4.1.2.2 Price, income and elasticity of demand
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
How are changes in TE influenced by PED?
If PED is elastic i.e. >1 a rise in price will cause total expenditure to fall and vice versa
If PED is inelastic i.e. <1 a rise in price will cause total expenditure to rise and vice versa
Therefore, the total expenditure of buyers depends on the PED of the good or service.
What are the determinants of PED?
Substitutes:(number of)
More substitutes there are more PE demand is likely to be and vice versa
Percentage of Income:
greater the POI, that a price change takes more PE demand is likely to be & vice versa
Luxury/Necessity:
Luxuries have more PE
Necessities have more PIE
Time
In the short run products are likely to be more price inelastic as consumers find it difficult to change their shopping habits
In the long run products are likely to be more price elastic as consumers adjust to changing market conditions
What does the term Income elasticity of demand mean (YED)?
measure of the responsiveness of demand to a change in income
What is the formula for YED?
%🔼QD/%🔼y
What is a normal good?
When demand for a product increases when incomes increase
Normal goods will always have a positive income elasticity of demand i.e. a + sign.
What is an inferior good?
When demand for a product decreases when incomes increase we call this an inferior good.
Inferior goods will always have a negative income elasticity of demand i.e. a – sign.
Example: Incomes increase by 15%. This leads to an increase in the demand for iPads of 20%.
The income elasticity of demand is:
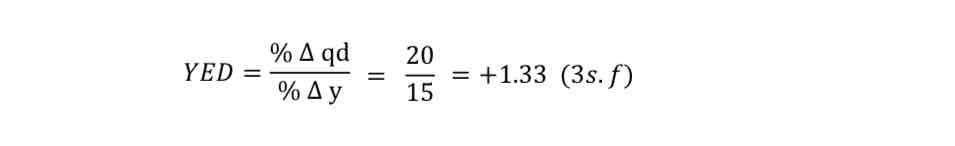
What are the 2 types of normal goods?
Necessities are product(s) and services that consumers will buy regardless of the changes in their income levels, they have a positive YED that is between 0 and 1.
Luxuries are products for which demand increases more than proportionally as income rises, they have a positive YED that is greater than 1.
What is YED determined by?
Whether the good is a necessity or a luxury
At higher standards of living increased consumer incomes see additional demand tend towards luxury goods as demand for necessities is satiated
The level of income of a consumer
Poorer consumers tend to spend their income on necessities
As they become wealthier the YED for necessities moves towards zero as consumers are satisfied with the amount of the product e.g. staple foods that they can buy
Normal goods that are necessities will have lower positive YED coefficients
As consumer incomes increase they are likely to spend some of their income on luxuries
These products e.g. cars and foreign holidays will have higher positive YED coefficients
Standards of living
Wealthier countries are likely to have consumers with higher disposable incomes
This means that they have greater spending power and are likely to use some of this greater income to buy luxury goods and services
Therefore, firms will produce superior products that meet the needs of these consumers e.g. high technology goods and complex financial services
The economic cycle
o When the economy is in recovery mode and leading into boom disposable incomes increase and consumers spend a greater proportion of this increase in income firstly on necessities and then on luxury goods
When the economy is in decline and leading into slump disposable incomes decrease and consumers spend a lesser proportion of their incomes on luxury goods, moving to necessities and then inferior good
What is cross elasticity of demand (XED)?
measure of the responsiveness of demand for one good, x to a change in price of another good, y
What is the formula for XED?

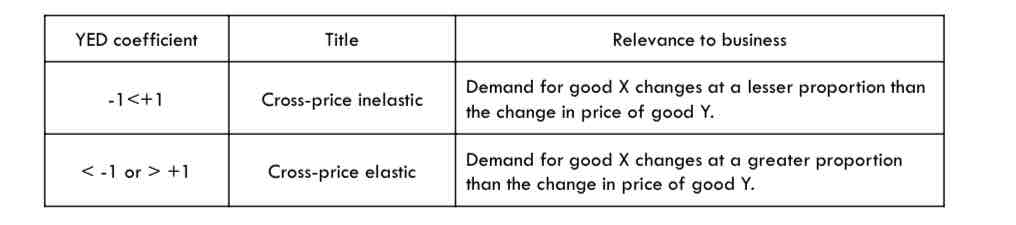
What do the YED coefficient mean?
The price of good Y (Mars Bars) increases by 10%. This leads to an increase in the demand for good X (Snickers) of 5%.
The cross-elasticity of demand is:
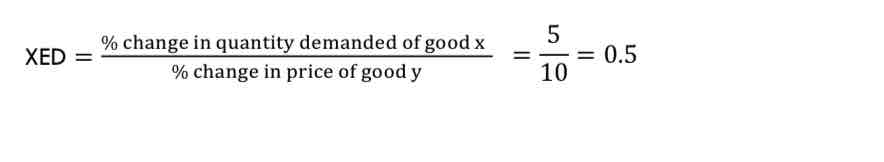
What are the determinants of XED?
Substitute
o Substitutes = positive cross-elasticity of demand
o As the price of good Y increases (positive) the demand for good X will increase (positive)
o Close substitutes have a higher XED
Complementary goods
o Complements will have a negative cross-elasticity of demand
o As the price of good Y increases (positive) the demand for good X will decrease
(negative)
o Close complements will have a higher XED as consumer demand for good X will be more sensitive to a change in price of good Y
Has no relationship
oThe change in the price of good X will have no impact on the demand for good Y
oXED will be 0
How will Firms attempt to change the cross-elasticity of their products?
Substitutes
o Firms will try to differentiate their products from the competition
o This can be done through advertising and branding of the product so that consumers are less likely to switch to competitor’s products
o A firm with plenty of close substitutes will be less able to increase its prices
Complements
o Firms will produce a range of complements to accompany their core products
o For example, Apple produce accessories, such as cases and docks, that consumers are likely to buy alongside their core products, such as the iPhone
o A firm that sells a range of complements is likely to increase total revenue