Opt 113 final: brainstem (overview, medulla oblongata)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what does the brainstem contain (generally)
reflex centers and cranial nerve nuclei
what does the brainstem do
connect tracts between the spinal cord, diencephalon, and cerebrum
what reflex centers are found in the brainstem
respiration, cardiovascular control, consciousness
what cranial nerve nuclei are found in the brainstem
3-12
what is the brainstem divided into
medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain
what is the other name for medulla oblongata
myelencephalon
what is the other name for the pons
metencephalon
what is the other name for the midbrain
mesencephalon
what forms the border of the medulla oblongata
spinal cord and pons
what is found down the middle of the anterior surface of the medulla
midsagittal anterior median fissure
what does the midsagittal anterior median fissure divide
pyramids
what do the pyramids contain
white matter motor/efferent tracts
what white matter motor tracts are found in the pyramids
corticospinal and corticobulbar
what occurs at the inferior/caudal end of the medulla
decussation of the pyramids
what is found on the superior lateral surface of the medulla
olives
what are the olives of the medulla
two bumps on the lateral medulla
where are the olives
lateral to the medulla
what is found on the dorsal most part of the medulla
medullary tegmentum
what is the medullary tegmentum continuous with
rostral pontine tegmentum
what is found within the medullary tegmentum
cranial nerve nuclei, reticular formation nuclei, other nuclei, white matter of sensory spinal tracts
the superior posterior medulla makes up what
part of the 4th ventricle floor
what projection is formed by the vagal cranial nerve nuclei in the medulla
vagal triangle
what projection is formed by the hypoglossal nerve nuclei in the medulla
hypoglossal triangle
what is found in the middle of the posterior surface of the medulla
posterior median sulcus
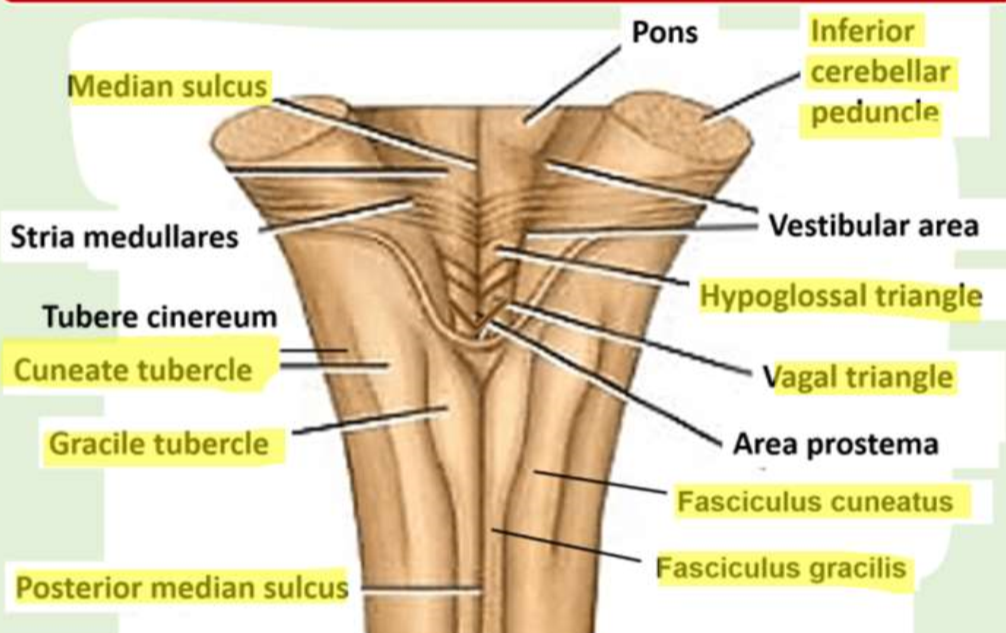
what does the posterior median sulcus separate
gracile tubercles
what are found lateral to the gracile tubercles
cuneate tubercles
where are the gracile nuclei found
in the gracile tubercles
where are the cuneate nuclei found
in the cuneate tubercles
what afferent information enters the gracile/cuneate nuclei
touch sensation from the spinal cord
how does touch enter the gracile/cuneate nuclei
though the gracile/cuneate funiculi
the gracile/cuneate funiculi are part of what
afferent posterior column medial lemniscal pathway
what olivary nuclei are present in the posterior medulla
inferior, dorsal, medial accessory
what are the olivary nuclei of the posterior medulla involved with
voluntary movement (motor cordination)
where do olivary nuclei of the posterior medulla send information
decussating fibers to the cerebellum
what 5 nuclei are found in the posterior medulla
nucleus ambiguous, solitary tract nucleus, dorsal nucleus of the vagus, hypoglossal nucleus, vestibulocnuclear complex
what cranial nerves are associated with the nucleus ambiguous
9, 10, 11
what function is associated with the nucleus ambiguous
controls muscles of the throat
what cranial nerves are found in the solitary tract nucleus
7, 9, 10
what afferent information is received by the solitary tract nucleus
visceral sensation and taste
cranial nerve 7, 9, 10 make up what
solitary tract
what cranial nerves are associated with the dorsal nucleus of the vagus
10
what function does the dorsal nucleus of the vagus have
controls parasympathetic functions of the vagus
what cranial nerves are associated with the hypoglossal nucleus
12
what cranial nerves are associated with the vestibulonuclear complex
8