Physical Examination of Dogs & Cats
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Be consistent & thorough
Write it down
Back off
Use restraint
Say Hello
Learn from experience
6 Important steps to take note before & during physical examination
F: Always perform a complete exam (topographic region) regardless of the presenting complaint.
T/F: When presented with a chief complaint, it is important to check it right away and focus firstly on it.
light or moderate
best type of restraint to use for the animal to reduce stress
sight
hearing
smelling
touch
4 major senses used by the vet during physical examination
Distant examination
This is done by observation prior to handling or restraining the animal, should never be omitted, and may best be undertaken during the period devoted to obtaining the history and taking note of the environment
general or the systematic examination
During this type of examination, the outer surface of the body and external orifices are also examined by inspection.
General expression
This is formed by looking at and listening to the patient from a slight distance
Sopor (sleepiness)
Stupor (aroused by strong stimuli)
Coma (cannot be aroused)
3 levels of consciousness
Pathologic behavior
This form of behavior can occur in such forms as self mutilation, compulsive actions (head-pressing, walking in a circle), convulsions, or aggression
Malaise (discomfort)
Lying (on its side or sternum)
Standing (with one leg, led extended or over-extended)
Position of the spinal column (arched, sagging, or stiffly extended neck)
Areas to look when examining for Posture
Level of consciousness
Behavior
Posture
Locomotion
Body shape
Nutritional condition
Coat
Abnormal sounds
Abnormalities that stand out
9 Areas to check during general impression
body weight
To evaluate the course of some illnesses or kinds of therapy, it is also desirable to measure ____ accurately
trunk; lumbar
Fat accumulates chiefly on the ____ and sometimes there is an extra accumulation bilaterally in the____ area.
retrobulbar fat
The eyes can be sunken because of the loss of____ and as a result the nictitating membrane can protrude.
Cachectic (Vey Thin)
Skinny/ Slim (Underweight)
Optimal
Overweight
Obese
Nutritional condition ordinal scale 1-6
1: Very Thin
BCS: Ribs are easily felt w/ no fat cover
2: Underweight
BCS: Bones are raised w/ minimal tissue between skin & bone
3: Ideal
BCS: Ribs are visible and easily felt
4: Overweight
BCS: Ribs are difficult to see or feel through moderate fat cover
5: Obese
Ribs are not visible and are difficult to feel through thick fat cover. In cats, fat hangs from the abdomen
2.9
Compared with cats of optimal weight, overweight cats are ___ times as likely to be taken to veterinarians because of lameness.
3.9
Obese cats are __ times more likely to develop diabetes mellitus than are cats of optimal weight.
T
T/F. At the usual distances in the examination room, no sounds are heard from an animal at rest.
Eructation
Flatulence
Respiratory sounds
Intestinal sounds
Joint disorders
Abnormal sounds include these 5
Thickened pinna
Swelling of one leg
Pumping or respiration
3 abnormalities that stand out
TPR - outside range
Age - older than 6yrs or younger than 12 mos
Weight - less than 2kgs or more than 34 kgs
Diarrhea or vomiting, trauma history
Abnormalities on physical exam
Findings that require a designated supervisor's evaluation include 5 factors like:
General Physical Examination
General impression (Distant examination)
Close Physical Examination
In Physical Examination of Dogs & Cat, 3 general processes are done
Inspection/observation
the use of the sense of sight, by which shape, color, and movement can be observed
Palpation
the use of touch, can obtain information about the shape, consistency, and temperature of the object being examined
Auscultation
the sense of hearing is used primarily to observe sounds occurring in the thoracic cavity; can be accomplished by pressing one's ear against the animal's body, but it is almost always done by use of an instrument that transmits the sound to the ear of the examiner
General inspection
type of inspection that is is a visual evaluation of the entire animal or of large parts of it
Local inspection
type of inspection where it is necessary to use a focal light source, usually a small penlight. Some cavities or passages are inspected with the aid of an instrument specially designed for the purpose, such as an otoscope or vaginoscope
Palpation
It involves utilizing the sense of touch as well as possible
Location
Size
Shape
Consistency
Painfulness
Movability
Borders and surfaces
Color and temperature
Related masses
Aspects important for characterization of a mass during palpation
bone, nerves
Tumors that grow in these areas causes too much pain
malignant
An indistinctly circumscribed mass could be an infiltrating _______tumor
melanin
Depositions of _____ can be the cause of a brown-black color.
regional lymph nodes
presence of multiple masses indicates involvement of ________
chest and back
Percussion is most commonly used on the ___ & ____ for examination of the heart and lungs.
F. It will change since heart is not resonant and the adjacent lungs
T/F: Dring percussion, when the examiner's fingers strike the chest over the heart the sound waves will not change in pitch
haircoat
reluctance
anatomy
The value of percussion in animals is limited by these 3 factors
F. pressure increases
T/F: There is a pressure wave corresponding to the changes in density, because where the medium becomes more dense, the pressure decreases
plessimeter/ pleximeter
In 1827, Piorry tapped on an ivory plate which he called ______
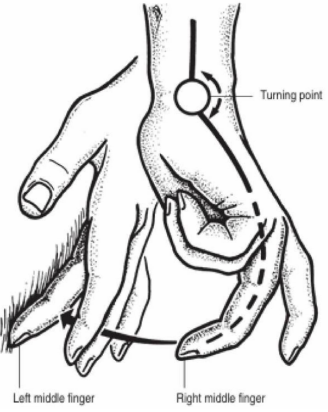
finger finger percussion
What do you call to this procedure?
7cm
Acoustic percussion does not penetrate beyond _____ cm into the thorax, and hence deeper lesions will not be revealed by this method.
5cm
In addition, consolidated lesions (tumor or fluid) must be at least ___ cm in diameter in order to produce damping that can be detected.
Sonorous percussion tone
Damped percussion tone
Tympanic percussion tone
In percussion of the trunk (thorax and abdomen), three main percussion sounds can be distinguished:
Sonorous percussion tone
This is the fairly low, strongly resonant tone that is heard by percussion of gas-containing lung tissue
Damped percussion tone
This can be heard over any part of the body that does not contain gas, such as muscles or liver. It is a short (cutoff) sound of low intensity.
Tympanic percussion tone
This tone contains more sound and is a little higher than the sonorous percussion tone. A good example of this tone is that from the gas-filled stomach. It occurs in smaller cavities (stomach, intestines), higher in pitch.
Flatness
This is checked in areas like bones such as the clavicle, ribs, sternum
Dullness
This is checked inn areas with dense organs such as the liver, spleen, heart
Resonance & Hyperresonance
This is observed in adult lung & child lung (respectively)
Tympany
This is checked in abdominal area such as intestines and stomach
placing the finger of one hand (pleximeter) flat in the intercostal space over the lung field
briskly tapping it with the middle finger of the opposite hand (plexor)
In small animals, thoracic percussion is usually performed by
placing a pleximeter (i.e., wood alock, metal block, or spoon) in the intercostal space and;
hitting it with a rubber reflex hammer (plexor).
In large animal species, the percussion procedure is usually paerformed by
Wood blocks
____ tend to create better resonance and are preferred as pleximeters
7cm; 5cm
Acoustic percussion can assess tissues to a depth of approximately cm and detect lesions as small as __ cm diameter
cranial ventral
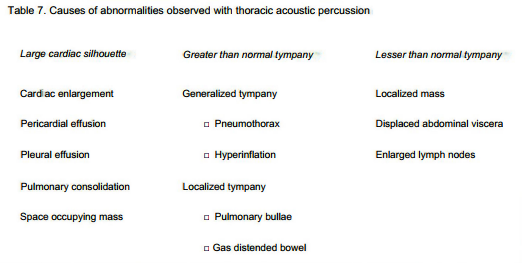
Note that the cardiac silhouette lies in the ________ portion of the lung field and manifests as an area of dullness
T
T/F: Enlargement of the cardiac silhouette, or variation in the tympany over the lung field may indicate thoracic disease.
…
Take note!!!
gas pressure or by tissue vibrations
Sounds can be generated in the body by rapid fluctuations in ____ or ____
Laennec
He first described indirect auscultation in 1819. He called his instrument, which consisted of a simple wooden tube, the stethoscope
Auscultation
a method of diagnosis by which the condition of some of the internal organs is determined by listening to the sounds they produce.
“Stethos” = chest
“phonein” = sound
Greek word where stethoscope is derived from
excessive dryness, excessive oiliness, evidence of dandruff, excessive shedding, or abnormal hair loss
Abnormal findings observed in haircoat
scabbing, rashes, lumps or bumps, areas of abnormal thickening, etc.
Abnormal findings observed in skin
redness, discharge, evidence of excessive tearing, cloudiness, etc.
Abnormal findings observed in eyes
discharge, thickening, hair loss
Abnormal findings observed in ears
symmetry, how well the pet breathes, whether there are any problems related to skin folds, etc.
Abnormal findings observed in nose & face
tartar build-up, periodontal disease, retained baby teeth, broken teeth, ulcers in or around the mouth, etc.
Abnormal findings observed in mouth & teeth
Pulse
PLNDS - swelling or pain
Legs - lameness, nerve probs
Abdomen - normal/ abnormal, discomfort
4 Areas palpated by vet
heart & lungs
2 areas auscultated by the vet
Signalment / History
General Appearance / Initial Observations
Vital Signs
Physical Exam (Systems Approach or Head to Toe)
Surgical / Anesthetic Risk Assessment
5 Processes of Physical Exam
BCS
Mentation
Posture & gait
Hydration status
General appearance components during examination
Loss of the elasticity of the skin (skin turgor)
_________ is first sign of dehydration. Check the skin of the upper eyelid and the neck for tenting
Vital signs
Evaluated in relation to presenting complaint, history and current health status
respiratory movements
pulse
body temperature
coat and skin
mucous membranes
peripheral lymph nodes
other notable abnormalities
The concept of 'general examination' includes these 7 components