memory and cognition unit 3 for final and ap testing
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Flashbulb Memories-
remember a scene exactly as it was-
like a picture
Episodic Memories-
remember a specific episode-
autobiographical
Semantic Memory-
information we just know. General
knowledge
Procedural Memory-
for step-by-step procedures
Explicit-
Easily Described: Flashbulb, episodic, semantic,
hippocampus
Implicit-
Not easily described: skills, conditioning,
procedural. In cerebellum.
Prospective-
what you intend to do in the future
Sensory Memory ( has echoic,eidetic and ionic)-
the imprint of information coming
in through our senses- this is held in our sensory
register very briefly
Iconic memory-
a very short snapshot- what
happens when we have visual coding
Echoic memory-
the brief imprint of sounds
Eidetic Imagery-
photographic memory
Long-Term Memory-
unlimited capacity,
reconstructive
Schemas
- a mold of past experience that helps
us interpret and organize information- can
contribute to false memories, though
Short-Term Memory has been replaced with
Working Memory
Pulls from both sensory and long-term
Phonologial Loop
(Verbal/auditory info)
-Why do you turn down the music when looking for an
address?
Visuospatial Sketchpad-
Visual info
Long-term potentiation:
probably how memory happens
Rapid stimulation strengthens synaptic connections- less stimulation needed to release neurotransmitter, more efficient
When drugs block LTP, we learn less
When drugs increase LTP, rats learn maze faster
Structural:
How does it look? Bold words? Capitals?
Phonemic:
How does it sound?
Semantic:
What does it mean?
serial position effect Primacy Effect-
We remember the first things we hear
serieal position effect Recency Effect-
We remember the most recent things we hear
Encoding- Translating information so it can be stored
which codes
Visual Code
Acoustic Code
Semantic Code
Better if we have two or more codes
Encoding:
Category Hierarchies: How your brain organizes
information. These work like files.
Mnemonic Devices-
Creating additional
associations/codes (acoustic, visual, semantic)
Method of Loci
Spacing effect:
spacing info out works better than all at once
Massed Practice:
All at once
Distributed Practice:\
Spaced out
Maintenance Rehearsal-
repeating it over and over again
until it can be stored
Elaborative Rehearsal-
relate info to something you know
autobigroaphical memory is…
easier to store
Context-Dependent Memories-
Depend on a
specific place to be accessed
State-Dependent Memories-
rely on emotional or
mental state (Mood Congruent)
Recognition-
Identifying information that has been
encountered before
Recall-
Bringing something back to mind
Relearning-
learning again what has been forgotten
Retrieval Practice
- Practice getting info out
Testing Effect:
testing yourself is helpful to learning
Decay-
fading away of memories- we think we are just
losing the connections to get there
Forgetting Curve:
Inadequate Retrieval:
Tip of the Tongue Phen.
Proactive-
Old info disrupts new
Source Amnesia-
remembering the correct event, but the
wrong context.(believing a dream or story is true)
Retroactive-
New info disrupts old
Infantile Amnesia-
no episodic memories before age of three
Probably because the hippocampus is not mature until two or so
Maybe due to encoding failure
Dementia-
Brain deterioration, Typically age-related but
not inevitable
“Where are my keys?”- normal
“What are keys used for?”- abnormal
Alzheimer’s Disease:
Most feared of all brain ailments.
Strikes 3% of the world’s population by age 75
Causes– deterioration of neurons that produce Ach.
Hereditary links– gene defect on the 19th and 21st
chromosome.
amnesia Organic
accident, disease- damage to hippocampus or
area of brain where the memory is stored
amnesia Inorganic
- traumatic experience, accident
Repression-
the mind pushes info away as a defense
mechanism (Motivated Forgetting, inorganic amnesia)
Retrograde Amnesia-
Forgetting the past- can be
localized or more general
Anterograde Amnesia-
Inability to make new
memories (hippocampus)
Dissociative Amnesia-
Psychological trauma results in
a specific, localized amnesia- repressed memories
Korsakoff’s Syndrome-
Amnesia related to long term
alcohol abuse. Thought to be caused by vitamin
deficiency. Can be R or A.
HM- Seizure surgery
caused severe anterograde
amnesia- could still learn new skills, not episodic
memories
Constructive Memory-Retrieval-
Pulling from files
Memory Consolidation-
storage-moving info into an organized long-term database
RE-consolidation- every time we review, we may smooth out old details (leveling) or incorporate new ones
Misinformation effect-
incorporating misleading information into recall of an event. (car crash)
Imagination Inflation-
we remember what we only imagined
(related to availability heuristic?)
Symbol-
an object or act that stands for something else
Examples of symbols- words, math signs, mental images
Concept-
a mental group. Animals, fruits, values,
Some are based on rules, while others are based on prototypes
Prototype-
The most basic example within a concept
Think of a shoe. What does it look like? Is it more like…
Whatever you pictured is YOUR prototype of the concept
‘shoe’
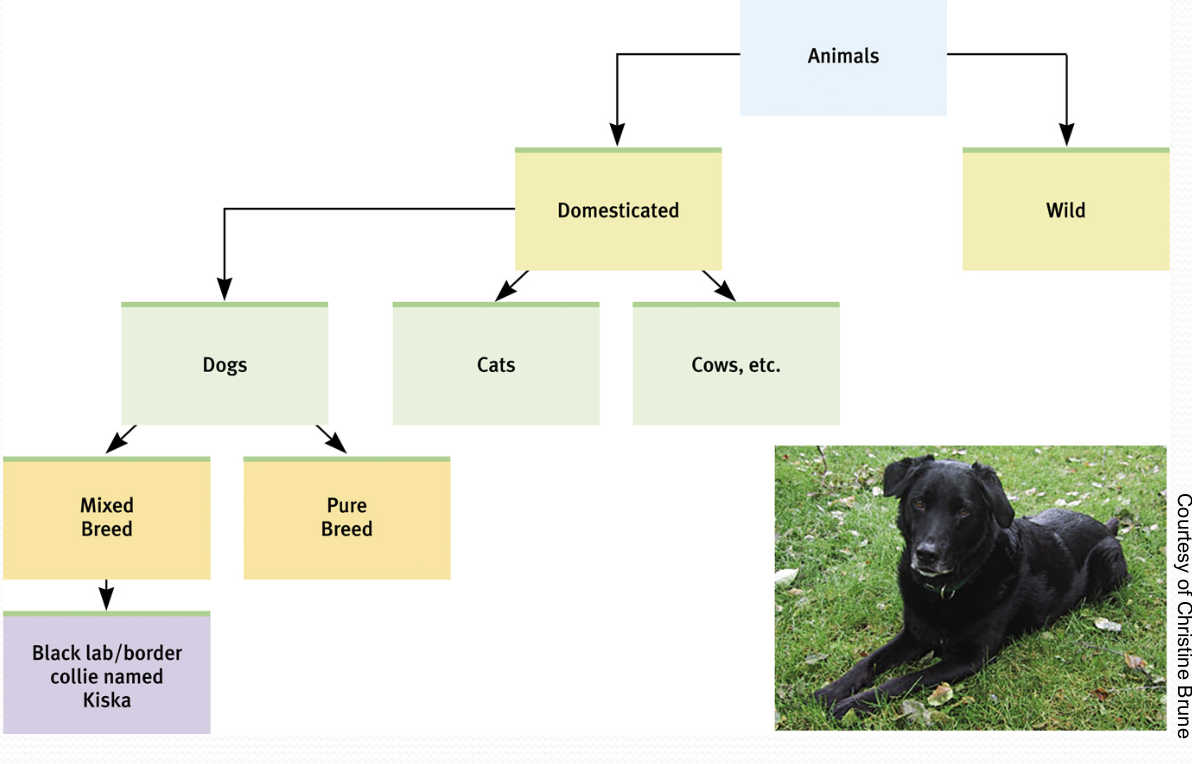
Category Hierarchies
We organize concepts into category hierarchies.
While categories are ways to organize
what we know,
…schemas are ways to
organize and interpret our experiences
Assimilating:
Fit the new experience into the old schema
Accommodate:
Change the old schema to fit the new
experience
Convergent Thinking-
one best solution, limited to the
available facts and established norms
Divergent Thinking-
Using new and different leads to
solve a problem
Metacognition:
Thinking about your thinking
Executive Function:
allow individuals to manage and control their thoughts, actions, and emotions effectively, essentially acting as the "brain's manager" to achieve goals
Algorithm-
a procedure that, when correctly used, all0ws you to solve a problem
Heuristic-
general rule that usually will help you find the
answer- a shortcut
Availability Heuristic-
Choosing based on how easily you
can think of examples(how many teenagers play sports?)
Ask yourself- How easily can I think of this?
Representativeness Heuristic-
Use a rule from what you
expect(coin flips, gender of babies) Does this match my
prototype of what seems normal?
Fixation:
Inability to see a fresh perspective:
Functional fixedness-
objects are seen only in terms
of their primary use
Mental Set:
Solving problems the same way again
and again.
Gambler’s Fallacy-
thinking past events influence random
future ones
Sunk-Cost Fallacy-
sticking with a bad plan because you
already lost too much on the bad plan
Overconfidence-
we believe our choices are right,
even if they aren’t
Belief Perseverance-
We cling to beliefs even after
they are discredited
Confirmation Bias-
we look for or overvalue evidence
that proves our beliefs
Framing Effect-
The wording affects our decision
making
Priming-
Activating certain connections to
increase likelihood of an answer
People are more likely to think of salt when they see the word pepper if they were previously exposed to the phrase salt and pepper.