Young families Childbirth
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 5 P's (main)
1. Passenger
2.Passageway
3. Powers
4.Position
5. Psychological response
2.Passageway
3. Powers
4.Position
5. Psychological response
2
New cards
What trimester is the pelvic size assessed
1st trimester
3
New cards
What is the most common type of pelvis in women
Gynecoid
4
New cards
What is the thinning of the cervix called
effacement
5
New cards
What is dilation?
widening of the cervix
6
New cards
how many cm is the complete dilation to birth?
10 cm
7
New cards
fetal presentation
the manner in which the fetus appears to the examiner during delivery
8
New cards
When assessing the passenger in birth what do we look at
1. fetal presentation
2. fetal Lie
3. Head size
4. fetal attitude
5. fetal Position
2. fetal Lie
3. Head size
4. fetal attitude
5. fetal Position
9
New cards
fetal lie
the relation of the long axis (spine) of the fetus to the long axis (spine) of the mother
10
New cards
How long is the anterior fontanel open
12-18 months
11
New cards
How long is the posterior fontanel open
8-12 weeks
12
New cards
breech presentation
when the baby's buttocks or both legs appear first during birth
13
New cards
What is the most common fetal lie
longitudinal
14
New cards
fetal attitude
Refers to posturing (flexion or extension) of the joints and the relationship of fetal parts to one another
15
New cards
What is station?
relationship of the ischial spines to the presenting part of the fetus and assists in assessing for fetal descent during labor.
16
New cards
What is engagement?
The largest transverse diameter of the presenting part (typically the head) has passed through the maternal pelvic brim or inlet
17
New cards
What number is associated with engagement
0
18
New cards
What is primary power
involuntary uterine contractions
19
New cards
What is secondary power
pushing
20
New cards
Psychological response
Maternal stress, tension, and anxiety
21
New cards
Normal fetal heart rate
110-160 bpm
22
New cards
What is a GI response to cervical dilation
Nausea
23
New cards
Why do we assess blood pressure between contractions
Blood pressure rises during an active contraction
24
New cards
Braxton Hicks contractions
intermittent painless uterine contractions that occur with increasing frequency as the pregnancy progresses
25
New cards
Prelabor
contractions are not regular and often stop with position change or movement,
26
New cards
true labor
regular contractions, discomfort radiates from the back, intensity increases with walking,
cervix effaced and dilated is true or false labor
cervix effaced and dilated is true or false labor
27
New cards
What is bloody show?
It is a small amount of blood at the vagina that appears at the beginning of labor and may include a plug of pink-tinged mucus that is discharged when the cervix begins to dilate.
28
New cards
first stage of labor
the initial stage of childbirth in which regular contractions begin and the cervix dilates
29
New cards
What hormones increase during the 1st stage of labour
Oxytocin, Estrogen, prostaglandins
30
New cards
latent phase of labor
Cervix 0-3 cm (non pharmacological pain management)
31
New cards
Active phase of labor
4-7 cm
moderate to strong contractions
regular q 3-5 min lasts 40-70 sec
moderate to strong contractions
regular q 3-5 min lasts 40-70 sec
32
New cards
transitional phase of labor
Phase of 1st stage of labor with 8-10 cm dilation patient has: strong contractions every 2-3 minutes - mother is irritable, anxious, and self-oriented
33
New cards
admission to L&D
Physical assessment
Progression of labor
allergies
birth plan
characteristics of pregnancy
Progression of labor
allergies
birth plan
characteristics of pregnancy
34
New cards
Herpes simplex virus during birth
Vaginal birth is not allowed when mother has visible symptoms
35
New cards
Amniotic fluid assessment
COAT (color, odor, amount, time)
36
New cards
labor induction
the process of initiating labor by artificial means
37
New cards
How is oxytocin administered?
IV
38
New cards
Risks associated with labor induction
Risk of preterm labour
Long labour
Lengthy exposure to high alert medications (with potential side effects)
Higher rate of cesarean delivery
Long labour
Lengthy exposure to high alert medications (with potential side effects)
Higher rate of cesarean delivery
39
New cards
rupture of membranes
spontaneous rupture of the amniotic sac with release of fluid preceding childbirth OR artificial rupture of membranes
40
New cards
artificial rupture of membranes (AROM)
artificial rupture of amniotic sac by outside means
41
New cards
spontaneous rupture of membranes
broken water, Natural rupture of the amniotic sac, which usually occurs at the height of an intense contraction with a gush of fluid out of the vagina.
42
New cards
assessment of amniotic fluid
- should be watery and clear
- odor should not be foul
- 500-1200 mL
- Nitrazine paper (if amniotic fluid, paper will turn dark blue because it is alkaline)
- odor should not be foul
- 500-1200 mL
- Nitrazine paper (if amniotic fluid, paper will turn dark blue because it is alkaline)
43
New cards
Leopold Maneuvers (Abdominal Palpation)
a series of four types of abdominal palpitation for determining fetal position
44
New cards
Fetal tachycardia
>160 bpm
45
New cards
Causes of fetal tachycardia
Maternal fever
Infection
Drugs (caffeine, cocaine, methamphetamines)
Infection
Drugs (caffeine, cocaine, methamphetamines)
46
New cards
Fetal bradycardia
47
New cards
Causes of fetal bradycardia
Fetal hypoxia
maternal position
heart block
medications
maternal position
heart block
medications
48
New cards
Why would an HCP do a vaginal examination
cervical effacement
dilation
fetal descent
dilation
fetal descent
49
New cards
second stage of labor
Full dilation
Intense contractions
BIRTH!!
Intense contractions
BIRTH!!
50
New cards
How long does labor last for a women that is nulliparous
50-60 minutes
51
New cards
How long does labor last for a women that is multiparous
20-30 minutes
52
New cards
Non Pharmacological therapy during labor
Hydrotherapy
Ambulation and position changes
Acupuncture and acupressure
Hot/ cold application
Attention focusing and imagery
Effleurage and massage
Breathing techniques
Ambulation and position changes
Acupuncture and acupressure
Hot/ cold application
Attention focusing and imagery
Effleurage and massage
Breathing techniques
53
New cards
Pharmacological pain management during labor
Systemic analgesia
-Opioids (butorphanol, nalbuphine, meperidine, fentanyl)
-Ataractics (hydroxyzine, promethazine)
-Benzodiazepines (diazepam, midazolam)
Regional or local anesthesia
-epidural block
-Opioids (butorphanol, nalbuphine, meperidine, fentanyl)
-Ataractics (hydroxyzine, promethazine)
-Benzodiazepines (diazepam, midazolam)
Regional or local anesthesia
-epidural block
54
New cards
Where is the placement for an epidural
L3-L4 of the spine
55
New cards
epidural injection
Involves injection of a local anesthetic AND an opioid analgesic
56
New cards
pros of epidural
Fully Awake
Can be adjusted
Ideally, allows for urge to push
Can be adjusted
Ideally, allows for urge to push
57
New cards
Cons of epidural
hypotension
intravascular injection
respiratory depression
intravascular injection
respiratory depression
58
New cards
episiotomy
surgical incision of the perineum to enlarge the vagina and so facilitate delivery during childbirth
59
New cards
operative vaginal birth
performed using either forceps or a vacuum extractor
60
New cards
How long should a women hold her breath while pushing
no more than 5-7 seconds
61
New cards
What is crowning?
It is the appearance of the infant's head at the vaginal opending during labor.
62
New cards
third stage of labor
delivery of placenta
63
New cards
How long can placenta delivery occur
Typically 3-5 minutes but can last upwards of 1 hr
64
New cards
fourth stage of labor
First 2 hours when mother and baby bond
Skin -skin contact and breastfeeding is initiated
Close monitoring for complications
Skin -skin contact and breastfeeding is initiated
Close monitoring for complications
65
New cards
What is perineal trauma
Damage is usually more pronounced in nulliparous women (tissues are firmer and more resistant)
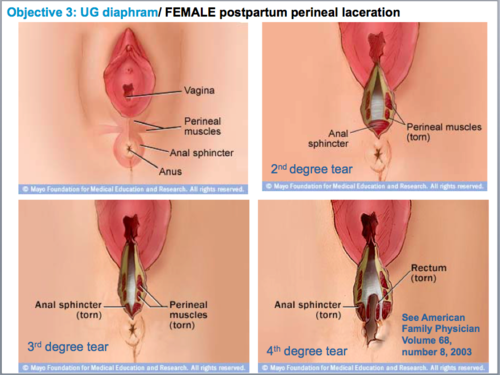
66
New cards
risk factors for perineal trauma
maternal position,
pelvic inadequacy,
fetal malpresentation,
macrosomia,
use of forceps or vacuum,
rapid labor,
prolonged 2nd stage of labor
pelvic inadequacy,
fetal malpresentation,
macrosomia,
use of forceps or vacuum,
rapid labor,
prolonged 2nd stage of labor