Biomolecules and Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the four categories of organic macromolecules essential to life?
Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.

What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
To provide quick energy for the body.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids.

What elements are commonly found in lipids?
Carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
What is the structure that tells cells what to do?
Nucleotides.
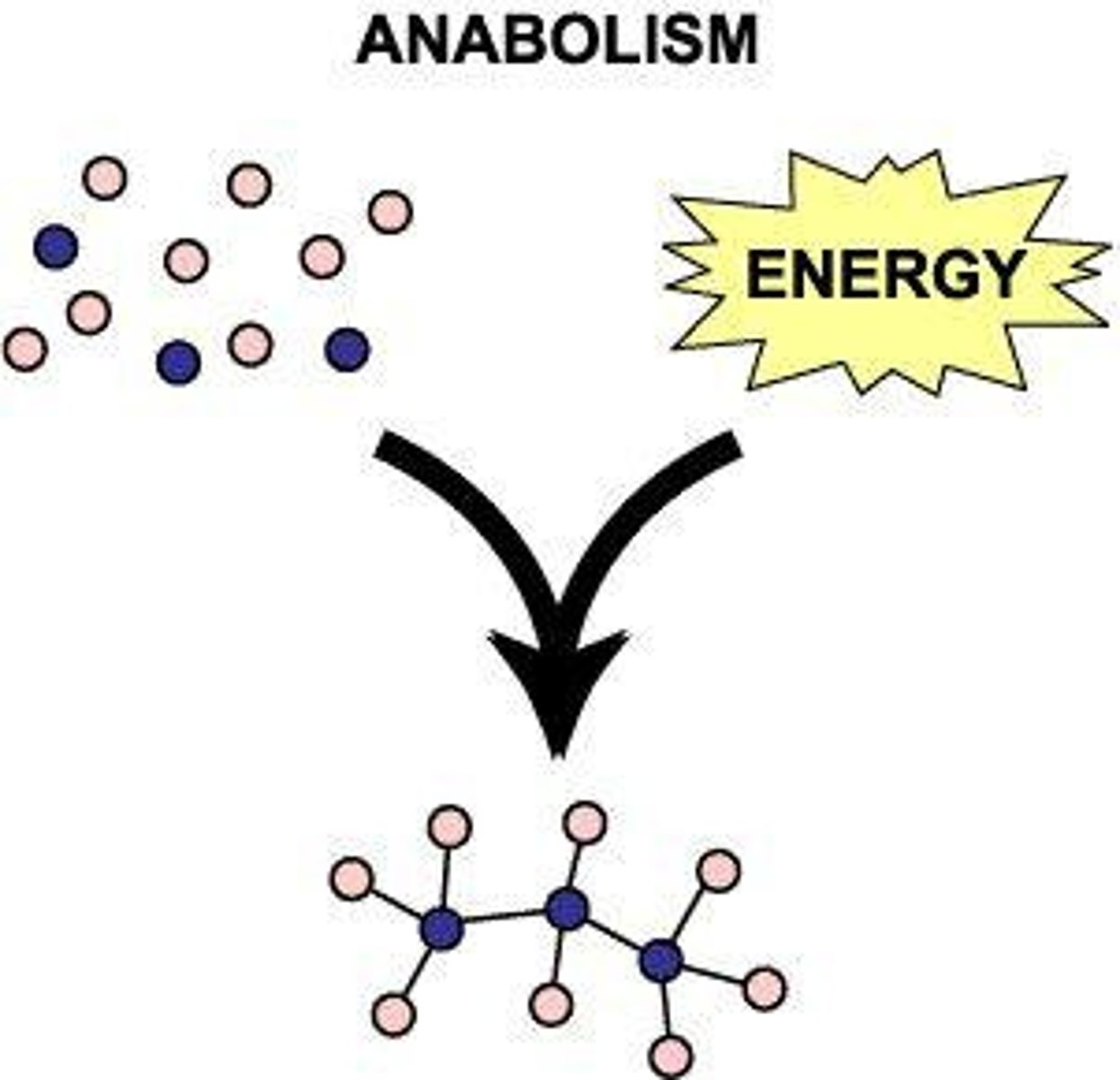
What is metabolism?
The sum of catabolic and anabolic reactions in the body.
What happens during catabolic reactions?
Molecules are broken down, such as digesting food for energy.
What occurs during anabolic reactions?
Molecules are built up, such as connecting sugars to store in the liver.
What is polymerization?
The process of building large molecules by joining smaller ones together.

What is a monomer?
A single unit or building block of a polymer.
What is a polymer?
A large molecule made up of many monomers.
What is the relationship between monomers and polymers?
Monomers join together to form polymers through anabolic processes.
What are examples of foods high in carbohydrates?
Bread and pasta.
What types of molecules are enzymes made from?
Proteins, which are composed of amino acids.
What are the three main types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
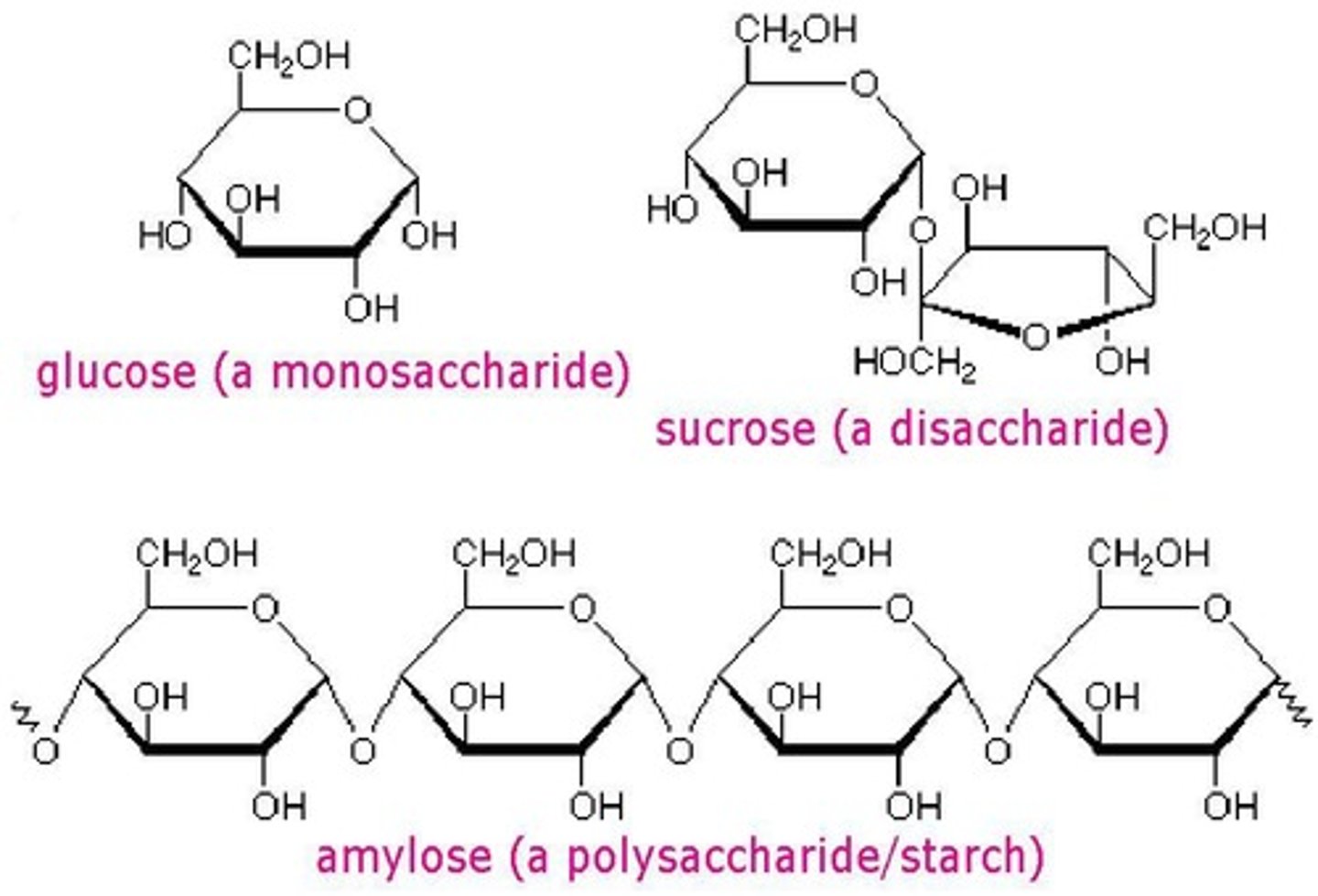
What is a monosaccharide?
The simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar molecules like glucose.
What is a disaccharide and give an example?
A disaccharide is formed from two monosaccharides; an example is lactose, made from glucose and galactose.
What is starch?
A polysaccharide made up of many glucose monomers linked together.
What enzyme breaks down starch?
Amylase.
What happens to salivary amylase in stomach acid?
It stops working.
How are monosaccharides absorbed into the bloodstream?
Through active transport and facilitated diffusion in the small intestine.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The amino acid sequence determined by DNA.

What enzyme does the stomach release for protein digestion?
Pepsin.
What is unique about pepsin's activity?
It is most active in the stomach's acidic environment.
How do proteases from the pancreas contribute to digestion?
They break down proteins and peptides for absorption.
What is the role of enzymes in the small intestine?
They complete the breakdown of food fragments that didn't fully digest.
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides.
What enzyme breaks down nucleic acids?
Nuclease.
What are the three components of nucleotides?
Phosphate group, sugar, and nitrogenous base.
What are the building blocks of fats (triglycerides)?
Three fatty acid chains connected to one glycerol molecule.
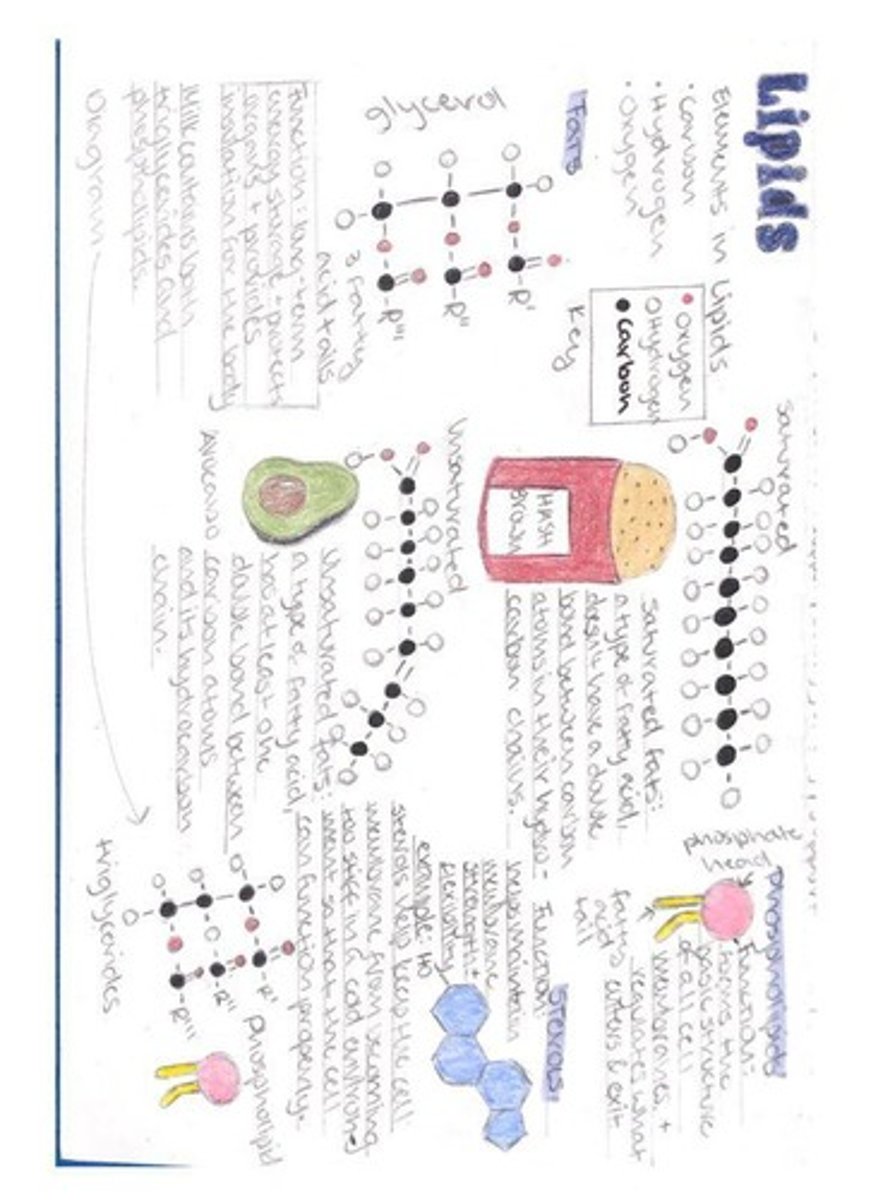
What is the role of bile in fat digestion?
To break down fats into smaller droplets for easier digestion.
How are fatty acids absorbed into the bloodstream?
They diffuse into the cell membrane and are packaged into transport containers.
What does the enzyme lipase do?
It splits triglycerides into two fatty acid tails and a monoglyceride.
What is the function of proteins in digestion?
They speed up chemical reactions as enzymes and provide transport tunnels for monomers.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The arrangement of two or more polypeptides wrapped together.
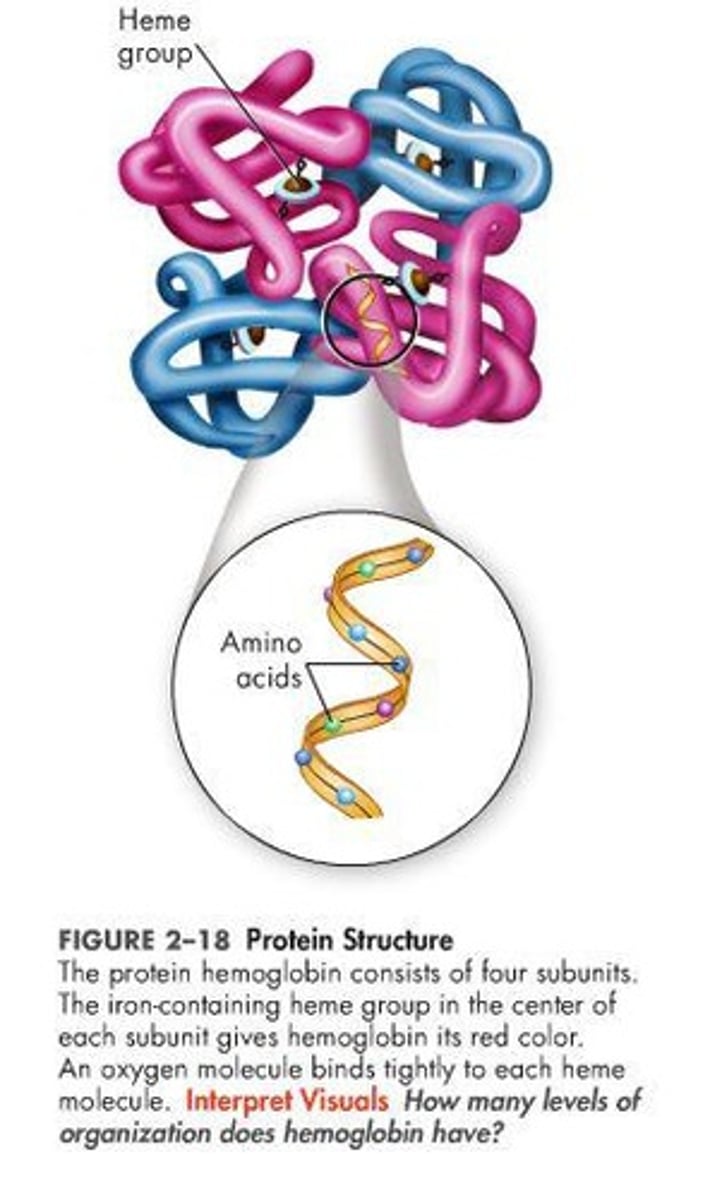
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
The formation of hydrogen bonds between amino acids, resulting in beta pleated sheets or alpha helices.
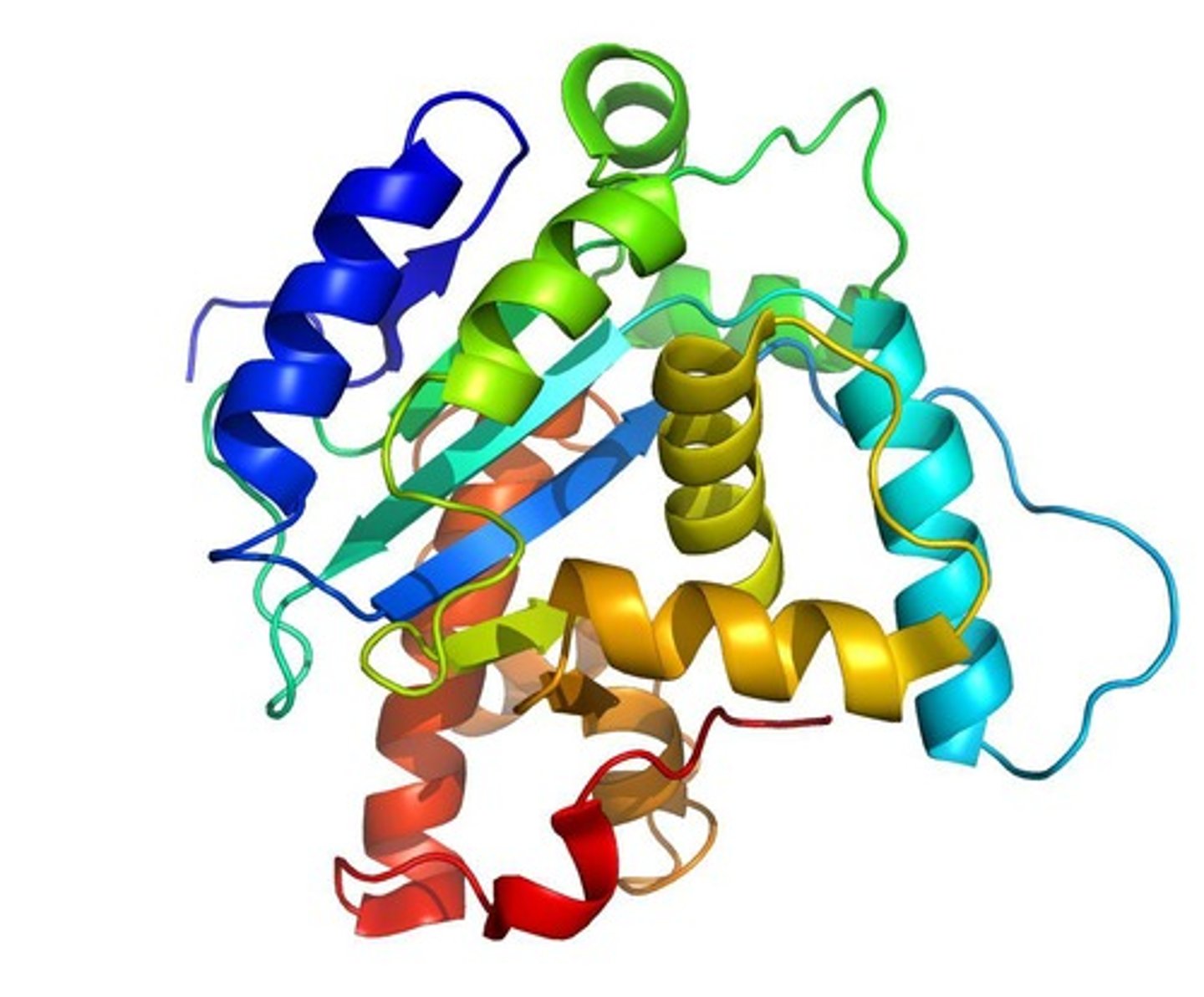
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The overall 3D shape formed by interactions between R-groups of amino acids.
What is the specificity of enzymes?
One enzyme can only match with one substrate.

What are the two types of digestion?
Mechanical digestion (physical breakdown) and chemical digestion (enzymatic breakdown).