MCB Practical
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Turbidity
The haziness or cloudiness of a liquid. The more turbid the sample is, the more bacteria is present
Lag Phase
Cells are adjusting to new conditions and synthesizing metabolic enzymes
Log Phase
Period of rapid division and exponential growth
Stationary Phase
Cell division slows due to limited nutrients and/or build up of waste. New cell growth is matched by an equal amount of cell death.
Death Phase
cells are dying due to limited nutrient and/or buildup of waste products
Generation Time
The amounf of time it takes for one cell to divide into two
Solid Media (Agar plates)
used to isolate bacteria
Liquid (broth) Culutre media
used to grow cells to high densities
T-Streak Plate Method
The quickest and most economical method of bacterial isolation
Simple Stain
Staining procedres which only use one stain
Direct Stain
A simple stain that colors the bacteria
Negative Stain
A simple stain which stains the background but leaves the bacteria unstained
Liquid Media
Liquid media such as nutrient broths are used to grow large numbers of orgnaisms and are used for various experiments and diagnostic tests
Media
Microorganisms are commonly grown on a variety of different food scources called media
Solid Media
Used to examine colony morphology of organisms and to help in isolating organisms. Most common solidifying agent added to media is agar.
Complex
Non-synthetic or undefined; their exact chemical composition is not known
Synthetic
Defined media; made up of a strict list of inorganic compounds and carbon sources
General Purpose Media
Used to grow up dense cultures of bacteria, support a wide range of organisms. Some examples are nutrient borht, nutrient agar, and tryptic soy broth.
Selective Media
they select for a certain type of microbe by supplying optimal conditions for its growth, while selecting against some potential competitors form the same habitat.
Differential Media
They allow certain bacteria to be differentiated from other, typically by a change of color, production of a cone clearing, etc.
What was the BPB Broth used to select for?
Enterococcus faecalis
MacConkey Agar
Example of differential media. Organisms that femrment lactose produce pink colonies and ones that don’t ferment lactose produce non-pink colonies.
Fermentation
Inneficient process involving anaerobic oxidation of substrates (sugars)
Products of fermentation
Always acid and sometimes gas
What does motility allow bacteria to do?
To colonize new environments, find nutrients, and escape harmful compounds
What is the most common organelle of bacterial motility?
Flagellum
Flagellum
One or more long protein filaments which rotate, causing cell motion.
Motility
The movement of bacteria under their own power, it is not random movement.
BPB Broth Results
Purple color : negative (no growth of bacteria)
Yellow color: positive (growth of bacteria)
Citrate Agar Test Results
Green: negative (no growth)
Blue: positive (growth, alkaline)
Yellow: positive (growth, acidic)
Exoenzyme
Enzymes that are secreted by the cell into their environment
Hydrolysis
Break down
Amylase
catalyzes starch hydrolysis
Casease
a collection of enzymes that hydrolyze milk protein, casein, into peptides and ultimately amino acids
Gelatinase
An enzyme that hydrolyzes gelatin
Catalase
An enzyme which protects cells from hydrogen peroxide
Oxidase
An enzyme which indicated the presence of cytochrome c, a component of some electron transport systems
Starch Plates Results
If there is a red halo around the bacteria that means that it is an amylase positive bacteria
If there is no red halo around the bacteria that means that is amylase negative
Casein Plates Results
If the casein has be hydrolyzed then there will be a clearing around the growth, this is because the caseinase enzyme was present
Gelatin Tubes Result
Liquid media: positive, gelatinase is present
Solid Media: Negatie, gelatinase is not present
Catalase Test Results
If there is immediate bubble formation then it is catalse positive, if there is no bubble formation then it is catalase negative
Oxidase Test Results
If there is a blue color change within 30 seconds then it would be oxidase positive and cytochrome c is present. No color change means oxidase negative and no presence of cytochrome c
Fermentation Test Results
If the tube is any color other than red that means that it is positive for growth
If the tube color is yellow, salmon, or orange that means that acid was a product, if the color is red or magenta then acid is not a product
If there is a gas bubble then is it positive gas production
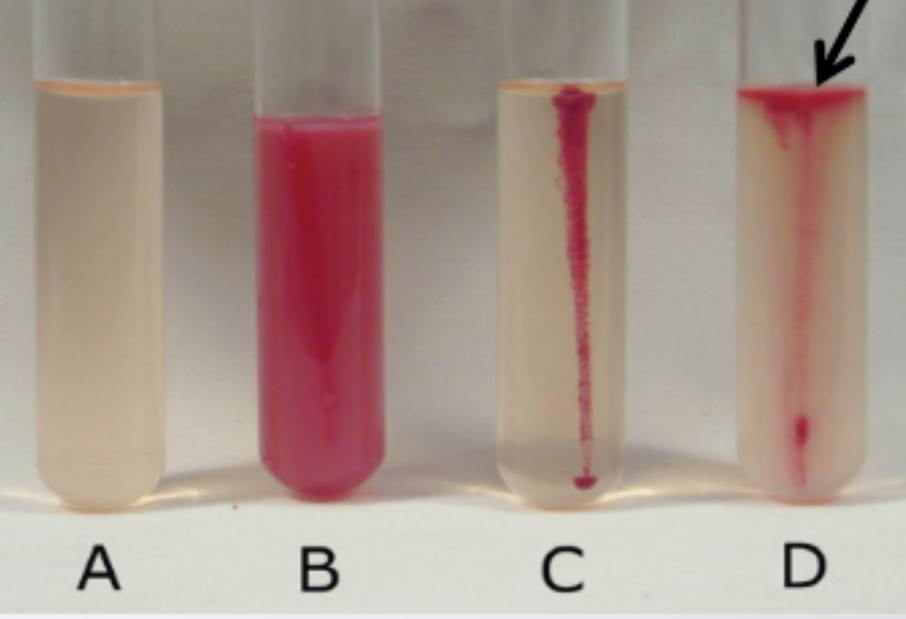
Motility Test Results
A: Control
B: Positive; not strict aerobe
C: Negative
D: Positive; obligate aerobe, moves to the top of the tube
Nutrient Agar Plate Results
It is just positve or negative for growth, if there is growth then its positive, if there is no growth then it is negative
MacConkey Agar Test Results
If there is growth on the plate then it would be positive for growth if there is no growth on the plate then it would be negative for growth
Color Change: if the color is pink then it is more acidic and it ferments lactose, if the color is not pink then it is neutral and does nto ferment lactose
Gram Positive Bacterial Cells
They have a thick peptidoglycan layer and retain crystal violet, so they are purple
Gram Negative Bacterial Cells
They have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane. The crystal violet washes out and safranin counterstains the membrane, they are pink
Gram Stain Procedure
Add 1-2 drops of crystal violet and wait 1 minute and then rinse the off with water
Add 1-2 drops of grams iodine, wait 1 minute and then rinse off with water
Add 1-2 drops of ethanol and immediately wash off with water
Add 1-2 drops of safranin wait 45 seconds and then rinse off with water
Dry the slide
Spore Stain
Identifies endospore-forming bacteria
certain bacteria sporulate under environmental stress
limited carbon sources (such as nutrient agar plates w/o glucose)
bacteria have evolved to sporulate as a mechanism to preserve their DNA when under environmental stress
Heat used during staining does not cause sporulation
Spore Stain Procedure
Prepare a slide, use bacterial smears not liquid media and let them air dry
Place a peace of pre-cur bibulous paper over the smear but do not heat fix
Add about 3-5 drops of 5% aqueous malachite green dye over the paper and let it sit for 5 minuutes
Using the slide holder, place the slide onto the aluminum tray on the hot plate
Monitor the bibulous paper and keep adding the dye, as needed, to keep the paper from drying, continue steaming for 3-5 minutes
After steaming discard the paper into the malachite green waste beaker and let the slide cool
Counterstain the smear with safraning and let it sit for 2 minutes, no heating.
Rinse the safranin and dry.
Spore Stain Results
If the bacterial species forms endospores, there should be green enedospore inside (and sometimes outside of) pink vegetative cells.
Coliform
Facultativelty anaerobic, gram-negative, noHEterendospore forming, rod-sahped bacteria that ferment lactose with acid and gas formation
Heterotrophic Plate Count
Quantitative method used to determine the overall quality of the water as well as the effectiveness of disinfeectants used in water treatments
Presumptive Test
Uses lauryl-tryptose (LT) broth which is
selective for intestinal bacteria (sodium lauryl sulfate)
differential gas production during lactose fermentation (durham tube)
Looking for gas bubbles created by lactose fermentation, which indicate possible coliform growth