REACTION MECHANISMS
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Reaction Equation
describes what happens in a chemical reaction
Reaction Mechanism
a detailed step-by-step description of how a chemical reaction occurs
Reaction Mechanism
sequence of bond-making and bond-breaking steps
Reaction Mechanism
involve the movement of electrons
Reaction Mechanism
provides a rationalization for chemical reactions
Reaction Mechanism
allows one to predict the likely outcome of a reaction
Heterolytic cleavage
asymmetrical cleavage of a bond (Ionic reactions)
Ionic reactions
Heterolytic cleavage – asymmetrical cleavage of a bond
Radical reactions
Homolytic cleavage – symmetrical cleavage of a bond
Radical reactions
Radical – high-energy species carrying an unpaired electron
Radical
– high-energy species carrying an unpaired electron (Radical reactions)
Homolytic cleavage
- symmetrical cleavage of a bond (Radical reactions)
heterolytic cleavage
In _, one atom (B in this case) takes both electrons from the broken bond. This creates a positively charged cation (A+) and a negatively charged anion (B-).
homolytic cleavage
In _, each atom takes one electron from the broken bond. This creates two radicals, which are species with unpaired electrons.
Nucleophiles
(Nu− or Nu:)
Electrophiles
(E+
Nucleophiles
electron-rich, nucleus-seeking reagents
Nucleophiles
typically have a negative charge (anions), lone pair, or multiple bonds
Electrophiles
electron-deficient, electron-seeking reagents
Electrophiles
typically have a positive charge (cations), or are polarizable molecules that
can develop an electron-deficient center
LEAVING GROUP (L−, L:)
ions or neutral molecules that are displaced from a reactant as part of
a mechanistic sequence
LEAVING GROUP (L−, L:)
displacement when a nucleophile attacks an electrophile that carries
a suitable leaving group (C-L)
rate-determining step
the slowest transformation in the sequence
rate of reaction
Rate = k [A] [B]
Rate
_ = k [A] [B]
rate of reaction:
dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reagents and
other variables indicates the number and nature of the molecules
involved in the rate-determining step
molecularity
number of reactant molecules involved in the rate-
determining step; usually equivalent to the kinetic reaction order
first
k[A] Reaction order:
A →
k[A] Probable reaction:
unimolecular
k[A] Molecularity:
second
k[A][B] Reaction order:
A + B →
k[A][B] Probable reaction:
bimolecular
k[A][B] Molecularity:
second
k[A]² Reaction order:
A + A →
k[A]² Probable reaction:
bimolecular
k[A]² Molecularity:
Transition State
cannot be isolated, or even
detected; energy maximum
Intermediate
stable and can be isolated;
energy minimum
• Substitution
• Elimination
• Addition
• Rearrangement
• Radical Reactions
TYPES OF ORGANIC
REACTIONS 5
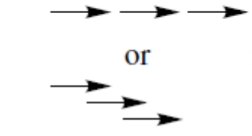
reaction (one step)

reaction (several steps)
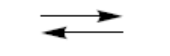
equilibrium

equilibrium (right-hand product favoured)

transformation in either direction (but not equilibrium)
resonance

curly arrow - movement of two electrons

curly arrow - movement of one electron

reaction with a converts A into B
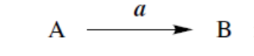
reaction with a in the presence of b converts A into B
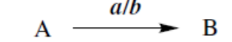
reaction with a in suitable solvent converts A into B
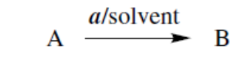
reaction with a at t °C, for h hours converts A into B
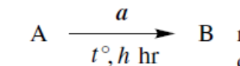
reaction with a first, then with b converts A into B
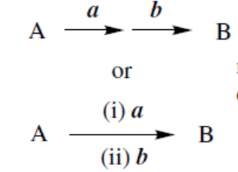
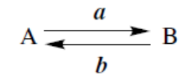
reagent a achieves conversion A → B, reagent b achieves conversion B → A