Tissues
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
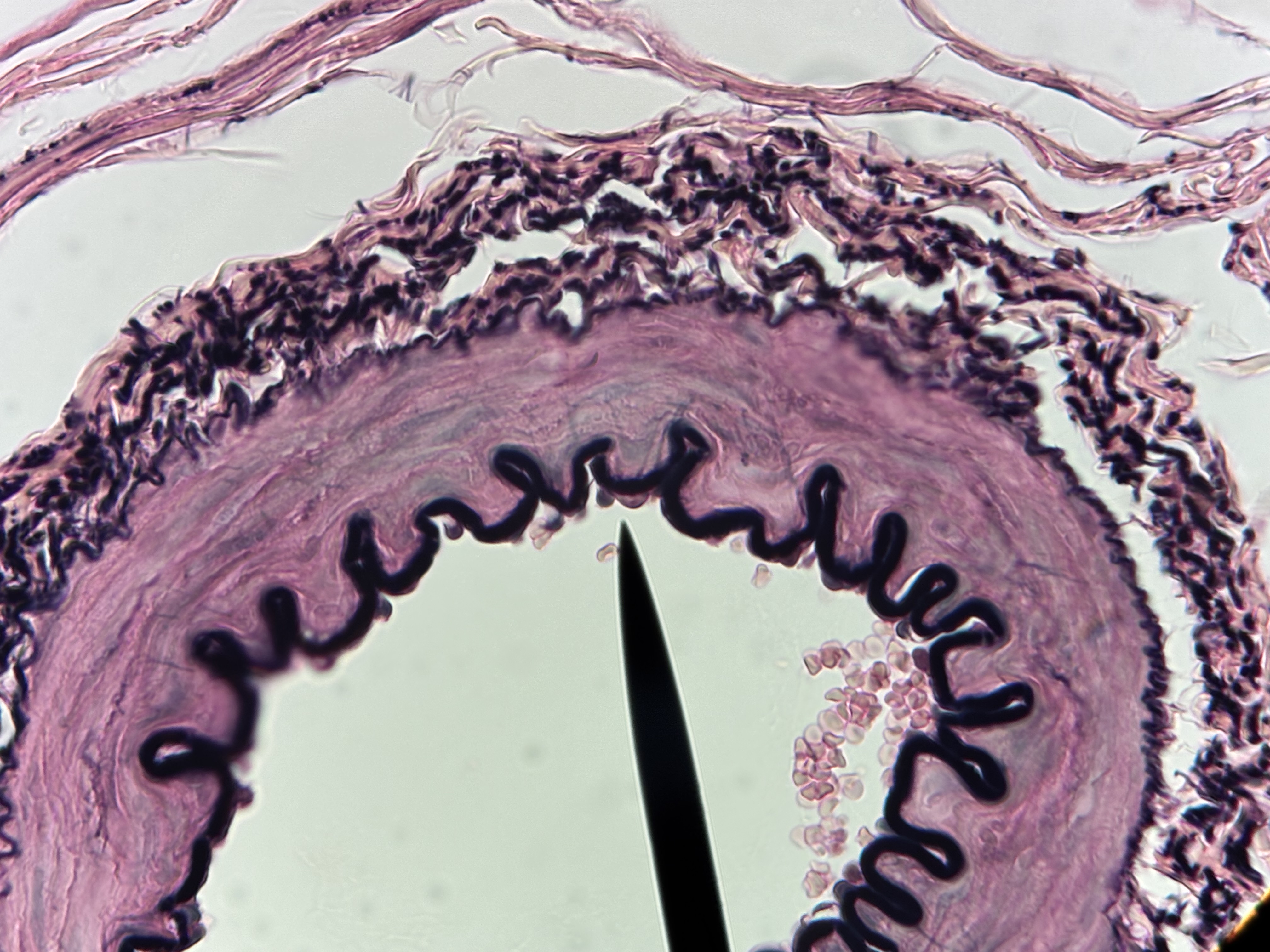
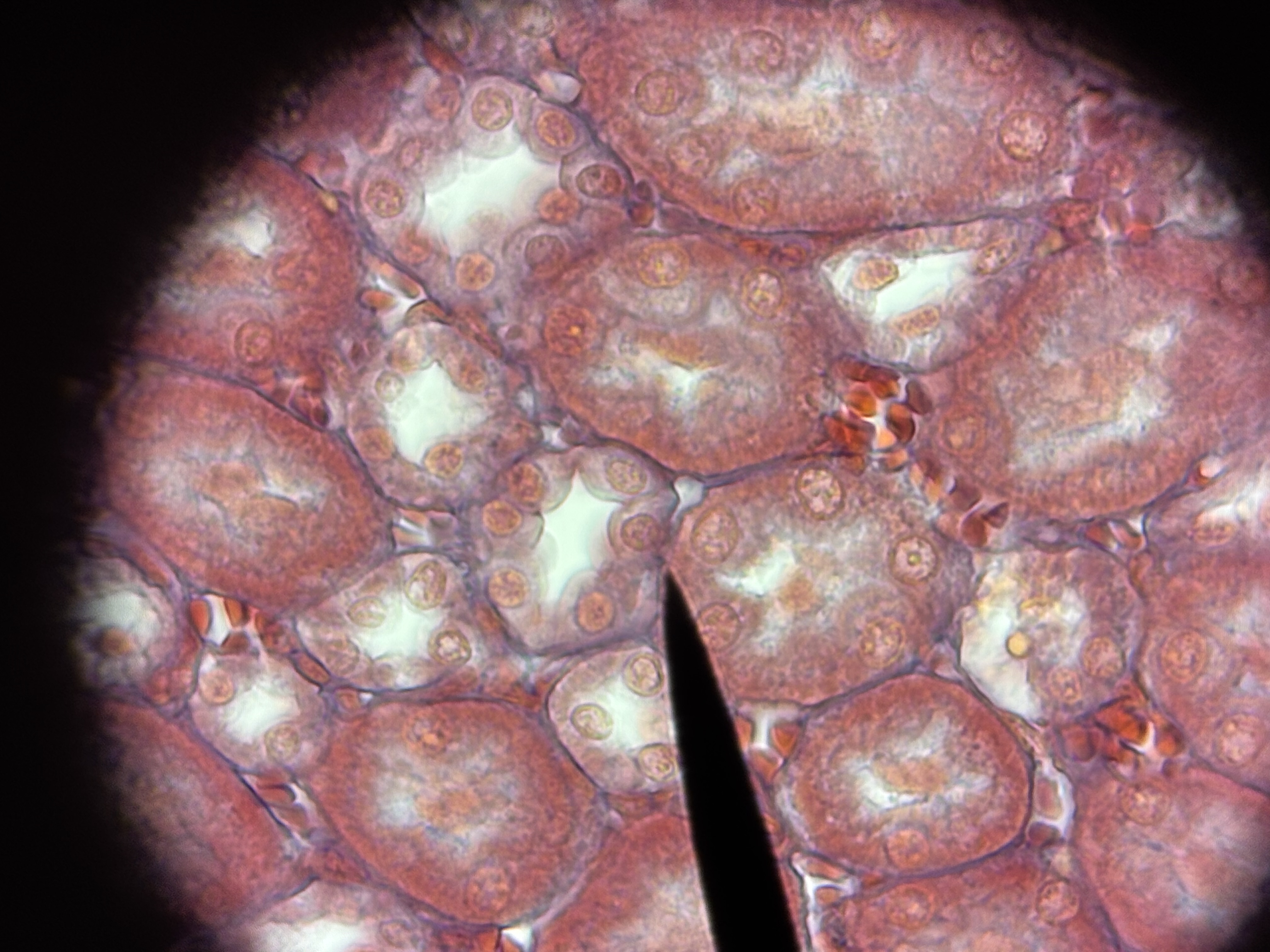
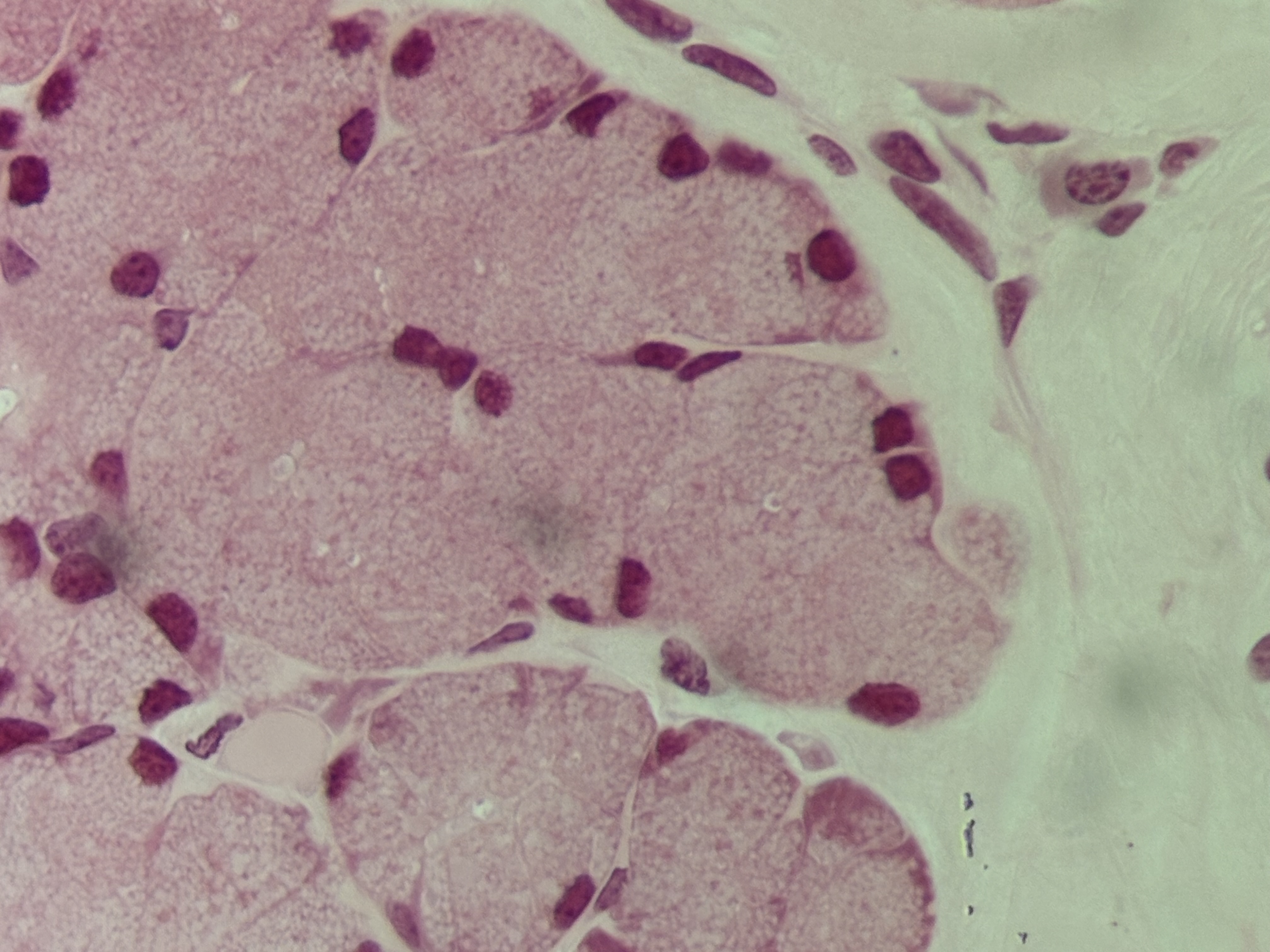
Simple cuboidal ET
Structure: single layer as tall as wide, cube cells, centrally located nucleus.
Function: absorption and secretion.
Location: sweat glands, kidney tubules.
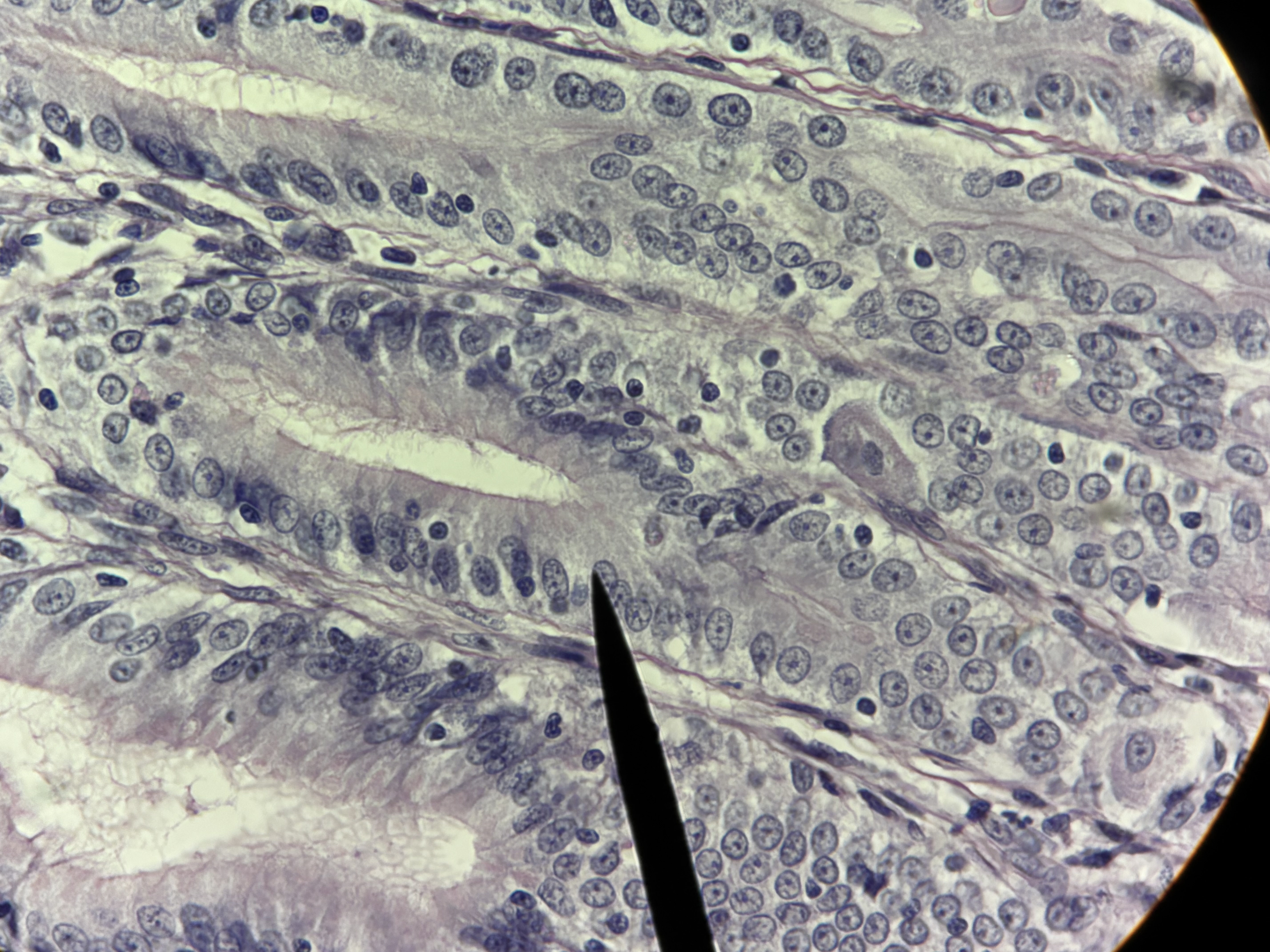
Simple Columnar ET
Structure: single layer, tall, narrow column shaped cells, oval shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise in the basal region, microvilli, May contain goblet cells.
Function: absorption and secretion.
Locations: stomach, small intestines, and gallbladder.
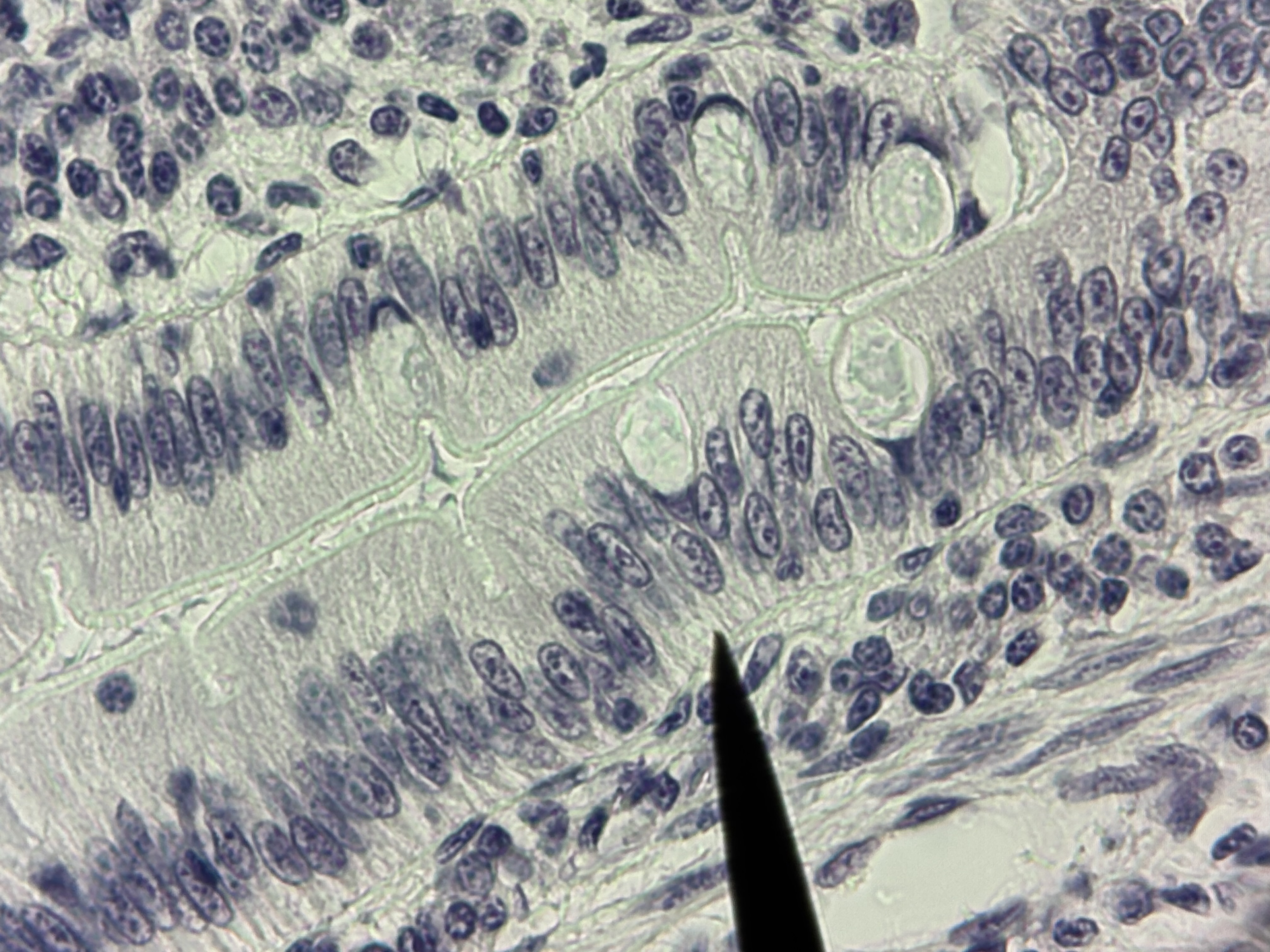
Simple Columnar ET with goblet cells and microvilli
Structure: single layer of tall, narrow, ciliated cells.Oval shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise in the basal region.Goblet cells present.
Function: secretion of mucin and movement of mucus along the apical surface.
Location: lining of uterine tubes and larger bronchioles
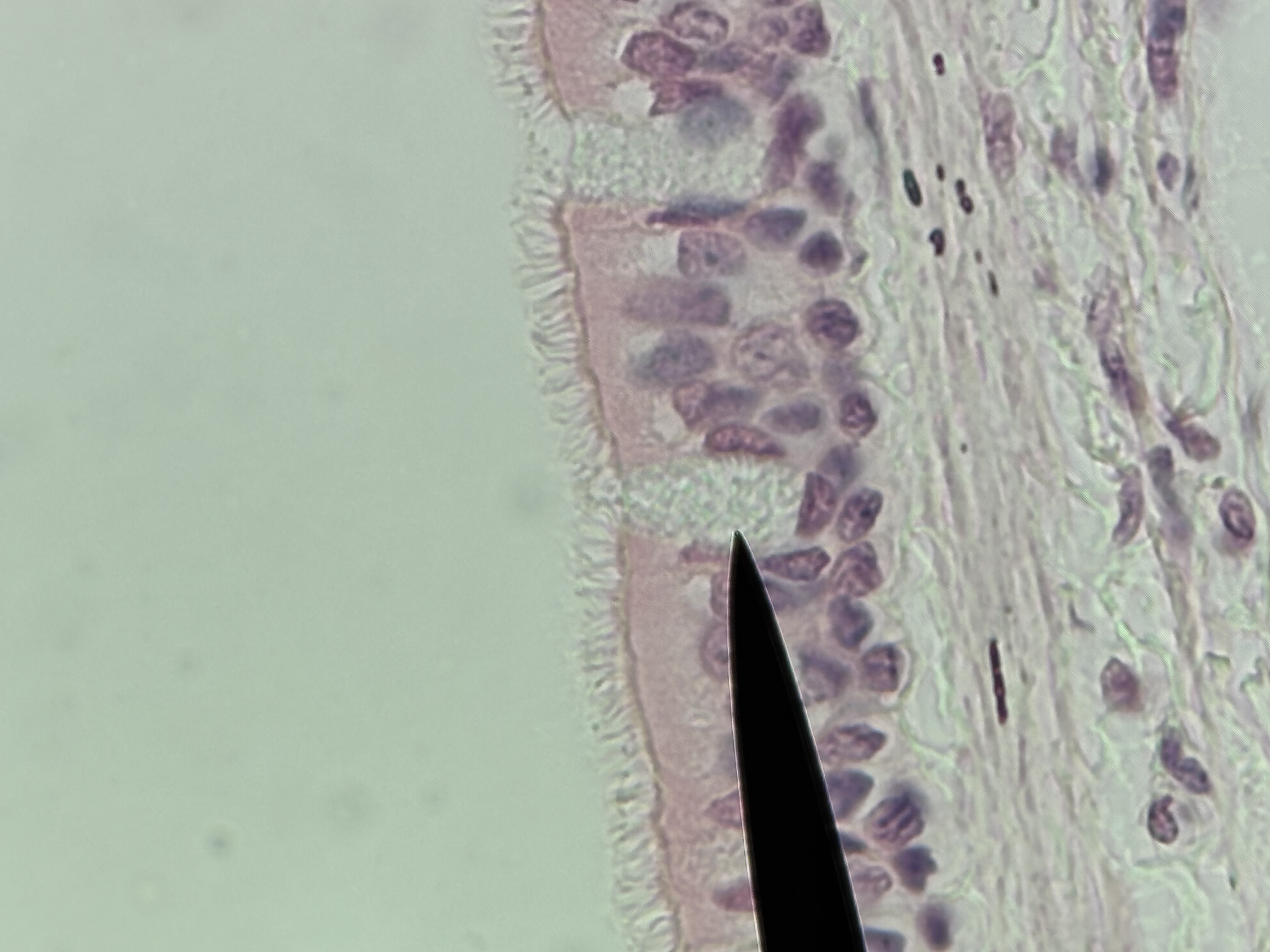
Psuedostratified Ciliated Columnar ET with goblet cells
Structure: single layer of cells with varying heights that appear multilayered. All cells connect with the basement membrane. Nuclei not in a line, goblet cells and cilia.
Function: protection, secretion and movement of mucus.
Location: airways of the trachea and nasal cavity.
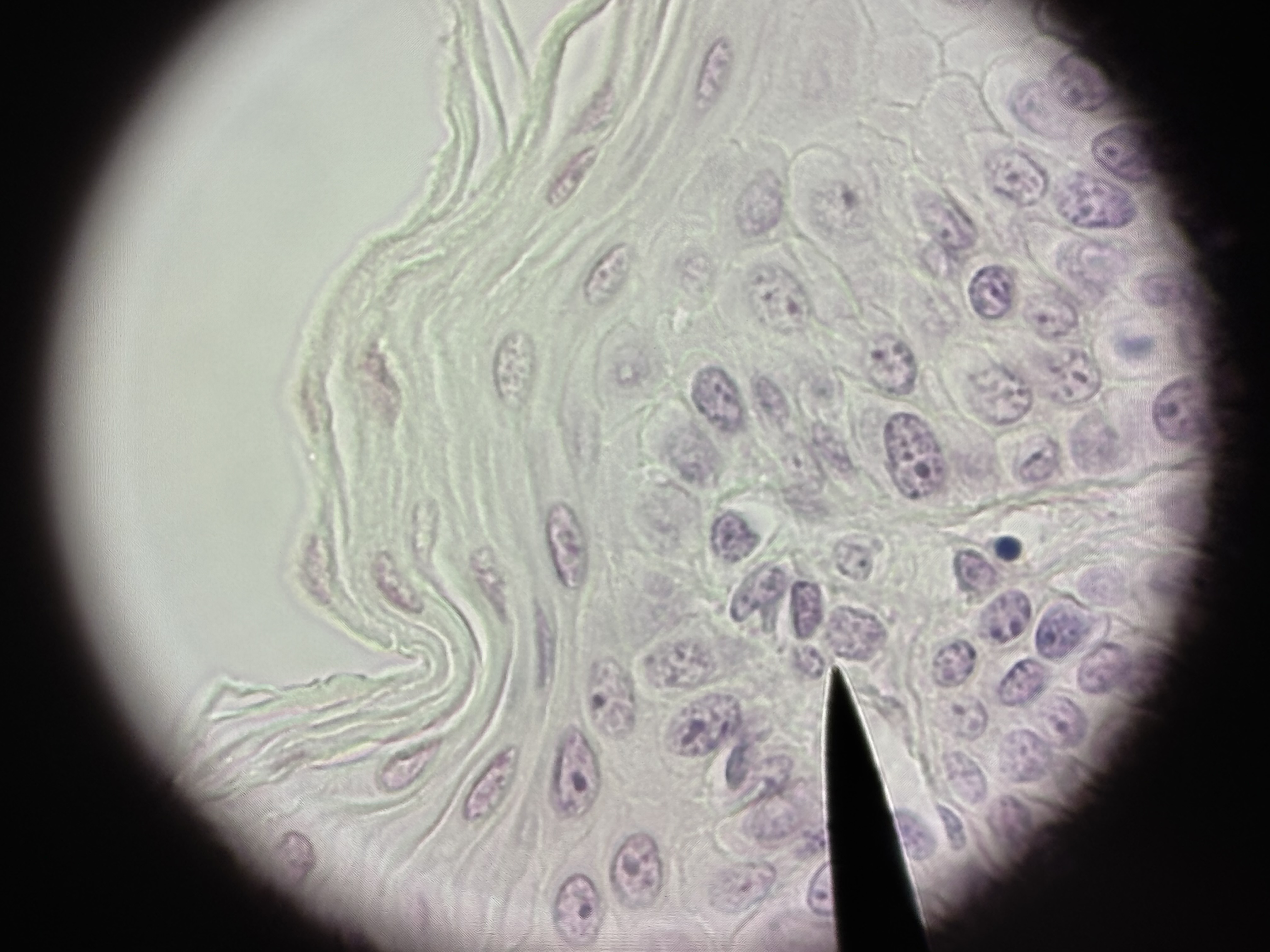
Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous ET
Structure: multiple layers of cells. Basal cells cuboidal or polyhedral. Apical cells squamous. Surface cell layer alive.
Location: vagina lining, mouth, esophagus, anus canal.
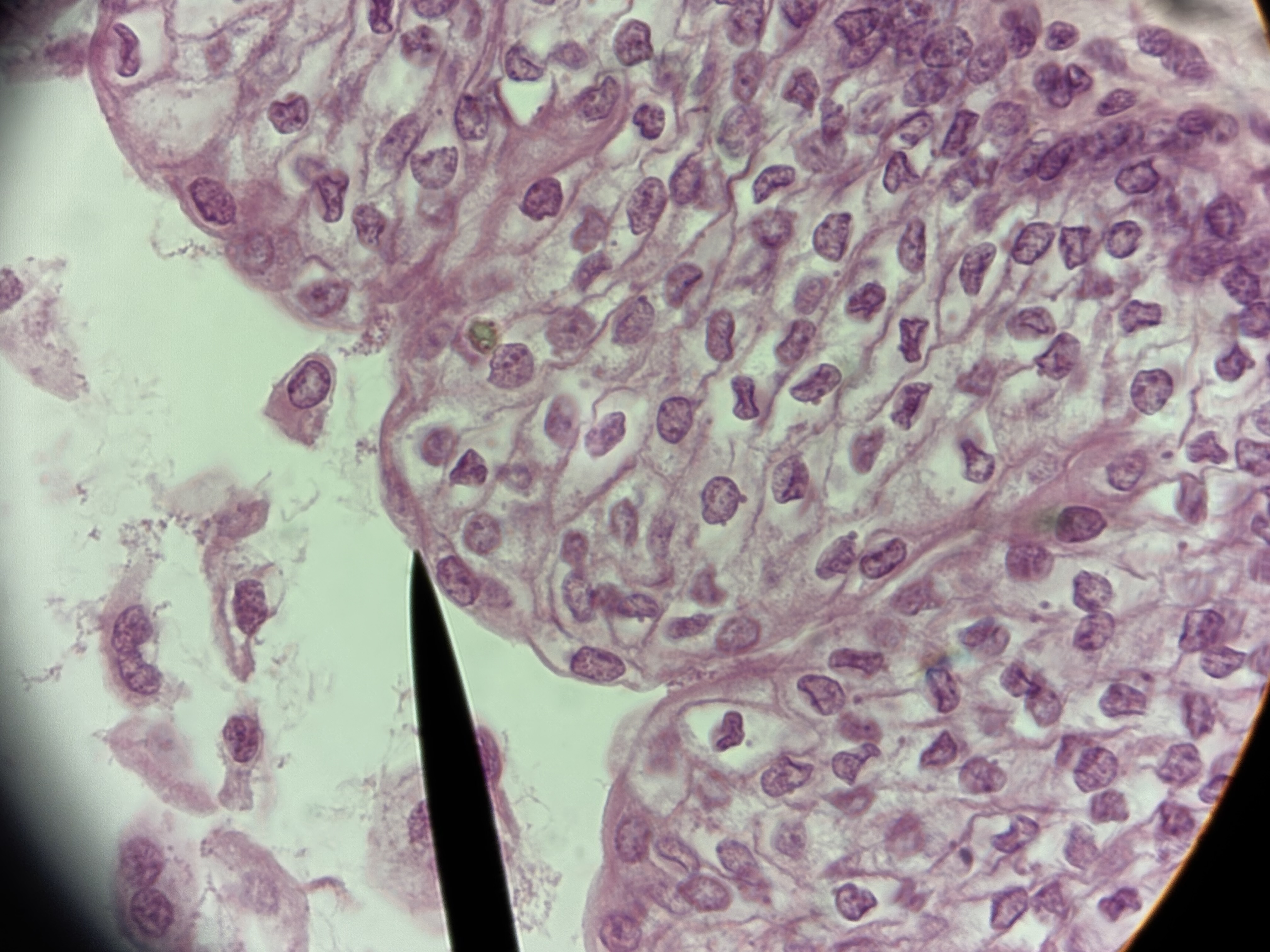
Transitional ET
Structure: Stratified cuboidal ET but does not stay. Apical layer can change shape due to stretching. cuboidal = not stretched. squamous = stretched
Function: distension and relaxation to accommodate urine volume changes
Location: lining of the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra.
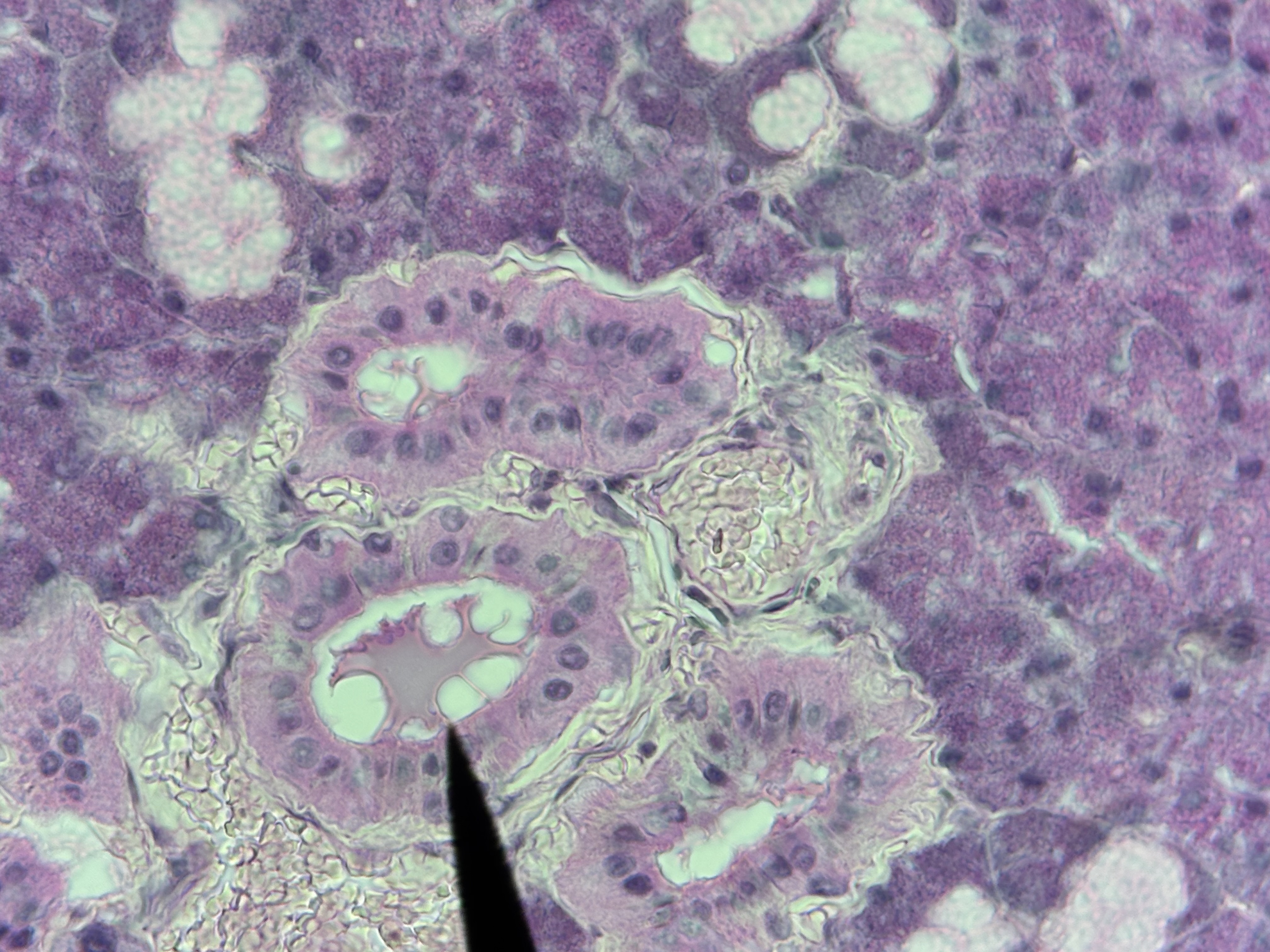
Glandular ET - Exocrine
Function: Secrete using a duct to a free surface.
Location: skin, stomach, sweat glands.
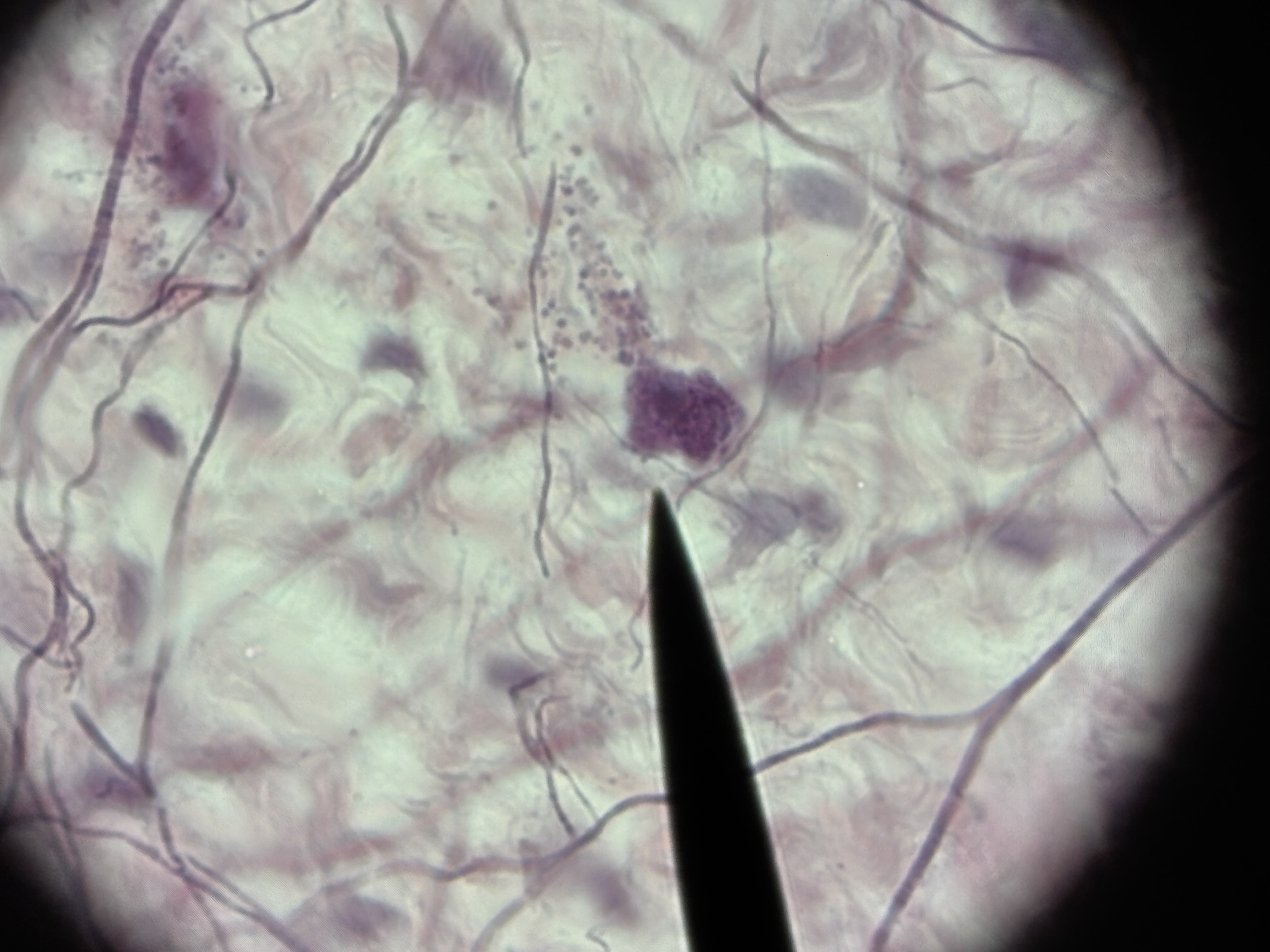
Areolar CT
Structure: Contains all 3 fiber types. Contains all cell types. Abundant vascularized GS is gel like. Scattered fibroblasts. Many blood vessels.
Function: connect tissues together. Provides metabolic support,
Location: surrounding nerves, vessels, and subcutaneous layer.
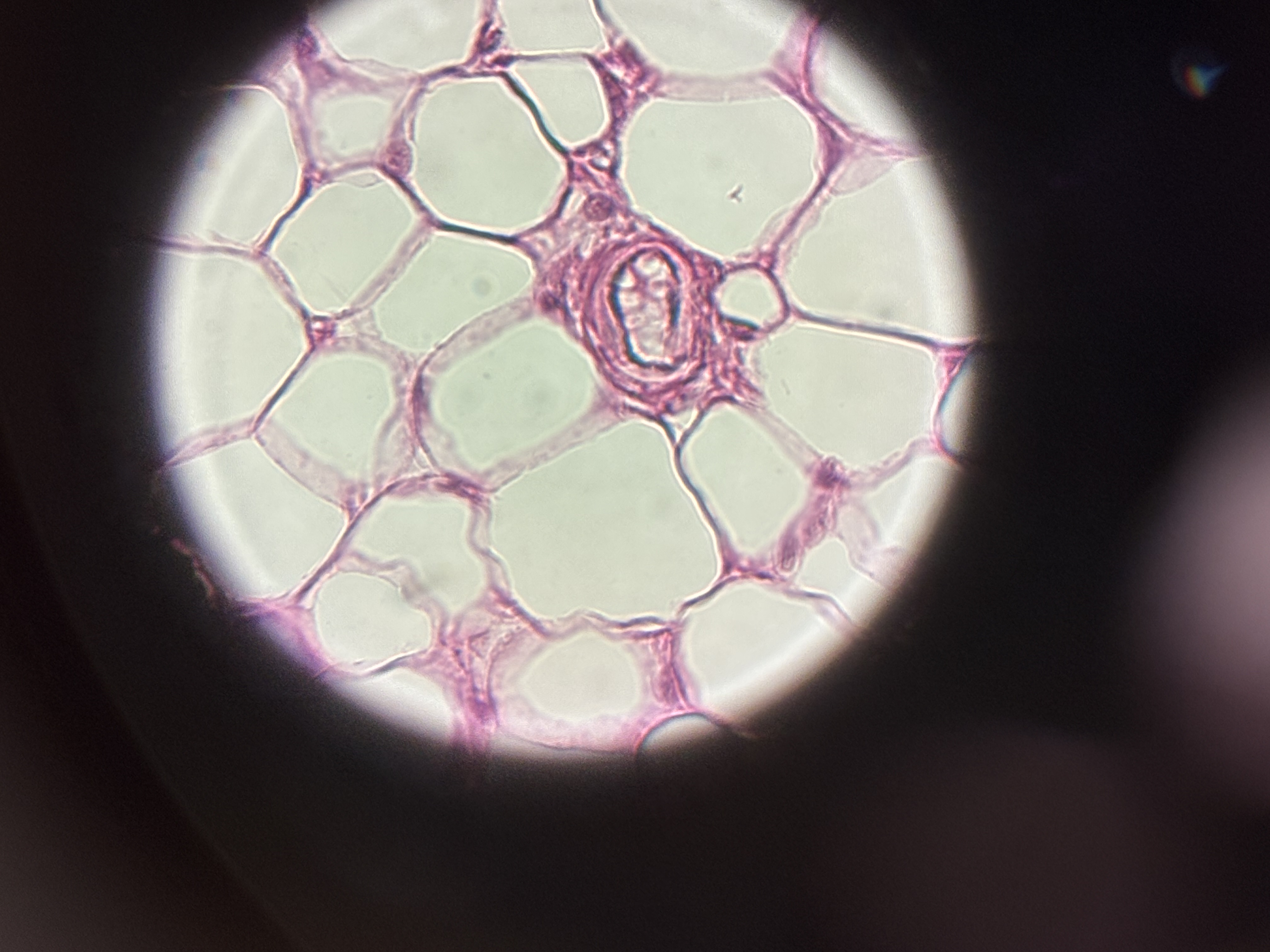
Adipose CT
Structure: fat tissue. Contains adipocytes. Most of central space is fat. Not many organelles. Nucleus is pushed to the side. Not much ECM.
Function: protection, provides energy, cushion, insulation.
Location: subcutaneous layer, surrounding kidneys and selected organs.
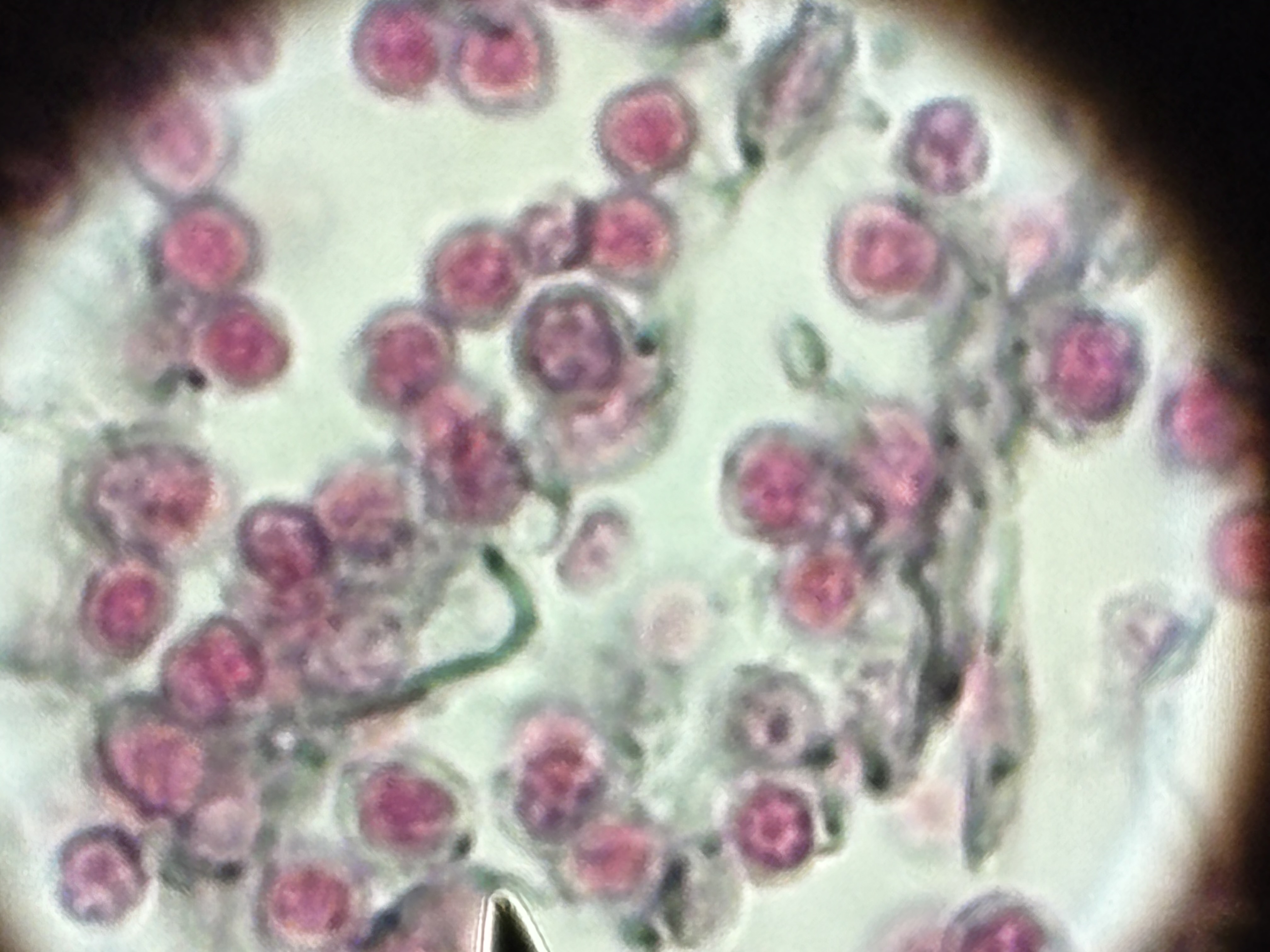
Reticular CT
Structure: mesh work of reticular fibers.
Function: support cells in soft organs. Forms stoma of lymphatic organs.
Location: soft organs: spleen, liver, lymph nodes, bone marrow.
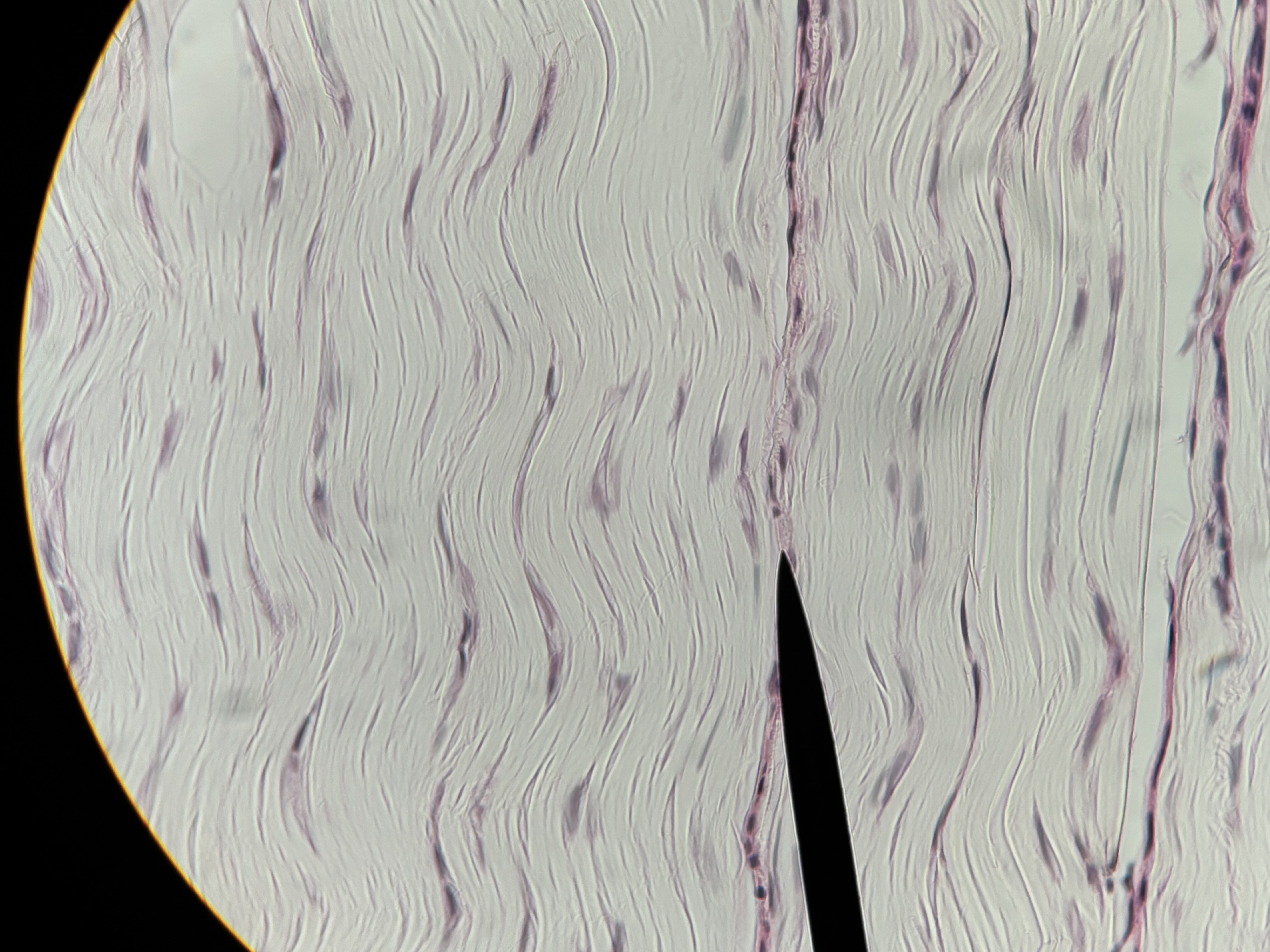
Dense regular CT
Structure: densely packed collagen fibers parallel to direction of stress.
Function: strength and flexibility in one direction. Connects muscle to bone and bone to bone.
Location: tendons and ligaments.
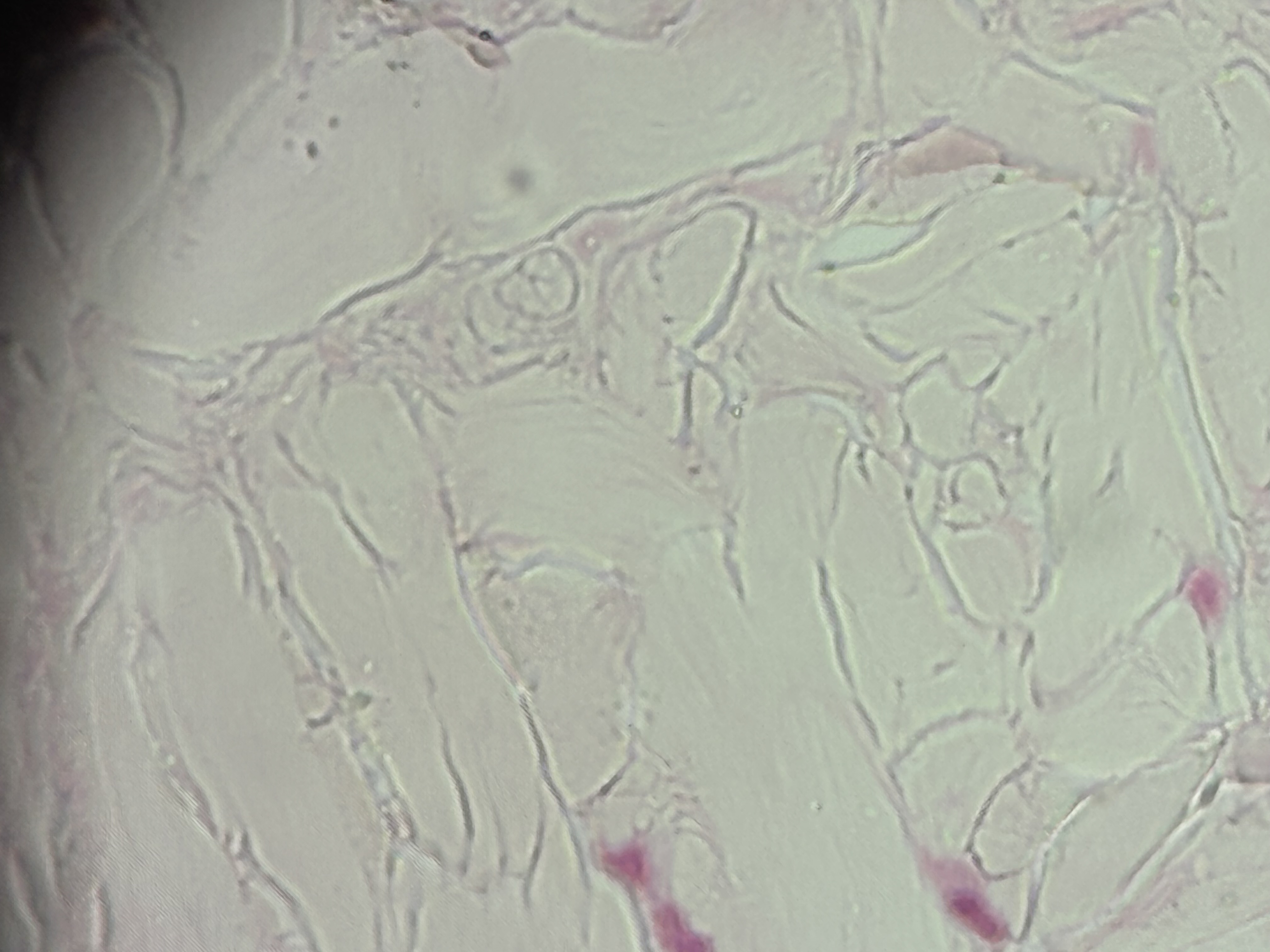
Dense irregular CT
Structure: densely packed interwoven collagen fibers. Irregularly clumped together and project in all directions.
Function: tensile strength in all directions.
Location: dermis of skin, capsules of organs.
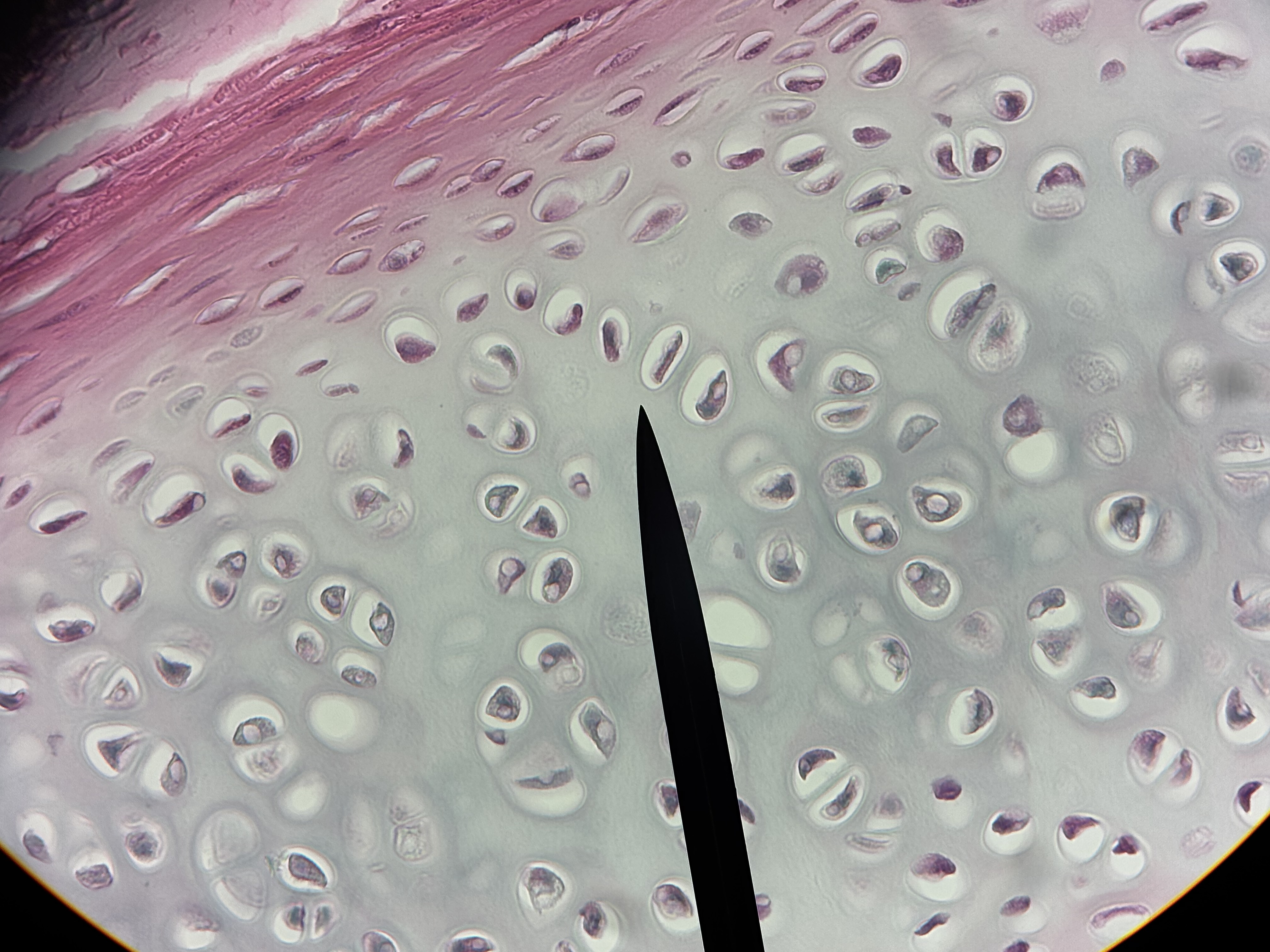
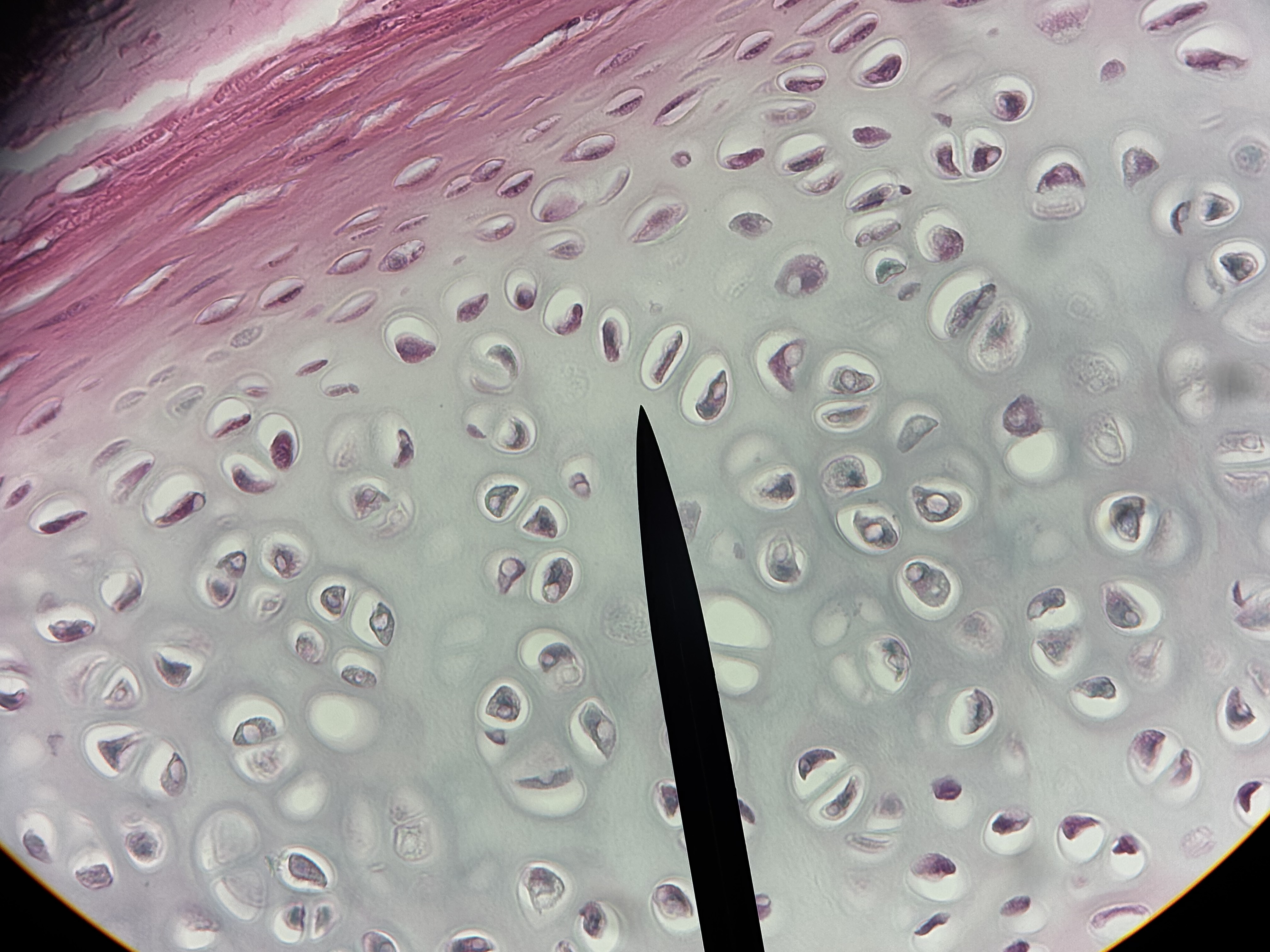
Hyaline cartilage
Structure: glossy appearing matrix. Lacunae house chondrocytes. Usually covered in perichondrium.
Function: smooth surfaces for movement at joints. Model for bone growth. Supports soft tissue.
Location: covers articular ends of long bones, most of fetal skeleton, costal cartilage: most of larynx, trachea, and nose.
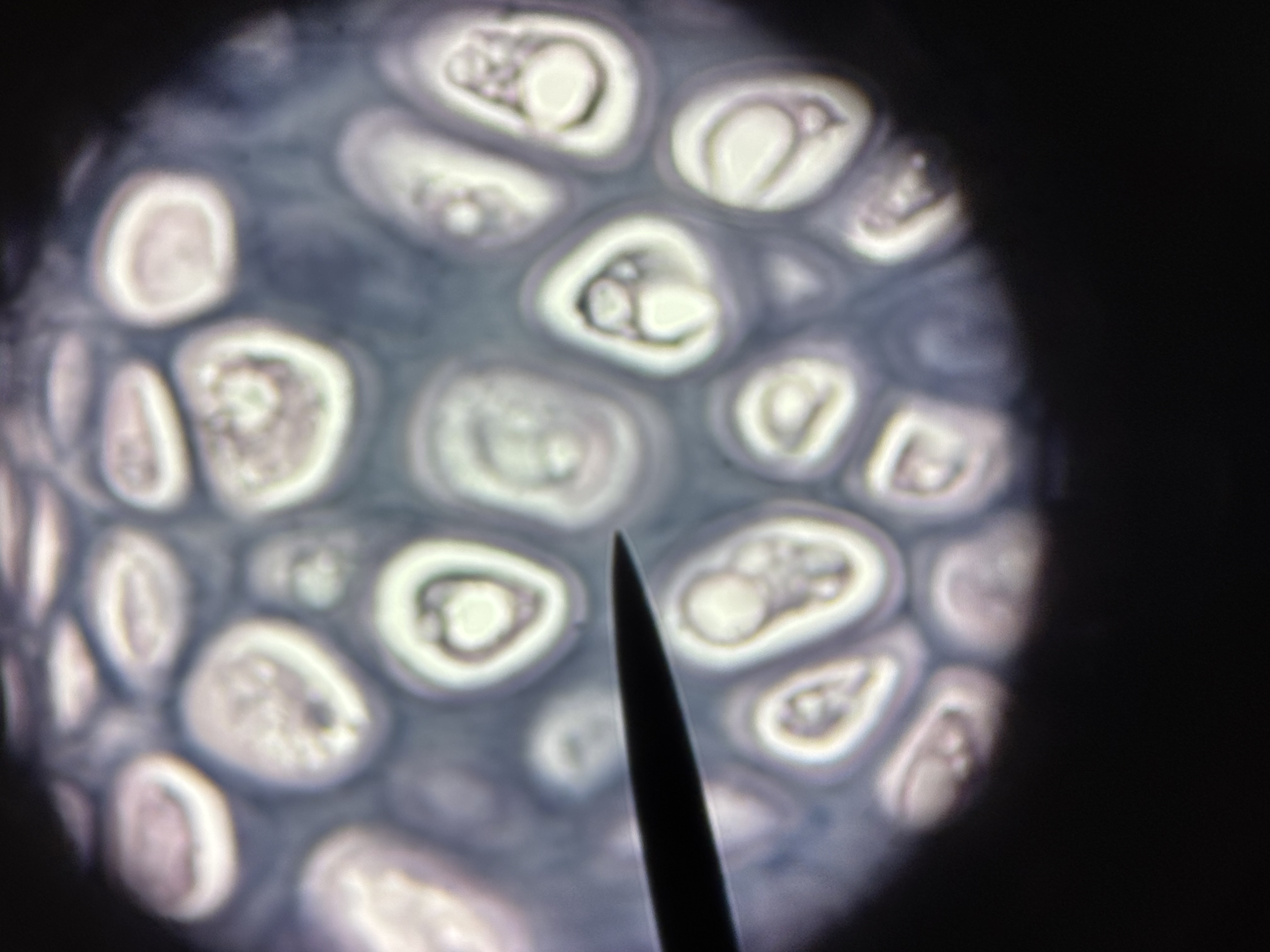
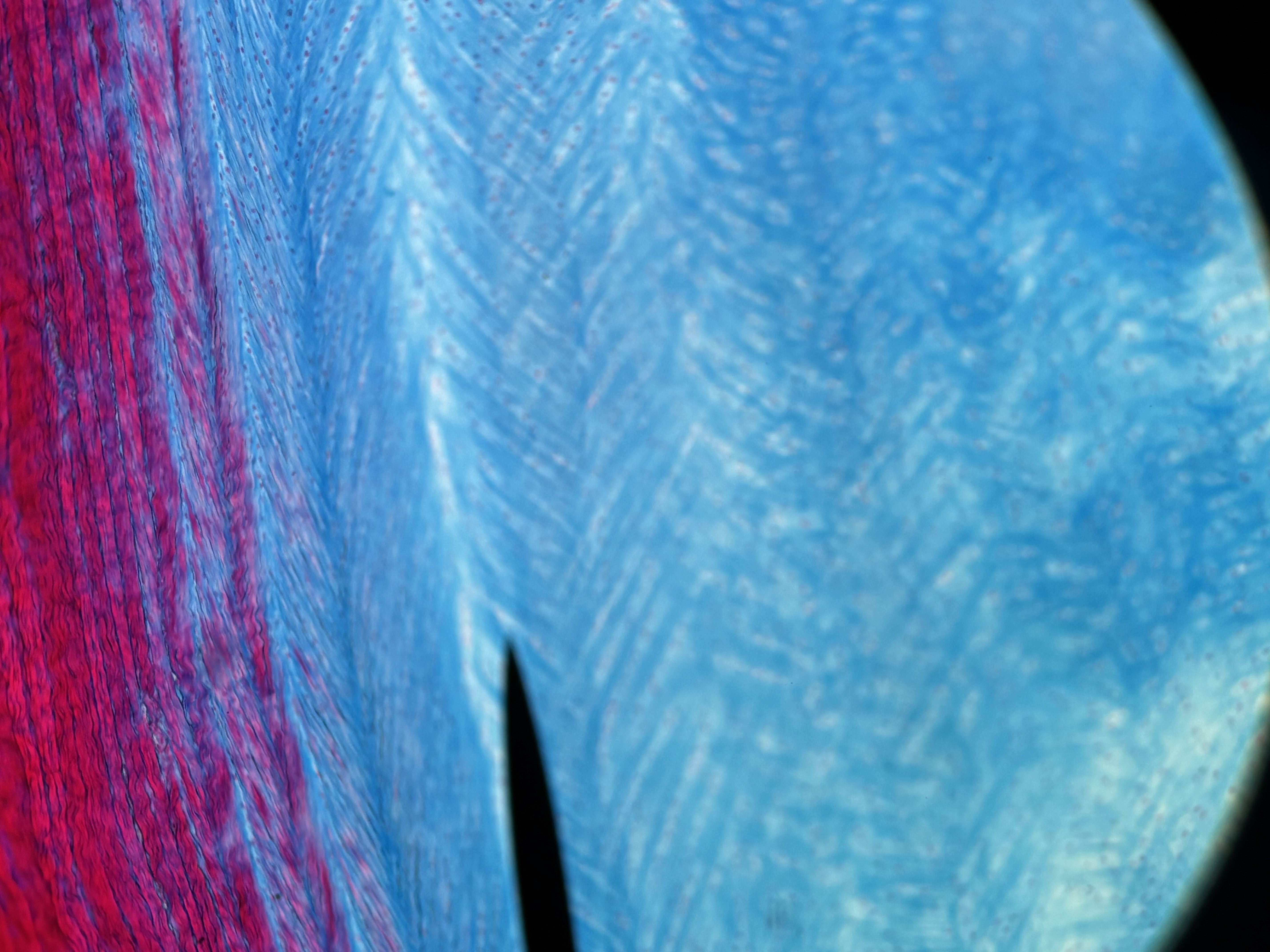
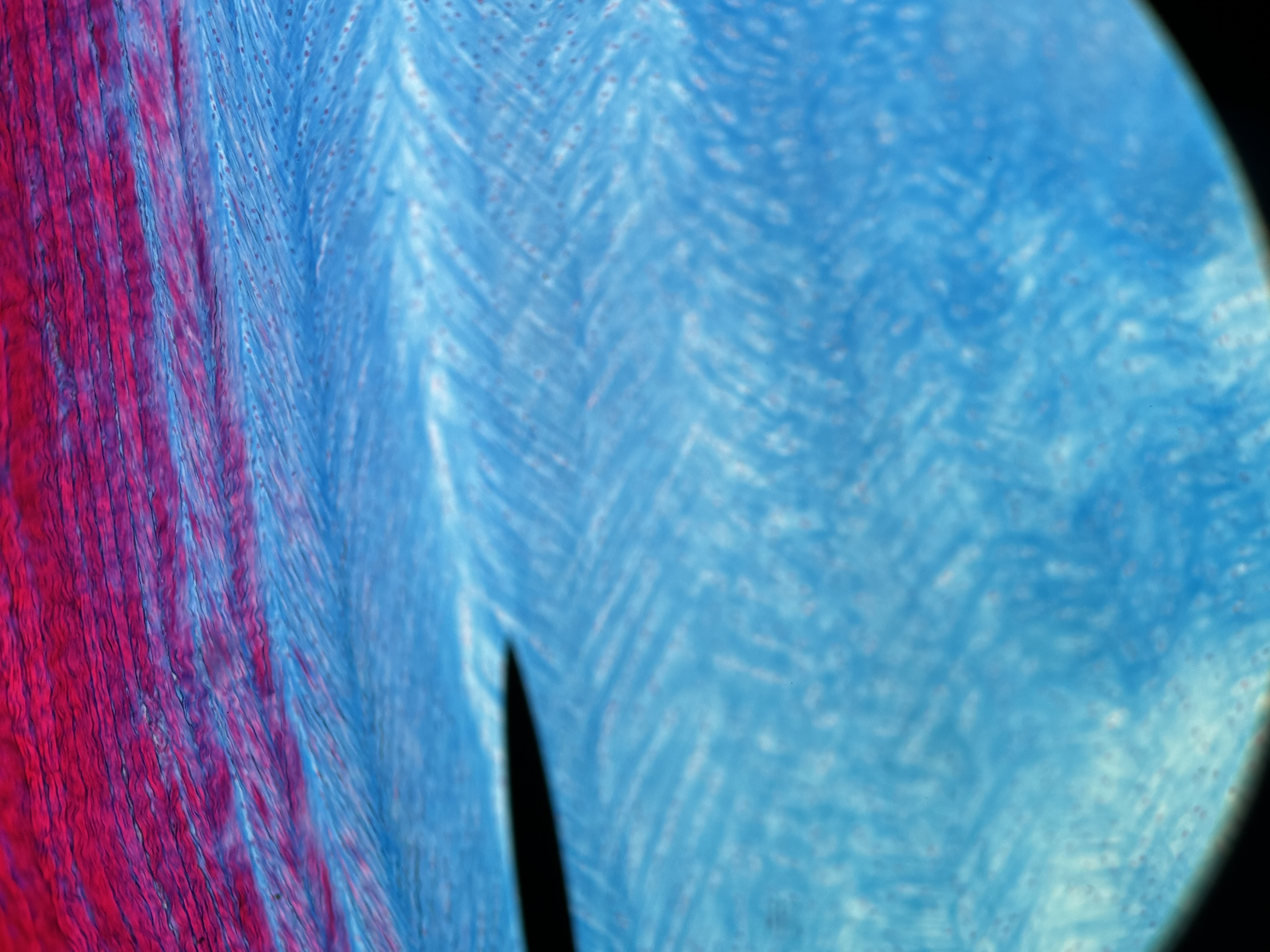
Elastic cartilage
Structure: contains abundant elastic fibers. Elastic fibers form weblike mesh around lacunae. Perichondrium present.
Function: maintains structure and shape while permitting extensive flexibility.
Location: external ear, epiglottis
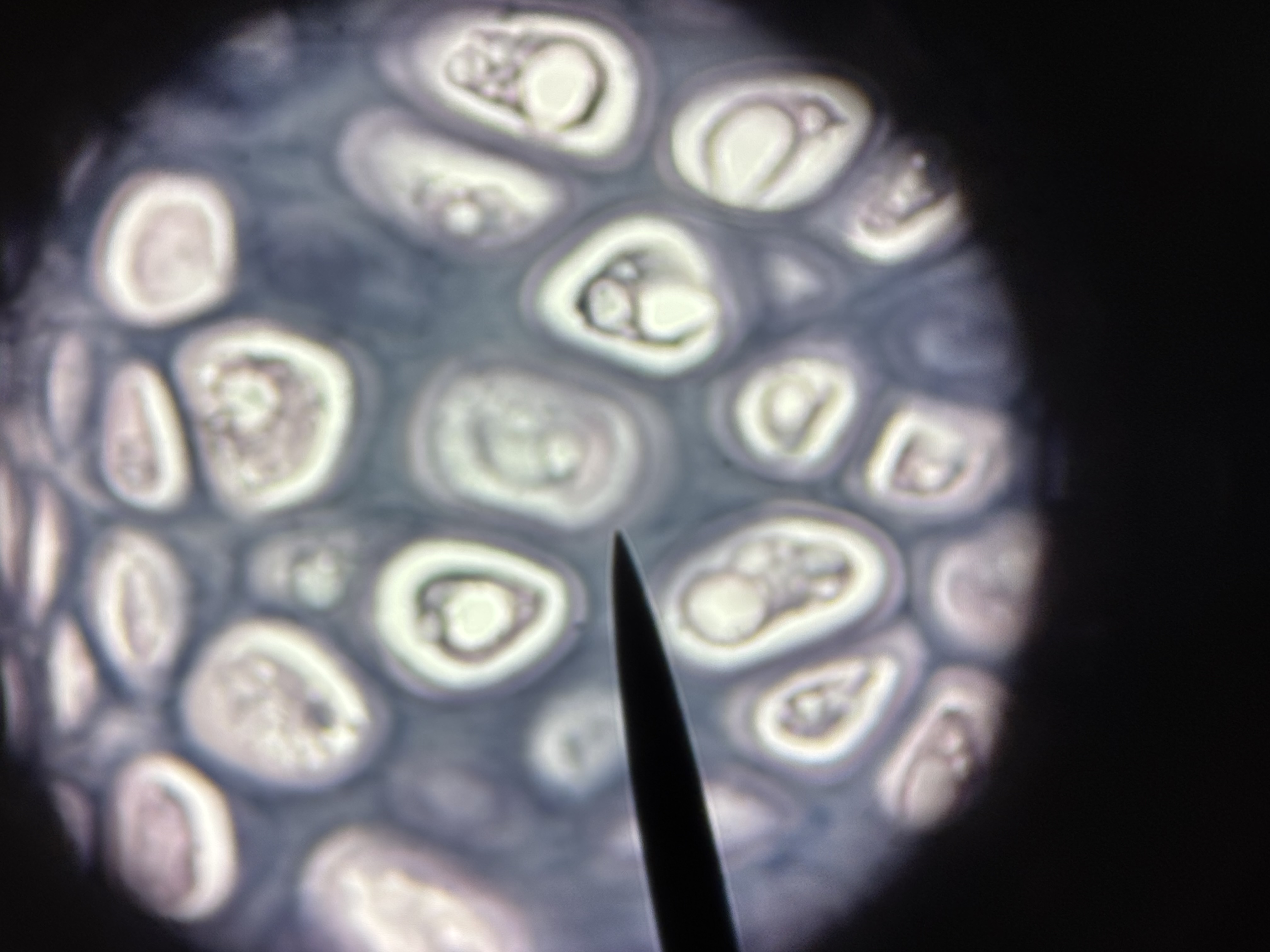

Fibrocartilage
Structure: easily visible, parallel collagen fibers in matrix. Lacunae house chondrocytes. No perichondrium.
Function: resists compression. Absorbs shock in some joints.
Location: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee joints.

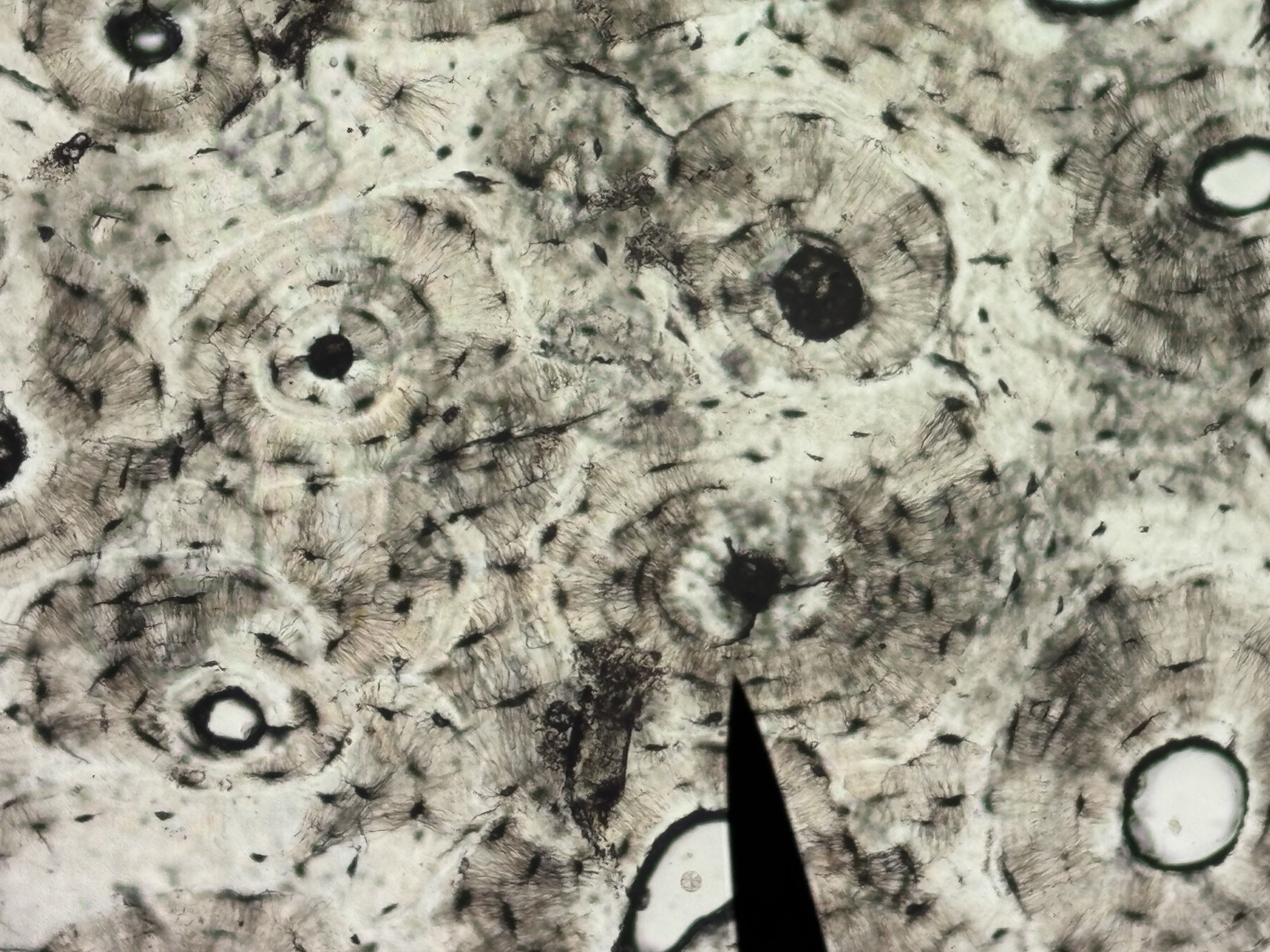
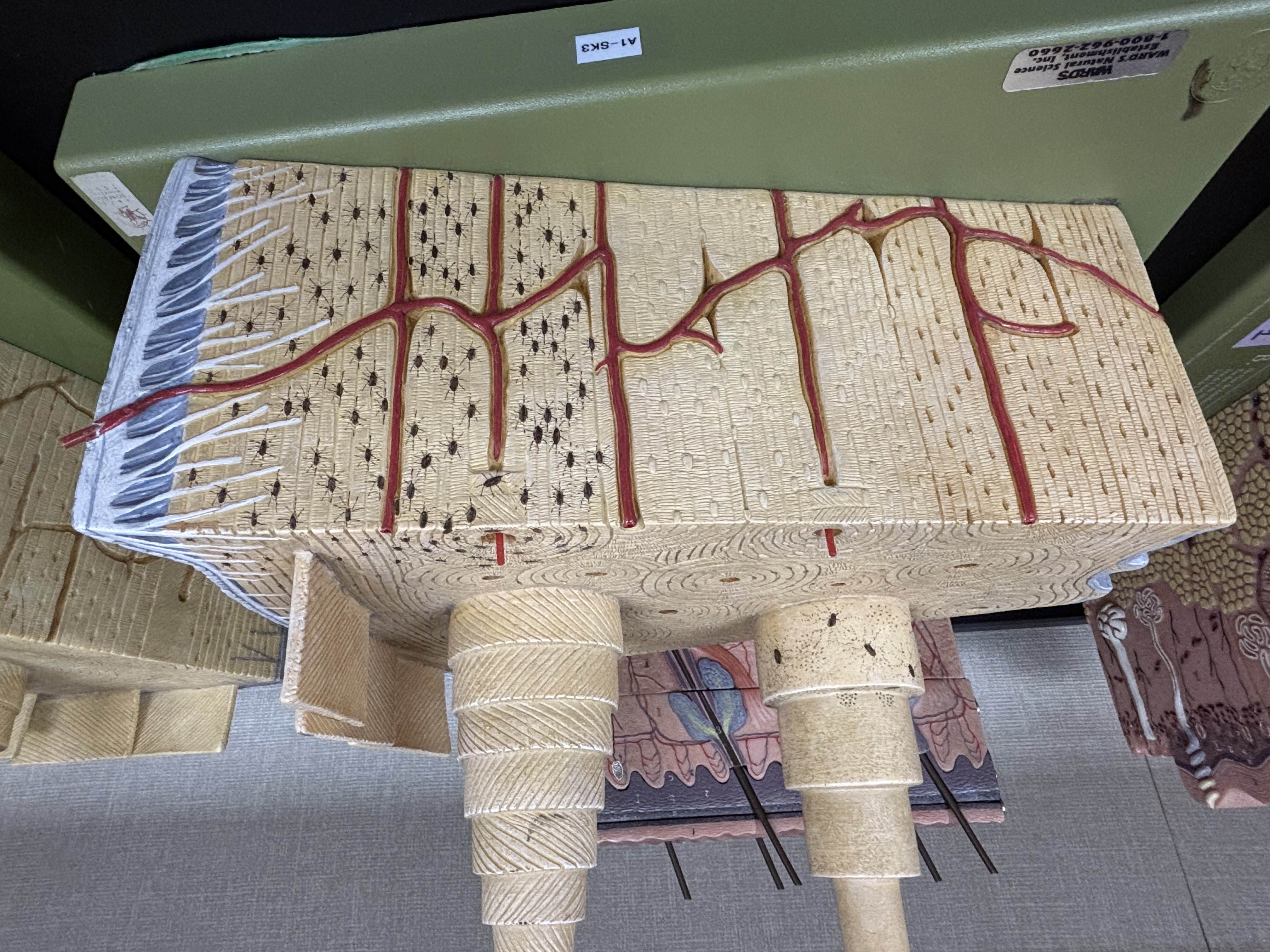
Compact bone
Structure: dense and solid. Organized into columns. Appears solid, perforated by vascular canals. Calcified matrix arranged in osteons
Function: supports soft structures, protects vital organs, provides levers for movement, stores calcium and phosphorus.
Location: outer layer of bones.

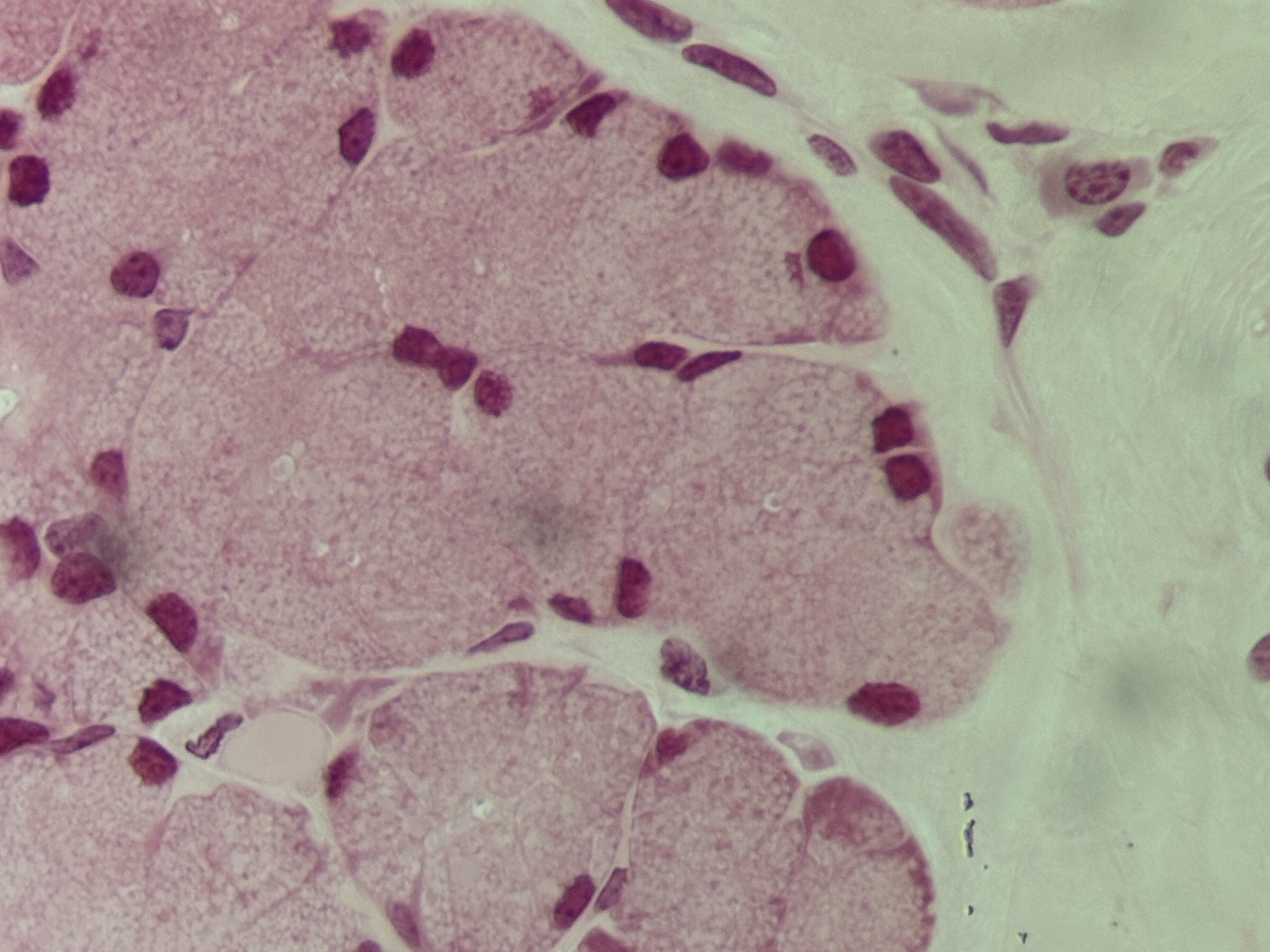
Plasma cells
Structure: small cells with a distinct nucleus derived from activated B-lymphocytes.
Function: form antibodies that bind to foreign substances, bacteria, and viruses.
Location: lymphatic organs, respiratory tract, salivary glands