Module 1.4: Surgical Instruments
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
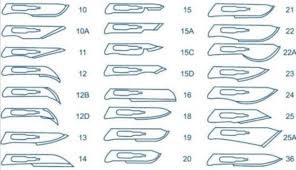
Scalpels
made of brass & the blade is made of carbon steel;
most frequently used has a reusable handle with a disposable blade;
may also be available in disposable type.
Handle # 3, 7, 9 – Blade # 10 , 11, 12, 15
Handle # 4 – Blade # 20, 21, 22, 23
Blade 10 - most used; round cutting edge
Blade 11 - known as stab knife
Blade 12 - hook with the cutting edge on the inside curvature
Blade 15 - smaller and shorter curve than #10
blade 23 - curved cutting edge that comes to more of a point than no. 20, 21, and 22 blades.
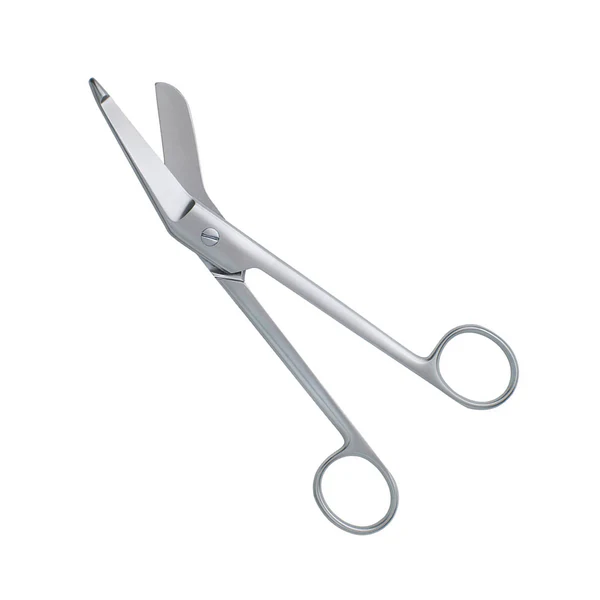
Metzenbaum scissors
used to cut delicate tissue; known as tissue or operating scissors

Straight Mayo Scissors
used to cut sutures and supplies; known as suture scissors

curved mayo scissors
used to cut heavy and tough tissues (fascia, muscles uterus, & breast); available in regular and long sizes.
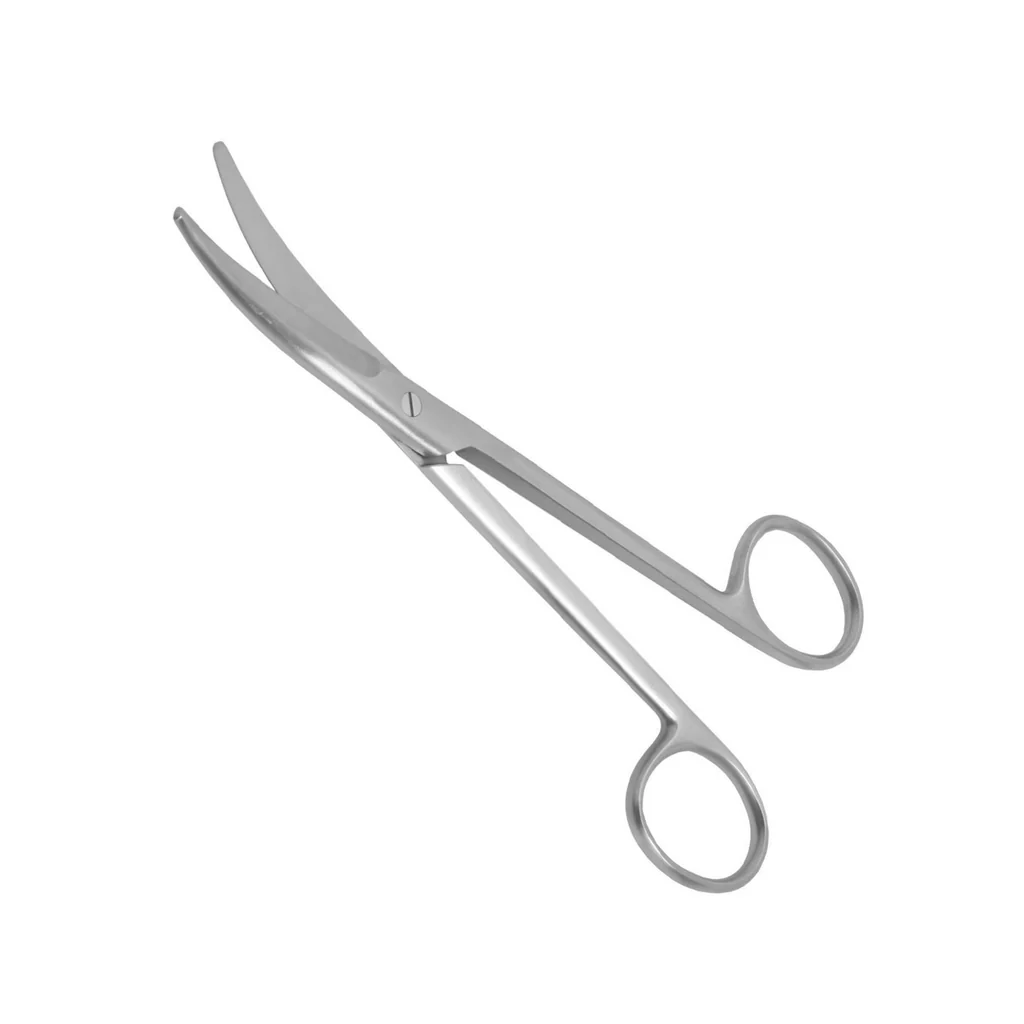

Wire scissors
have short, heavy blades ; they are used instead of suture scissors to cut stainless steel sutures ; Heavy wire cutters are used to cut bone fixation wires.

Dressing / Bandage scissors
used to cut drains and dressings and to open items such as plastic packets.
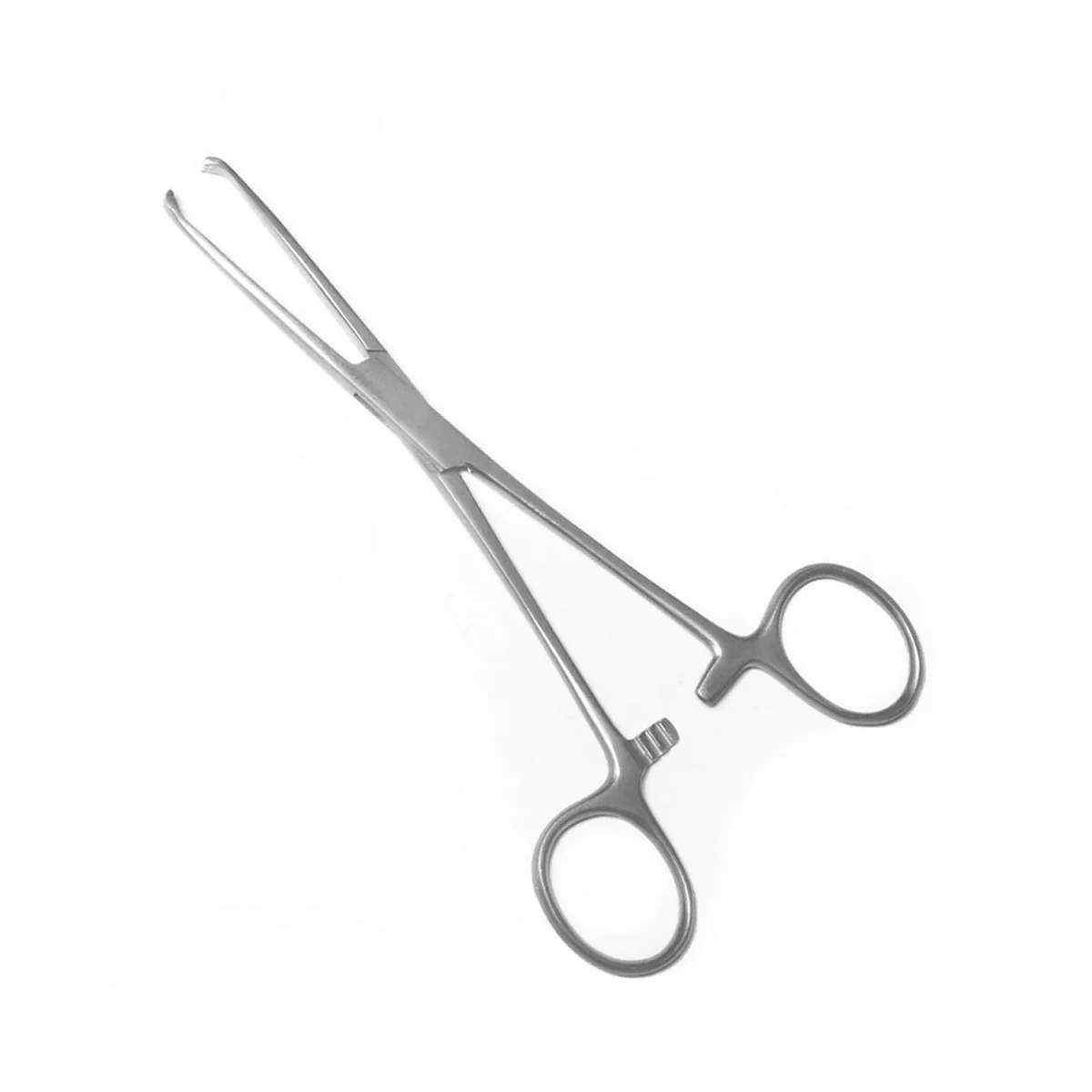
Sharp Dissector
includes biopsy forceps and punches, curettes (has a sharp edge with loop, ring or scoop on the end), snares (a loop of wire may be put around a pedicle to dissect tissue such as a tonsil, then the wire cuts the pedicle as it retracts into the instrument and the wire is replaced after use)

Tissue Forceps
used often in pairs, to pick up or hold soft tissues and vessels

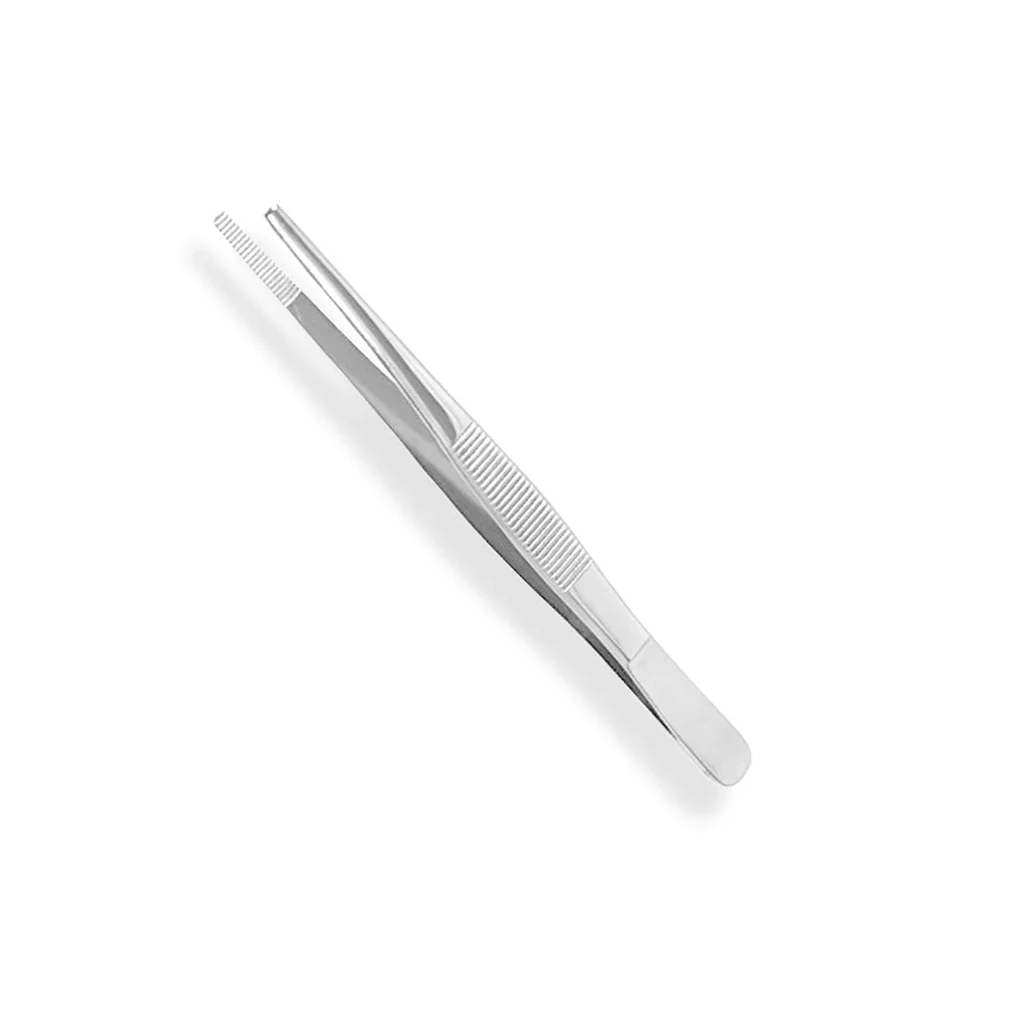
Thumb Forceps / Smooth / Non toothed Forceps
used to hold delicate tissues ; are tapered with serrations at the tip ; maybe straight or angled, short or long and delicate or heavy.

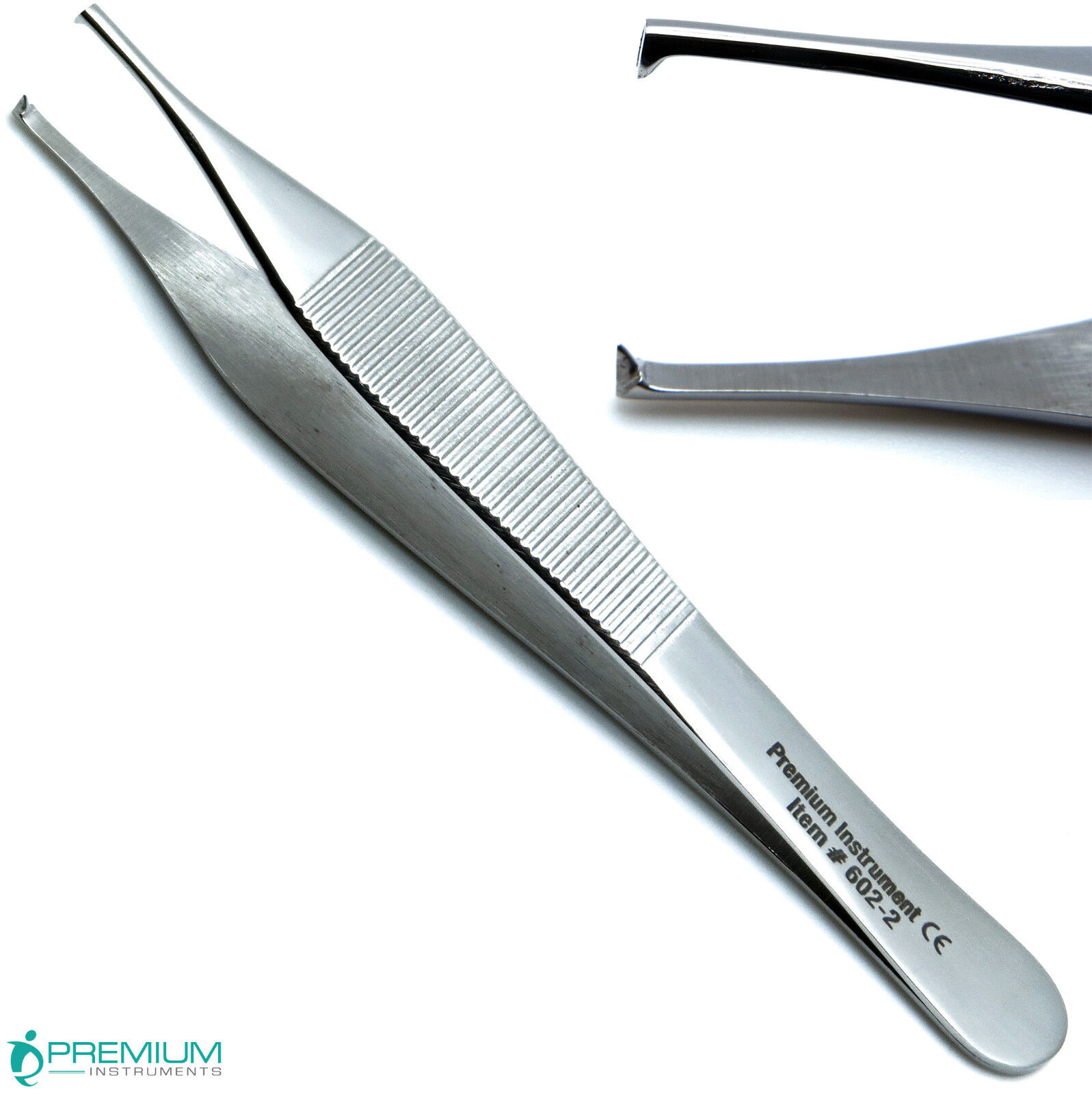
Toothed / Pick up / Rat Tooth Forceps
have a single tooth on one side that fits between two teeth on the opposing side; use to hold tough tissues.

Allis Forceps
has a scissor action. Each jaw curves slightly inward with a row of teeth at the end ; Holds tough tissue gently but securely
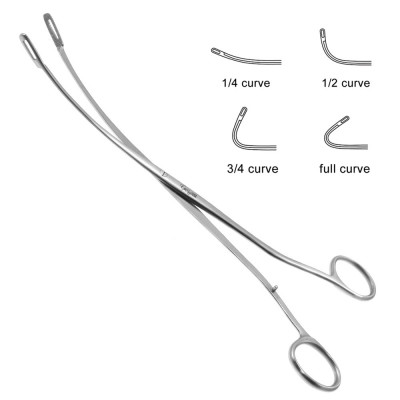
Babcock Forceps
the end of each jaw is rounded to fit around a structure or to grasp tissue without injury
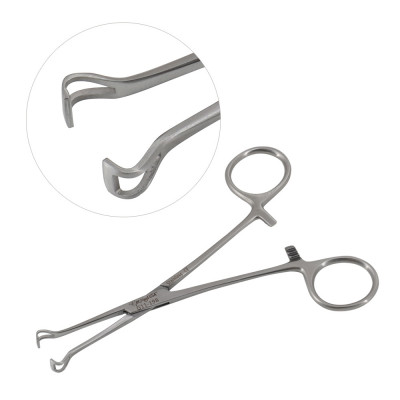

Stone Forceps
used to grasp calculi such as kidney stones or gall stones;
either curved or straight forceps ;
have blunt loops or cups at the end of the jaws.
Tenaculum
curved or angled points on the ends of the jaws penetrate tissue to grasp firmly; may have a single tooth or multiple teeth
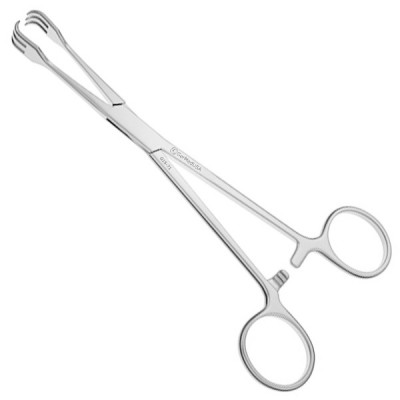

Bone Holders
includes vice-grip, pliers and other types of heavy holding forceps use to stabilize the bone.
Hemostatic Forceps
usually have two opposing serrated jaws that are stabilized by a box lock and controlled by ringed handles. When closed, the handles remain locked on ratchets;
most commonly used surgical instruments;
used primarily to clamp blood vessels;
either straight or curved slender jaws that taper to a fine point;
Crile / Stet / Tag Forceps
for shallow layers of tissues
Kelly Forceps
for deep layers of tissues or cavity
Crushing Clamps
used to crush tissues or clamp blood vessels;
fine tips are used for small vessels and structures while longer and sturdier jaws are needed for larger vessels, dense structures and thick tissues.

Non Crushing Vascular Clamps
used to occlude peripheral or major blood vessels temporarily
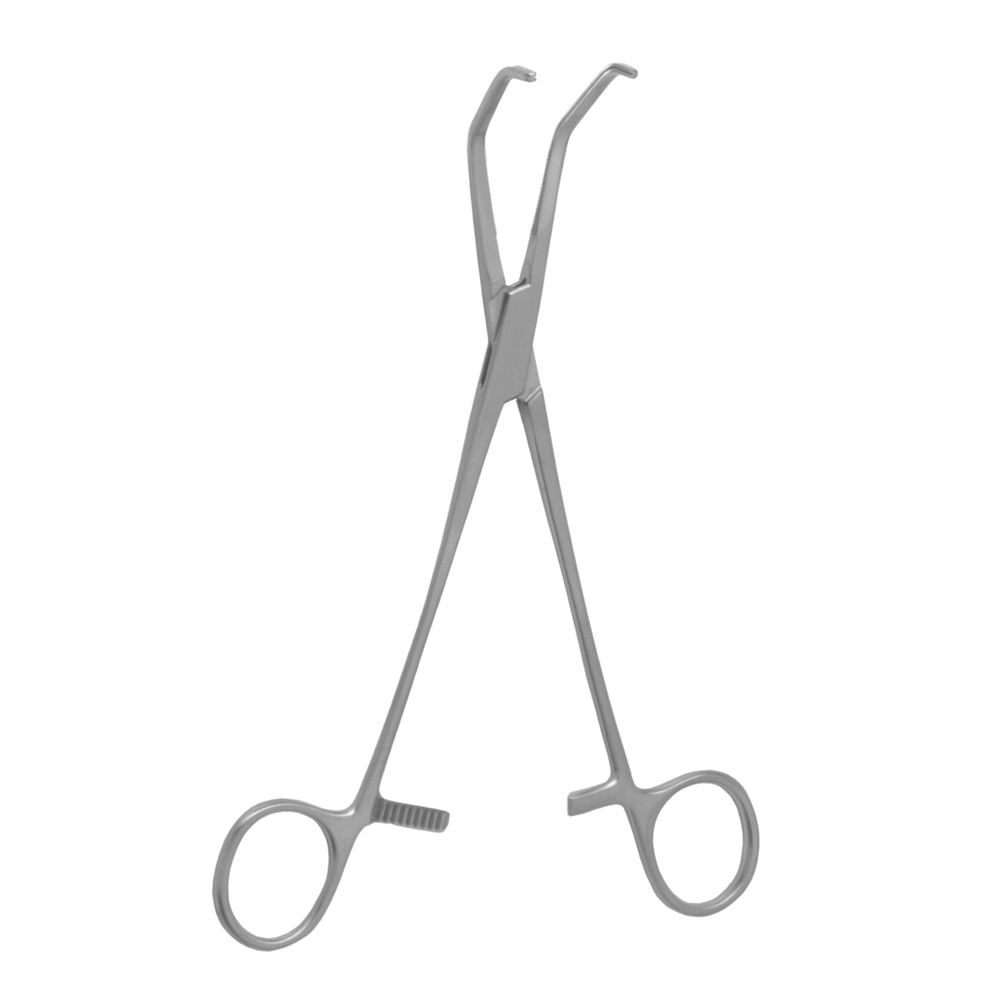

Handheld or Non Self-Retaining Retractors
usually used in pairs and held by the first or second assist
some have blades on one end, either curved or angled, dull or sharp while some have blades on both ends.

Self - Retaining Retractors
may have shallow or deep blades, some have ratchets or spring locks to keep the device open, while others have wing to secure the blades;
some holding devices have two or more blades that can be inserted to spread the edges of incision and hold them
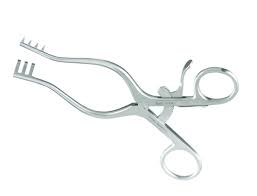
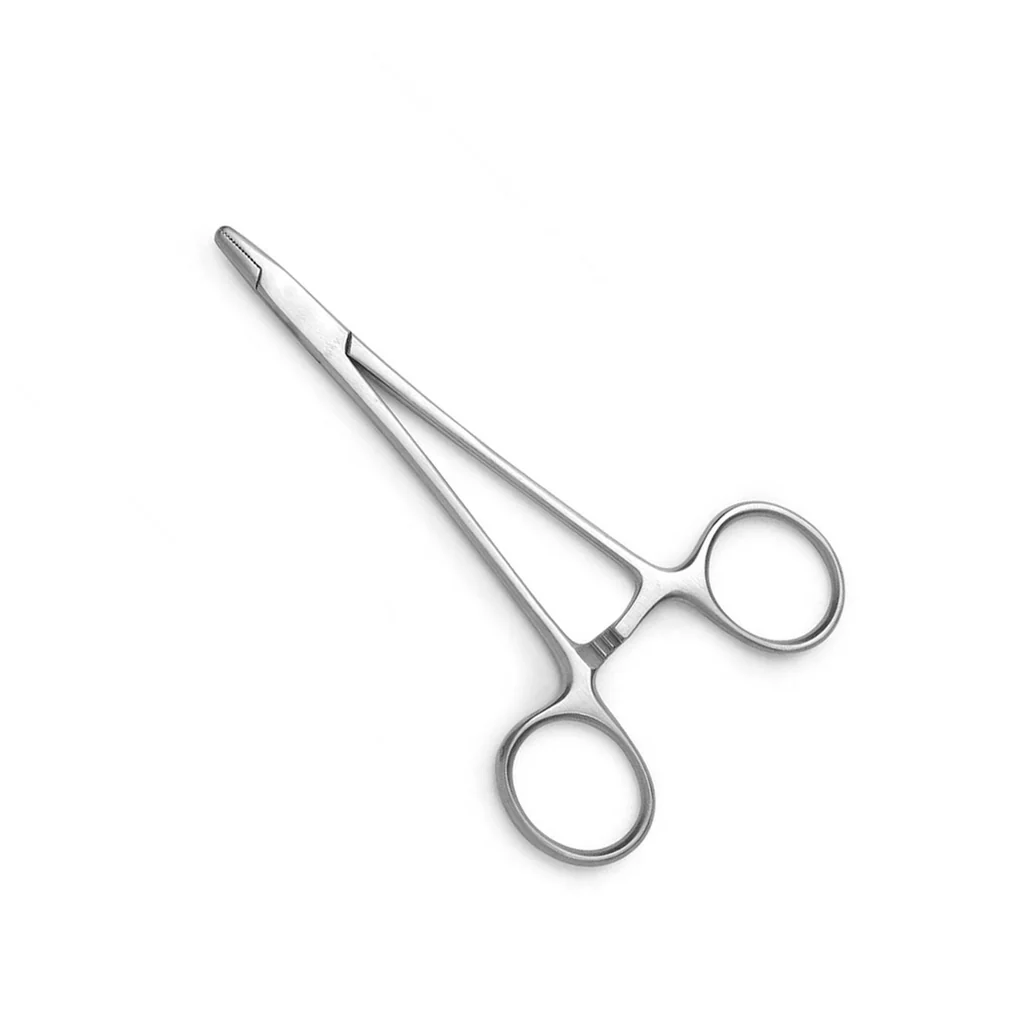
Needle holder
used to grasp and hold curved surgical needles;
resembles hemostatic forceps but the basic difference is the jaws;
has a short, sturdy jaws for grasping a needle without damaging it or the suture material.
the size of the needle holder should match the size of the needle;
either long or short, with serrations on jaws, some are non;

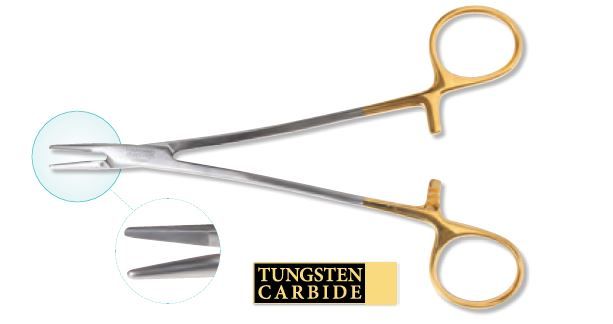
TUNGSTEN CARBIDE JAWS
jaws with an insert of solid tungsten carbide with diamond cut precision teeth designed to eliminate twisting and turning of the needle in the needle holder; can be identified by the gold plating on the handles.
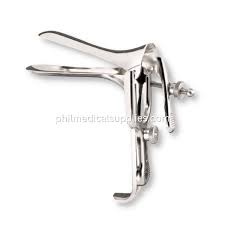
Speculum
has a hinged, blunt blades that enlarges and holds a canal open such as the vagina, or a cavity, such as the nose
Endoscopes
made of a round or oval sheath that is inserted into a body orifice or through a small skin incision;
used for viewing in a specific anatomical locations.

Suction
is the application of pressure (less than atmospheric pressure) to withdraw blood or fluids, usually for visibility at the surgical site;
made of style tip and sterile tubing;
style of the suction tip depends on where it is to be used and the surgeon’s preference.

Poole Abdominal Tip
is a straight hollow tube with a perforated outer filter shield that prevents the adjacent tissues from being pulled into the suction apparatus.
used during abdominal laparotomy or within any cavity in which copious amount of fluid or pus are encountered.

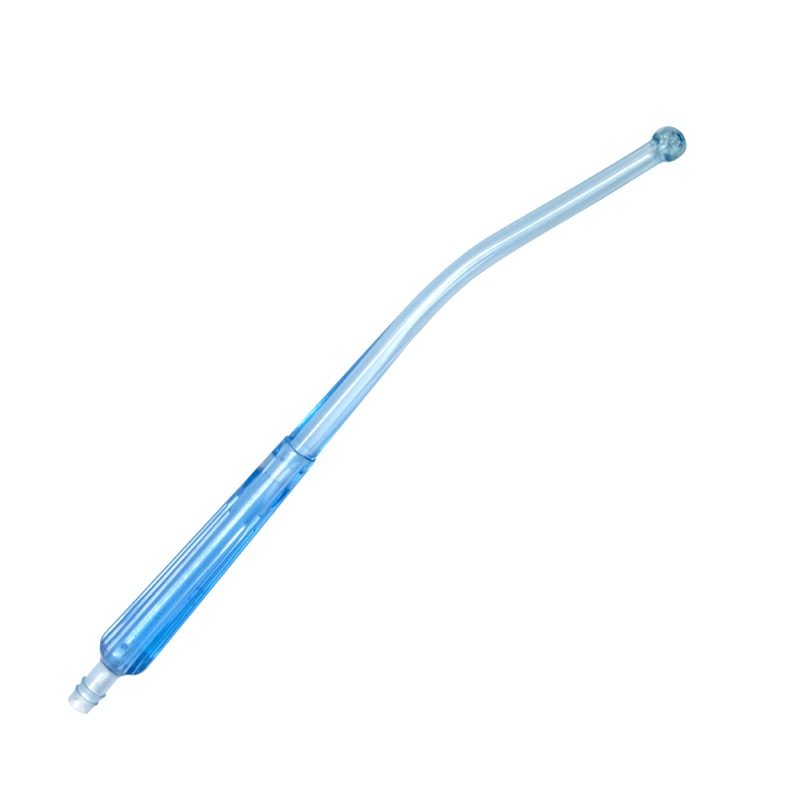
Frazier Tip
is a right angle tube with a small diameter; used when little or no fluid except capillary bleeding and irrigating fluid is encountered, such as brain, spinal, plastic and ortho procedures

Yankauer Tip
is a hollow tube that has an angle for use in the mouth or throat.

Aspiration
done manually to obtain a specimen like blood, body fluid, or tissue for laboratory examination or to obtain bone marrow for transplantation which is frequently done with a syringe and needle.
Trocar
has a sharp cutting edge at the end of a hollow tube intended to cut through tissues for access to fluid or a body cavity.
has a fitted blunt end cannula inside to keep fluid or gas from escaping until the cannula is removed.
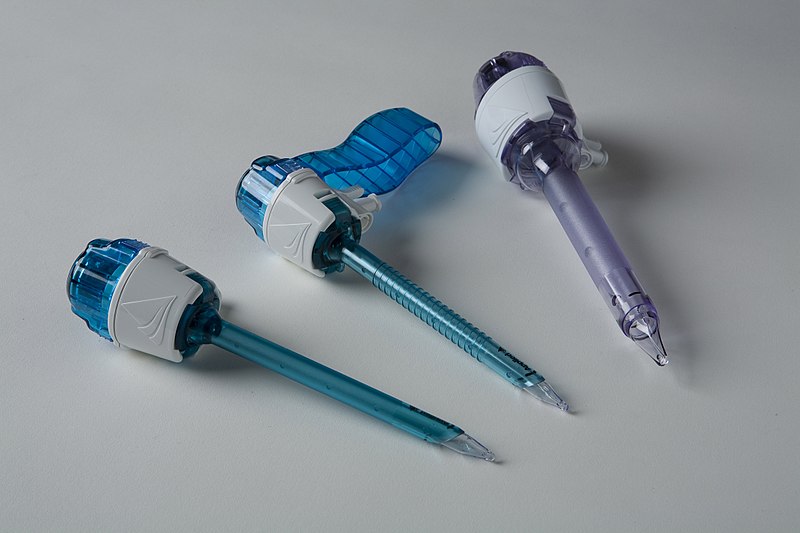
Cannula
has a blunt end and perforations around the tip to aspirate fluid without cutting into tissues; also used to open blocked vessels or ducts for drainage or to shunt blood flow from the surgical site.
Dilators
used to enlarge orifices and ducts

Probes
used to explore a structure or to locate an obstruction.
