Atrial and Junctional Rhythms Review
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to atrial and junctional rhythms, their characteristics, rates, causes, and treatments.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What are Atrial Rhythms characterized by?
Atrial rhythms arise from ectopic pacemakers in the atria, with varying P wave presentations and possible conduction variations through the AV node.
What is a Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)?
A PAC is an early heartbeat originating from the atria, which interrupts the regular rhythm and can occur due to stimulants or ischemia.
What is the typical heart rate range for Atrial Tachycardia?
Atrial Tachycardia typically has a rapid heart rate ranging from 150-250 beats per minute.
What defines Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia (PAT)?
PAT involves a sudden start and stop of rapid heartbeats, typically characterized by bursts of 3 or more PACs in a row.
What distinguishes Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) from Wandering Atrial Pacemaker (WAP)?
MAT has a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute, while WAP has a heart rate of less than 100.
What is Atrial Flutter?
Atrial Flutter occurs when an irritable atrial focus fires rapidly, producing sawtooth flutters waves instead of normal P waves, with rates of 250-350 for atrial beats.
What is Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)?
A-Fib is characterized by chaotic electrical activity in the atria, leading to ineffective atrial contractions and an uncountable atrial rate.
What differentiates Controlled A-Fib from Uncontrolled A-Fib?
Controlled A-Fib is defined as having a ventricular response of less than 100 bpm, while Uncontrolled A-Fib has a ventricular response greater than 100 bpm.
What identifies Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)?
SVT refers to tachycardias originating above the ventricles, typically presenting with a heart rate usually over 130 bpm.
What are Junctional Rhythms?
Junctional rhythms originate in the AV junction and can present with inverted P waves, absent P waves, or short PRI.
What is Junctional Bradycardia?
Junctional Bradycardia is a slow rhythm originating from the AV junction with a heart rate less than 40 bpm.
What is the heart rate for Accelerated Junctional Rhythm?
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm has a heart rate between 60-100 bpm.
What are Premature Junctional Complexes (PJCs)?
PJCs are premature beats originating in the AV junction, characterized by altered P wave presentation and occurring before the next sinus beat.
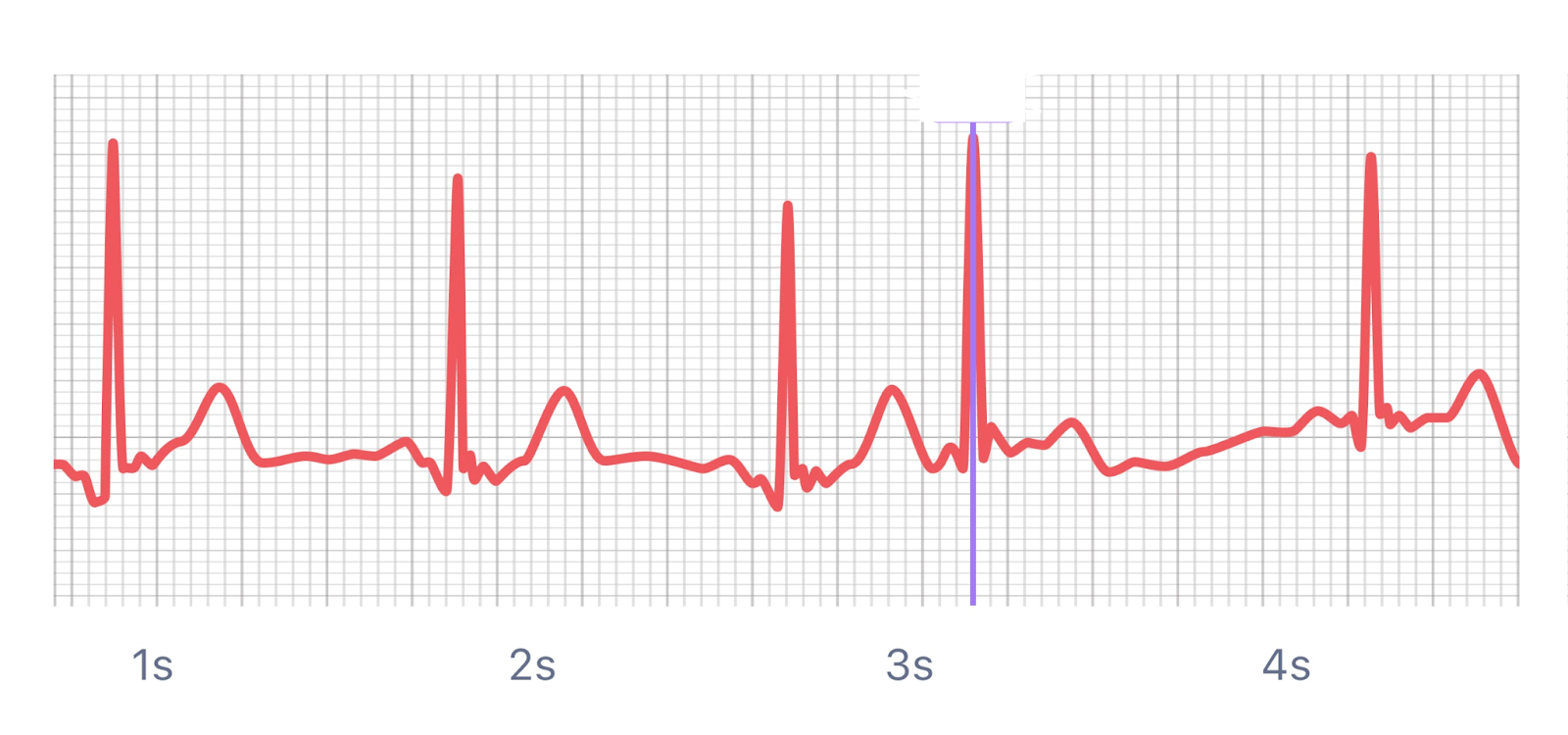
What is this rhythm?
Premature Atrial Contractions
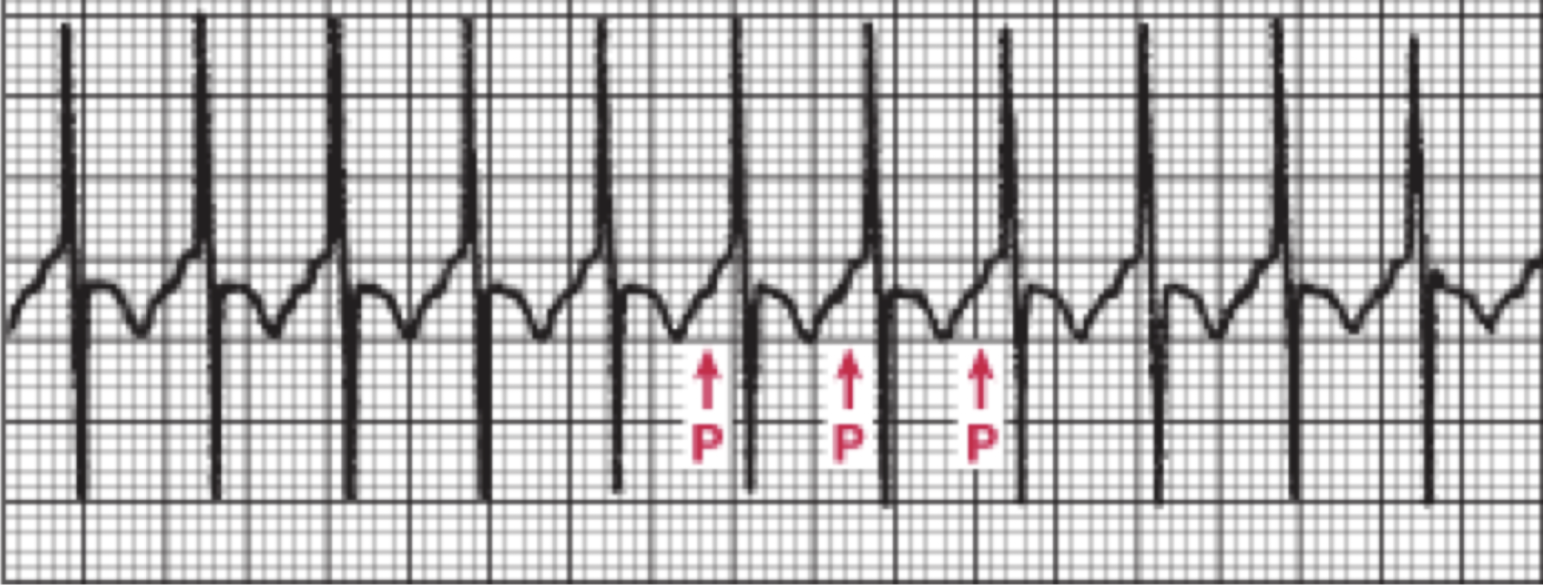
What is this rhythm?
Atrial Tachycardia
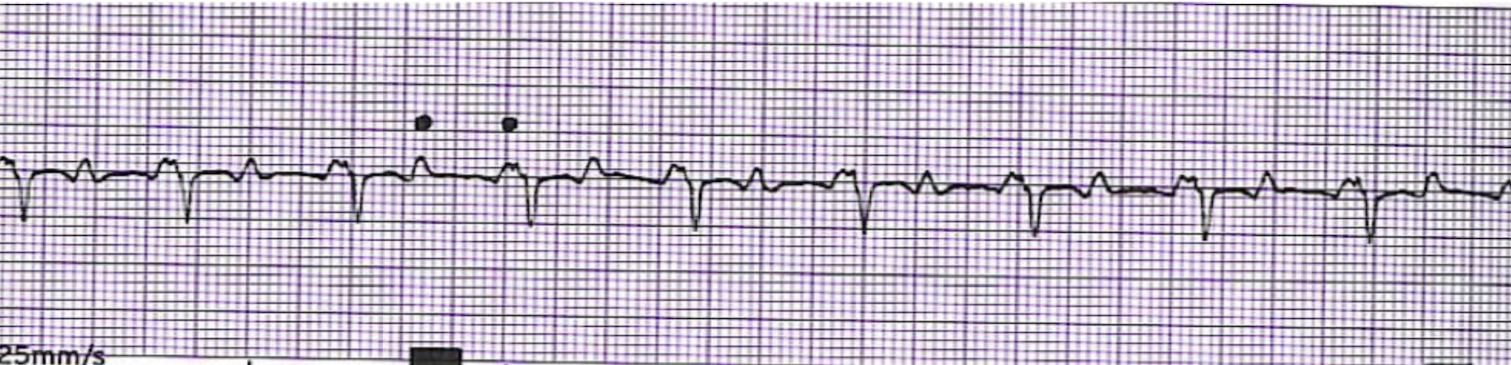
What is this rhythm?
Atrial Tachycardia with 2:1 Block
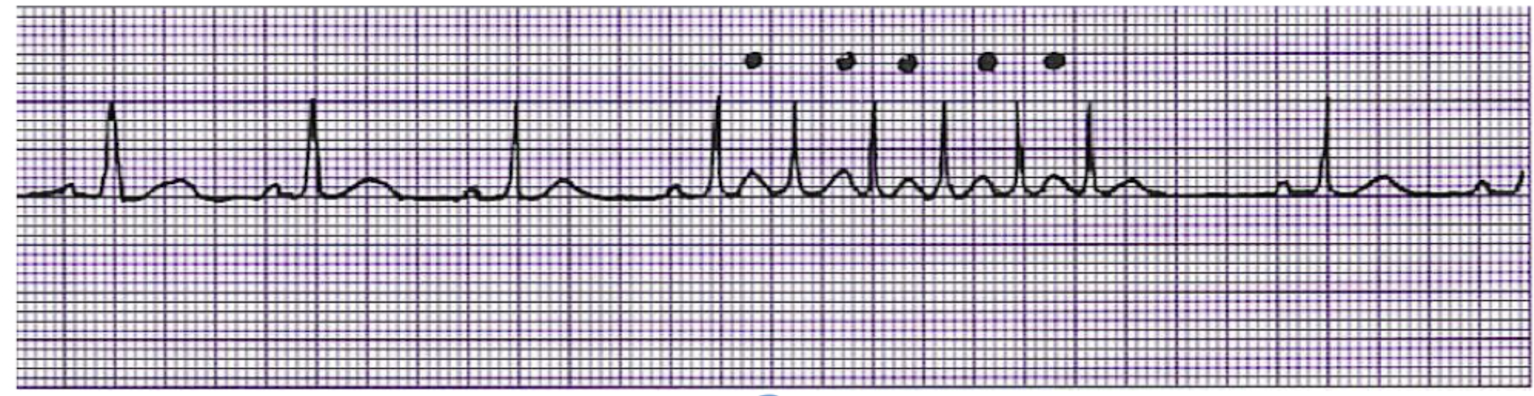
What is this rhythm?
Paroxysymal Atrial Tachycardia
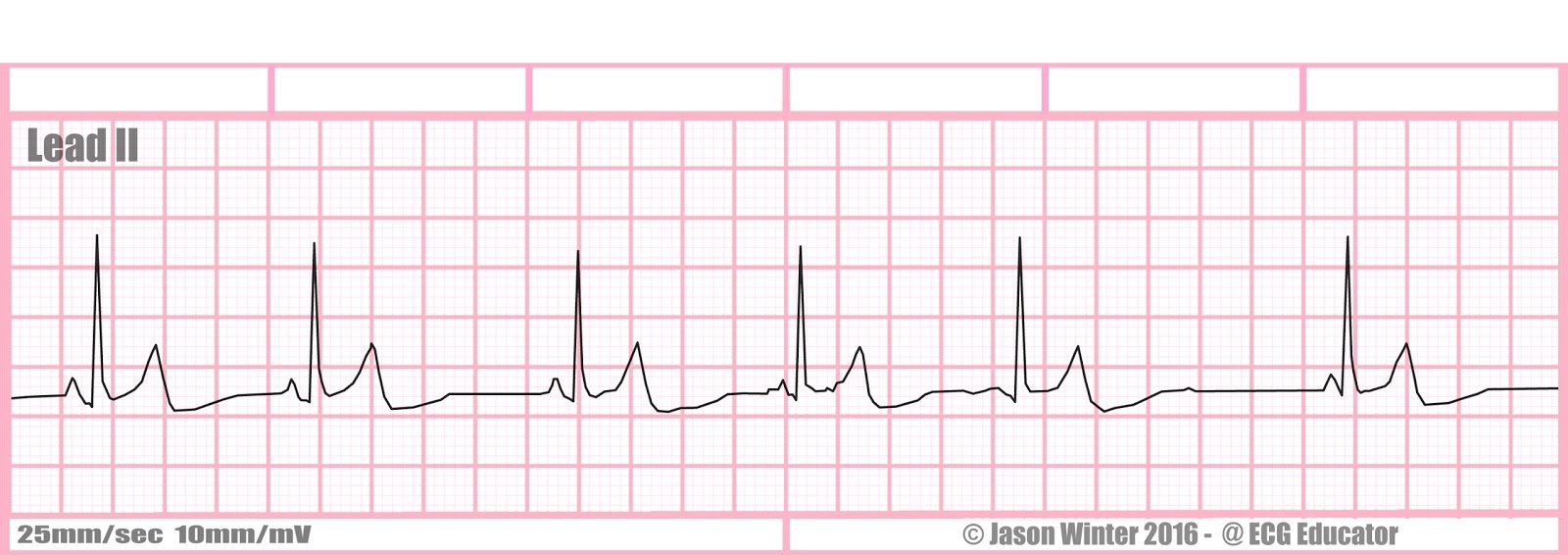
What is this rhythm?
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker

What is this rhythm?
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
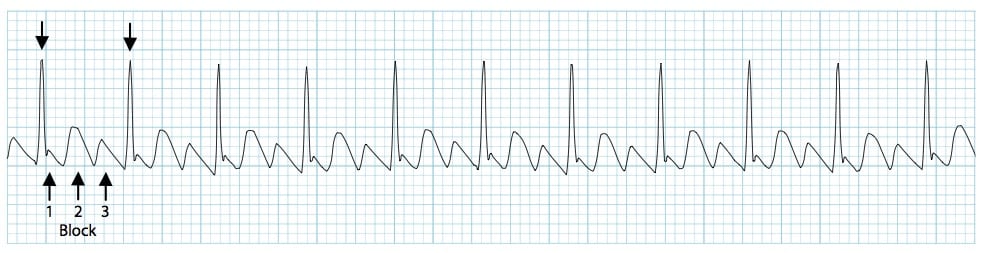
What is this rhythm?
A-Flutter
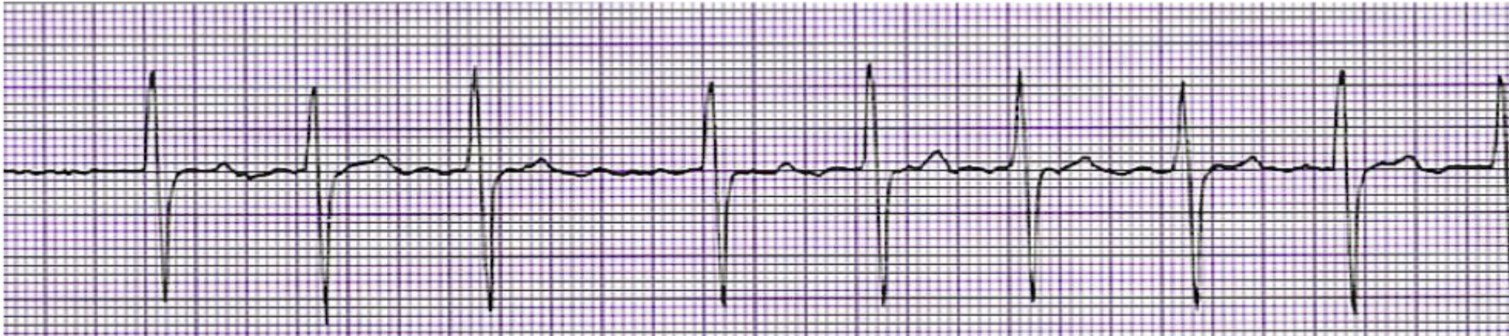
What is this rhythm?
A-Fib
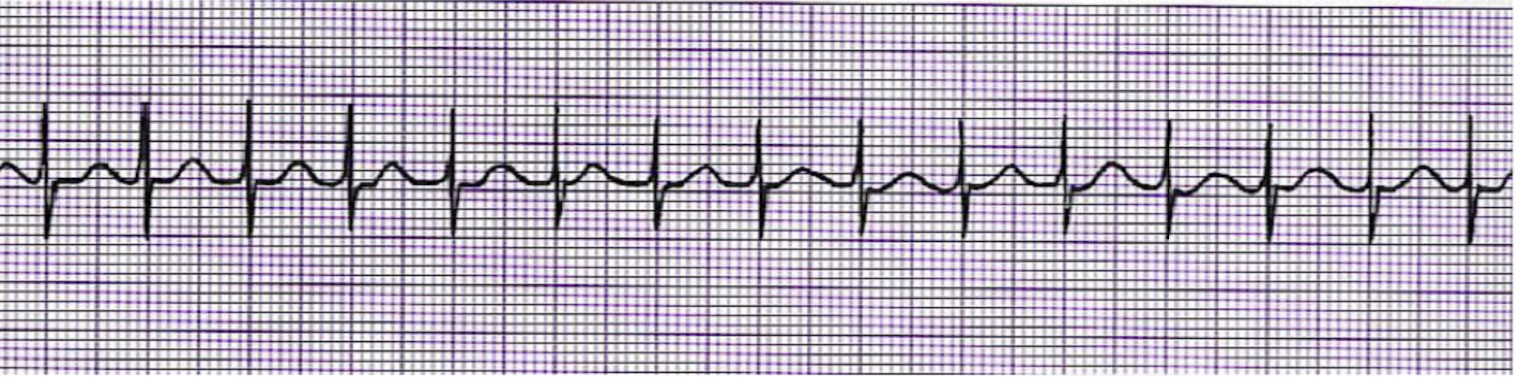
What is this rhythm?
SVT
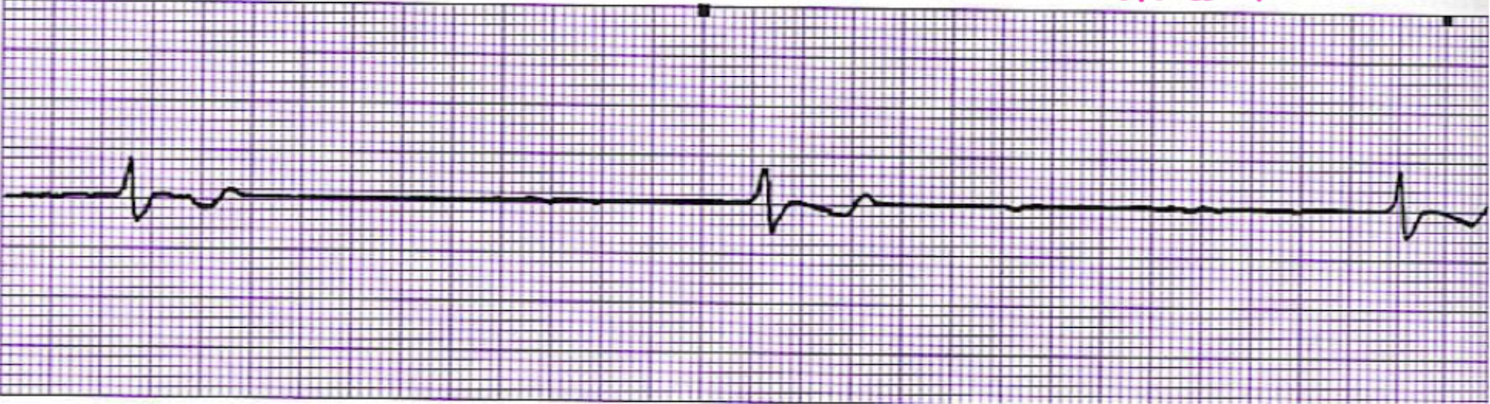
What is this rhythm?
Junctional Bradycardia
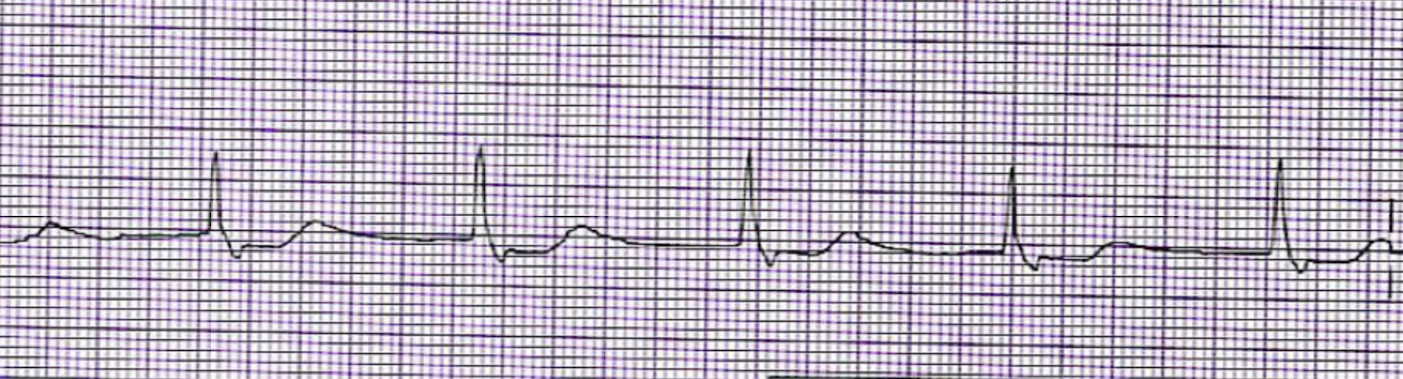
What is this rhythm?
Junctional Escape Rhythm
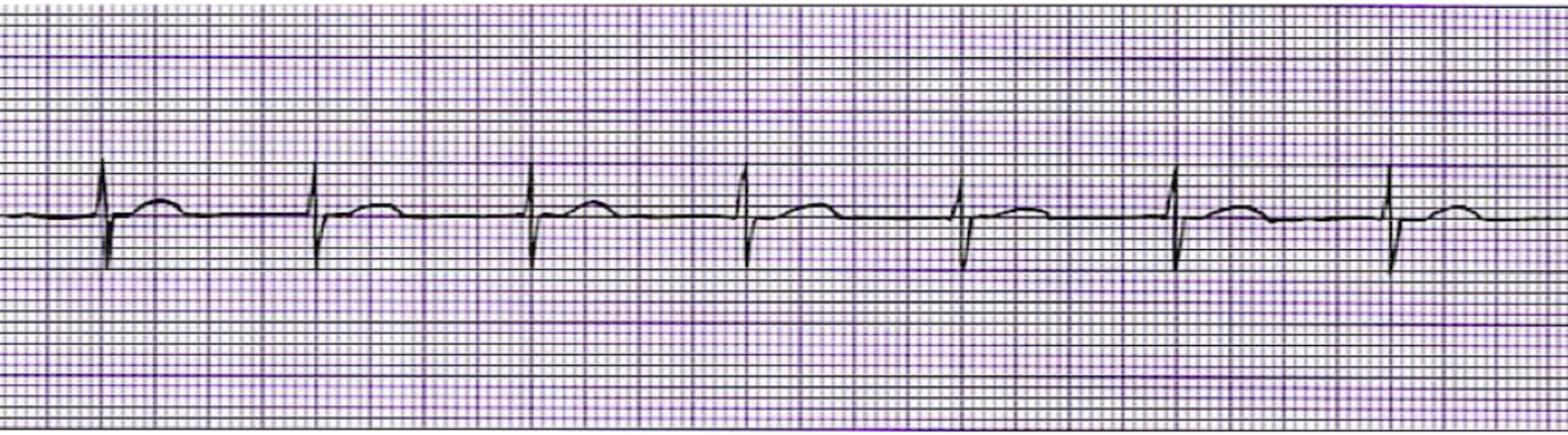
What is this rhythm?
Acclerated Junctional Rhythm
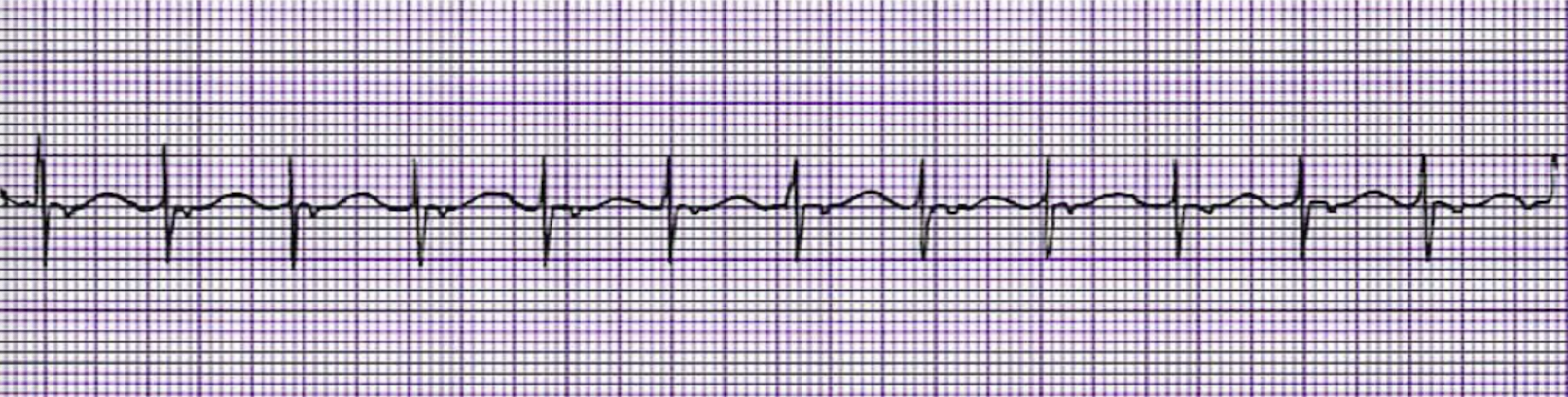
What is this rhythm?
Junctional Tachycardia
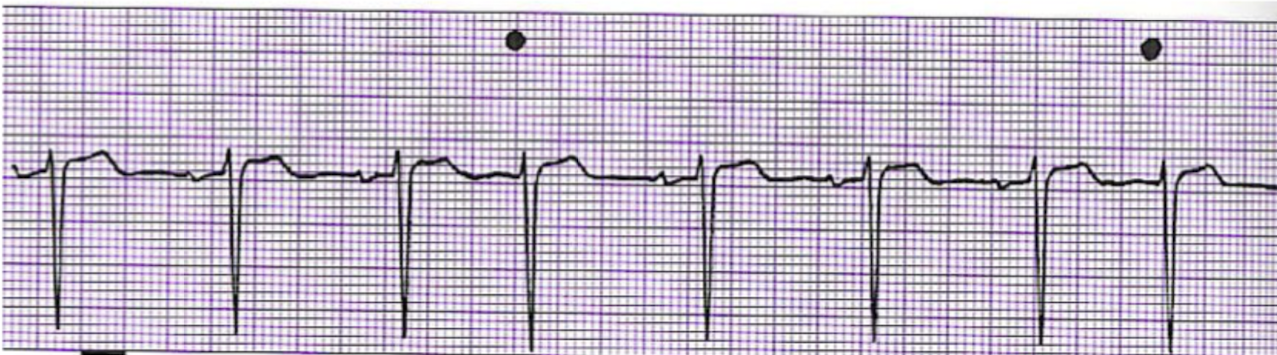
What is this rhythm?
Premature Junctional Complexes
Why is warfarin prescribed for a patient with atrial fibrillation?
To prevent clot formation in the atria, which can lead to embolic stroke.
What two arrhythmias originate in the atria and cause a fast, irregular rhythm?
Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
Which PMH factor is a risk for premature atrial contractions (PACs)?
Smoking.
Which cardiac rhythm is commonly associated with chronic lung disease?
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT).
How can you differentiate WAP from MAT on an EKG?
WAP has HR
What rhythm presents with narrow QRS and no visible P waves?
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
Which rhythm originates in the AV junction with a rate over 100 bpm?
Junctional tachycardia.
What is the normal range for Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)?
0.91–1.30.
What ABI range indicates mild peripheral arterial disease?
0.70–0.90.
What ABI range indicates moderate PAD?
0.40–0.69.
What ABI value indicates severe PAD?
Less than 0.40.
What are findings you may see with severe PVD?
Shiny skin, hair loss, dependent rubor, weak pulses.
Why should heating pads not be used to relieve PVD symptoms?
Risk of burns due to decreased sensation and poor circulation.
In which condition should the legs be elevated above the heart?
Peripheral venous disease.
What is the priority after a carotid endarterectomy?
Apply pressure and monitor for bleeding and neurological changes.
What is the priority intervention after a cholecystectomy?
Cough, turn, and deep breathe to prevent pneumonia.
How long does it take for a plaster cast to dry completely?
24–72 hours.
What is the diagnostic test of choice for appendicitis?
Abdominal ultrasound.
What signs may indicate appendicitis?
RLQ pain, fever, nausea, elevated WBCs.
What foods should be avoided in cholecystitis?
High-fat, high-cholesterol foods.
What positioning is appropriate after hip surgery?
Use abductor pillow; avoid crossing legs or bending past 90 degrees.
What are nursing considerations after an ORIF?
Prevent infection, no external rotation, no hip flexion >90°.
What is the priority action for suspected peritonitis?
Obtain peritoneal fluid for testing.
What stool appearance is seen in bile duct obstruction?
Pale or clay-colored stool.
What does a pulseless, pale, painful extremity likely indicate?
Compartment syndrome.
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
Fasciotomy.
What should a nurse say to a patient grieving a new amputation?
Would you like to talk about how you're feeling?
What organs are removed first in a brain-dead organ donor?
Heart and lungs.
What is the priority if a brain-dead donor's BP suddenly drops?
Administer IV fluid bolus to maintain perfusion.
What is a major risk after percutaneous nephrostomy?
Fluid leakage into retroperitoneal cavity.
What causes most kidney stones?
Diet high in calcium and uric acid with dehydration.
What discharge teaching is needed for a patient with kidney stones?
Drink 2–3 liters of fluids daily.
What are signs of bleeding after thrombolytic therapy?
Decreased LOC and dilated pupils (suggesting brain bleed).
What should you do if a patient becomes hypotensive during thrombolytics?
Stop the infusion and notify the provider.
What are signs of anterior MI on EKG?
ST elevation in V2–V4.
What symptoms are associated with anterior MI?
Chest pain, crackles from pulmonary congestion.
What leads indicate an anterolateral MI?
V3–V6, I, aVL.
What leads indicate inferior MI?
II, III, aVF.
After cardiac cath, the patient asks to bathe. What do you say?
No submersion or bathing within 24 hours due to site.
How do nitrates help angina?
Vasodilation reduces preload and oxygen demand.
What are interventions for peaked T waves?
EKG, nitrates, oxygen, cardiac markers.
What symptom suggests bleeding from thrombolytics?
Sudden neurological changes.
What is the best first nursing action for a suspected brain bleed?
Stop thrombolytics and assess neuro status.
What should be avoided after a cardiac cath?
Submerging the puncture site in water.
What patient statement after a cath indicates understanding?
I won’t take a bath or go swimming for a few days.
What lab must be monitored with warfarin therapy?
INR.
What is the therapeutic INR range for A-fib on warfarin?
2.0–3.0.
What education should be given for warfarin?
Avoid vitamin K-rich foods, use soft toothbrush, monitor for bleeding.
What should be done if the INR is critically high?
Hold warfarin and notify the provider.
What foods are high in vitamin K?
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and broccoli.
What vital sign change may indicate retroperitoneal bleeding?
Sudden hypotension and back pain.
What is a retroperitoneal bleed a complication of?
Cardiac catheterization.
When should the nurse notify the provider after cardiac cath?
If the patient reports severe back pain or hypotension.
How should you position the leg after cardiac cath?
Keep the leg straight and flat.
What are signs of adequate perfusion post-op?
Warm skin