PLTW: Human Body Systems: Unit 2
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is the CNS?
brain/spinal cord
What is the PNS?
nerves spread all over the body (cranial nerves are still PNS)
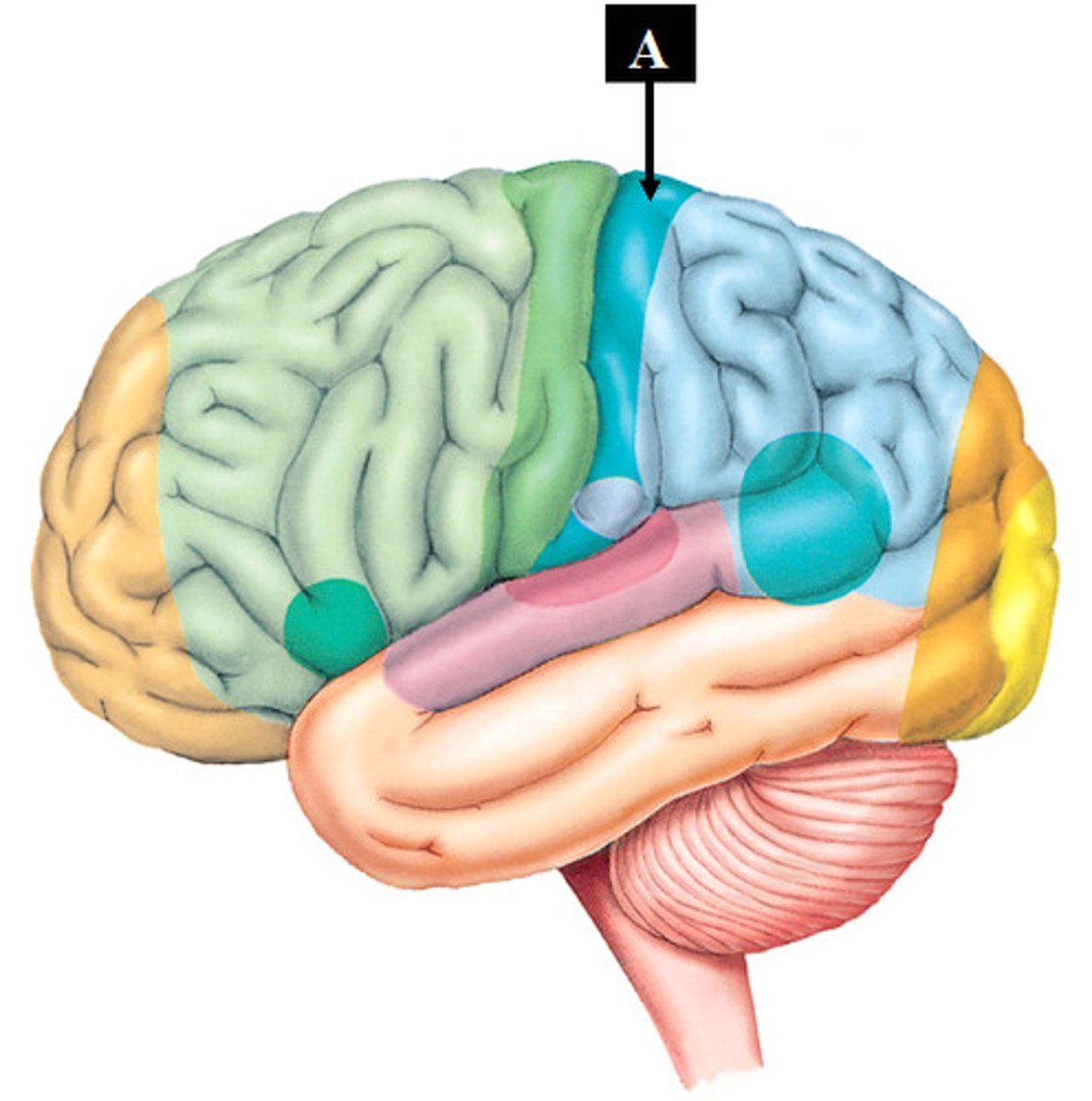
What is the cerebrum?
Major 4 lobes of the brain (parietal, frontal, occipital, temporal)
Locate the frontal lobe.
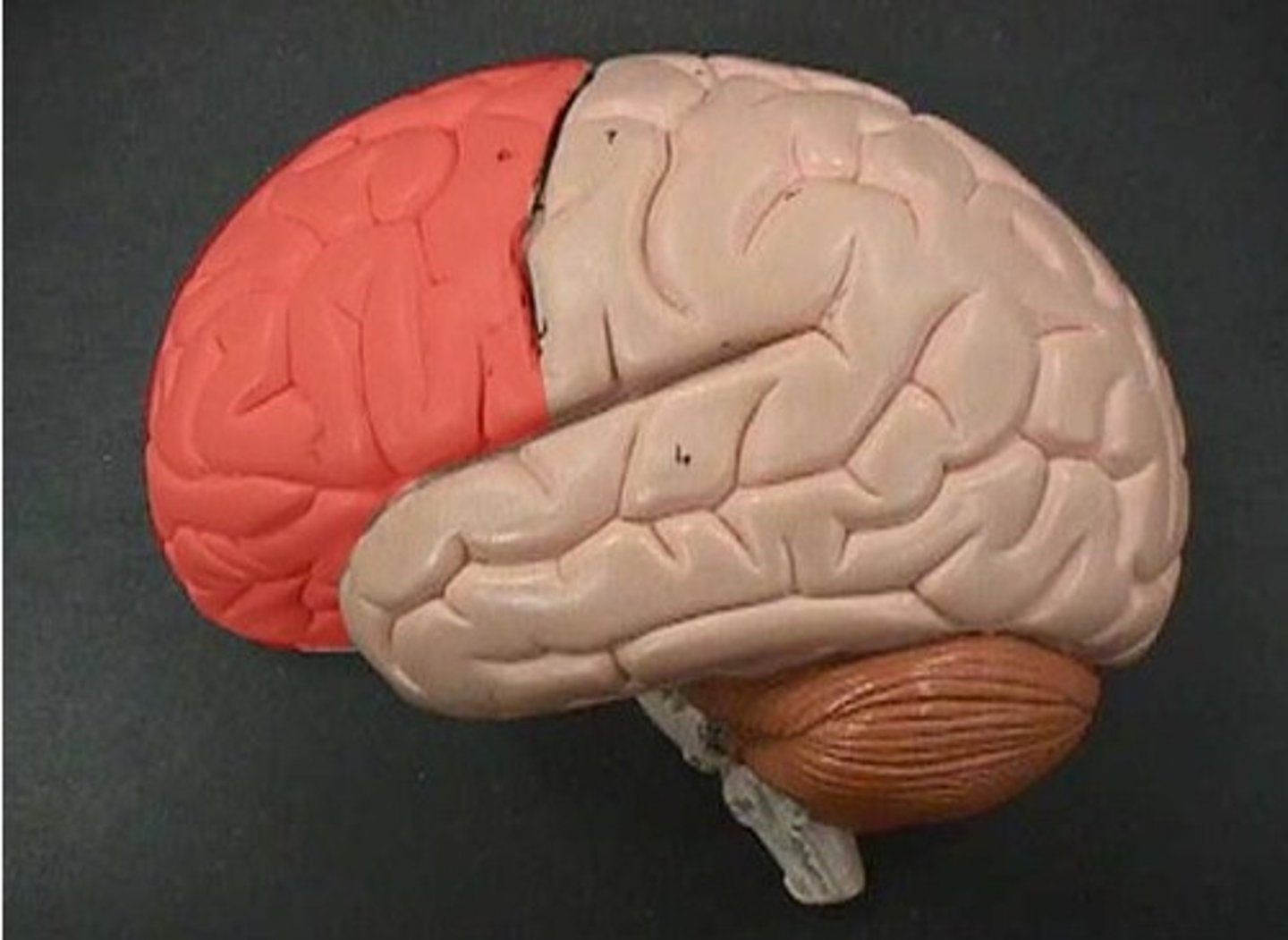
Locate the parietal lobe.
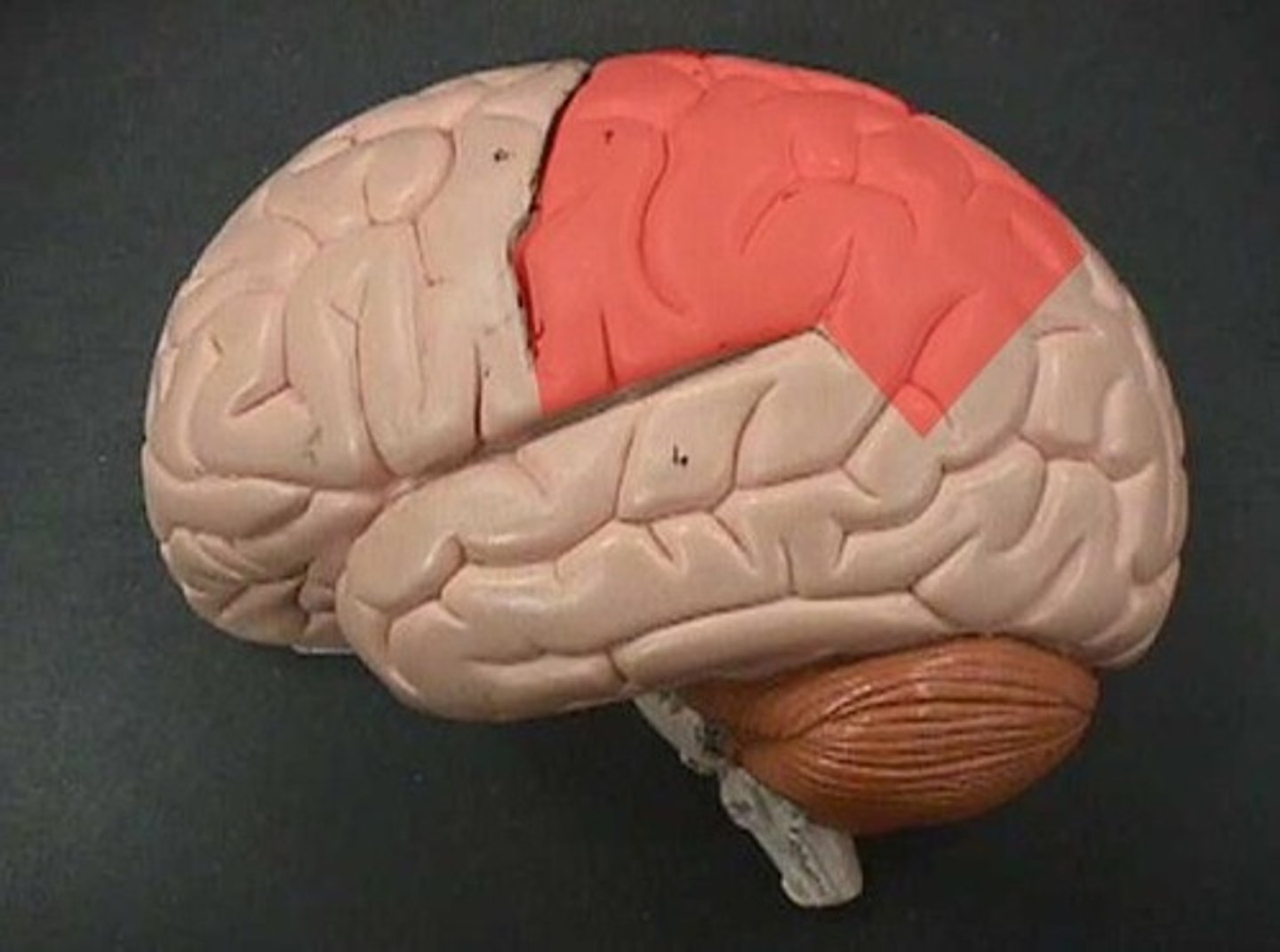
Locate the occipital lobe.
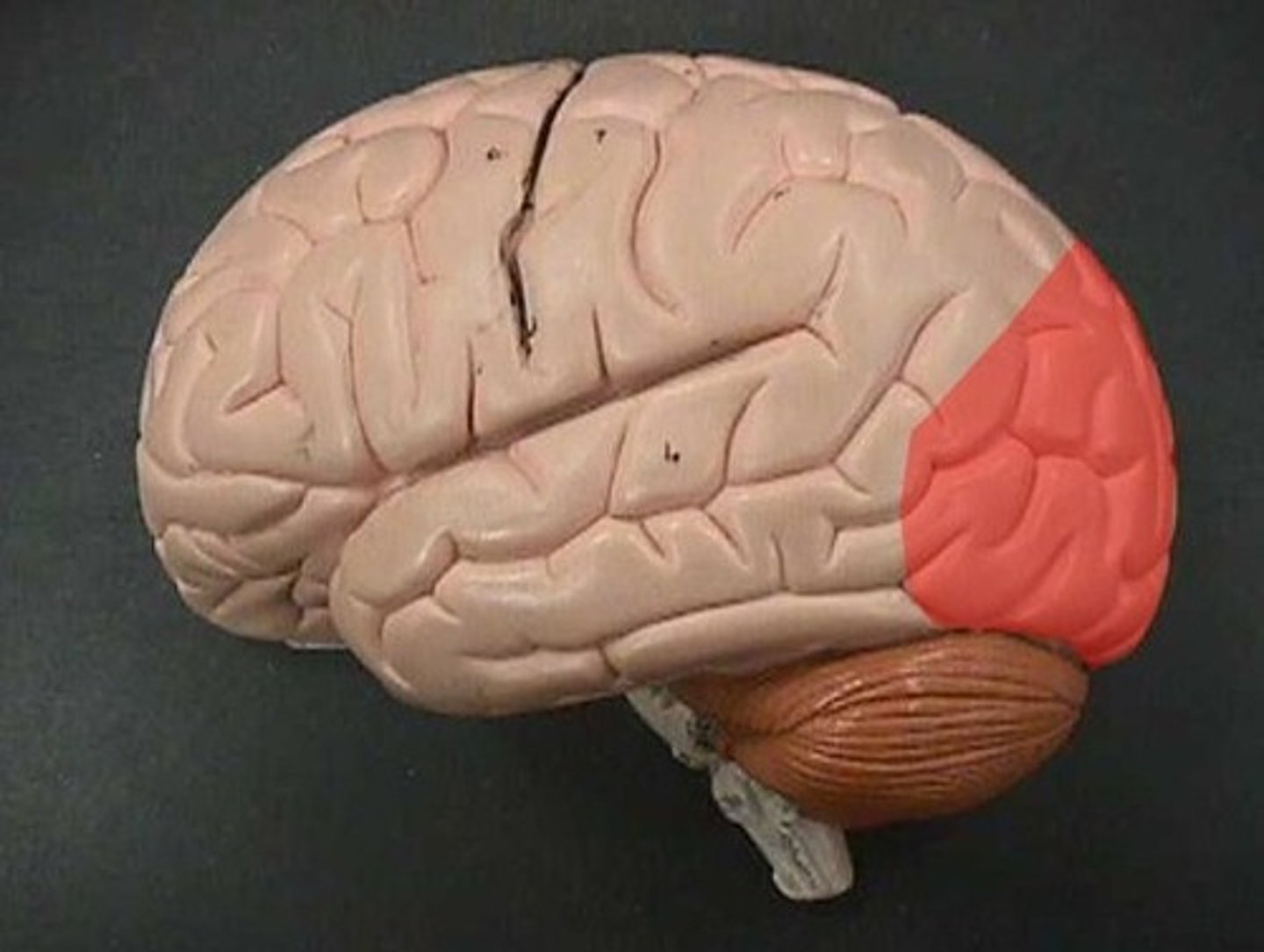
Locate the temporal lobe.
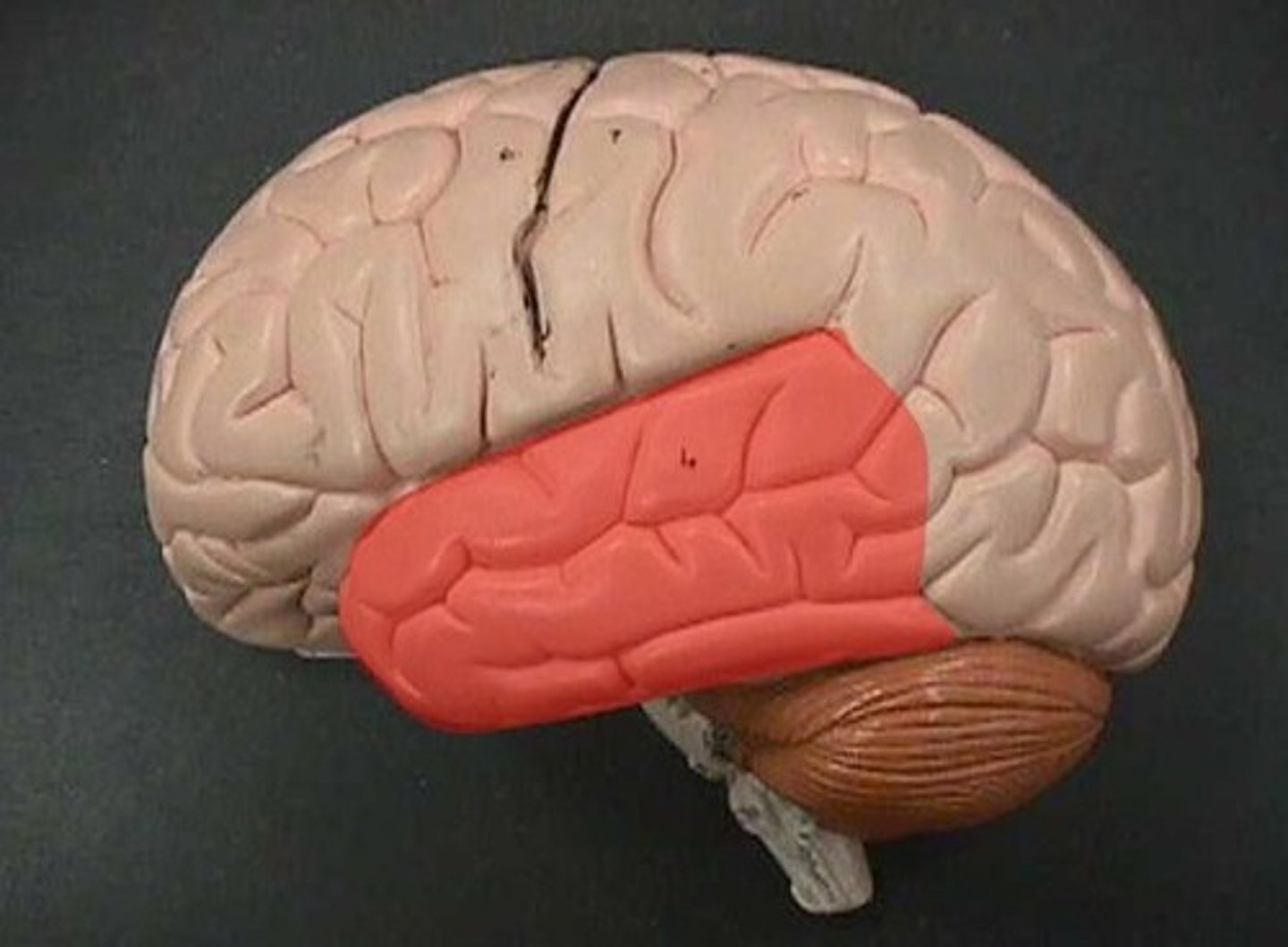
Locate the cerebellum.
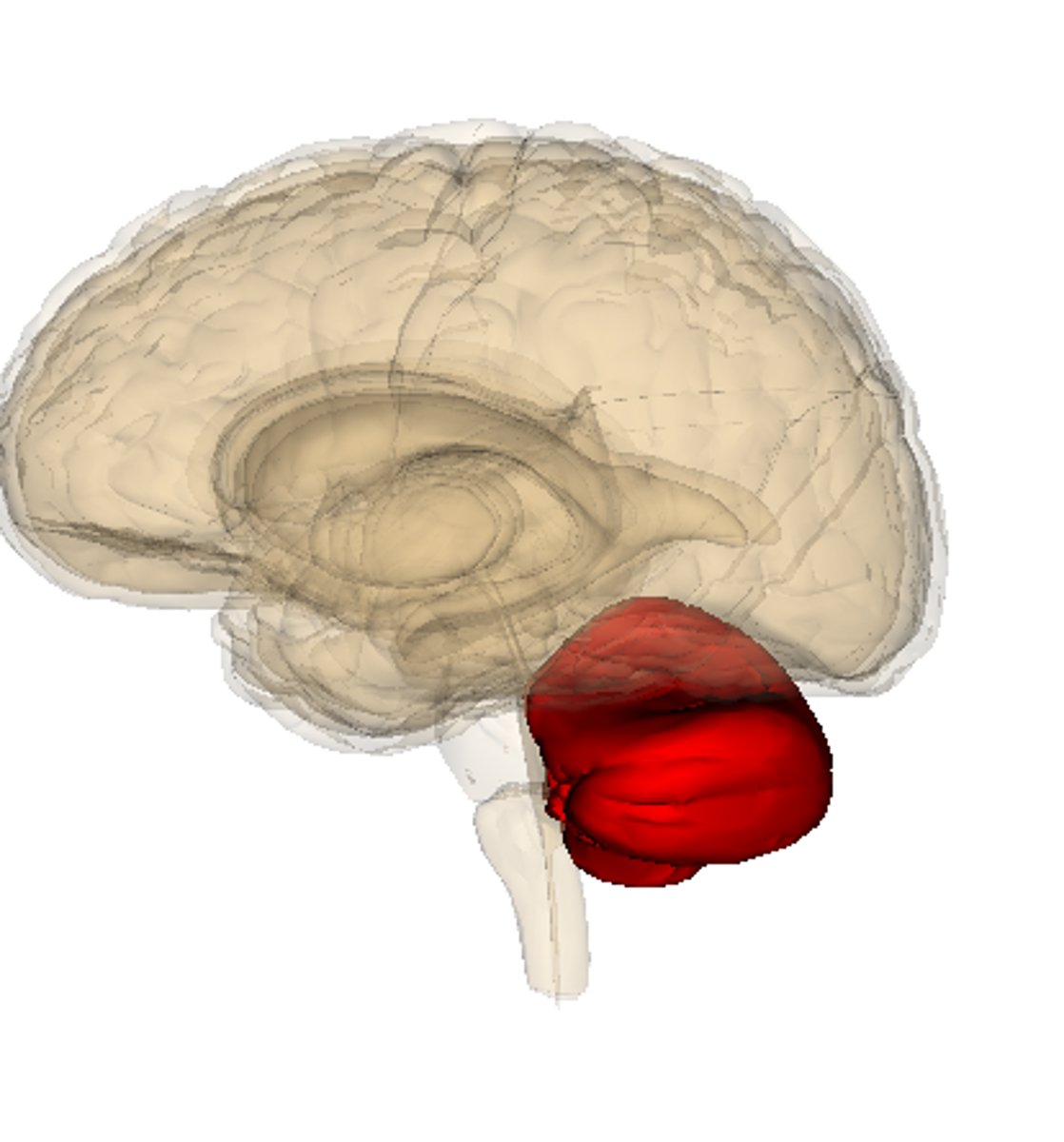
Locate the brain stem.
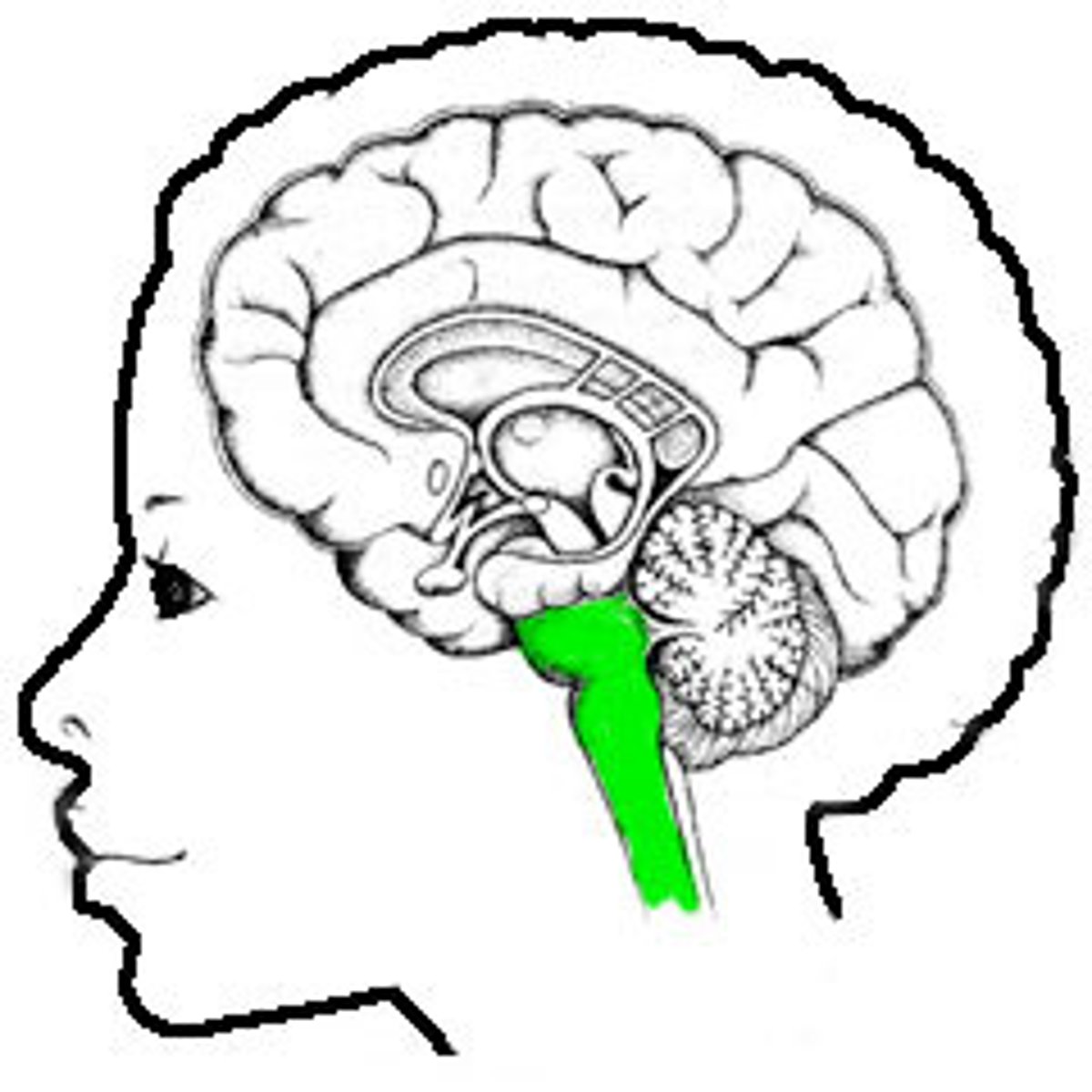
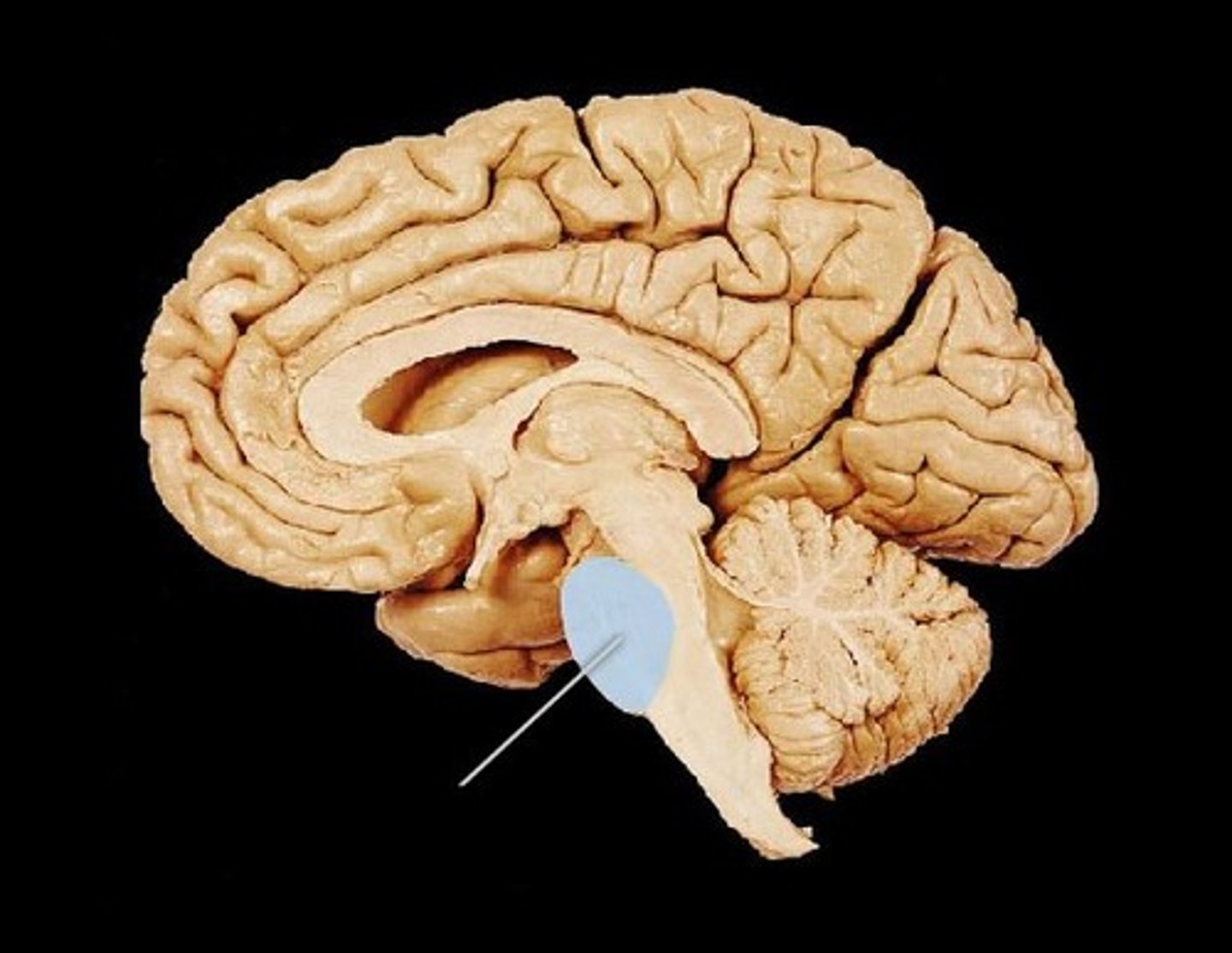
Locate the pons.
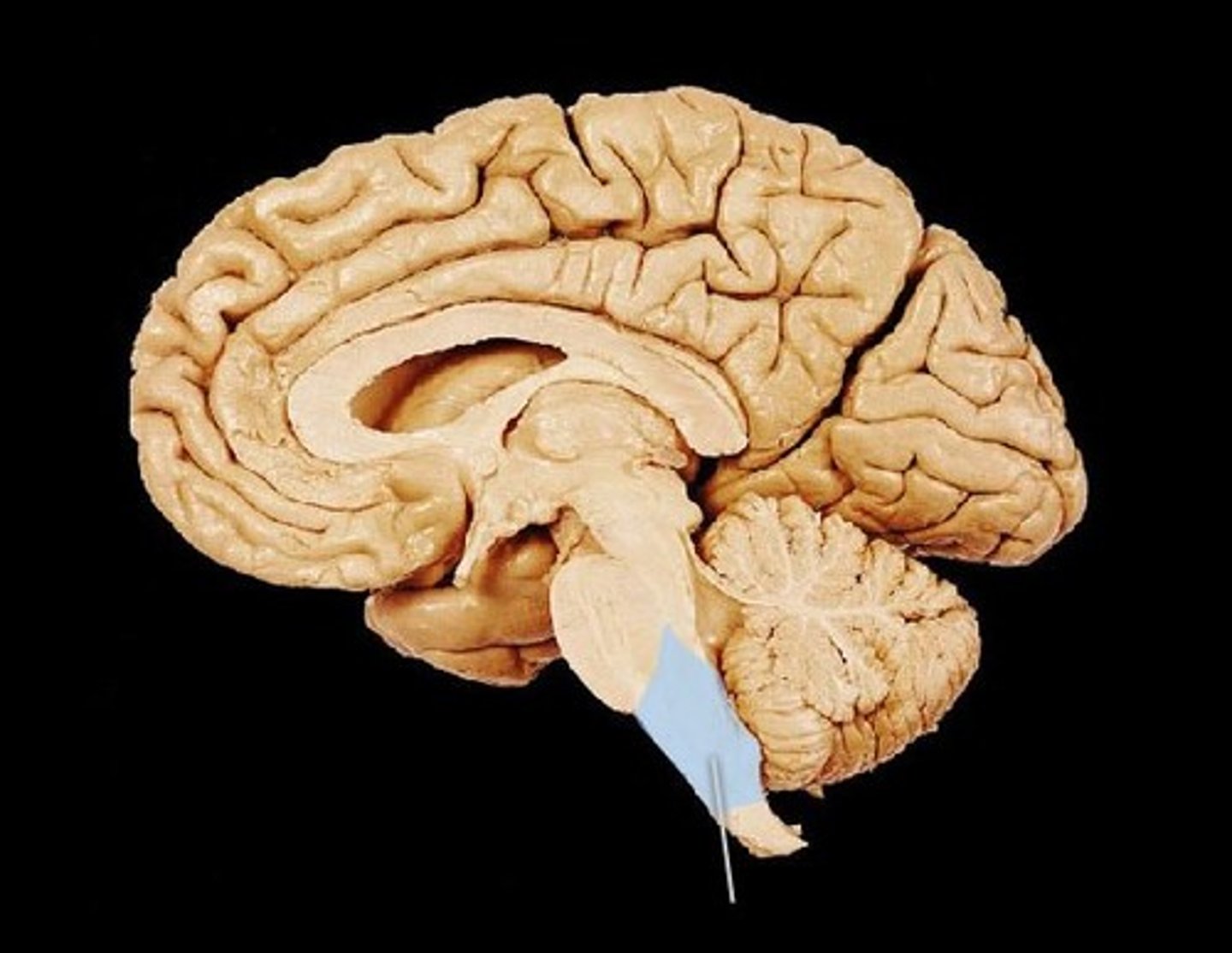
Locate the medulla oblongata.
What are the gyri?
"peaks" of the folds that cover the brain
What are the sulci?
"valleys" of the folds that cover the brain
Locate the motor cortex.
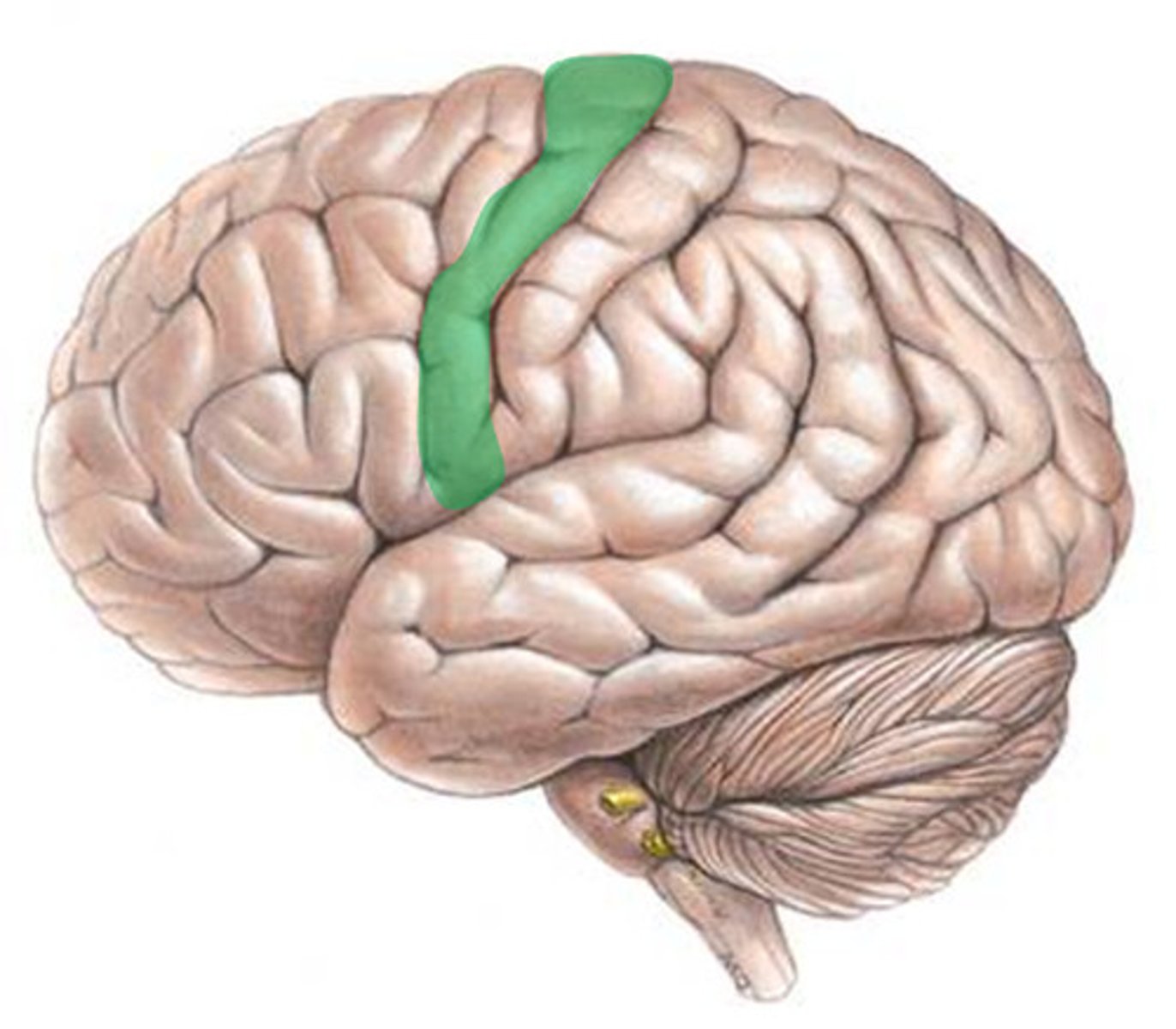
Locate the sensory cortex.
What does the FRONTAL lobe control?
manners
speech production
language understanding
movement
smell
reasoning
problem solving
emotions/personality
happiness
taste
self control
long term memory
What does the PARIETAL lobe control?
short term memory
bodily sensations
What does the OCCIPITAL lobe control?
short term memory
sight
What does the TEMPORAL lobe control?
SMELL, HEARING
short term memory
musical ability
language understanding
What does the CEREBELLUM control?
balance
muscle coordination
What does the BRAIN STEM control?
breathing
heart rate/blood pressure
sleeping/waking
What does the CEREBRAL CORTEX control?
taste
What does the HYPOTHALAMUS control?
thirst/hunger
smell
sleeping/waking
The gyri and sulci of the brain help to increase its ___________________.
surface area
What is the polarity of a MOTOR neuron?
multipolar
What is the polarity of a SENSORY neuron?
unipolar or bipolar
What does an INTERNEURON/RELAY neuron do?
relays messages from sensory neurons to motor neurons (makes up CNS)
What is the polarity of an INTERNEURON?
multipolar
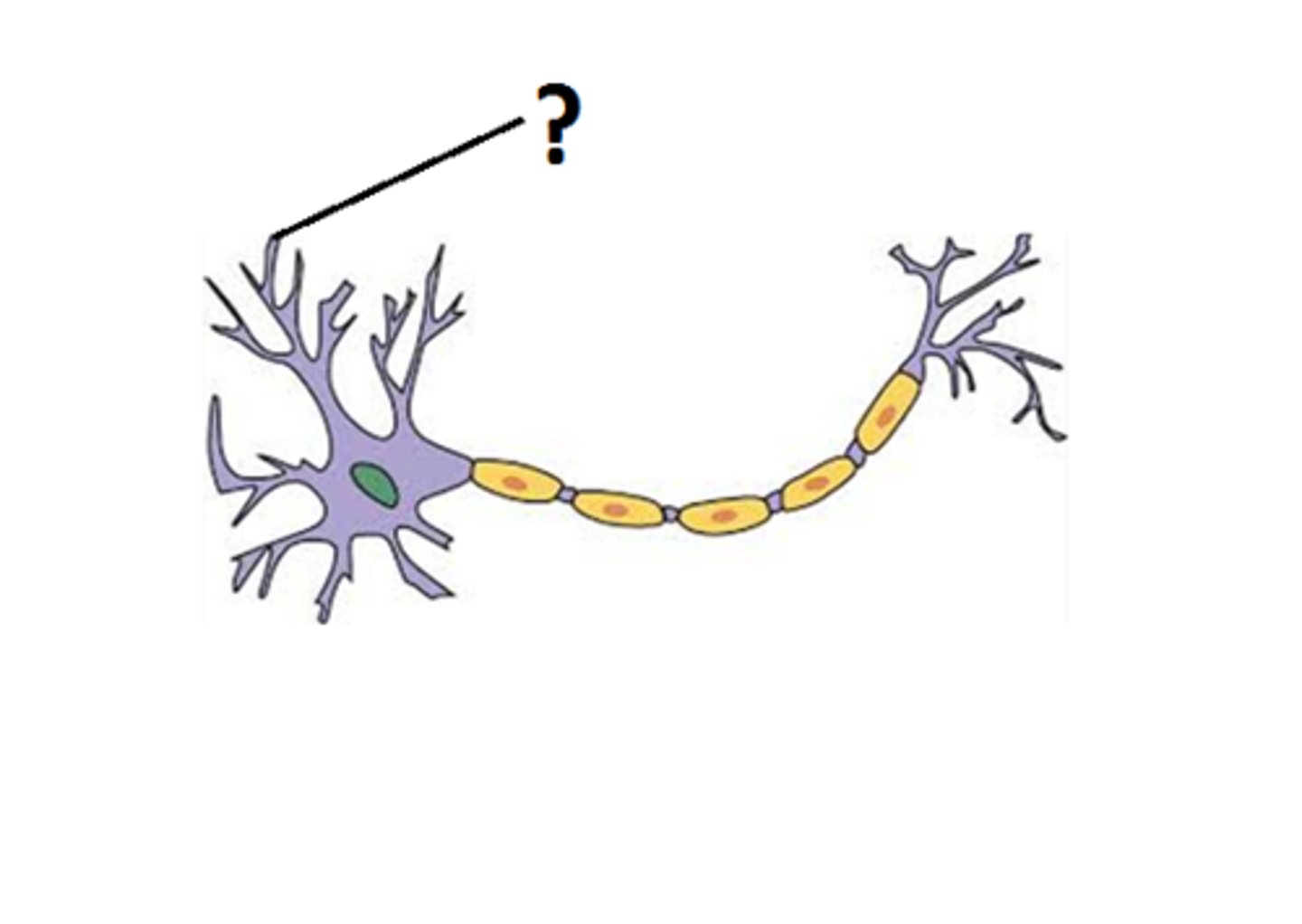
What are dendrites?
receives signals from other neurons, conducts impulses TOWARD the body of a neuron
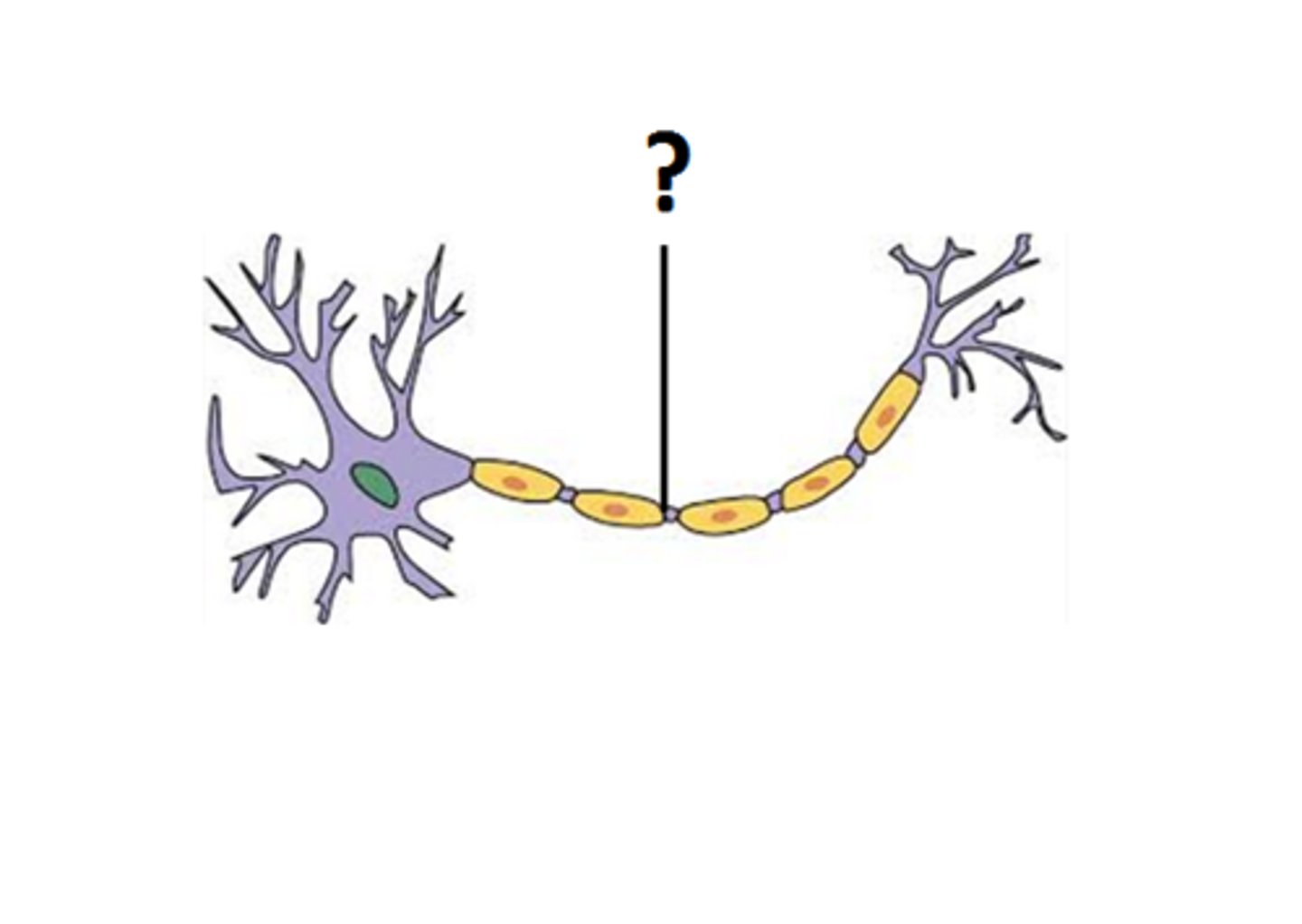
What is the axon?
conducts impulses from the cell body to other cells; moves impulses AWAY from the cell body
What are axon terminals?
endings where axons make synaptic contact with other nerve or effector cells (ex muscle)
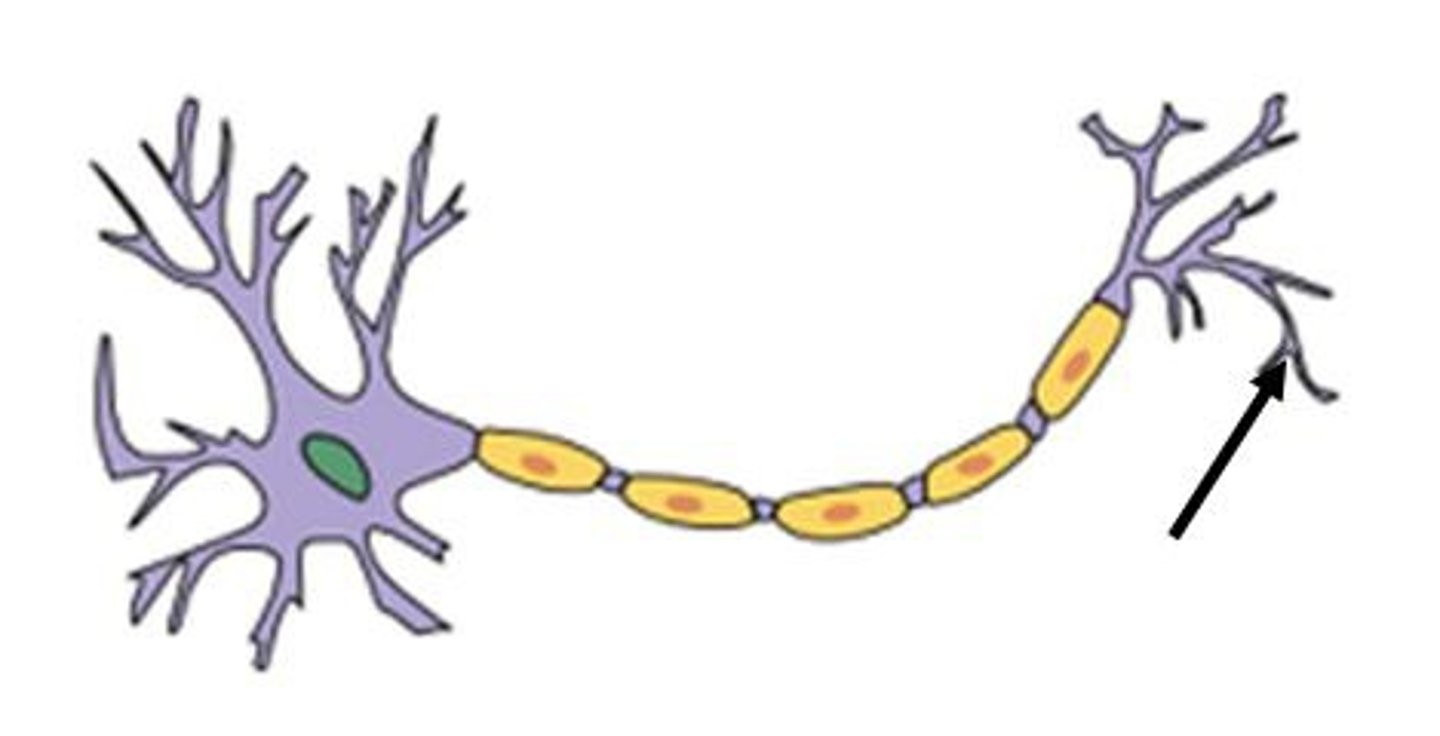
What is the myelin sheath?
insulated covering of an axon; interrupted at nodes of Ranvier; prevents neuron from jumping off course, ensuring that the message reaches it's destination.
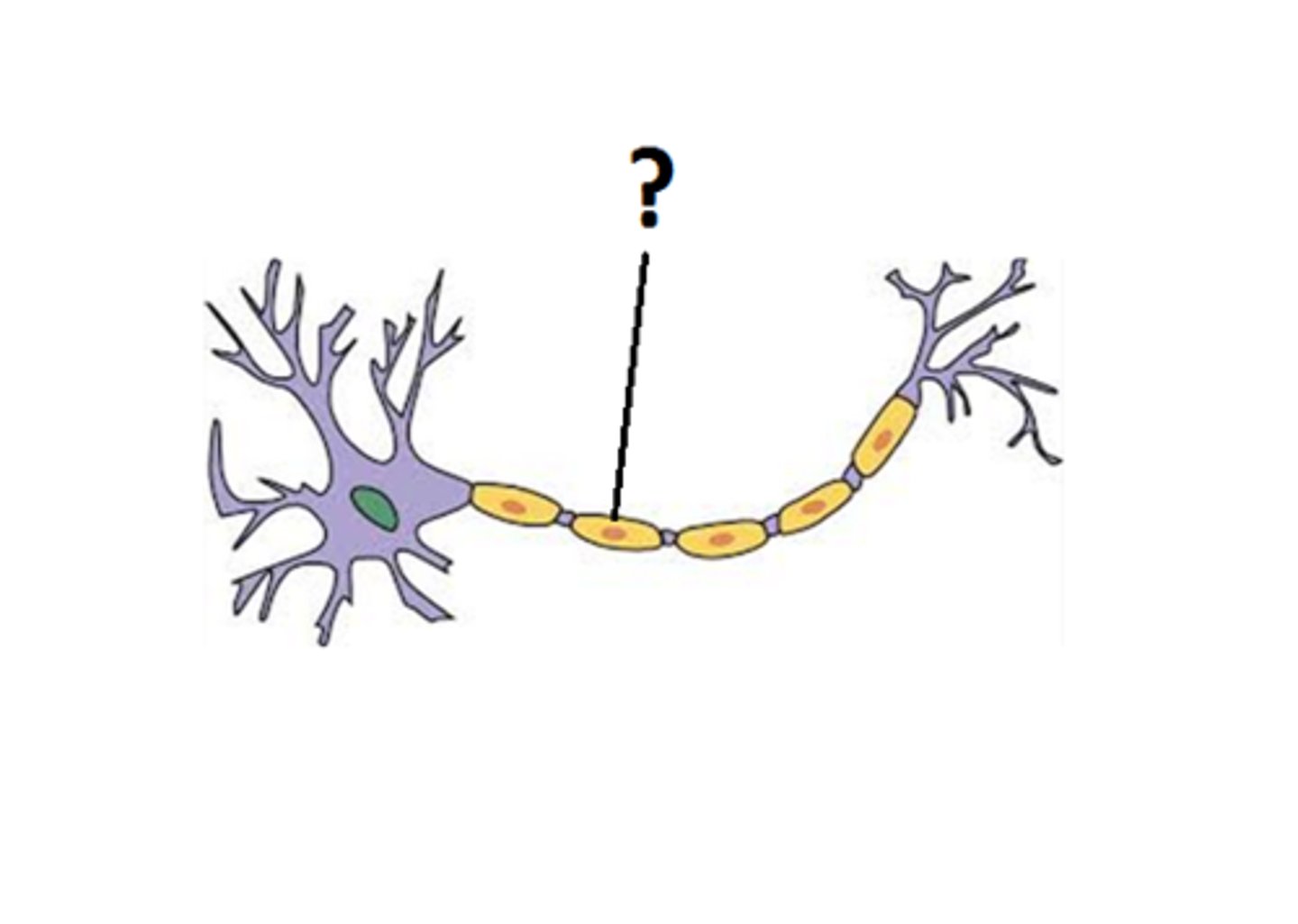
What are the nodes of ranvier?
a gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve; allows for ion flow across the membrane (represented by letter G)
What is the synapse?
junctions formed when nerve cells meet up; neurotransmitters move impulses across this gap
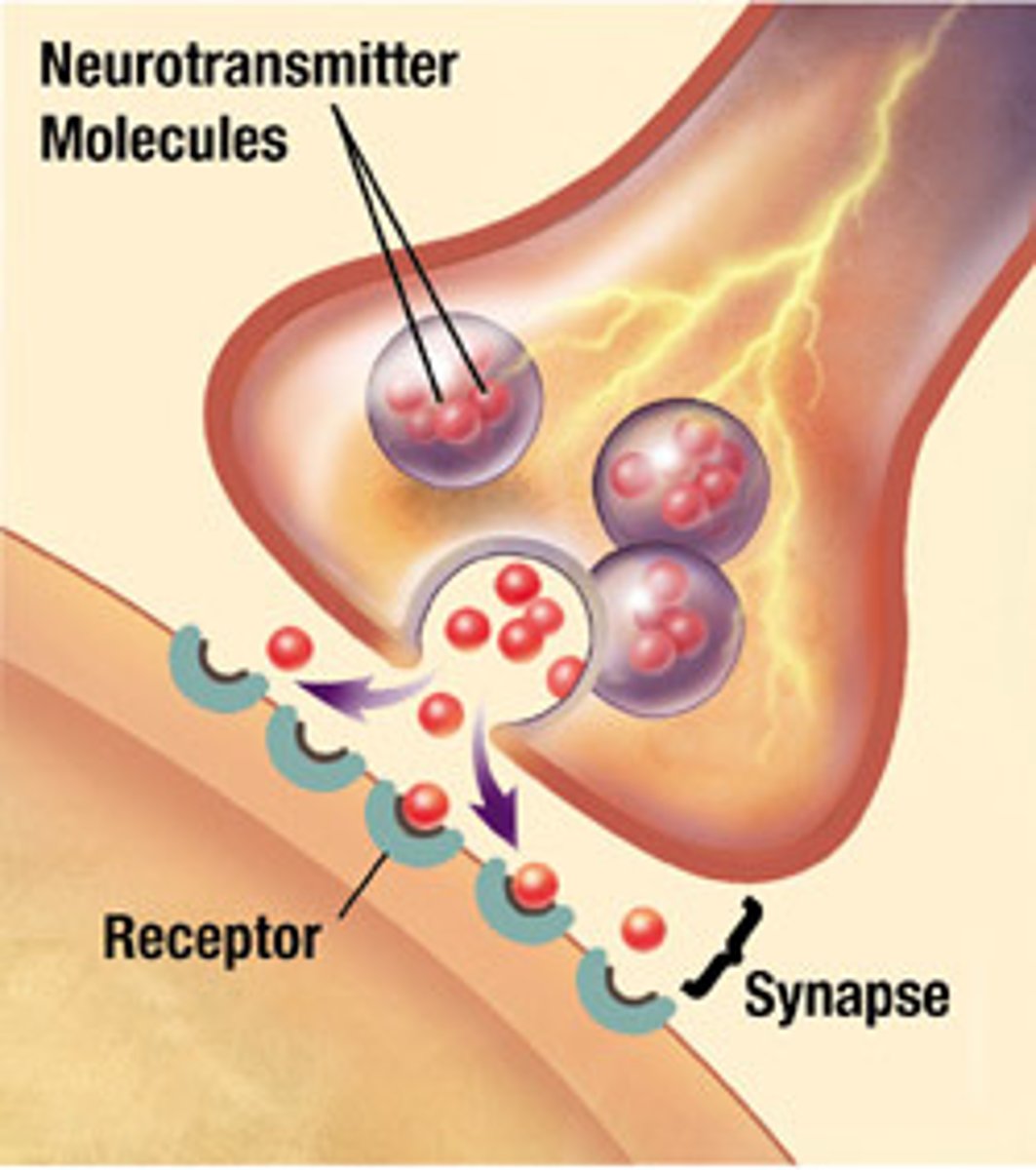
What is a neurotransmitter?
these transfer nerve impulses from one nerve fiber to another within two separate nerve cells
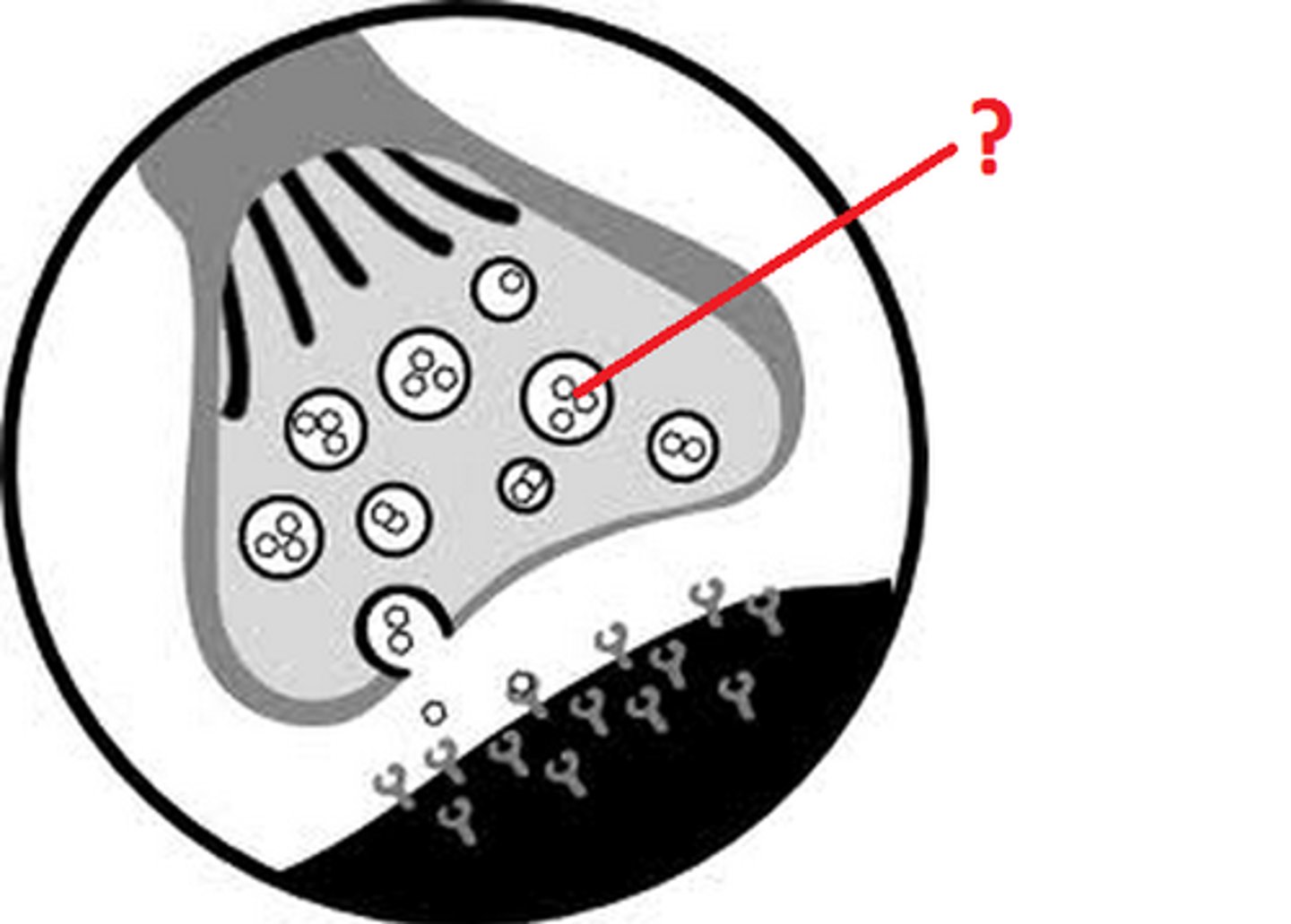
What do we call electrical messages that are sent down the axon of a neuron?
action potentials
How is an action potential generated?
a sudden reversal in charge
In a cell at rest, there is more _(Na+/K)_ on the outside of the cell membrane. The outside has a _(+/-)_ charge.
Na+
+
Does the Na+/K+ pump work via active or passive transport?
Active-- moving to a level of higher concentration by using energy
What causes the inside of the membrane to reverse charge and begin the action potential?
The potassium channels close and Na+ rushes in which temporarily reverses the charge/depolarizes that area of the membrane.
Explain how neurons convey information using both electrical and chemical signals.
ELECTRICAL signals move down the axon to the axon terminal where they signal neurotransmitters (which are CHEMICAL signals) to move into the synaptic cleft.
What is the synaptic cleft?
space between two nerve cells that are about to pass on the message
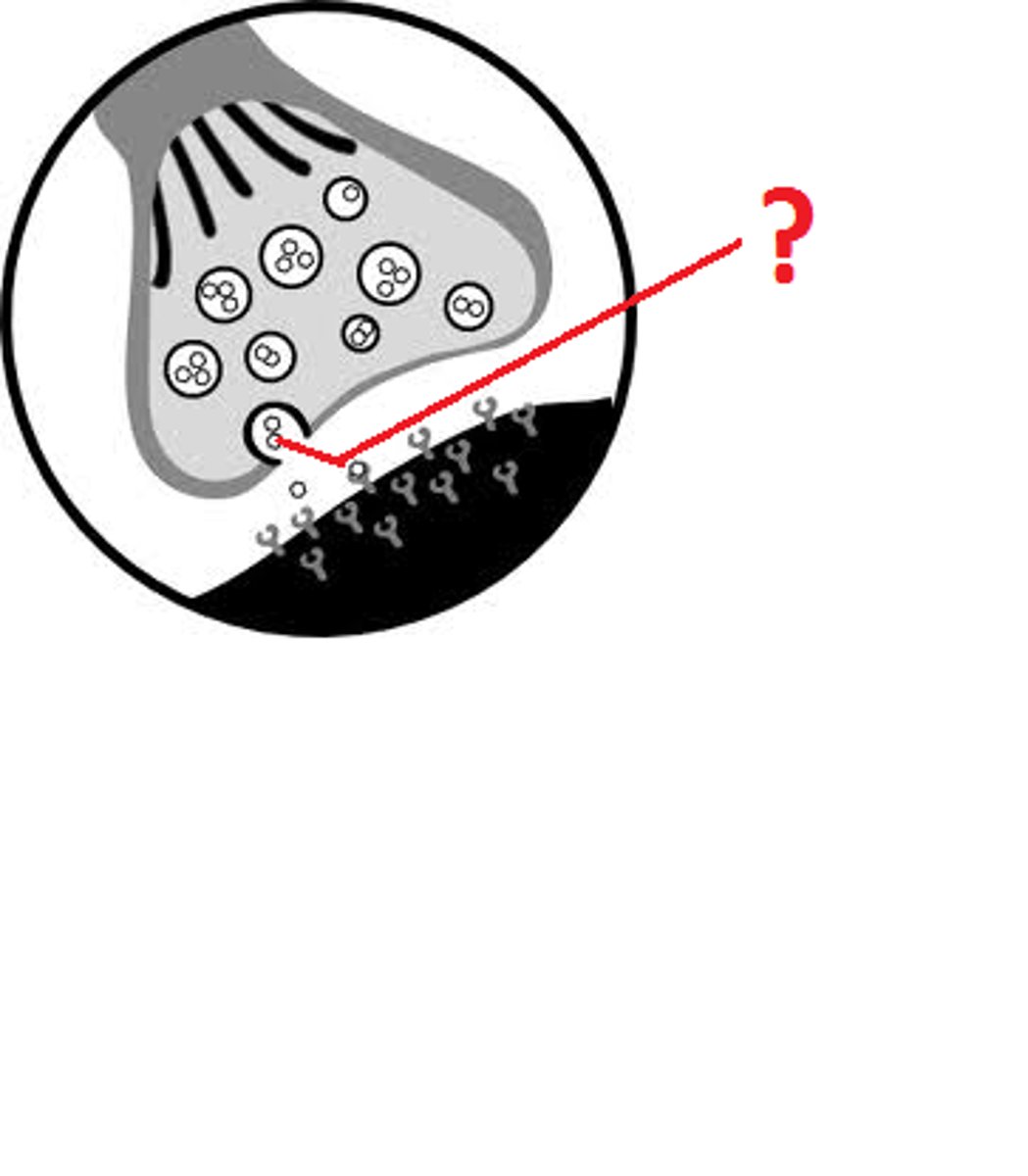
What are the vesicles?
round sacs containing neurotransmitters at the axon terminal
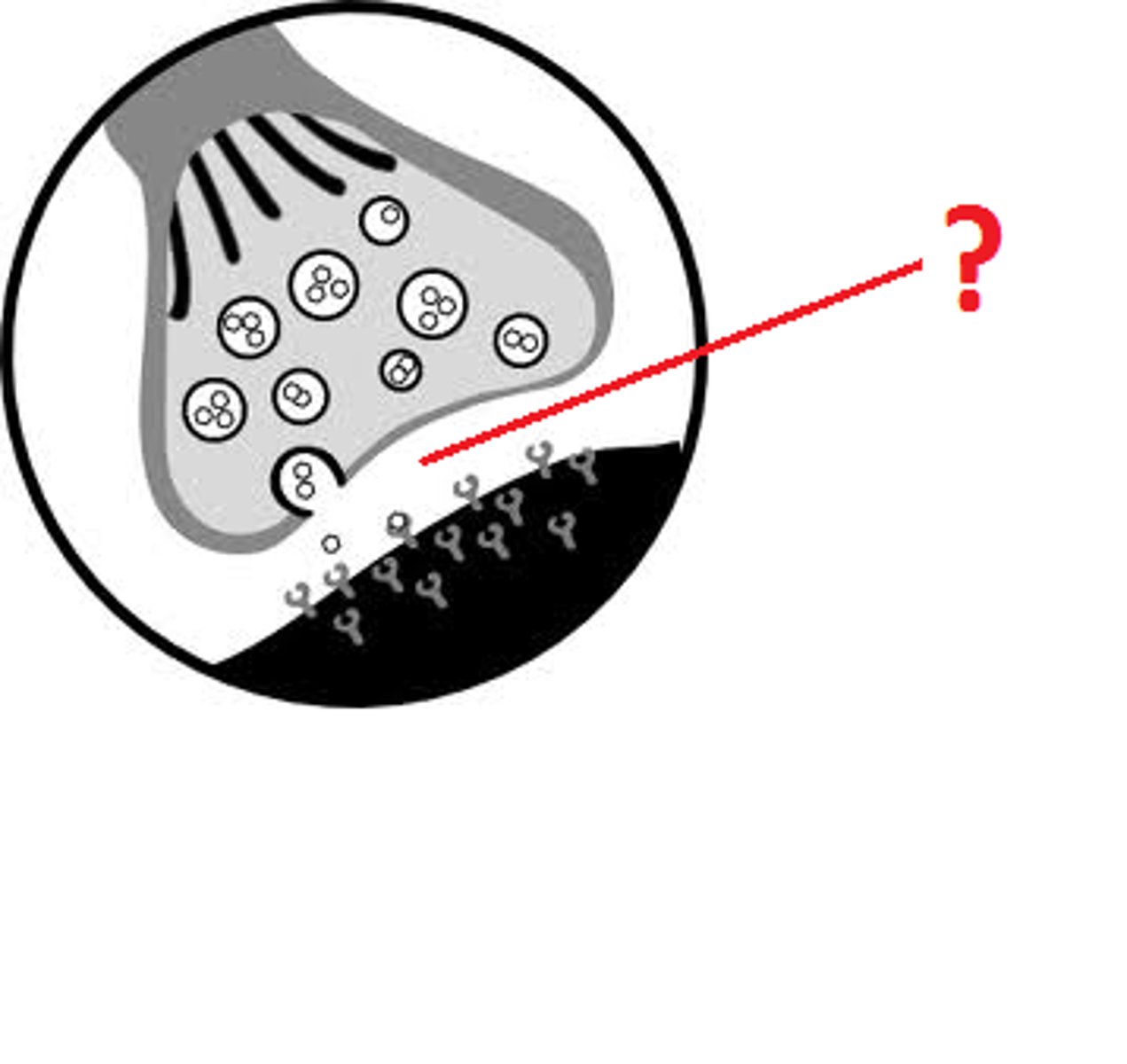
Where are the receptors?
coating the side of the opposite cell, specific to its neurotransmitter
The automatic response of a muscle to a stimulus is called _________________________.
reflex
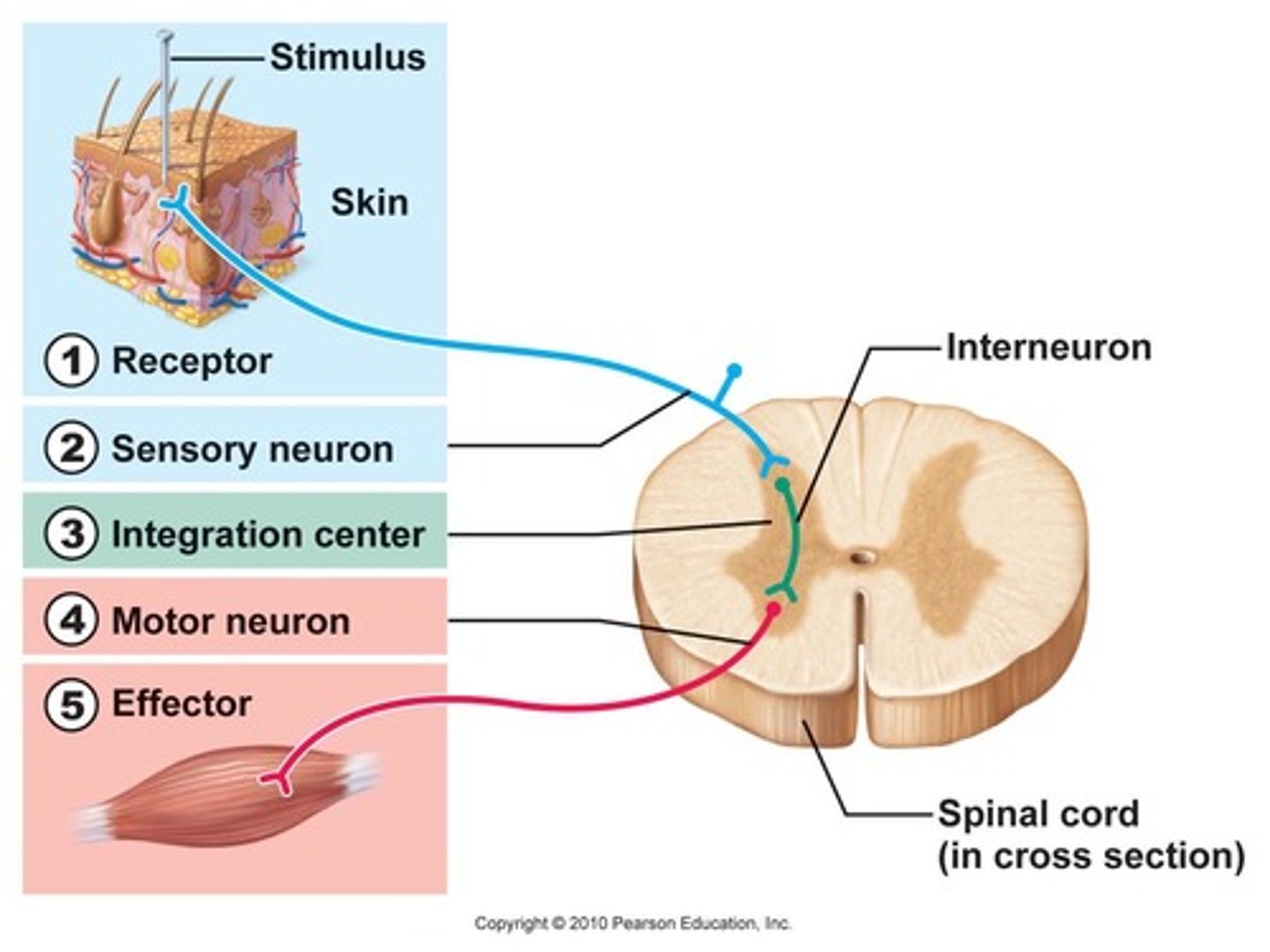
How does the knee jerk response work?
1)tendon just below the knee is tapped
2)quad muscles contract and leg extends
3)stretching of the muscle activates nerve impulses
4)impulses travel to the spinal cord
5)motor neurons are activated
6)motor neurons travel back to the muscle, resulting in contraction
KNOW THIS REFLEX ARC!!! (see reverse)
https://backyardbrains.com/experiments/img/BYB_Exp3_Pic3.png
What is a hormone?
A chemical signal that is formed in specialized cells, travels in body fluids, and coordinates the various parts of the organism by interacting with target cells.
How do hormones interact with target cells?
Hormones travel through blood looking for their specialized target cells which have receptors that the hormone fits into (like a key).
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Endocrine~ secretes a hormone that will be of use INside of the body
Exocrine~ secretes a fluid OUTside of the body
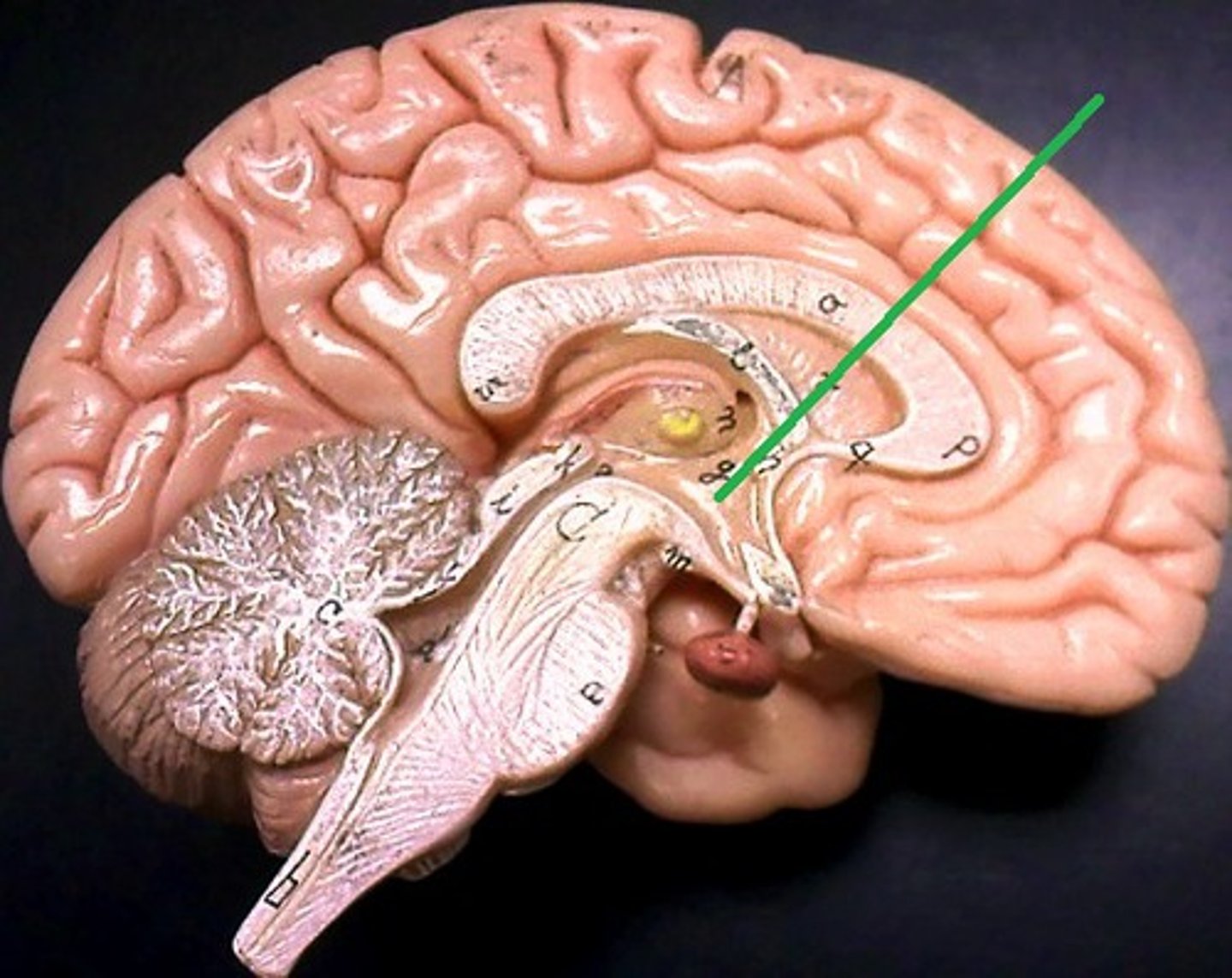
What is the hypothalamus and where is it located?
The ventral part of the vertebrate forebrain; functions in maintaining homeostasis, especially in coordinating the endocrine and nervous systems; secretes hormones of the posterior pituitary and releasing factors, which regulate the anterior pituitary.
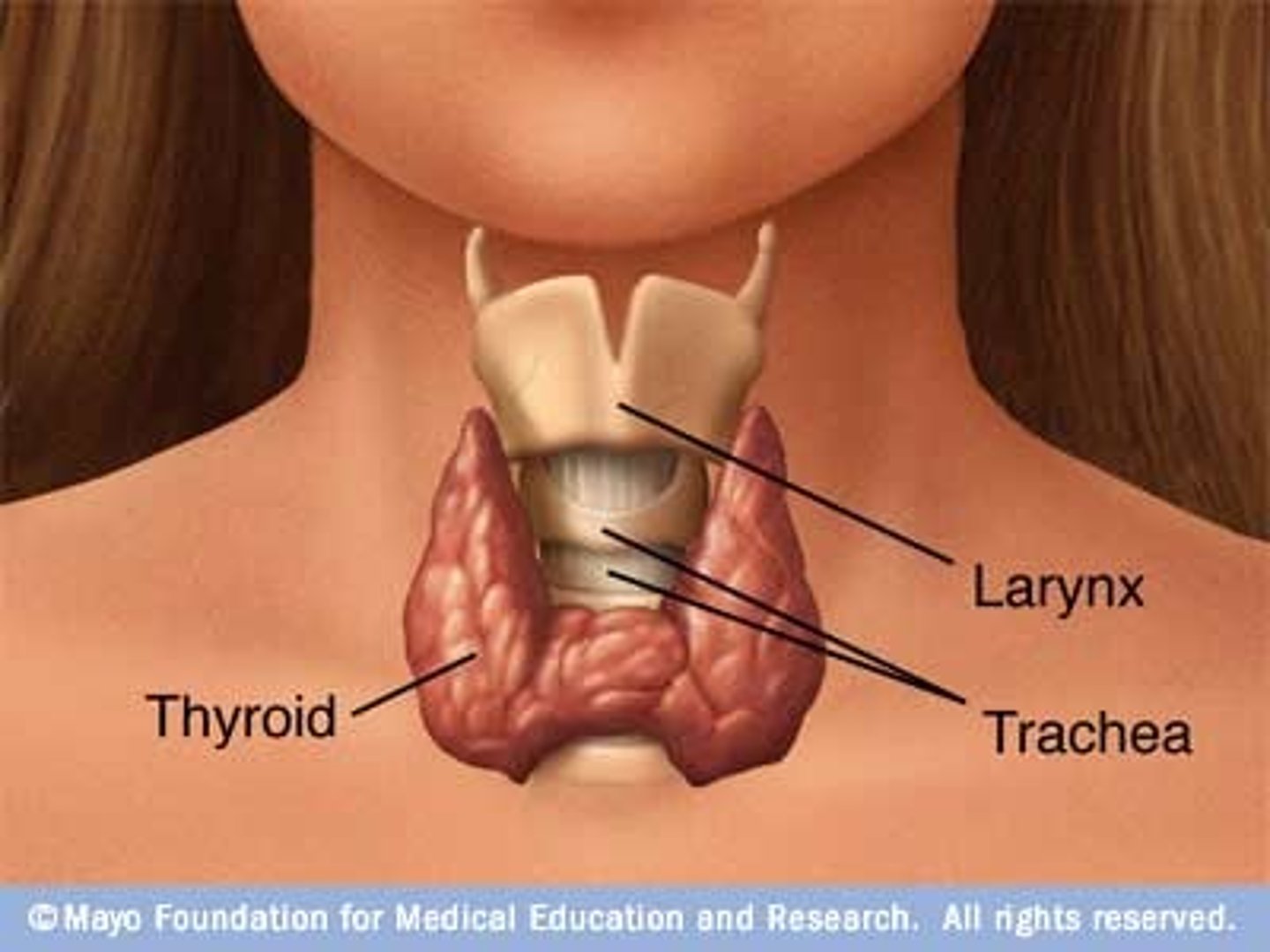
What is the thyroid gland and where is it located?
Endocrine gland that secretes the hormone thyroxine and thyrocalcitonin which regulates metabolic rate.
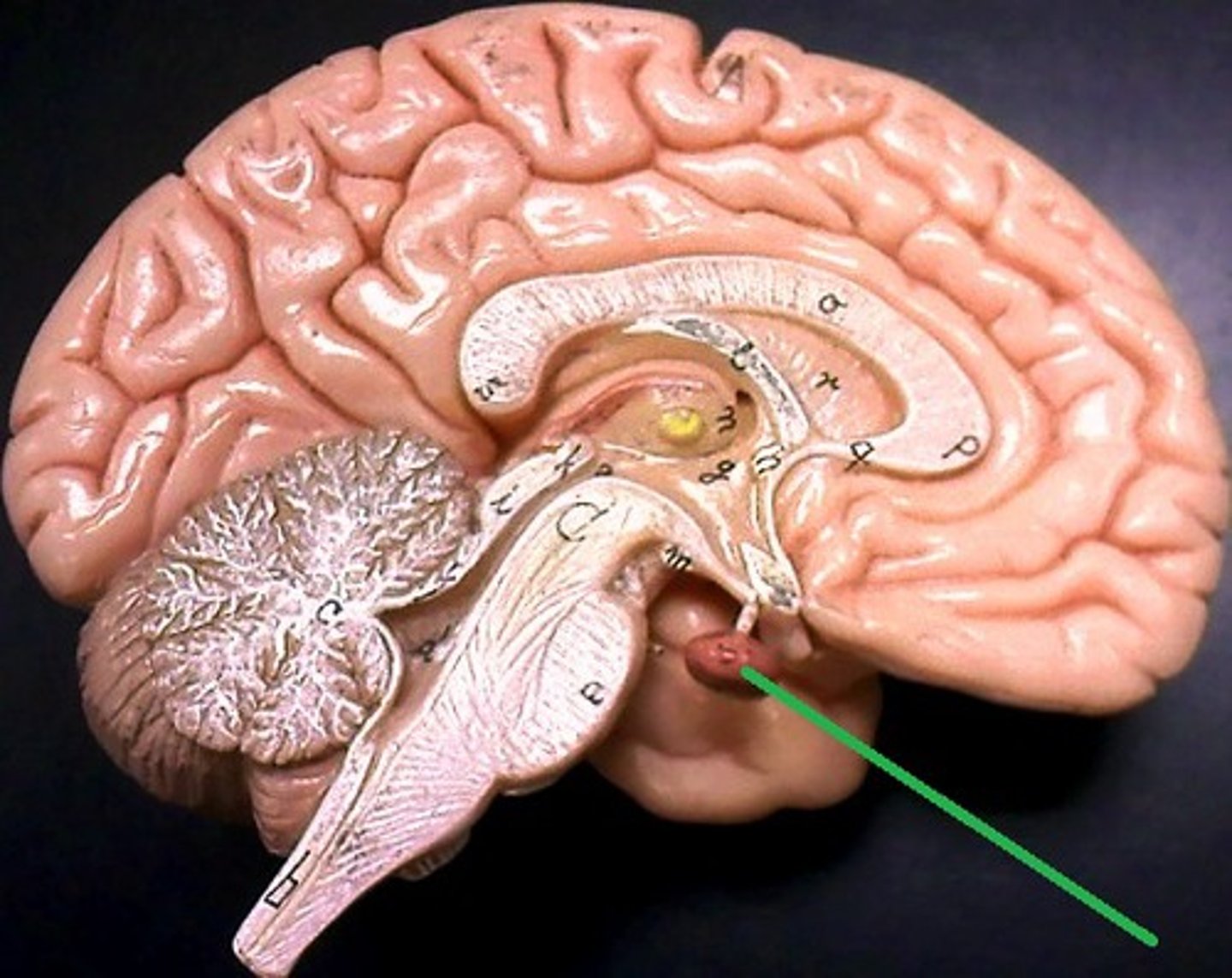
What is the pituitary gland and where is it located?
An endocrine gland at the base of the hypothalamus, stores and releases two hormones produced by the hypothalamus (posterior lobe), and produces and secretes many hormones that regulate diverse body functions (anterior lobe)
Describe 2 ways in which communication in the endocrine and nervous systems are the same and one way in which they are different.
Endocrine makes tangible fluid where nervous system simply produces thoughts and feelings/nervous system responses are more short term than the long term metabolic regulations of the endocrine system.
Both use chemical signals to transmit info (endocrine=hormones, nervous=neurotransmitters).
How do the endocrine system and nervous system work together to control communication in the body?
The hypothalamus is located in the brain yet controls many glands via the pituitary gland. Hormones provide the brain w/ feedback and affect many of its thoughts and emotions so it can properly control other parts of the body,
Compare/contrast hormones and neurotransmitters.
Similar~ both are chemical signals that help control communication within the body
Different~ hormones are transmitted through blood while neurotransmitters are moved through nerve cells at the synapse; hormones control cells and their actions while neurotransmitters control entire systems/muscle groups
What was plaguing Grant Bell?
A pituitary tumor