BME211 Week 3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
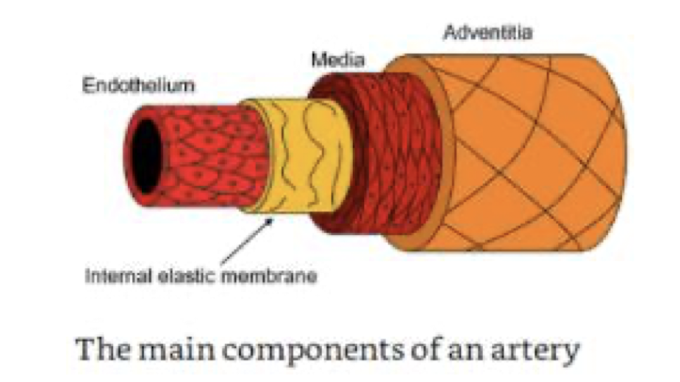
Structure and Composition of Arteries
Arteries consist of three layers—intima, media, and adventitia—and are composed of collagen, elastin, and smooth muscle cells.
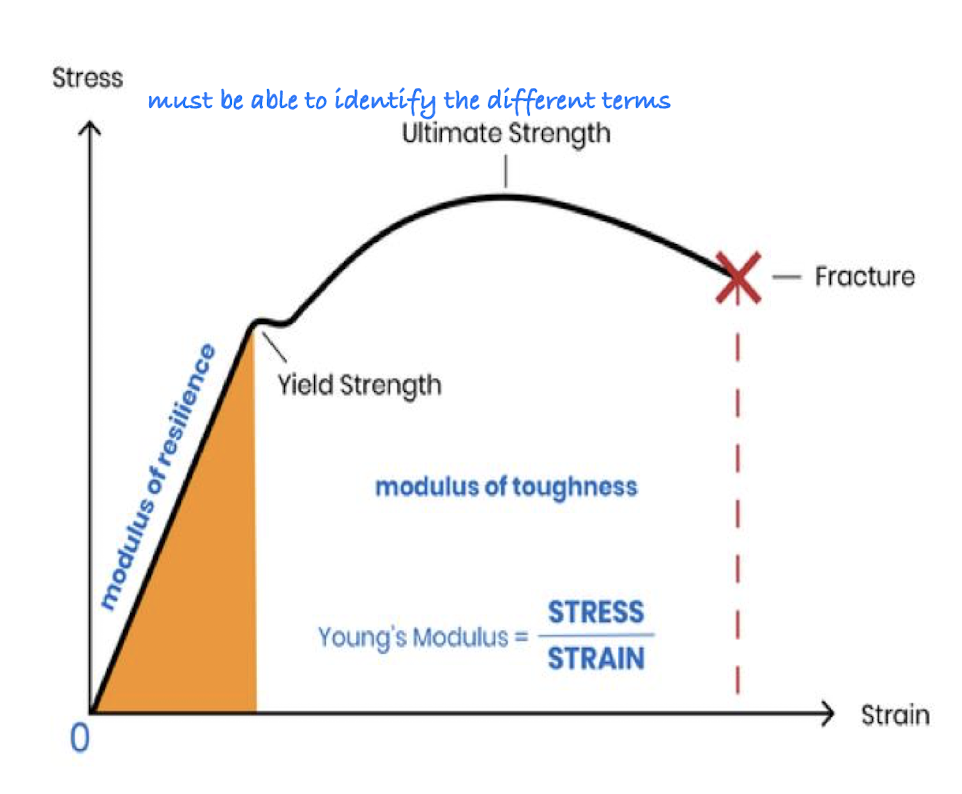
Mechanical Perspective of Vessels
Vessels are dynamic structures that endure various pressures and stresses to regulate blood flow.
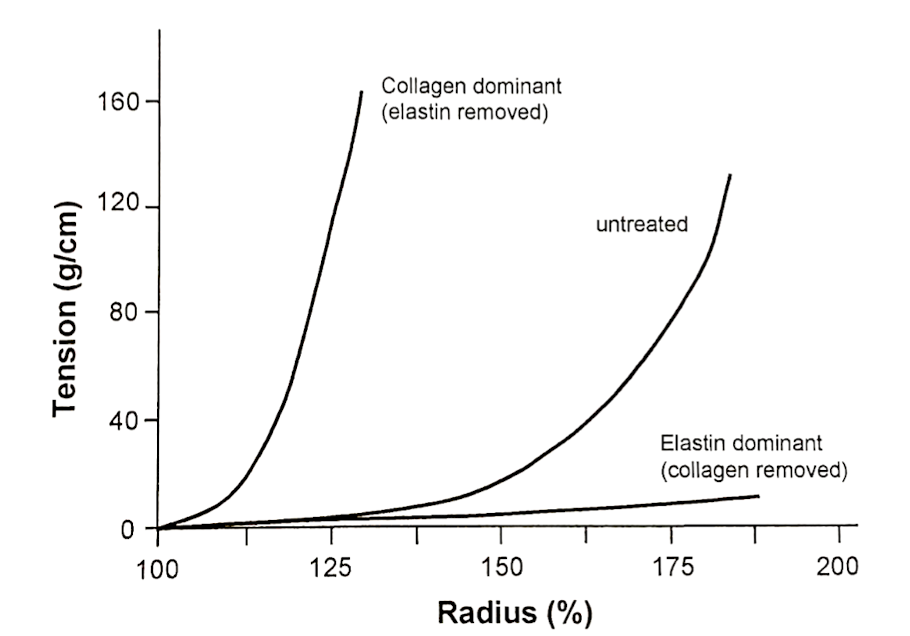
Tension-Radius Behavior for an Artery
Wall tension in arteries increases with the radius; larger arteries require more tension to withstand the same pressure (Laplace's Law).
Pulse Wave Velocity
The speed at which pressure waves propagate through arteries, reflecting arterial stiffness.
Turbulent vs. Laminar Flow
Arterial flow can be smooth and orderly (laminar) or disordered (turbulent), with turbulent flow occurring in narrowed or diseased arteries.
Rotating and Axial Flow
Blood flow in vessels comprises both straight (axial) and swirling (rotational) components, influencing flow dynamics.
Murray's Law
Principle describing the optimal vessel branching pattern to minimize energy loss and maintain efficient blood flow.
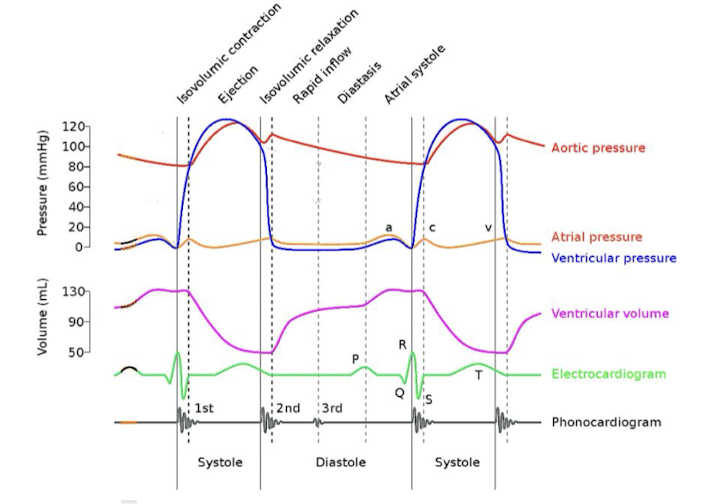
Cardiac Cycle
Heart chambers undergo sequential contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) during each cardiac cycle.
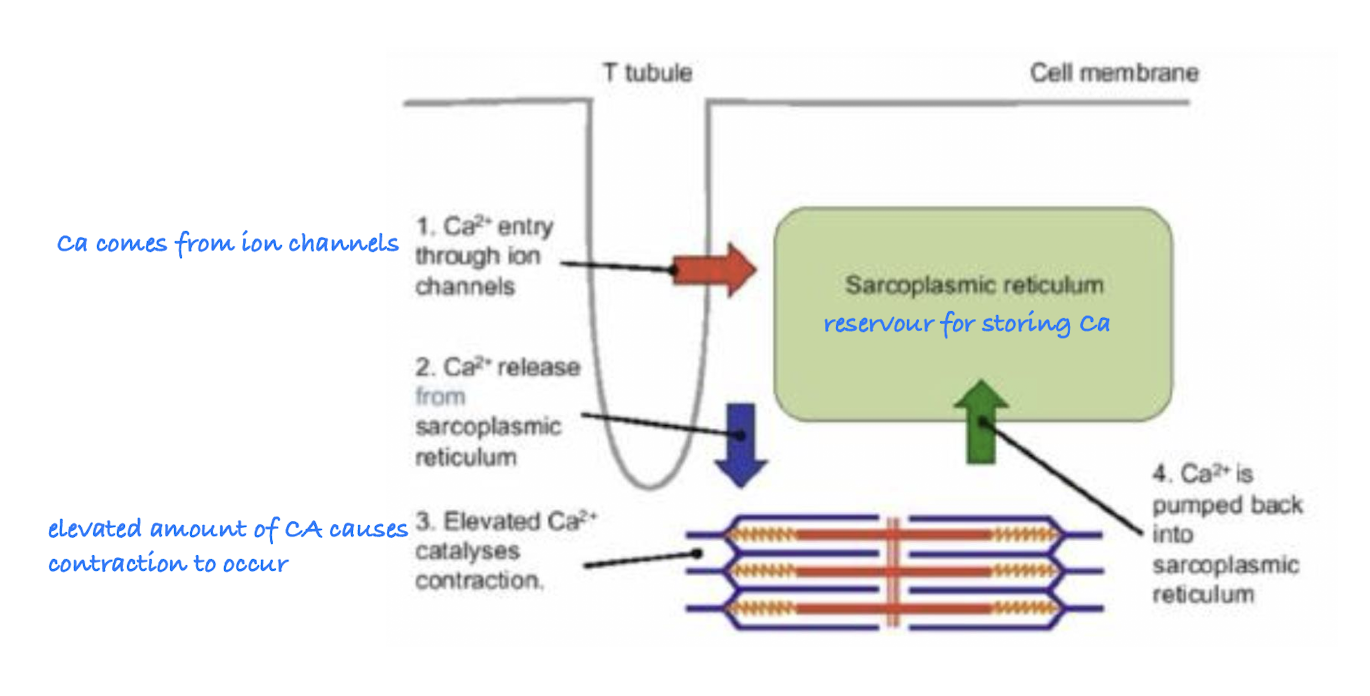
Molecular Component of Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Involves calcium influx triggering actin-myosin interactions leading to muscle contraction.
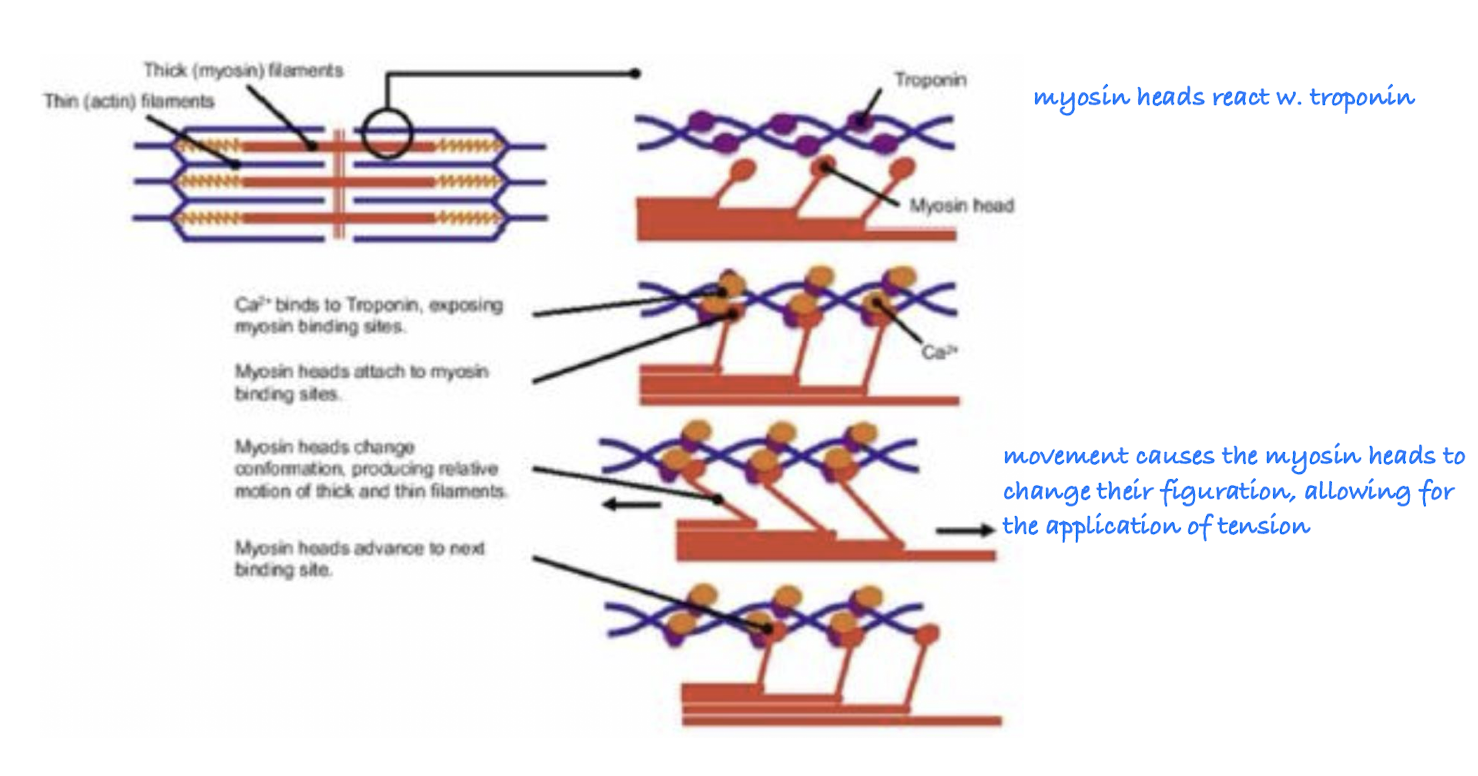
Molecular Components Involved in Tension Generation
Actin, myosin, tropomyosin, and troponin regulate muscle contraction in the heart.
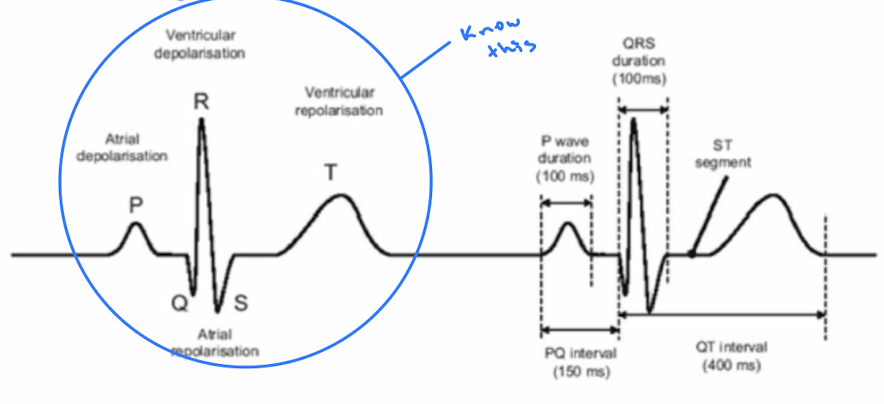
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Explained
P Wave: Atrial depolarization.
QRS Complex: Ventricular depolarization.
T Wave: Ventricular repolarization.
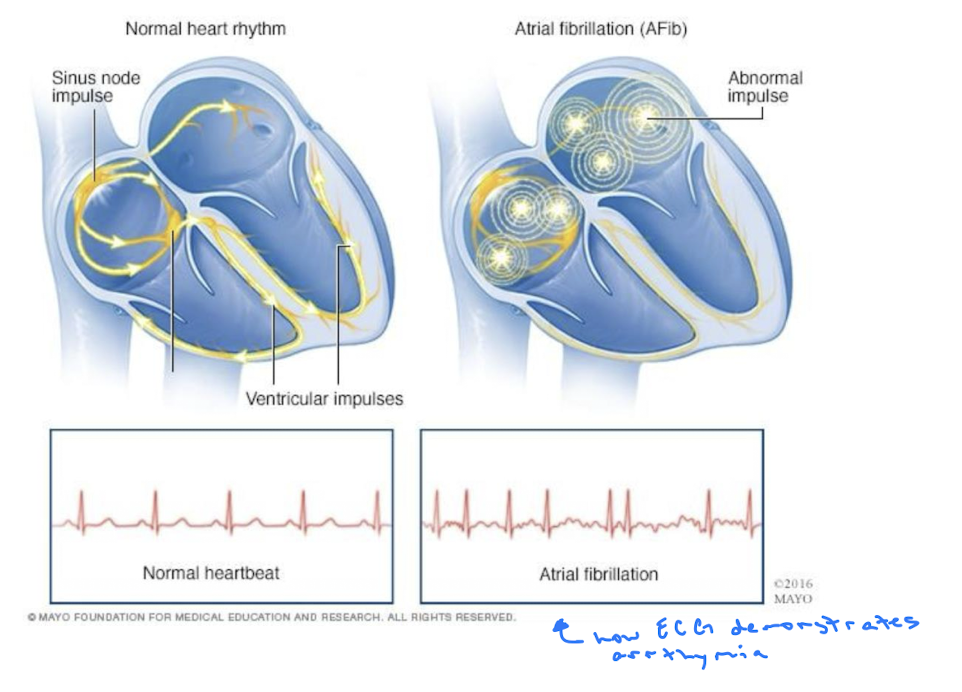
Atrial Fibrillation
Irregular, rapid heart rhythm caused by disorganized electrical activity in the atria.
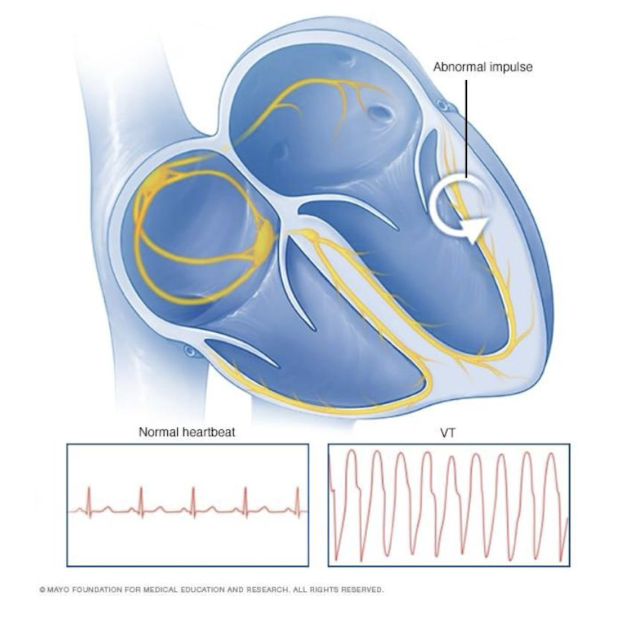
Ventricular Tachycardia
Fast, abnormal heart rate originating from the ventricles, potentially life-threatening.
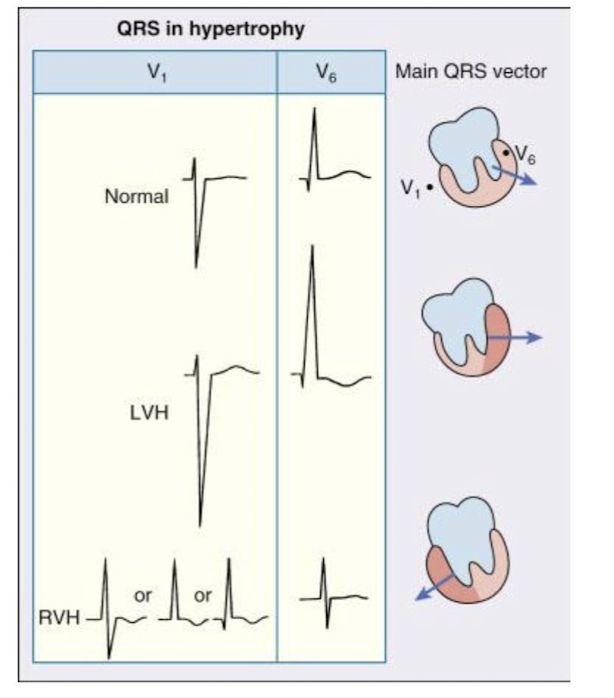
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Thickening of ventricular walls often due to high blood pressure or heart disease.
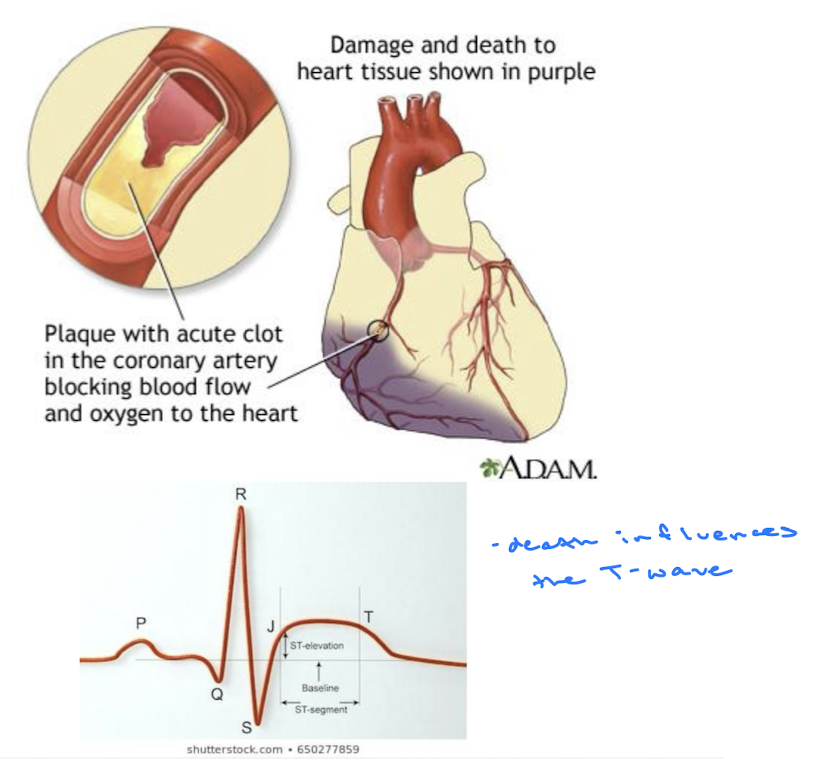
Myocardial Infarction
Commonly known as a heart attack, results from blocked blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to tissue damage.
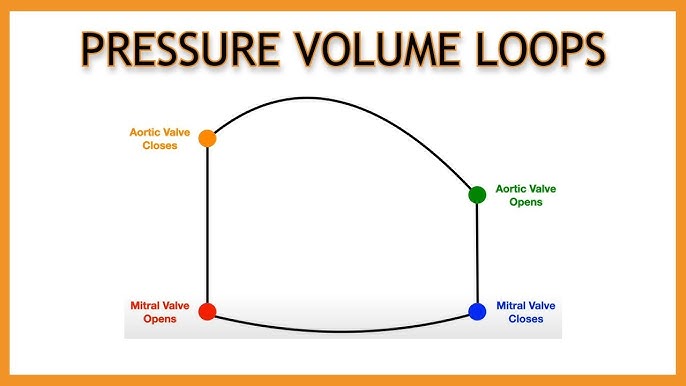
Understanding the Pressure-Volume Loop
Graphical representation of the cardiac cycle illustrating the pressure-volume relationship in the ventricles, used for heart function assessment.