cooked biochem
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
what is the common oxidized product in citric acid cycle
acetyl coa
product of glycolysis
pyruvate
which molecule provides a C skeleton for nonessential amino acids
pyruvate
what happens in anaerobic respiration
pyruvate to lactate
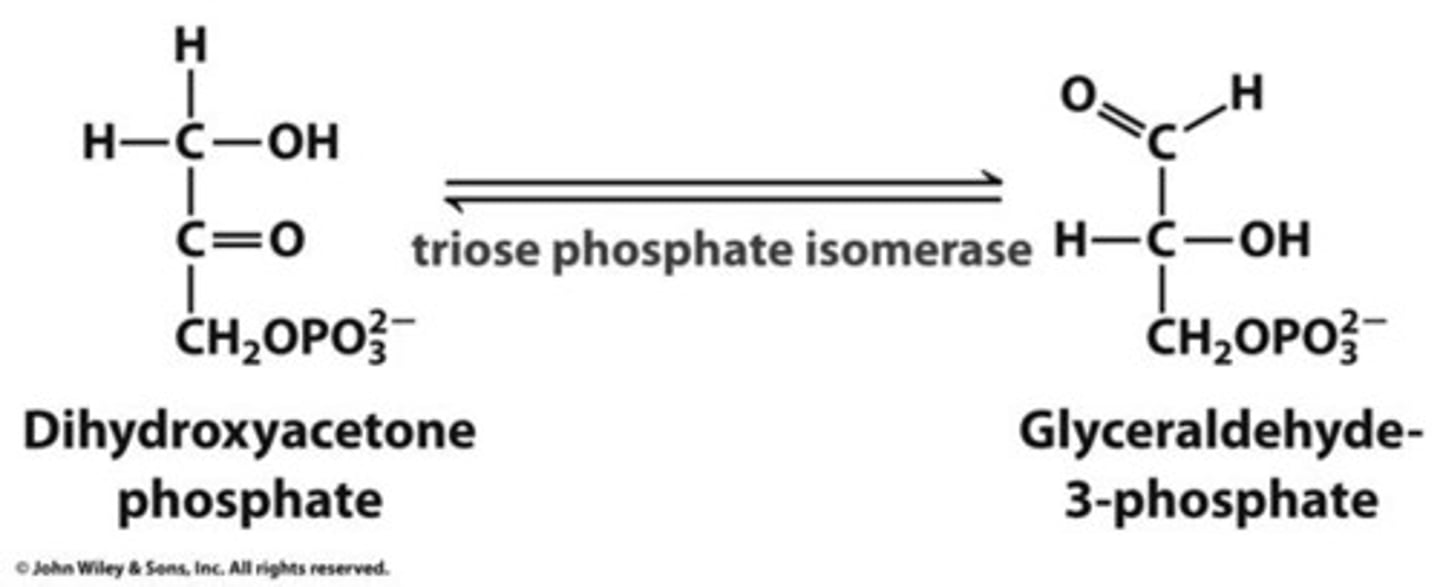
triose phosphate
an intermediate in the Calvin cycle, also known as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
precursor for fatty acids and cholesterol
acetyl coa
how many AAs must be in diet
8 (arg semi essential)
main product of catabolism
acetyl coa
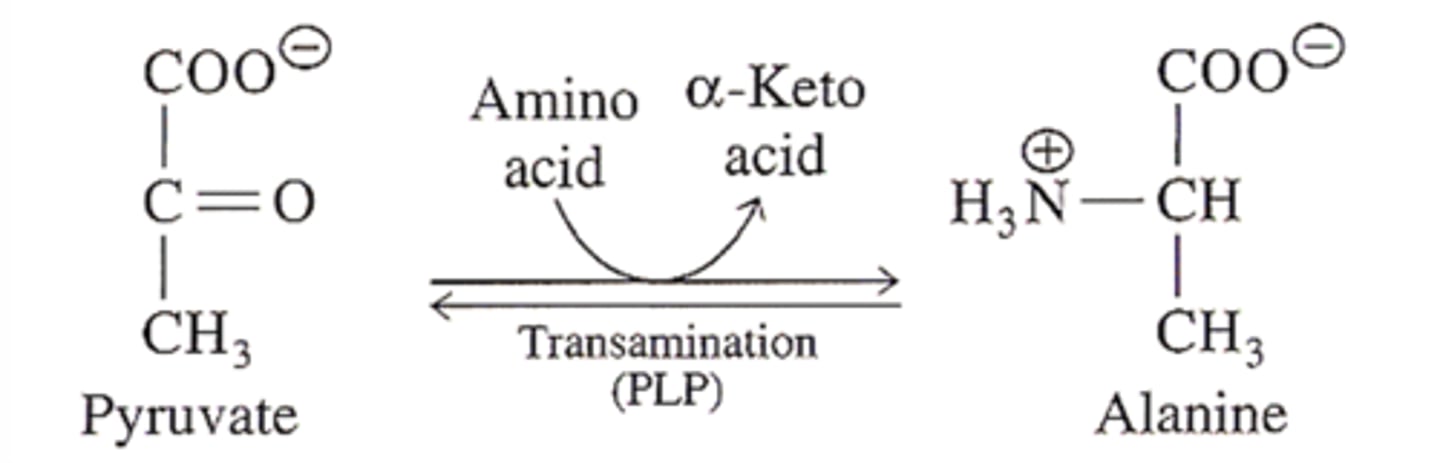
transamination
The process by which an amino group from one amino acid is transferred to a carbon compound to form a new amino acid.
what does pyruvate transamination give
alanine
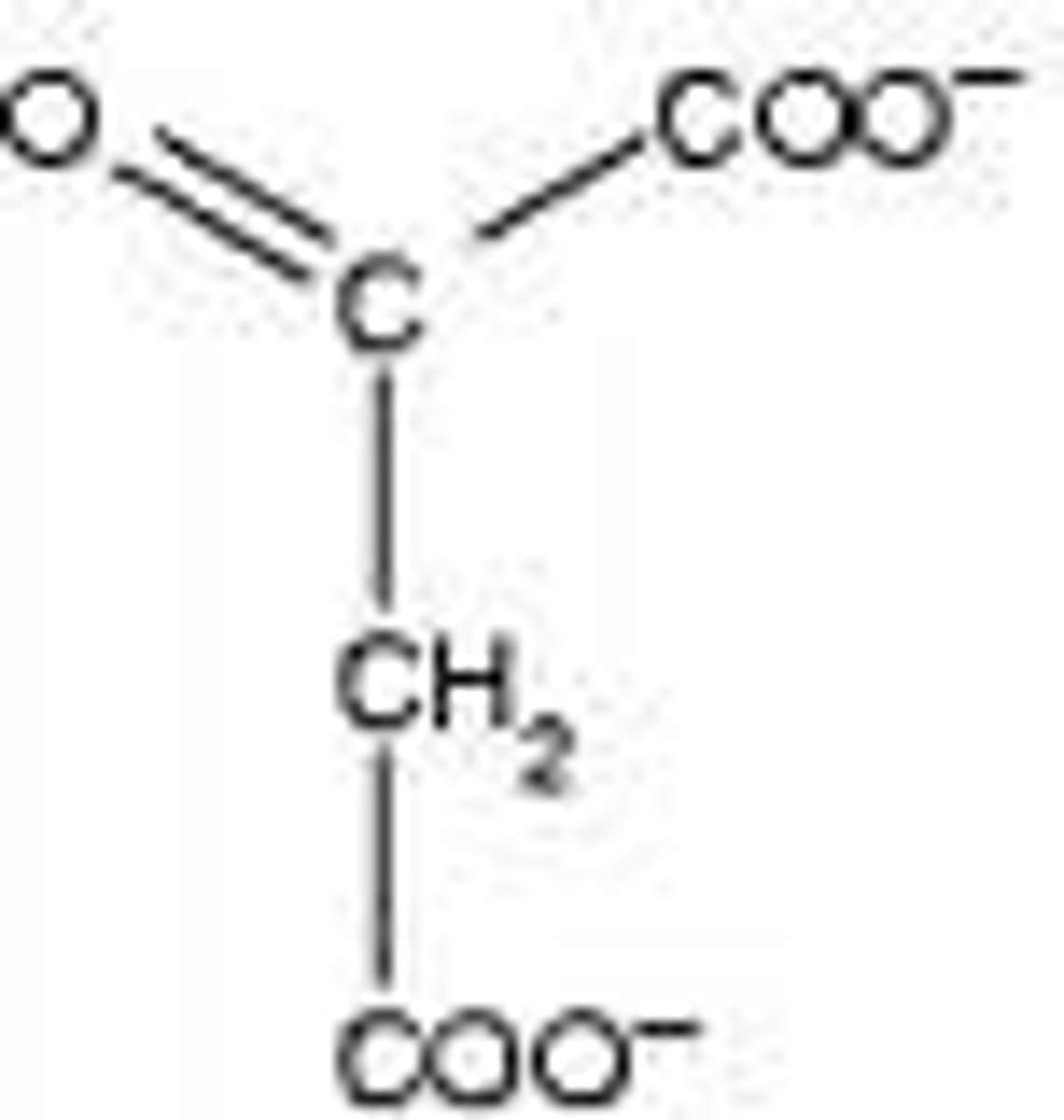
Oxaloacetate
molecule the combines with alanine to deaminate it to form aspartate
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
(if spiked) indicates that liver cells or cells in other organs are damaged, and the enzymes have leaked into the bloodstream
what is formed by the reductive amination of ketoglutarate
glutamate
what enzyme catalyzes reductive amination of ketoglutarate
glutamate dehydrogenase (favors glutamate synthesis)
what enzymes involved in glutamate to glutamine
glutamine synthetase and lambda glutamyl phosphate
what provides N for aspartate --> arginine
glutamine
serine oxidation (what is oxidizing agent), what does it do
NAD+, changes OH to ketone
glycine formation (why special)
STRONGLY FAVORED
what reduces proline, what molecule cyclizes
NADPH, glutamyl phosphate
cysteine comes from what AA
methionine
what process is a disulfide bridge formed by
oxidation
phenylalanine hydroxylation
irriversible (done by phenylalanine hydroxylase and NADPH)
if diet has enough phenylalanine...
tyrosine nonessential, BUT tyrosine cant replace phenylalanine
Tetrahydrobiopterin
a cofactor needed to stabilize the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (phenylalnine to tyrosine by NADPH)
mixed function oxidases
(AKA monooxygenase or hydroxylase) oxidize two different substrates simultaneously (REDOX) O2 to substrate and water
where does hydroxylation of proline and lysine occur
ONLY ON ACTAUAL COLLAGEN NOT SPEARATELY
oxidase
adds electrons to oxygen
p450s
ENZymes capable of bio transforming drugs in the liver mostly
Lock- Key Model
Complementarity in size, shape, charge, lipophilicity
Induced Fit
Conformational change upon binding that allows for higher affinity and tighter binding
Transfer amino group of one molecule to another (often AA to keto group)
Transaminases
Which of the following enzymes is a mix-function oxidase?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Which amino acid will form disulfide bridges?
Cysteine
What type of enzyme are P450s?
Oxidases
Which statement is true about essential Amino acids?
They cannot be synthesized
Glutamate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction
Reductive amidation of ᵳ-ketoglutarate
Which transamination reaction is strongly energetically favored?
Glycine synthesis
Why can’t essential AA undergo transamination?
transamination only occurs with AA that can be synthesized
what cuts protein into peptides in stomach
pepsin
trypsin
an enzyme from the pancreas that digests proteins (SMALL TO SMALLER) in the small intestine
Chymotrypsin
One of the main pancreatic proteases; it is activated (from chymotrypsinogen) by trypsin. (cut up proteins in small intestine
Aminopeptidase + carboxypeptidase
in small intestine - degrade peptides into amino acids; splits off one amino acid at a time
2 fates of amino acid
oxidized for energy (remove amino group - urea cycle) (entry into central metabolism - glycolysis citric acid cycle)
recycled into proteins
Why do we have to metabolize amino acids?
All of the above
some animals excrete nitrogen as
uric acid
trafficable amino acid
glutamate
alpha ketoglutaric acid
an intermediate product of the citric acid cycle (accepts amino group) N scavenger)
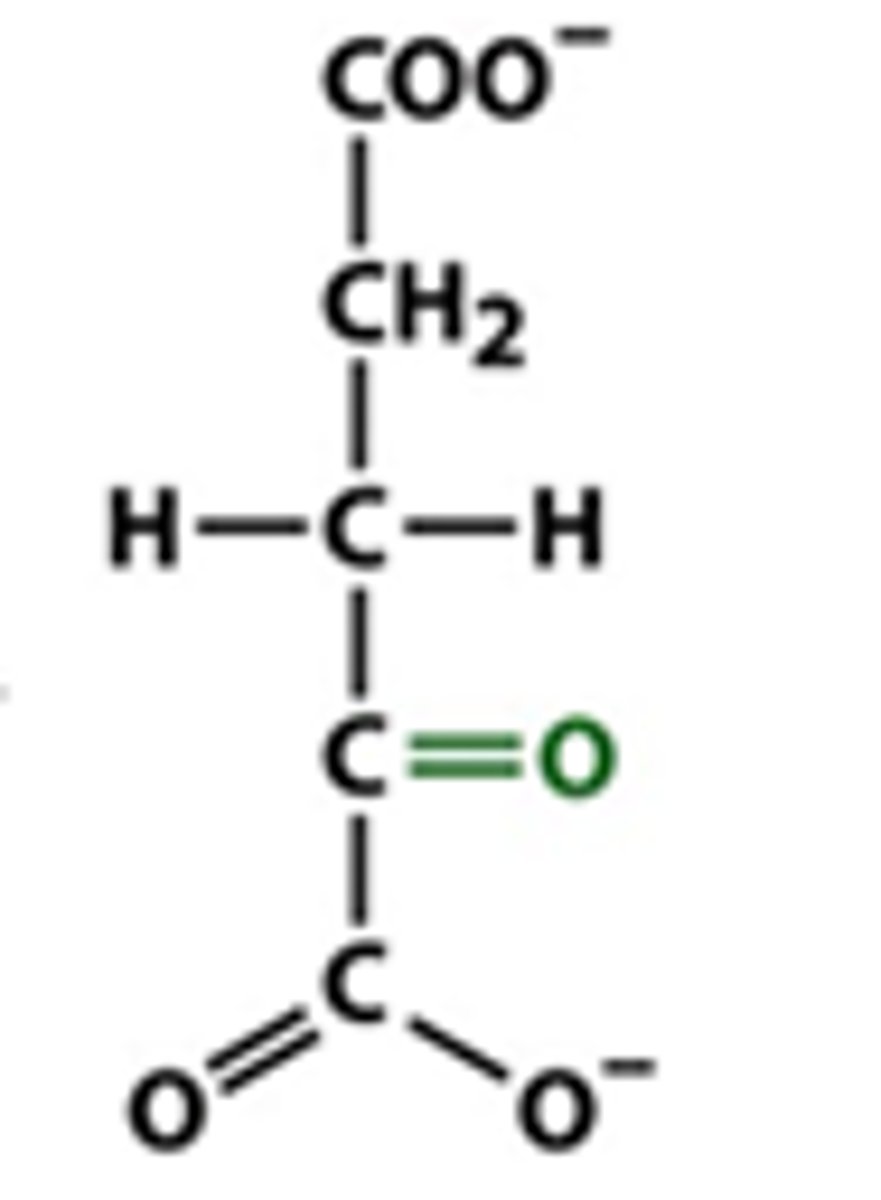
what happens when you add an amine to alpha ketoglutarate
glutamate
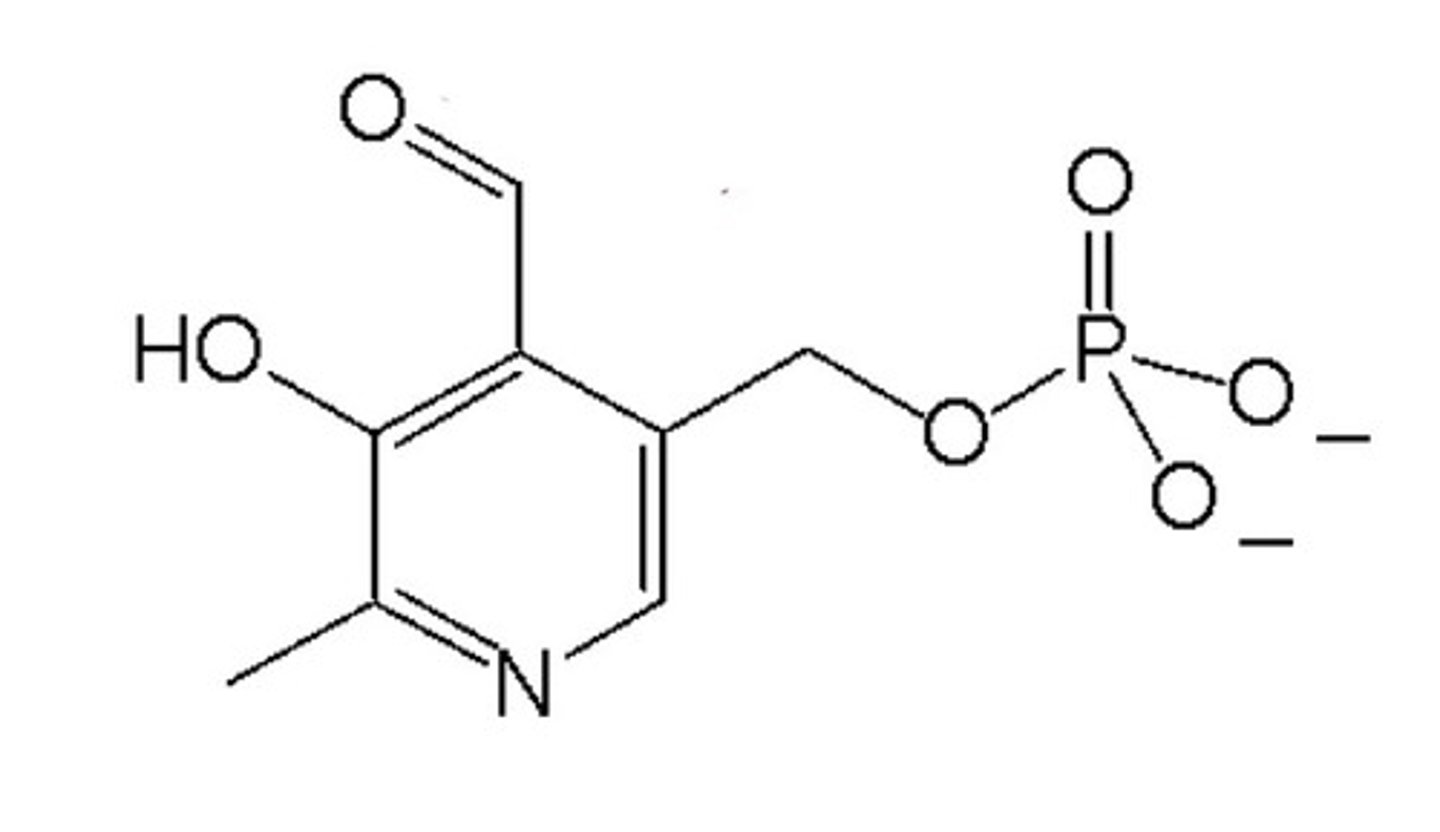
pyridoxal phosphate
The major coenzyme form of vitamin B6
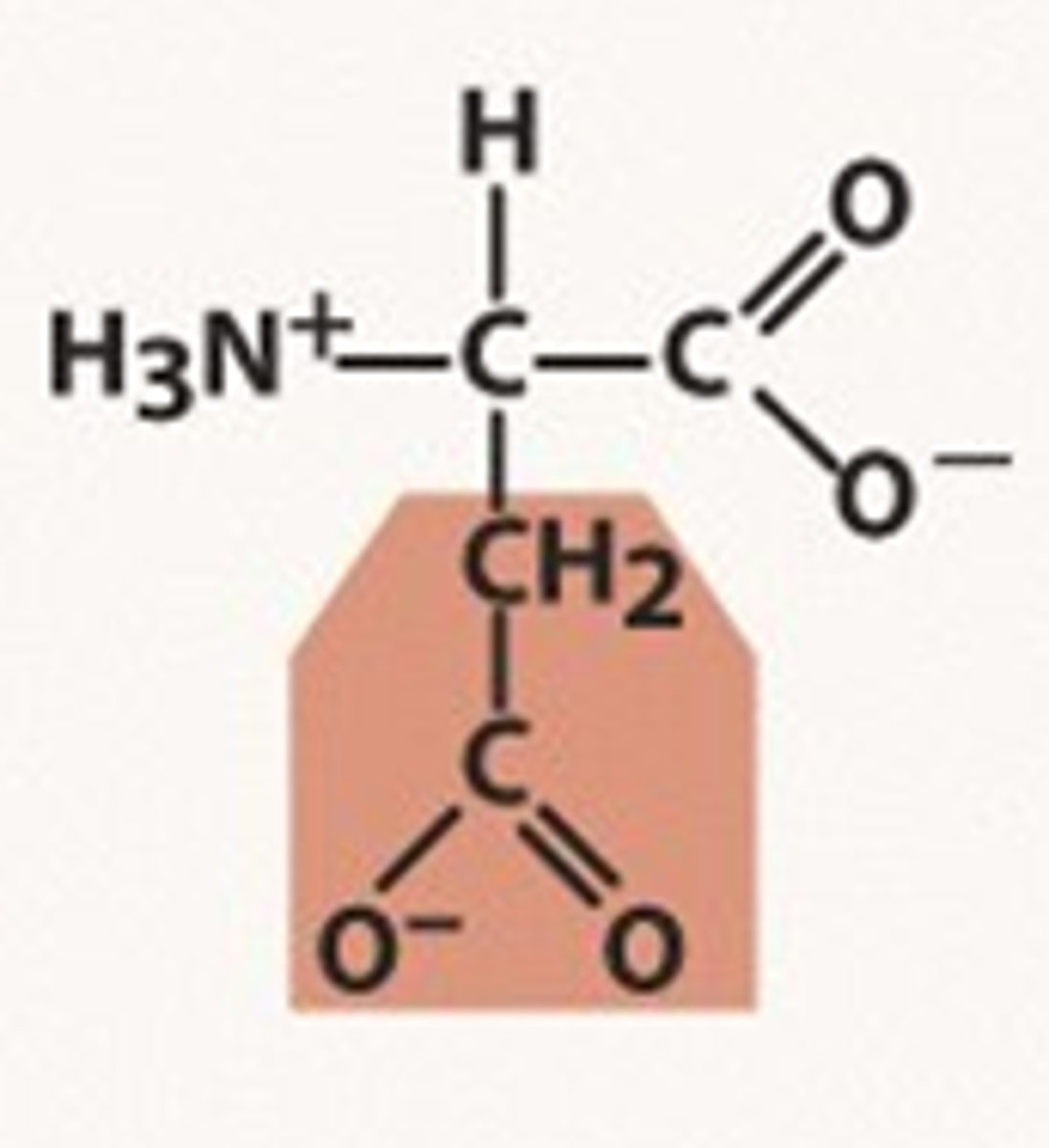
Schiiffbase
imine
Transfer of one amine to alpha-ketoglutarate results in synthesis of _________________. Transfer of a second amine results in
synthesis of _________________.
glutamate (e.g., transamination).
glutamine (e.g., glutaminesynthetase).
AST (aspartate aminotransferase) in bloodstream
sign of liver damage
what is ammonia captured in
glutamate
excess ammonium stored where
glutamine
glutaminase
Enzyme converting glutamine to glutamate; catalyzes the release of ammonia from glutamine in the mitochondria?
ammonia in glutamate removed by what
glutamate dehydrogenase
transdeamination
the combined action of aminotransferase and glutamate dehydrogenase (transamination + oxidative deamination); pathway for ammonia excretion
Oxidative Deamination
removes an ammonia molecule directly from the amino acid
Transamination
The process by which an amino group from one amino acid is transferred to a carbon compound to form a new amino acid.
Acts as temporary storage of nitrogen
glutamine
glutamate dehydrogenase
catalyzes the reversible oxidative deamination (removes ammonia from glutamate) of glutamate and makes intermediate α-ketoglutarate
where does ammonia get removed from glutamate
mitochondria
Where do the two nitrogens in urea come from?
Carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
1st step of nitrogen acquiring (needs ATP)
Rate Limiting Enzyme of Urea Cycle / initiates
Converts CO2 and NH3 to Carbamoyl Phosphate
where do most urea cycle reactions occur
cytosol followed by the mitochondrial matrix
Ornithine
Amino acid involved in urea cycle combines with carbamoyl phosphate (acts as a carrier molecule that accepts an ammonia group to become citrulline)
Citrulline
Intermediate formed from ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate.
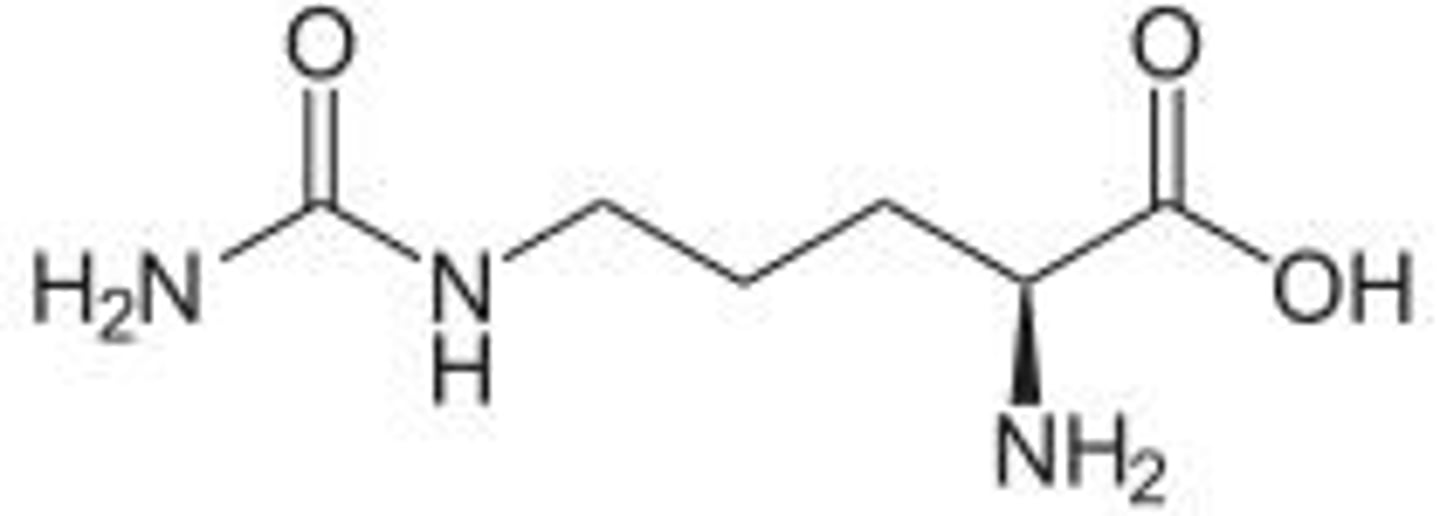
when does citrulline go to the cytosol
when the phosphate of carbamoyl phosphate goes into mitochondrial matrix
citrulline
kidneys convert to L arginine
how does one amino group enter the urea cycle
as carbamoyl phosphate
how does the second amino group enter the urea cycle
in the form of aspartate
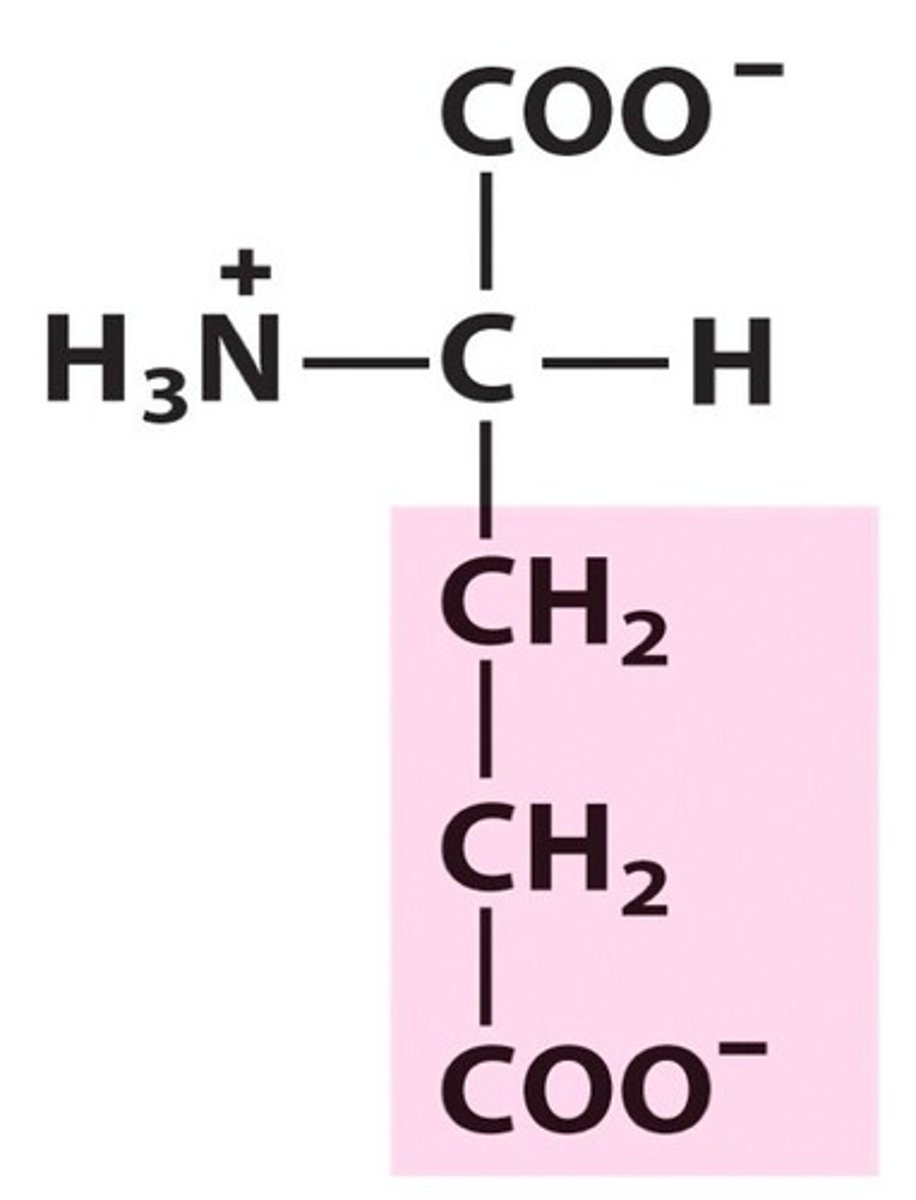
Oxaloacetate
A four-carbon molecule that binds with the two-carbon acetyl unit of acetyl-CoA to form citric acid in the first step of the Krebs cycle.
How does ammonia from glutamine enter the urea cycle?
after glutamine is broken down by the enzyme glutaminase inside liver cells, releasing both ammonia and glutamate
argininosuccinate
Intermediate formed from citrulline and aspartate.
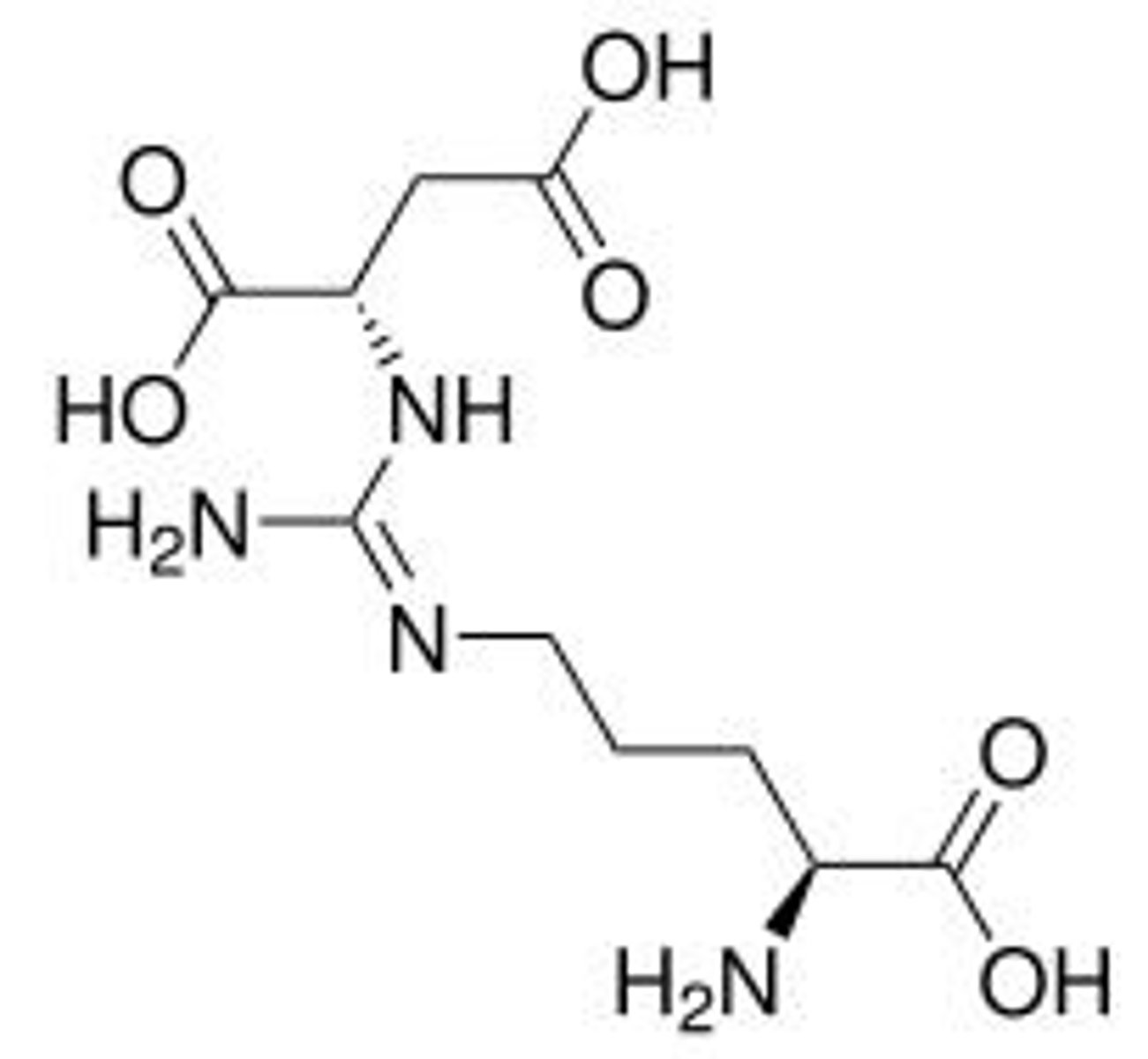
citrullyl - AMP
Intermediate formed during argininosuccinate synthesis.
2 sources of N for urea
aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate
Ketogenic
Describes amino acids that can be converted into intermediates that then turn into acetyl coa (USED FOR ENERGY)
AAs to pyruvate
Trp, Ala, Ser, Gly, Thr, Cys
CAT GSS
another name for niacin
Vitamin B3
what can tryptophan be used to make
niacin (vitB3)
what do e coli produce in gut (good for gut)
indole derivatives
serotonin
feel good (made from TRYPTOPHAN) sleep, mood, pain, digestion
what is the first drug to combat serotonin deficiency
serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) prozac (block/ inhibit the reuptake of serotonin so it can stay around longer
enzyme for pyruvate to acetyl coa
pyruvate dehydrogenase
AAs metabolized to alpha ketoglutarate
Pro, His, Arg, Glu, Gln
PHAGG
alpha-ketoglutarate
a compound that participates in the formation of nonessential amino acids during transamination
what amino acid goes directly to aketoglutarate but others must be converted to it
glutamate
what is folate
Aka vit B9 -required for hemoglobin and amino acid synthesis (CRUCIAL DURING EARLY PREGNANCY) reduce birth defects in brain and spine
Succinyl-CoA (AA's)
Threonine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Valine
TIM V
succinyl coa
used for energy, made from alpha ketoglutarate
AAs metabolized to fumarate
tyrosine, phenylalanine
Phenylketonuria
phenylalanine hydroxylase is missing--> cant metabolize phenylalanine
is a disease leading to toxic accumulation of phenylalanine
AAs metabolized to oxaloacetate
aspartate,
asparagine
oxaloacetate function
acetyl group acceptor to carry intro citric acid cycle for oxidation
oxaloacetate pathway
asparagine-->aspartate-->oxaloacetate
asparaginase use
treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced
citrate formed by
condensation of acetyl coa and oxaloacetate
citrate
A compound that is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle (krebs cycle)
Citrate chelates (binds) calcium ions, preventing blood clotting and thus is an effective anticoagulant
asparaginase
treatment for leukemia