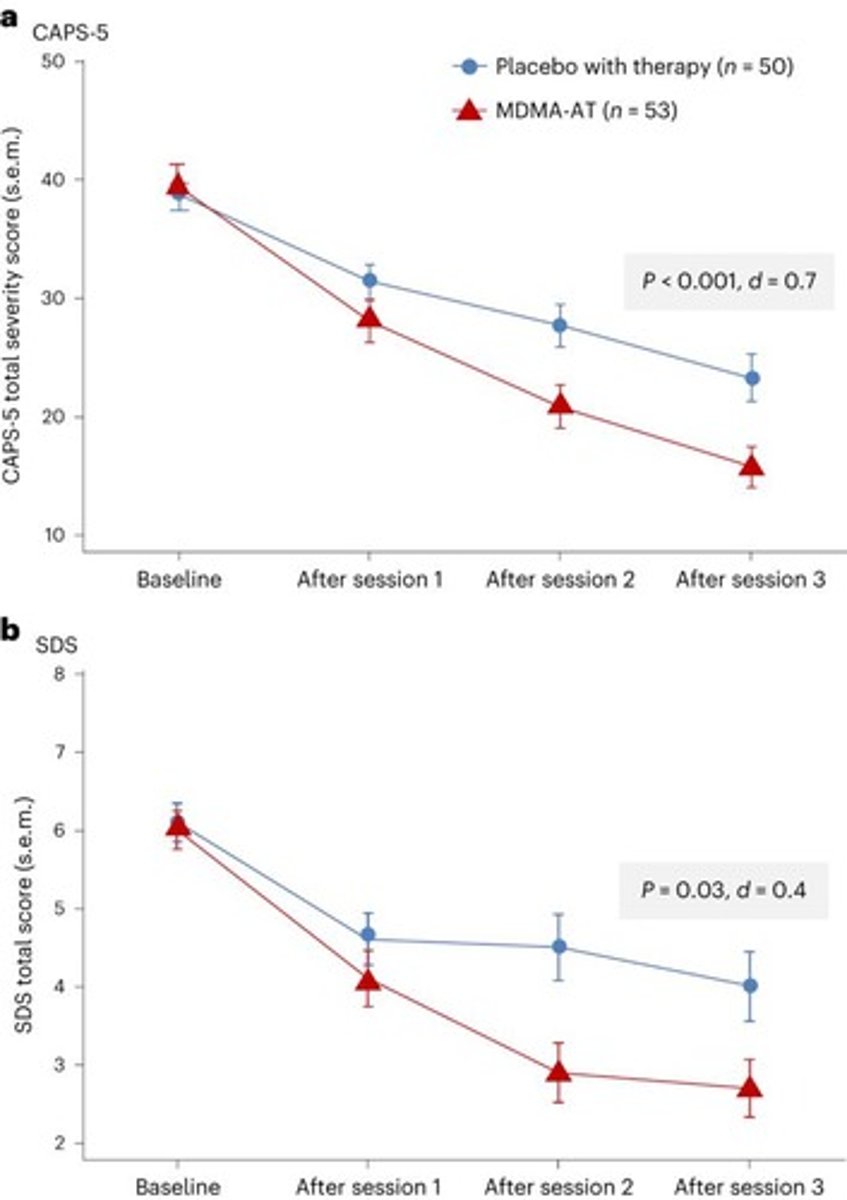
What was the outcome of the randomized double-blind study on MDMA for PTSD?
Significantly reduced PTSD symptoms and the drug was well tolerated.
Is the psychedelic trip necessary for positive therapeutic outcomes?
This is controversial; some studies suggest therapeutic effects can occur without the trip.
What is De. Sparta's perspective on psychedelics for treatment?
Not suitable for everyone, especially those with a history of psychotic episodes, and should be done in a controlled environment.
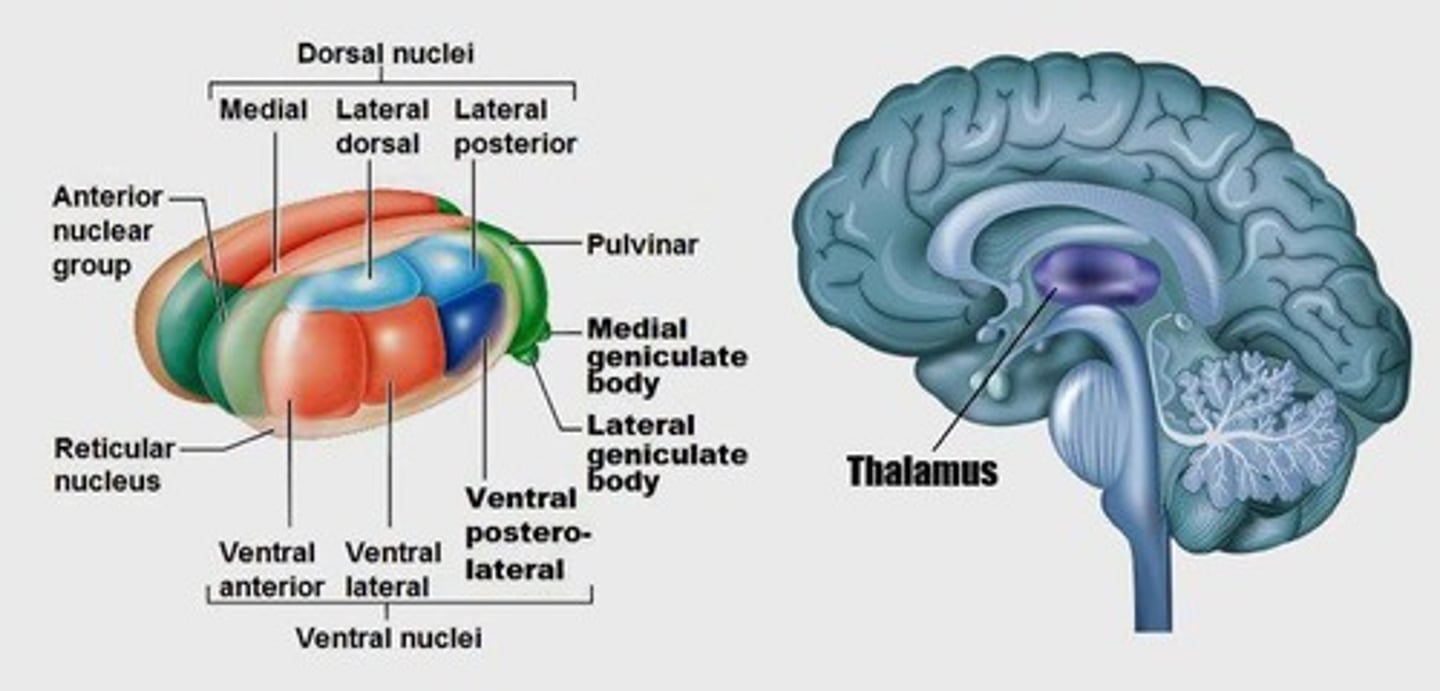
What is the thalamus often referred to as?
The 'gateway' to the cerebral cortex.
What are the three main structures of the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.
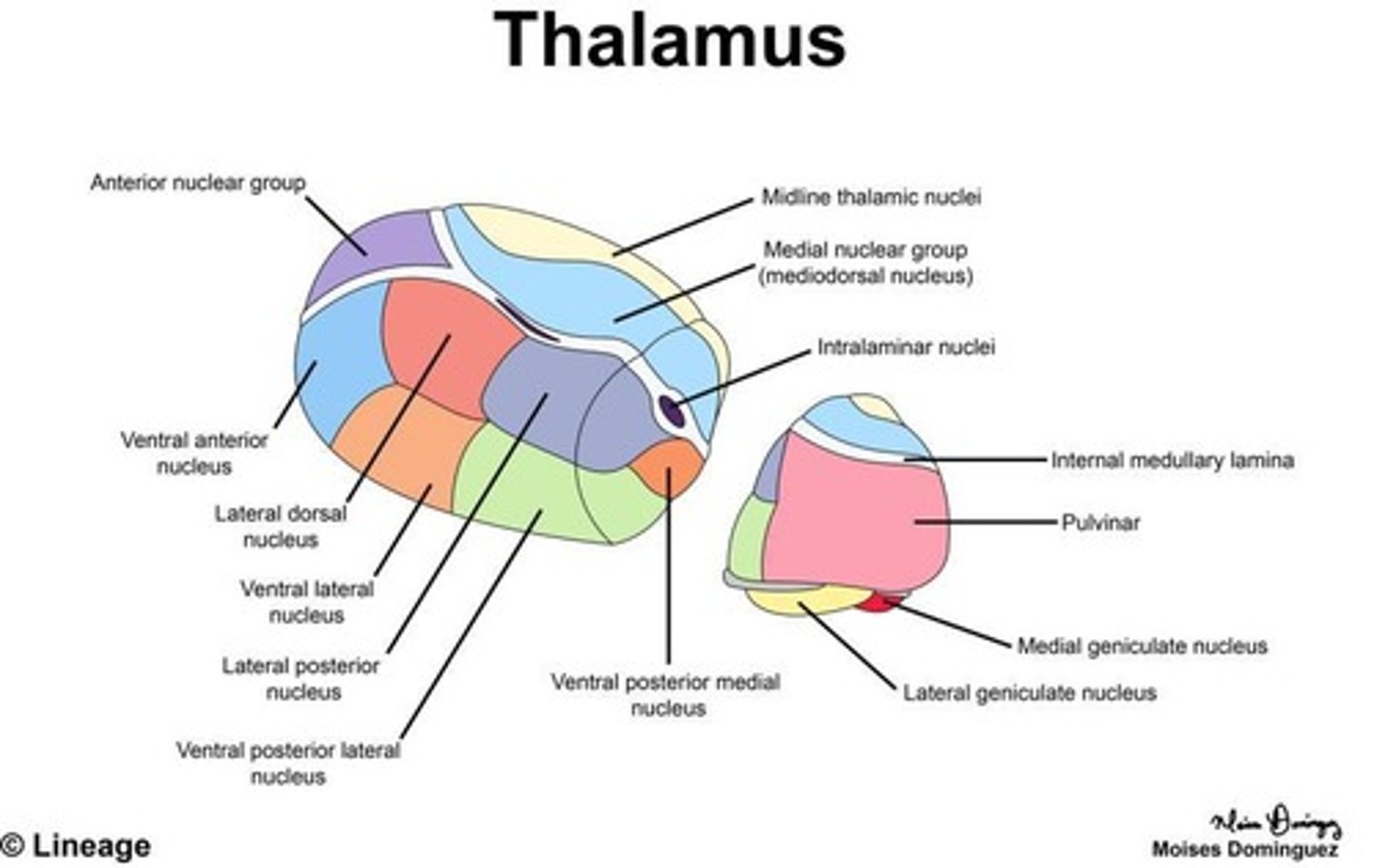
What is the main function of the thalamus?
To act as a relay station for information coming into the cortex.
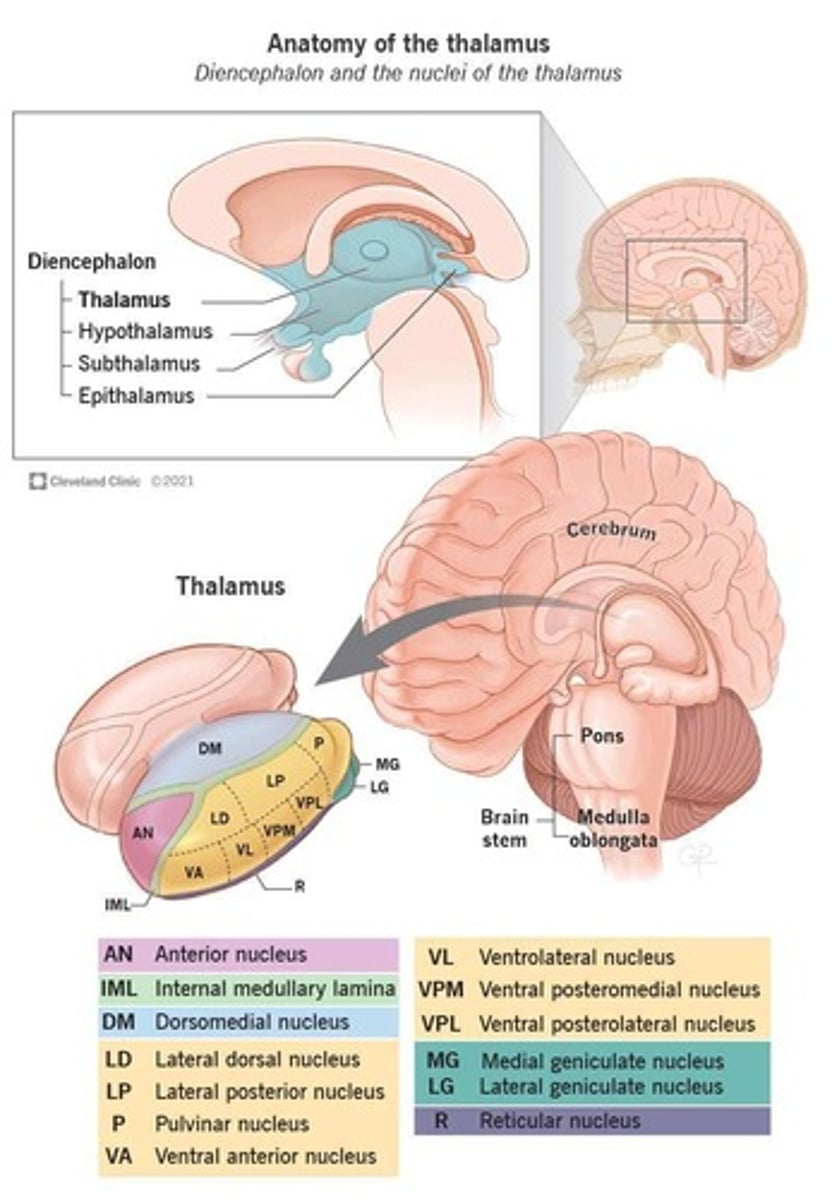
What types of information does the thalamus process?
All sensory information except olfaction, as well as some motor and memory information.
What are thalamocortical fibers?
Fibers that project from the thalamus to the cortex.
What are the anterior nuclei of the thalamus involved in?
Emotional behavior and memory.
What functions are associated with the medial nuclei of the thalamus?
Affective behavior, decision making, judgment, and memory.
What is the role of the lateral nuclei of the thalamus?
Involved in sensory and motor processing.
What does the medial geniculate nucleus relay?
Auditory information.
What does the lateral geniculate nucleus relay?
Visual information.
What is the function of the motor thalamus?
To relay input from involuntary motor centers to the motor cortical areas.
What is the role of the sensory thalamus?
To process somatosensory input from the body and head.
What is the cognitive thalamus primarily involved in?
Behavioral flexibility, memory processes, and cognition.
What are some potential thalamic disorders?
Unconsciousness, sleep disorders, aphasia, movement disorders, and pain syndrome.
What is the epithalamus?
The most dorsal part of the diencephalon, forming the roof of the third ventricle.
What does the pineal gland secrete?
Melatonin, which helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
How does light affect melatonin production?
Light inhibits melatonin production, while darkness activates it.
What is DMT and its significance?
A tryptamine linked with near-death experiences and psychedelic effects.
What experiences are associated with DMT?
Inner peace, out-of-body experiences, and communicating with sentient beings.