Week 8: Disability Paradox
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
How do we define pathogenesis?
The origin of the disease
study of the origin and development of disease
How do we define salutogensis?
looking at the factors that support health rather than factors that cause disease (pathogenesis)
Assets approach:
Gratitude
Self-efficacy
Hardiness
Empathy
Humor
What produces health
_________ and _________ factors can influence a persons health
Personal
Enviromental
Personal
Persons characteristics
Self-efficacy
Environmental
The physical, social and attitudinal (external to the person)
Social Support
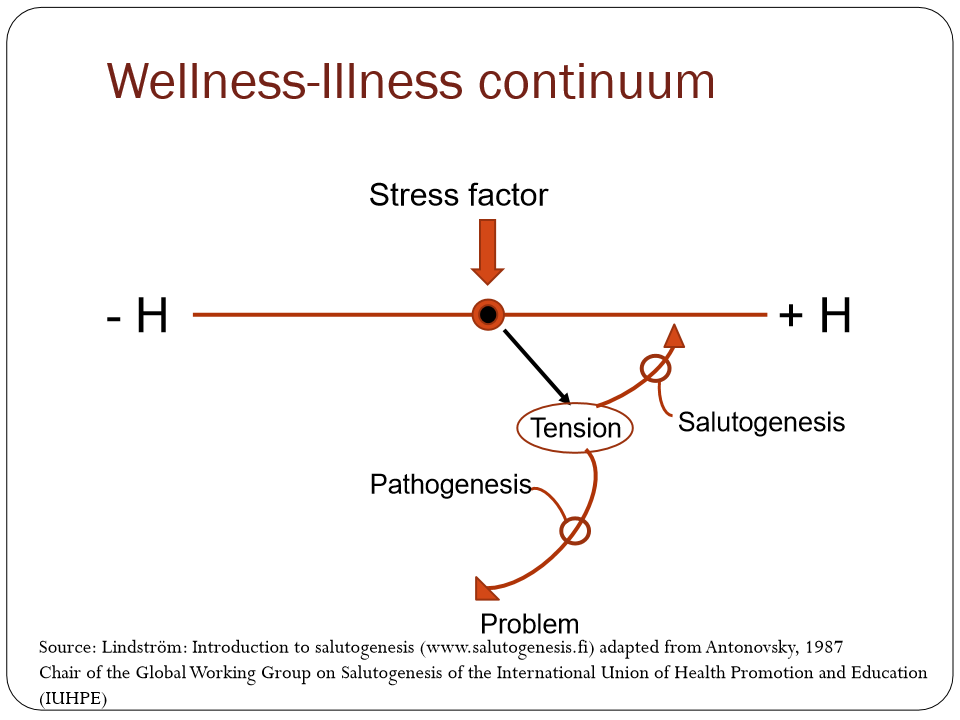
What is the wellness-illness continuum?
Health is a continuum
+H :complete health
- H : negative health
throughout your life there will be stress factors (changes in life) ) and this will impact health by creating tension in the body
Salutogensis can kick in and bring them to good health
Other pathology sets in and brings the person to the lower part of the continuum
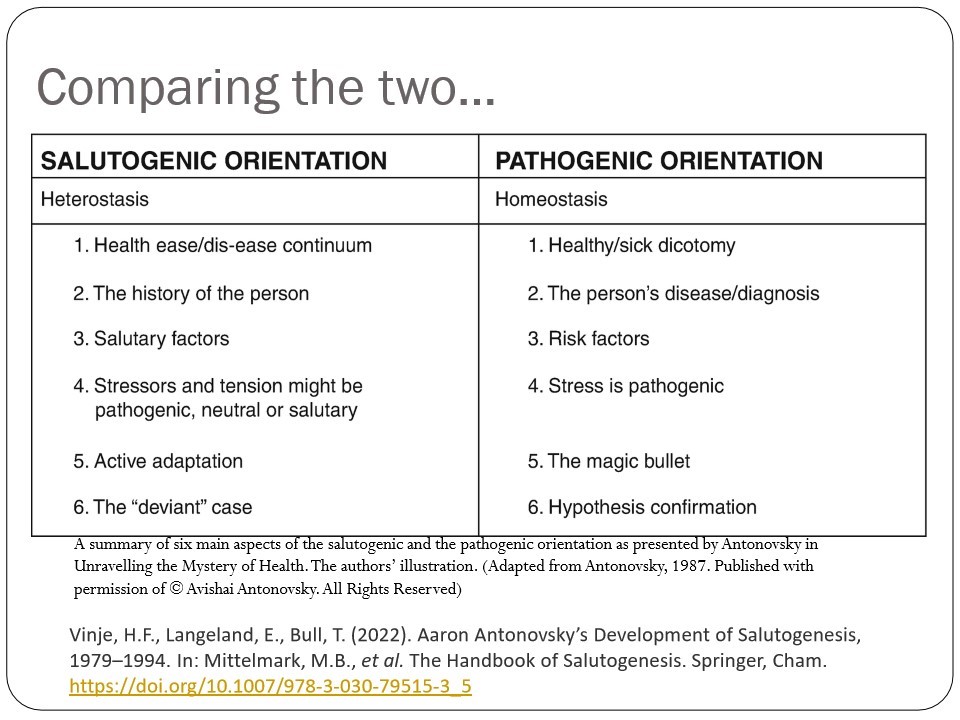
Compare Salutogenic Orientation with Pathogenic Orientation
The Sense of Coherence (SOC)
SOC = general orientation towards the world
WHEN A PERSON IS CONFRONTED WITH A STRESSOR, SOMEONE WITH A HIGH LEVEL OF SOC:
Will believe that the challenge is understandable: COMPREHENSIBILITY
Will believe that the necessary resources to adapt are available: MANAGEABILITY
Will believe that the demands and challenges are meaningful and warrant investment and commitment: MEANINGFULNESS
What have they done in terms of Salutogenesis and health promotion?
Implementing salutogensis in public health to have a better public health policy
Develop their personal skills
Reorient health services
Work with peoples assets
Why do people with important disabilities report having a good or excellent quality of life when most of the external observers perceive that these people seem to live an undesirable daily existence?
External observes have negative attitudes that are held by the public and health professionals towards people in situations of disability
Judgement that people in these situations of disability do not have a good quality of life as those without a disability
What are the two parts of the disability paradox?
External Observers
Quality of Life
Negative Attitudes
Sociocultural conditioning that starts at a young age (5 yrs)
The beautiful body
Emphasis on productivity and success
Socio-economic factors (disability = poverty, burden on the economy)
Attribution of “sick role”
Disability = status degradation
What are the links between negative attitudes and health
Perception of a negative attitude/stigma towards a person may reduce their help-seeking
Negative attitudes towards a patient with a stroke predict shorter long-term survival
If a person with a disability internalizes the discrimination they face, this is associated with higher levels of psychological distress and lower quality of life
Negative thoughts can feed pessimism and increase an individual’s stress
Social isolation has a negative effect on quality of life
Positive Attitudes/thoughts associated with health
convenience of a wheelchair
Family does not treat them differently
Better life expectancy
Less depression
Better immune function: resistance to colds
Better psychological and physical well-being
Reduced number of deaths tied to cardiovascular disease
Better adaptation in moments of stress/great challenges
What can increase Quality of Life?
Improved quality of life of people with spinal cord injuries
Education increases quality of life because it increases access to the job market, stable social ties and a sense of control over one’s life
Social support helps reduce a person with a disability’s stress and creates ties to the community
What percent reported a good quality of life?
54.3% report a good quality of life
Comparison: 80-85% people without disability report good quality of life
What are some factors that contribute to a good quality of life?
Acknowledging their impairment
Having control of their psyches and bodies
Being able to maintain certain roles
Having a “can do” approach to life
Finding a life purpose, sense and harmony in life
Spirituality
Emotional exchange
What percent reported a passable or bad quality of life?
45%
Factors that contribute to a bad quality of life?
Pain: loss of control: of body, social life, and environment
Pain often invisible, credibility questioned
Fatigue: loss of energy, difficulty planning a full life and maintaining roles
No clear direction in life, no spirituality
Explain the balance PWD have for those who reported a good quality of life.
Between body and mind: maintaining roles and functions,
“can-do” approach: people who perform and take satisfaction from their roles are intellectually conscious of their realizations about what they can expect from their bodies’ biological functioning (p.985)
Resilience: individual characteristic to psychologically resist life’s challenges (Balance: body and mind)
Context: environment: Social support Quality of life
Explain the lack of balance PWD has for those who reported a bad or passable quality of life.
Lack of balance between mind, body, spirit and the environment.
Pain has caused deterioration of the relation between mind and body
Incomprehensible —> depression
Fatigue: deterioration between body and mind, body does not respond to the spirits’ wants.
Environment: feeling detached from the outside world
Impairment does not lead directly to negative perceptions of health but _______ and ________.
Limitations and restrictions
Friedreich’s Ataxia (FA)
degenerative neurological disease characterized by cerebellar degeneration (damage to pathways between the cerebellum and the spinal cord).
1-20,000 to 1-50,000
Symptoms of FA
Lack of muscular coordination
Lack of energy
Communication difficulties
Often hearing difficulties
Difficulties with fine motor skills
How was it for John to accept his visible disability?
there were negative attitudes
heartbreak
big muscular man — pitiful
“Negative side too obvious”, burden on the family and close loved ones
Restrictions on participation in his normal activities and employment
The real problem is “accepting our personal limits that go beyond our physical difficulties
Look the disability paradox notes