Experimental chemistry
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Pipette accuracy
Accurate fixed volumes eg. 10.0cm³
Cannot measure odd volumes like 26.0
Burette accuracy
Most accurate, can measure a range of volumes to the nearest 0.05cm³
Electronic balance scale
Measure accurately to 0.01g
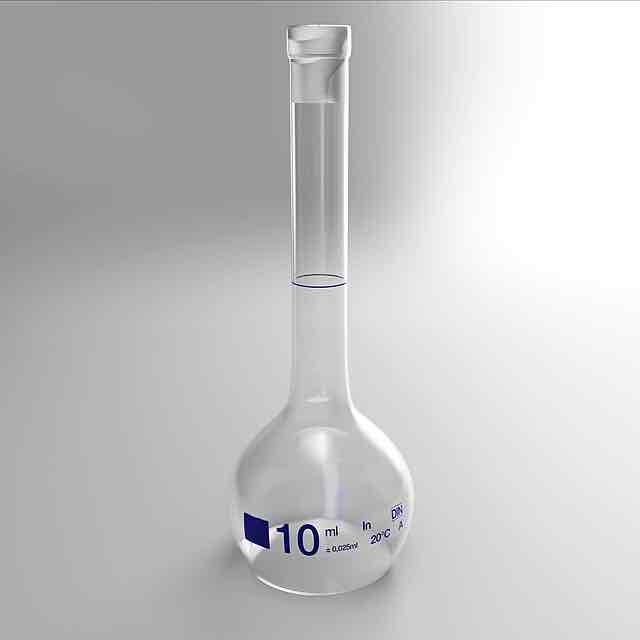
Volumetric flask
Measures accurate fixed volumes that are larger, eg 100 cm^3 |

Thermometer
Nearest 0.5 degrees ,, so either .0 or .5
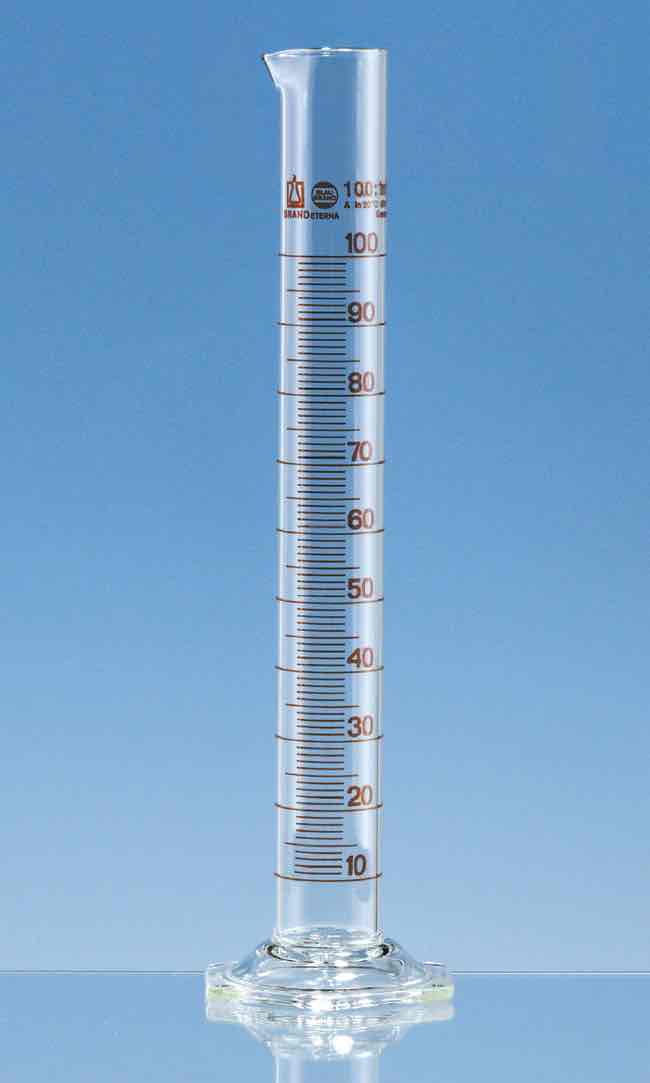
Measuring cylinder
Can measure a range of volumes to the nearest 0.5cm³

What common experiment can be used to test for rate of reaction
Volume of gas produced
Or
Mass of substance gained/lost
Draw and label the set up for measuring volume of gas
And how must the gas be collected?
Plot into a table and measure volume of gas at regular time intervals
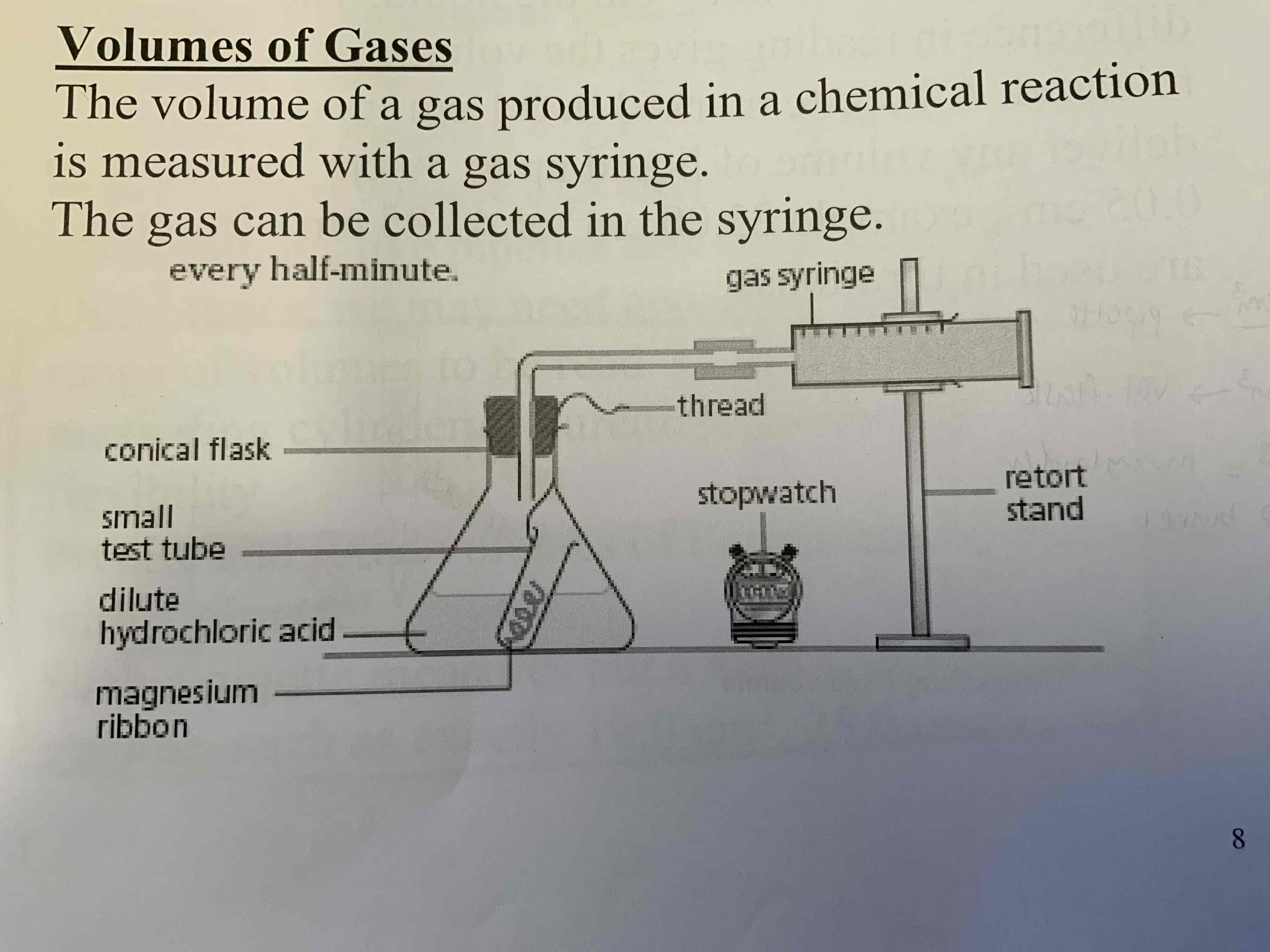
What is the density of air
28.9
When to use water displacement and some examples. Draw set up
When gas is insoluble to slightly soluble in water
Density does not affect gas collection
Eg. Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide
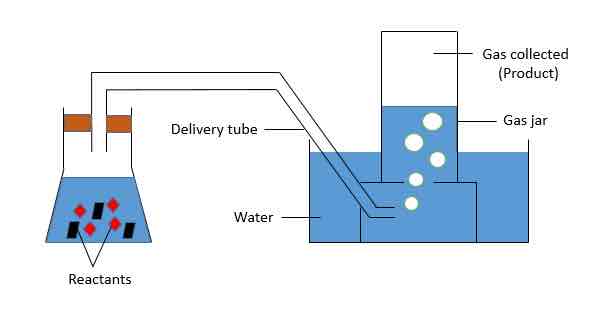
Downward delivery and some examples
Can be insoluble or soluble
Denser than air
Eg. Chlorine
Upward delivery
Can be soluble or insoluble
Less dense than air
Eg. Ammonia
3 drying agents
Conc. Sulfuric acid
Quicklime - calcium oxide
Fused calcium chloride
Suitability for conc. Sulfuric acid and examples of gases using this drying method
Most gases can be dried with conc. Sulfuric acid
Not suitable for gases that react with The acid eg. Ammonia
Suitability for quicklime (calcium oxide) and examples of gases using this drying method
Ammonia gas, use this method to dry
Not suitable for gases that react with calcium oxide (eg. Co2)
Must be freshly heated before use
Suitability for fused calcium chloride and examples of gases using this drying method
Hydrogen, nitrogen, co2
Not suitable for gases that react with calcium chloride (eg. Ammonia)
Must be freshly heated before use
What to look out for for separation of substances
difference in melting boiling points \
Impurities will affect mbp - make boiling point for liquid higher and melting point for substance lower
Definition of a mixture
A mixture consists of 2 or more substances that are NOT chemically combined
Separation using solid-solid mixture (4) and elaborate
magnetic attraction - for magnetic substances
Sieving - to separate solids with different particle sizes
Using suitable solvents - suitable solvent is used to separate solid-solid mixtures in which only one of the solids is soluble in the solvent - relies on different solubilities in different solids (common solvents are water and alcohol, eg. Ethanol)
Sublimation - to separate substance that changes from solid to gaseous state directly
Separating solid-liquid mixtures and elaborate 4
filtration (separate an insolubl solid from a liquid)
Evaporation to dryness - must have different boiling points. separates a dissolved solid from its solvent (vapourise all the solvent (which has a lower bp) by evaporating the mixture, then the solid will remain)
Crystallisation - separates a pure solid (that has broken down into solution) from its saturated solution. A saturated solution is one where no more solute can be dissolved in it (read the example in image. IMPT!)
Simple distillation - separates a pure solvent from a solution (eg. Separating water from seawater, which leaves the salt behind.) Relies on the solid and liquid components in a mixture having different boiling points, so the liquid will boil and evaporate first, leaving the salts behind in the flask
Define and difference between homogenous mixture vs heterogenous mixture → will affect separation technique for liquid-liquid mixture
HOMOgenous mixture → miscible liquids that form a uniform solution (1 layer - link to bio homozygous is 1 also)
HETEROzygous mixture → immiscible liquids
Separating liquid-liquid mixtures
separating funnel: separates immiscible liquids. Higher density liquid remains at the bottom of funnel while liquid with lower density floats on top. Then lower layer can be tapped off
Chromatography - separates a mixture of substances with different solubilities in a given solution ( the more soluble component travels faster and further up the paper than ;less soluble components)
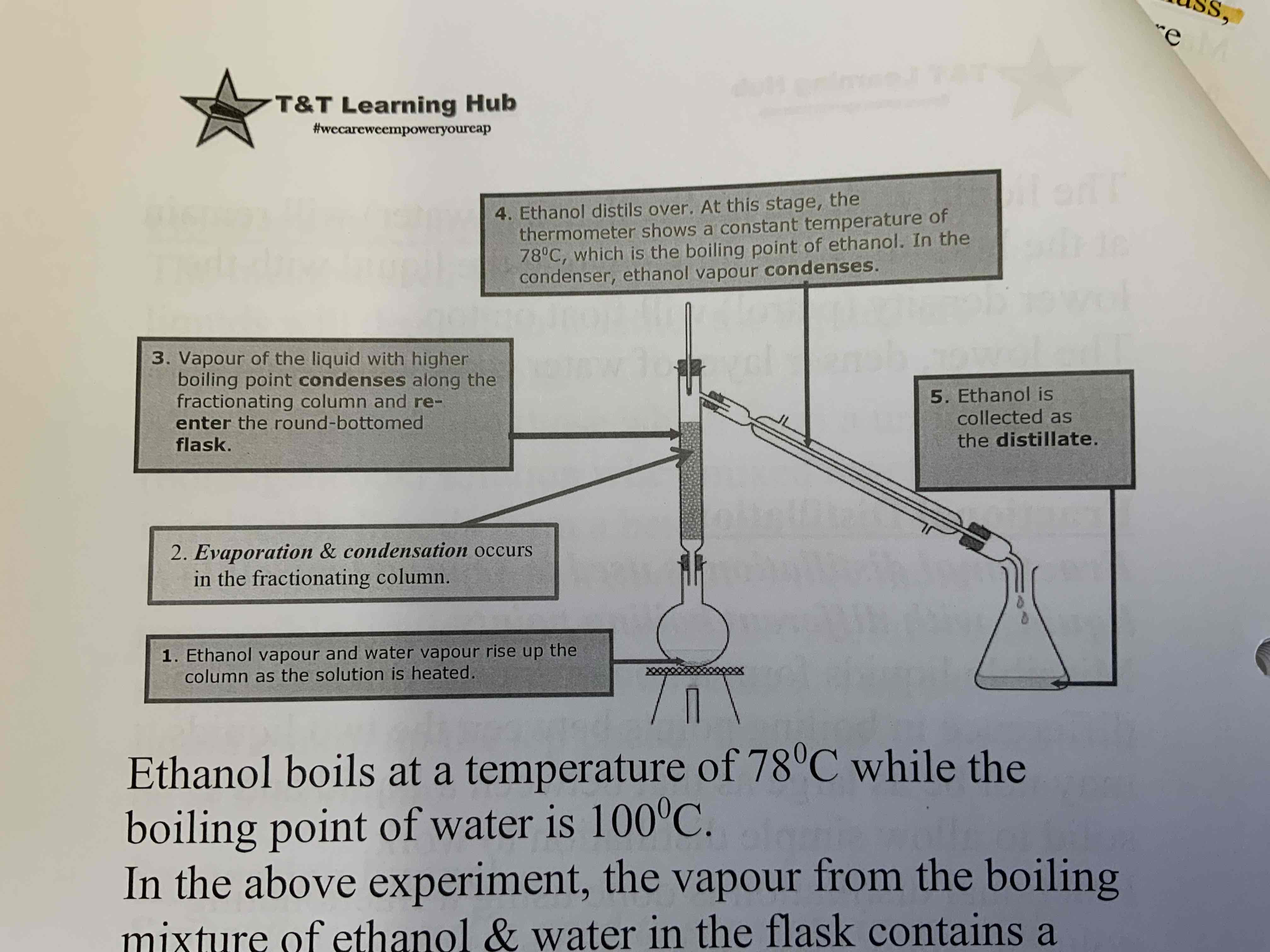
Fractional distillation - separates miscible liquids with different (but very close) boiling points: heat the solution at the temperature of the lower boiling point one. The lower bp solution will form into a gas and then rise up and condense in the condenser, while the vapour of the other liquid with higher boiling point will condense along the fractionating column (wont reach condenser cuz it requires higher temp to do so)
How to determine purity of substances (eg. For they give u a chromatography set up and ask to determine how many substances in Z)
Or if they give a Graph where some substances have variable mbp)
Pure substance has specific mbp under fixed conditions (eg. Water)
Mixtures melt / boil over a range of temperatures
Pure substance shows only one spot on a chromatogram