WJEC AS Chemistry Unit 1.3 - Chemical Calculations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Relative atomic mass
The average mass of one atom of the element relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of Carbon-12
Relative isotopic mass
The mass of an atom of an isotope relative to one-twelfth the mass of an atom of Carbon-12
Relative formula mass
The sum of the relative atomic masses of all atoms present in its formula
Relative atomic mass equation
Sum of; mass number of isotope x % abundance
Uses of a mass spectrometer
Determining the relative atomic mass of each different isotope of the element
Determining the relative abundance of each isotope of the element
VIADD
Vaporisation
Ionisation
Acceleration
Deflection
Detection
Vaporisation in mass spectrometry
the sample of heated, vaporising into a gaseous state before it is injected into the mass spectrometer
Heater retains the sample as a vapour
Ionisation in mass spectrometry

Acceleration in mass spectrometry
An electric field accelerates the positive ions to high speed
Deflection in mass spectrometry

Detection in mass spectrometry

Molecular ions
positive ions formed in the mass spectrometer from the whole molecule
When a vaporised compound passes through a mass spectrometer, an electron is knocked off a molecule to form a positive ion
Mass gives the relative formula mass of the compound
Energetically unstable and some will break up into fragments
Fragmentation
Splitting of molecules, in a mass spectrometer, into smaller parts
When the element is passed into the ionisation chamber, an electron is knocked off the molecule to give a molecular ion. These ions will be unstable, and some will break apart into fragments
2 fragment ions at different masses = exist as isotopes
Ionisation mass spec equation
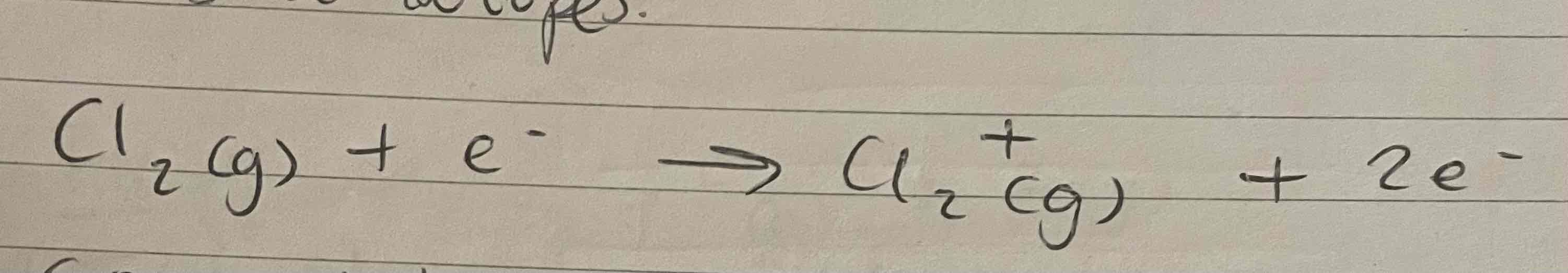
Fragmentation equation mass spec

Empirical formula
The simplest formulae showing the simplest whole number ratio of the number of atoms of each element present
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. Simple multiple of the empirical formula. Usually the relative formula mass is needed to determine molecular formula
Determining empirical formulae

Determining molecular formulae
Determine mass of empirical formula
Determine number of the units of the compound by dividing the relative molecular mass by the calculated mass
Multiply empirical formulae by the number of units in a molecule
Moles of a gas equation
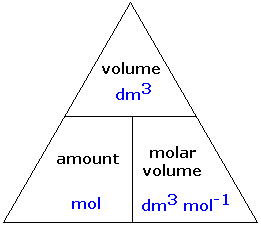
Ideal gas equation
pV=nRT
p in Pa
V in metres cubed
T in K
Atom economy
Mass of required product/total mass of reactants x100
Percentage yield
Mass (or moles) of product obtained/maximum theoretical yield (or moles) x100
Percentage error
Error/reading x100
Error; one half of the smallest division of the apparatus scale
Two measurements —> double error
Values with approx 1% error = 3sf
Values with approx 10% error = 2sf
Relationship between mass, moles and relative atomic mass
n= m/Mr
m=n x Mr
Mr=m/n