KMT and gas laws, KMT & Gas Laws
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
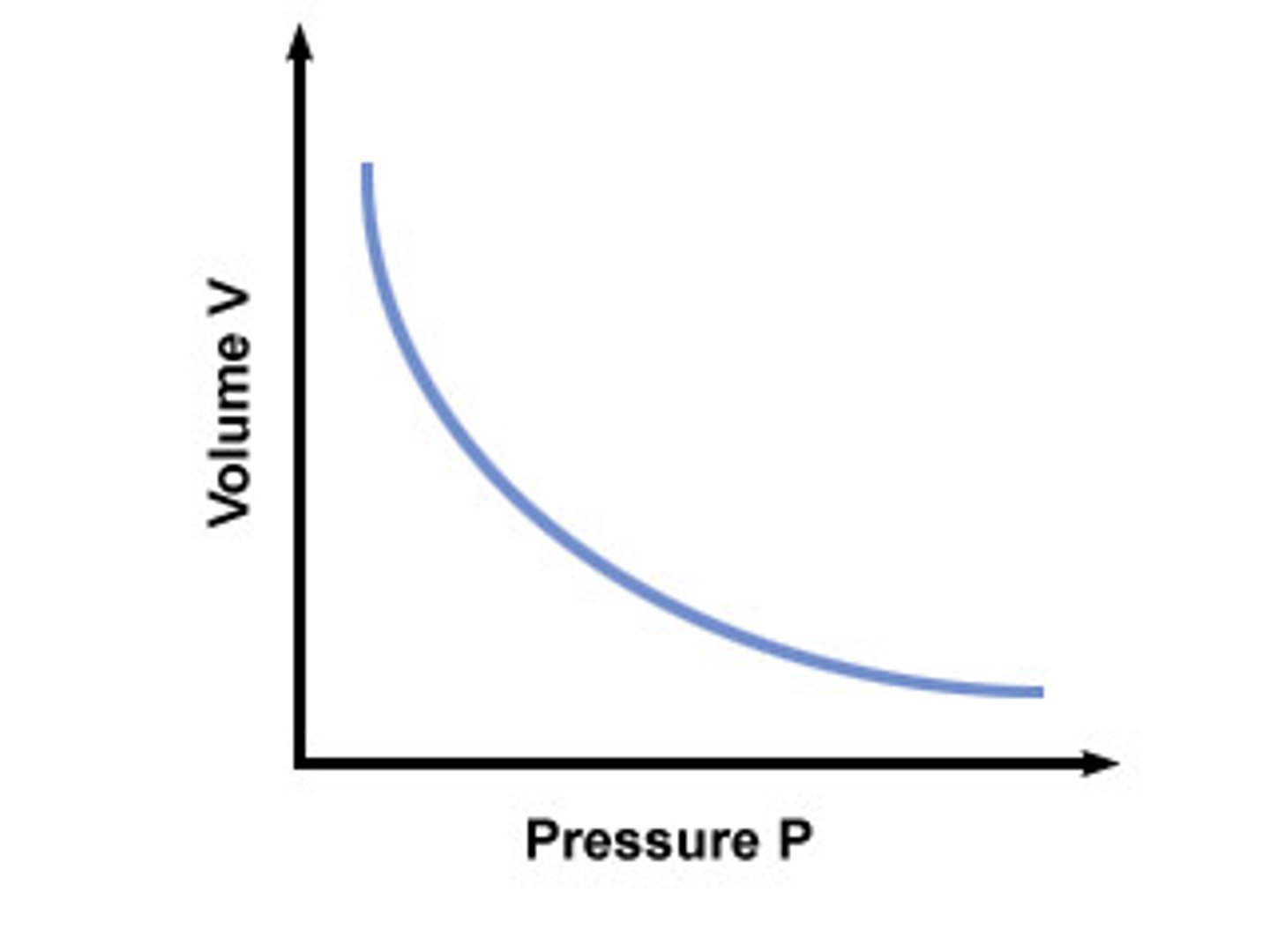
Boyle's Law
As pressure increases, volume decreases
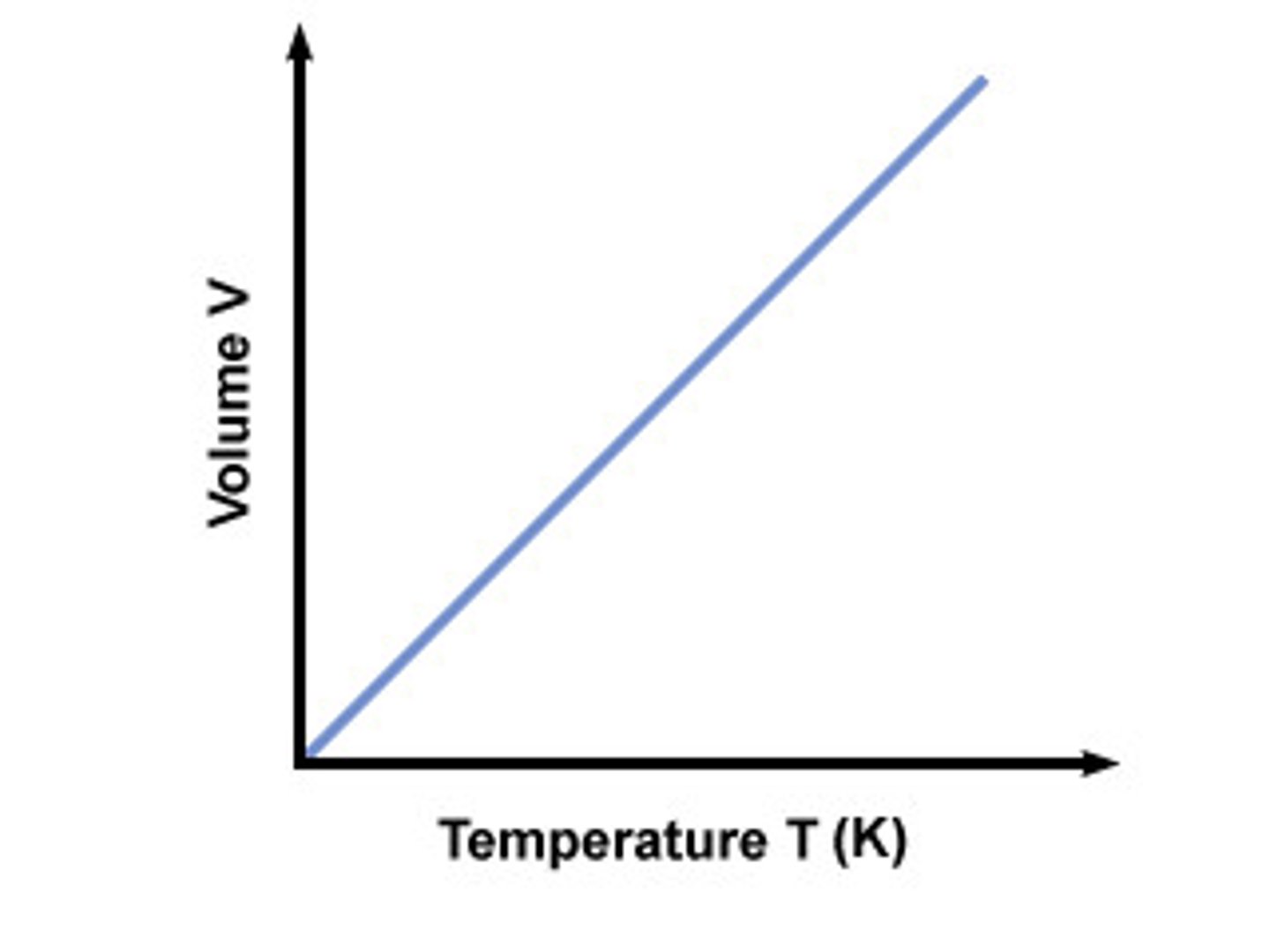
Charles' Law
As temperature increases, volume increases
p1v1=p2v2
formula for boyle's law
v1/t1=v2/t2
formula for charles' law
p1v1/t1=p2v2/t2
formula for combined gas law
PV=nRT
formula for ideal gas law
The pressure will increase because the heated gas increases the overall average kinetic energies of the molecules. When the molecules are heated up and have higher average kinetic energy, the molecules will move faster, thus hitting the rigid container more frequently, resulting in an increase of pressure. Or, you can look at it from PV=nRT, according to this formula, you can see that pressure is proportional to temperature. So if temperature goes up, pressure will go up (V, n, and R are held constant)
Enclosed gas in rigid (lidded) container. What happens when you heat it + why?
collisions with gas particles on the walls of a container
What makes pressure?
Expandability
a gas will expand to take the shape of whatever container it is in. This agrees with kinetic molecular theory because gas particles move randomly in all directions, and there are no attractive or repulsive forces between particles
Fluidity
A gas had the ability to flow. This agrees with KMT because there are no attractive or repulsive forces between gas particles which might prohibit their ability to flow and because gas particles are in constant, rapid, random motion.
Low Density
The density of a gas is about 1/1000 the density of the same substance in the liquid state. This agrees with KMT because the particles are so much farther apart in the gaseous state.
Compressibility
the volume of a given sample of gas can be greatly decreased. This agrees with KMT because of the large amount of space between gas particles, and so they can be pushed closer together.
Diffusion and Effusion
Gases spread out and mix with one another, even without being stirred. This agrees with KMT because of the constant, random motion of gas particles.
evaporation
phase change, liquid to gas

condensation
phase change, gas to liquid

sublimation
phase change, solid to gas

deposition
phase change, gas to solid
freezing
phase change, liquid to solid
melting
phase change, solid to liquid
kinetic molecular theory (motion)
matter is composed of particles that are in constant motion
kinetic molecular theory (attraction)
there are forces of attraction between particles that depend on the distances between particles
kinetic molecular theory (temperature)
the higher the temperature, the faster the particles move
ideal gas conditions
high temperature, low pressure, low molecular mass
kelvin scale
degrees C + 273
Charles' law
pressure held constant, direct relationship
Boyle's law
temperature held constant, indirect relationship
Gay-Lussac's law
volume held constant, direct relationship
law of partial pressure
all the partial pressures add up to the total pressure