econ 200 - midterm 1
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
market economy
an economy in which private individuals, rather than a centralized planning authority, make the decisions
market
buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service
how are market boundaires set
changes based in SCOPE of trades being made (small business vs CEO)
competitive amrket
a market in which fully informedd, price taking buyers and seller easily trade a standridized good or service
price taker
a buyer or seller who cannot affect the market price. In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price takers as a consequence of many sellers selling standardized goods
standardized good
a good for which any two units have the same features and are interchangeable
transaction costs
the costs incurred by buyer and seller in agreeing to and executing a sale of goods or services
are transcation costs in competitive markets
nope!!! you dont have to pay anything for the privieldge of buying or selling in the makret. (like getting gas - you dont have to have special equitment to get gas or pay a fee for enterance)
four characteristics of perfectly competitive markets
participants are price takers, standarized good, full infomration, no transaction costs
participants are price takers
neighter buyers nor sellers have the power to affect the market price
standardized good
any two units of the good have the same features and are interchangebale
full info
market participants know eveyrthing about the price and features of the good
no transaction costs
no cost to participate or exhcnage in the market
are perfectly compettive markets common
nope!!
why do we assume perfect competitive if markets in the real world are rarely like that?
leads us to useful insights because it’s simplified
demand
describes how much fo something people are willing and able to buy under certain circumstances
overall market demand
adding up all individual choices people made when deciding to buy/not buy a certain product (diff peopel bought their first phone at diff prices, some were willing to buy some were not)
quantity demanded
the amount of a particular good that buyers will purchase at a given price during a specified period
law of demand
a fundamental characteristic of demand that states that, all else equal, quantity demanded rises as price falls
when all else is held equal (when all other factors remain the same), quantity demanded rises as price falls
also known as ceteris paribus
ceteris paribus
law of demand
what is ceteris paribus used for
to isolate the expected effect of single change in the economy.
example: prwdicted what would ahppen to cell phones if cell phone prices go down
if cell phone prices god down, holding all else EQUAL, quantity demanded will go up
what statement is super impirtant when using ceteris paribus
“hold all else equal” → cannot apply if the eocnomy is not doing well in said situation, etc.
when the trade-off between costs and benefits tips toward benefits
more people will want to buy the good
nonprice detemrinates of demand
incomes, expectations and tastes (all factors OUTSIDE of prices) that impact a choice to buy a product
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase (demand) at various prices
because the law of demand says that the quanity of a product demanded will be DIFFERENT AT EVERY PRICE LEVEL
what does the demand schedule assume
fatcors other than price remain the same / all else is held equal
demand curve
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers will demand at various prices
demand curve picture / structure deatils
downward slope
inverse relationship between price and quantity
only reps the relationship between price and quanity demanded with EVERYTHING ELSE HELD CONSTANT - if not, curve shifts
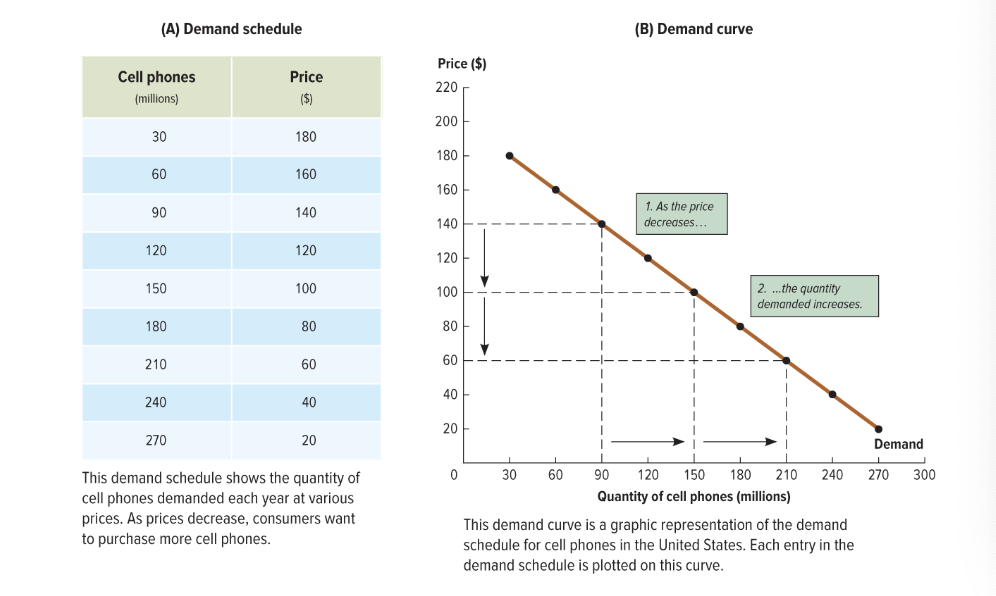
what does demand curve represent
shows quanityies of a particular good that consumers will demand at various prices
CONSUMER’S WILLINGNESS TO BUY/the highest amount consumers will pay for any given quanity
non price detemrinates of demand can be divided in 5 major caterogries
consumer prefereneces
the rpices of related goods
income of the consumers
expectations of future prices
the number of buyers in the market
what do non price detemrinates impact
either the benefits or the opporutuity cost of buying a good, even if the price remains the same
non price detemrinates deal with prices though…why do you call if non-price then?
differentiates them from the effect of the current price of the good on demand for that good
consumer preferences =
oikes and dislikes that make buyers more or less inclined to purcahse a good
some are constant
some arise from personality traits
some are due to external events
substitutes
goods that serve a similar-enough purpose that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other
if two good are quite similar
complements
goods that are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make consumers more likely to purchase the other
complements example
peanut butter and jelly
cereal and milk
if the price of one increases, demand of rthe other will likely decrease
normal goods
goods for which demand increases as income increases (what most goods are)
inferior goods
goods for which demand decreases as income increases
canned food, when income rises, less likely to buy these
expectations (notes)
if consumers expect prics to fall in the future, they may postpone a purchase → demand decreases. or they delay in upgrading their product in hope that the current model price drops
if expecting prices ot rise, they may wish to purchase a ssoon as possible, more demand
increase in the number of potential buyers →
increase in demadn in that market and vice versa
if one of the five nonprice detemrinates of demand changes (?)
whole demand curve shifts , either to the left or right
HORIZATONAL SHIFT (becayse it affects the quanityt demanded at EACH price)
when quanity demaded at a price is now higher, the point of the demand curve corresponinding to that price is now…
further right!!!
when quanity demaded at a price is now lower, the point of the demand curve corresponinding to that price is now…
further left!!
demand curve SHIFTS picture
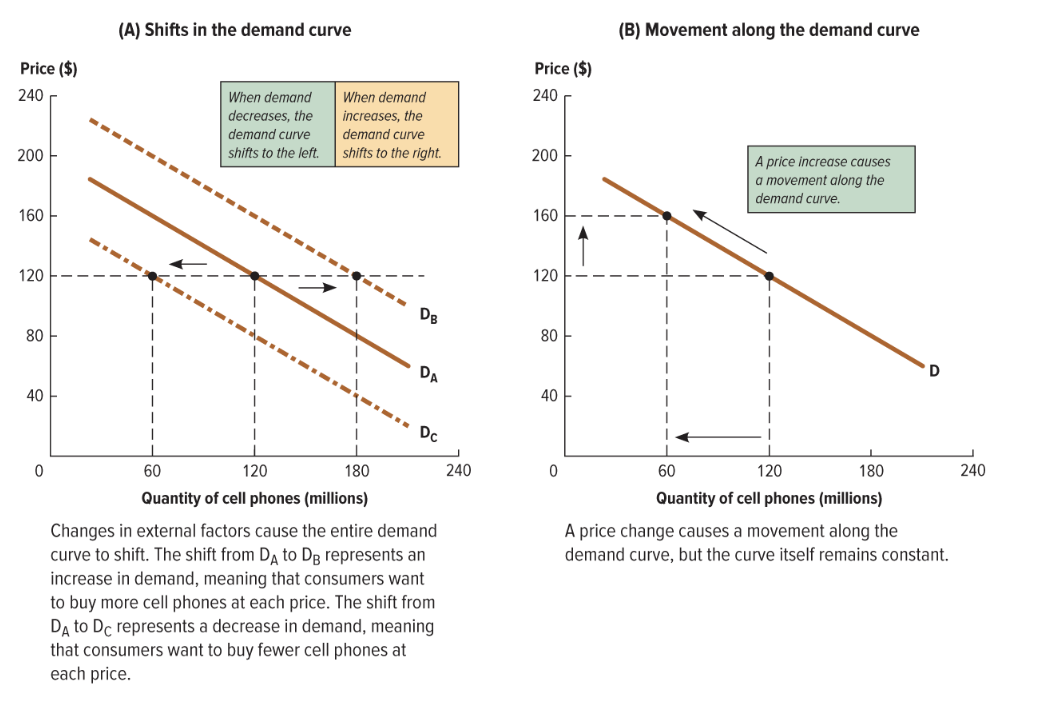
what are shifts in the demand curve caused by?
chnages in the nonprice deteminates of demand
reciession would lower incomes and move the whole demand curve to the left (“demand decreases”)
what if the price goes up but there r no changes in the nonprice detemrinnts of demand
the demand curve is about the demand at any possible price, not JUST current market price
we dont have to shift the curve
look at diff point of the curve to see what would happen
how to find the quanity that consumers will want to purchase at this new price.?
move along the existsing demand curve form the old price ot the new one
supply
how muhc of a good or service producers will offer for sale under given circumstances
quantity supplied
the amount of a particular good or service that producers will offer for sale at a given price during a specified period
law of supply
a fundamental characteristic of supply that states that, all else equal, quantity supplied rises as price rises
teh higher the price of a good…
the more of that good producers will want to supply and vice versa
how to find overall makret supply
adding up the indviduals decisison of each producer. each prodcuer will have a differnet rpice point at which it decides its worthwhile to supply cell phones (law of supply)
why does supply vary with price?
because the decision to produce a good is about the TRADE OFF between the benefit the producer will recieve from selling the good and the opporutunity cost that go into it.
when prices rise of a product, but not the raw materials needed to make said product…
the producers will increase their activity/supply!!!. when prces drop, they cut back
supply schedule
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
supply curve
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
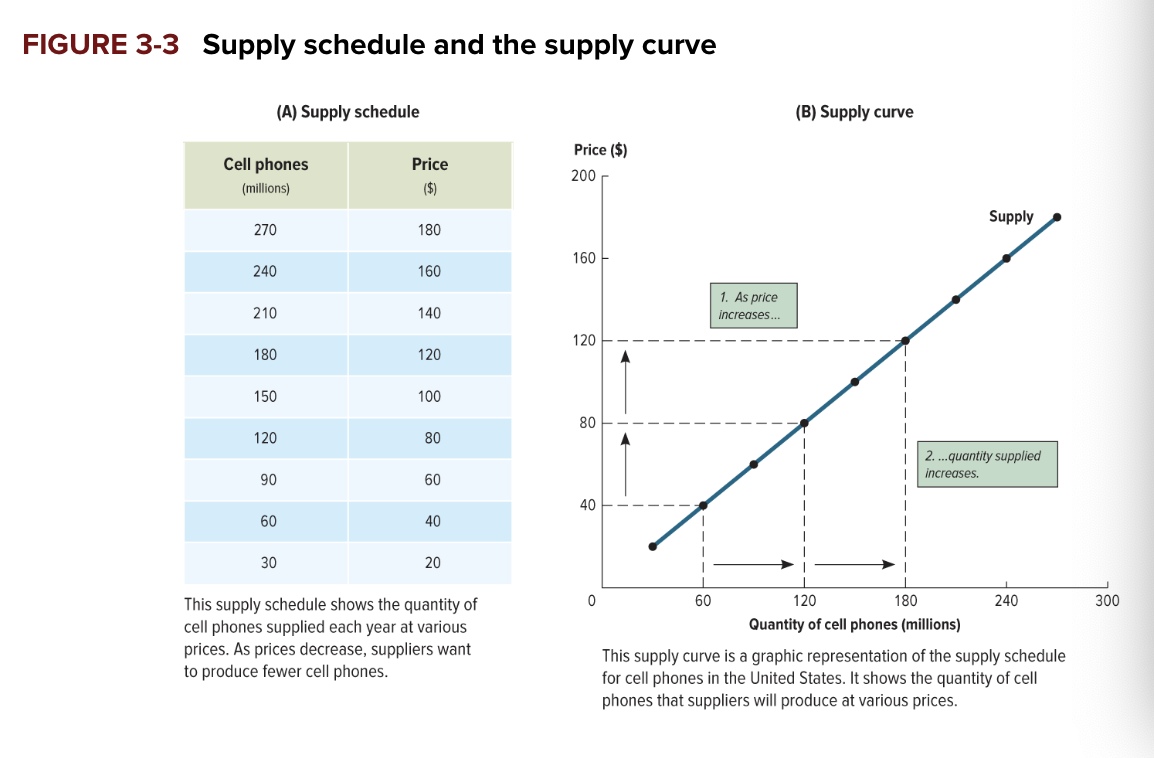
what does supply curve show
producer’s willingess to sell. the minimum price producers must recieve to supply any given quantity
what impacts the producers willingness to supply a good or service
nonprice factors (just like demand)
when a nonprice determinat of supply changes… what happens
the entire supply curve will shift
five major cateorgies of nonprice determinates of supply
prices of related goods
tech
prices of inputs
expectation
the number of sellers
what do the nonprice determinates of supply show
determines the opportunity cost of production RELATIVE to the price (aka the trade-off that producers face).
why does the price of related goods detemrine supply?
IT AFFECTS THE OPP. COST OF PRODUCTION
ur a farme.r if the rpice of corn increases, the quanity of wheat you are willing to grow…
falls. why? because each acre u devote to wheat is one fewer acre you can use to grow corn.
what is the effect of price of the inputs used to produce a good on cost
when prices of inputs rise, production cost rises, and the quanity of the prodcut that producers r willing to supply DECREASES (bc less profit)
when input prices falll..
supply increases!
expectations of price example - and how that affects supply
expecting prices of houses to go up in the future →hold off on buidling NOW so you can make more profit later → less supply.
prices of real estate expected to fall → projects r rushed to compleetion so they can sell at a higher price
the number of sellers in the market is considered to be BLANK of the supply curve
a fixed part of it. the number of seller does not change based on price (in the short run). the only thing that changes is the amount sellers r willing to provide based on price (higher price of good = more supply)
non price factors can cause the number of sellers to change in a market and move the supply curve, tho!! true or false
true!!! like lisencing requirements
changes in price cause suppliers to move to ____ on the same supply curve
a different point
what actually shifts the full supply curve itself
changes in the nonprice determinants
what increases/decreases supply
a change in a nonprice determinant
what changes (increases/decreases) the quanitity supplies
a change in the price!!!
increase in supply shifts the curve to the
right
a decrease in supply shifts the curve to the
left
language used to show a SHIFT of the entire supply curve
"increase/decrease in supply” ( caused by a change in one of the nonprice determinantes of supply )
language used to show MOVEMENT ALONG the supply curve
say that a change in price causes “an increase/decrease in the quantity supplied”
interaction of supply with demand =
prices and quanities exchanged in the REAL WORLD
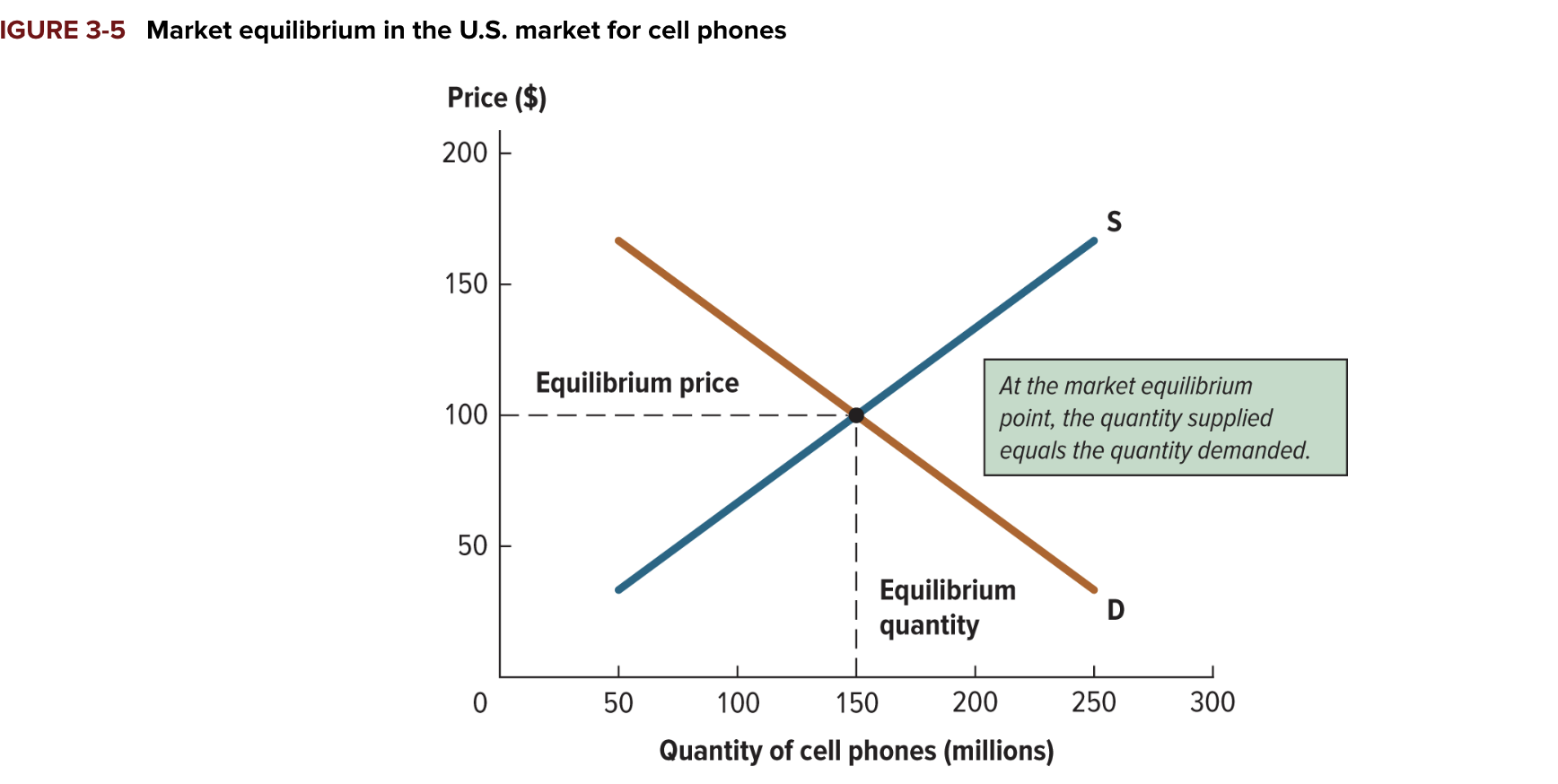
equilibrium
the situation in a market when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded; graphically, this convergence happens where the demand curve intersects the supply curve
equilibrium price
the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded
equilibrium quantity
the quantity that is supplied and demanded at the equilibrium price
when a market works well, what happens with the quanity and the supply
the qyanity supplies exactly equals the quanityt demanded
market equilibrium graph
shortage / excess demand
a situation in which the quantity of a good that is demanded is higher than the quantity supplied
when do sellers have an incentive to increase/decrese the price
at any price above or below equilibrium
money making incetives…
drive the market toward the equailibrium price
a shift in either curve supply or demand will. change what
change the market equailibrium
shift is supply and demand curves examples
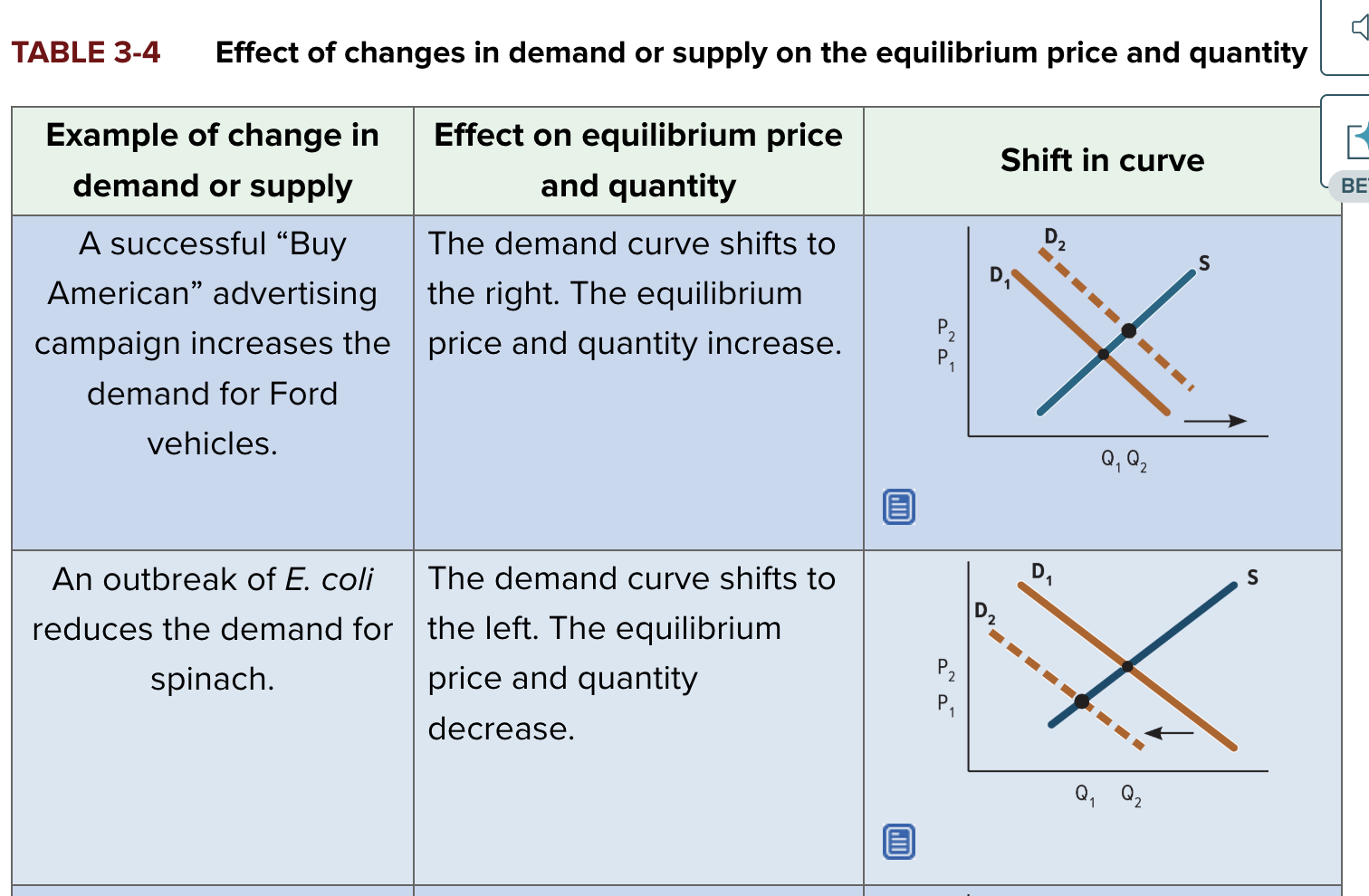
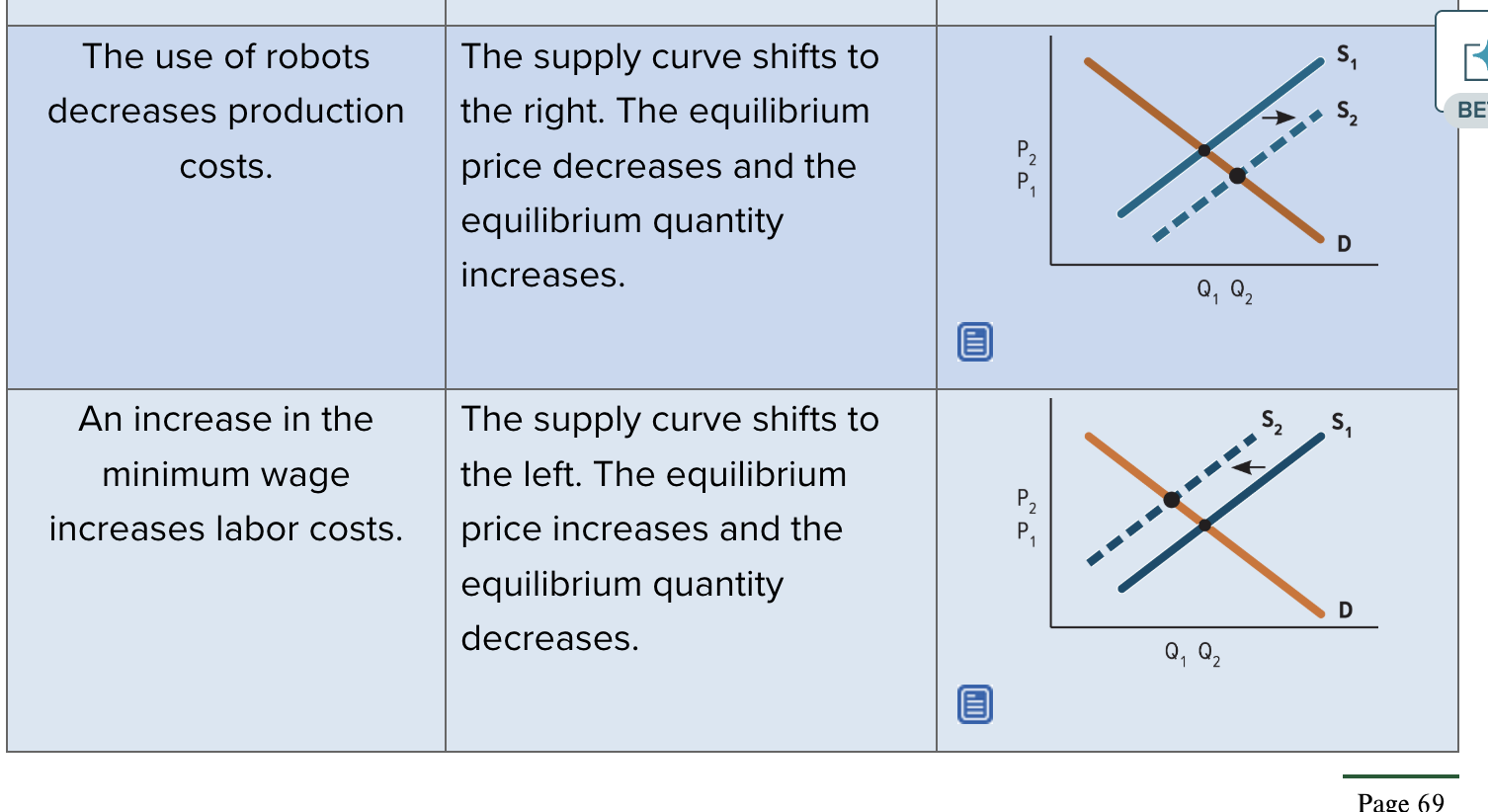
shift is supply and demand curves examples 2
when supply increases, the price does what while the quantity does what
price decreases and quanitity increases
when demand increases more than supply increases (when they both shift…)
consumers purchase more cell phones at a higher price
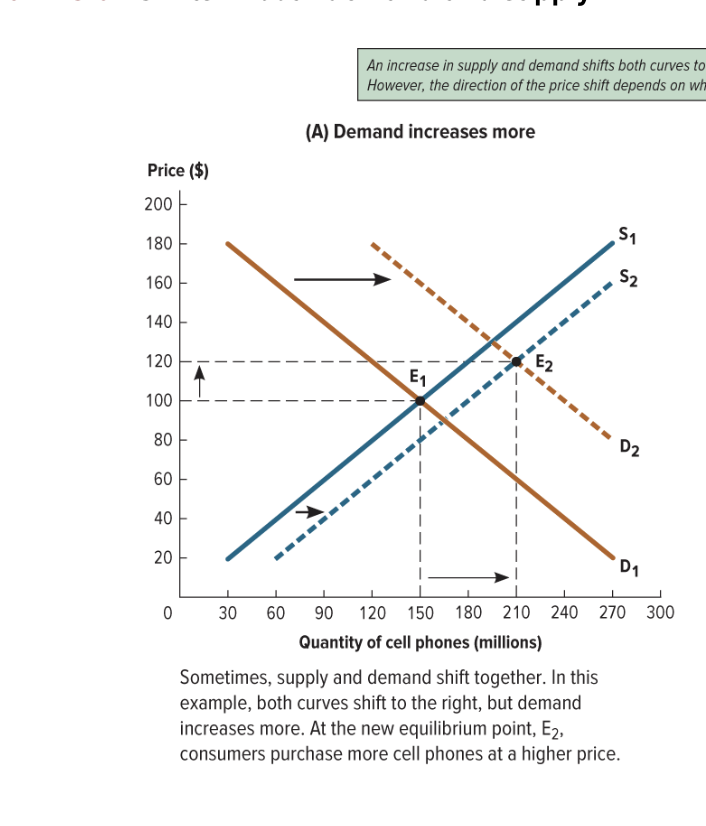
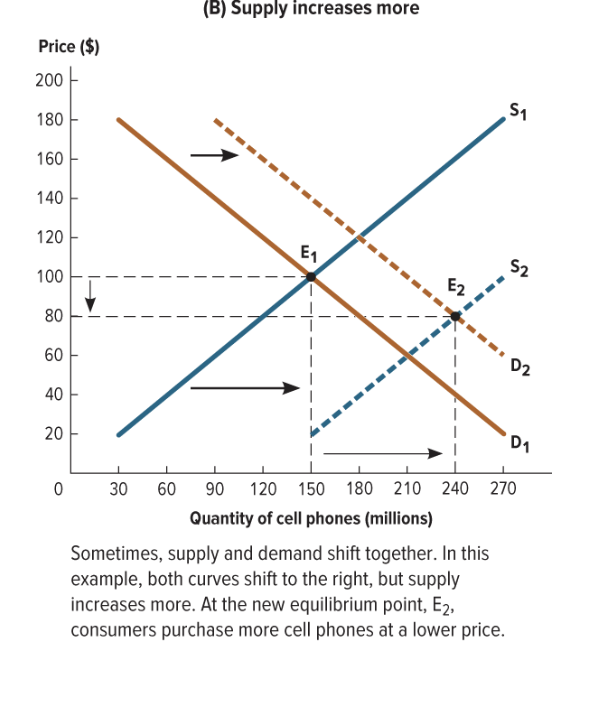
when supply increases more than demand does when they both shift
consumers pruchase more cell phones at a LOWER price
holding all else equal, and increase in demand leads to an …. in price and an increase in supply leads to a …. in price
increase, decrease
what is possible to predict when supply and demand shift together
either the direction of the change in quanity OR the direction of the change in price without knowing just how much the curves shift
what can you predict when supply and demand shift in the same difection
the driection of the change in quantuty but nit the direction of the change in price
when supply and demand shift in opposute directions, what is/is not predictable
the chnage in price is predicatble but not the change in quantity
supply demand change table
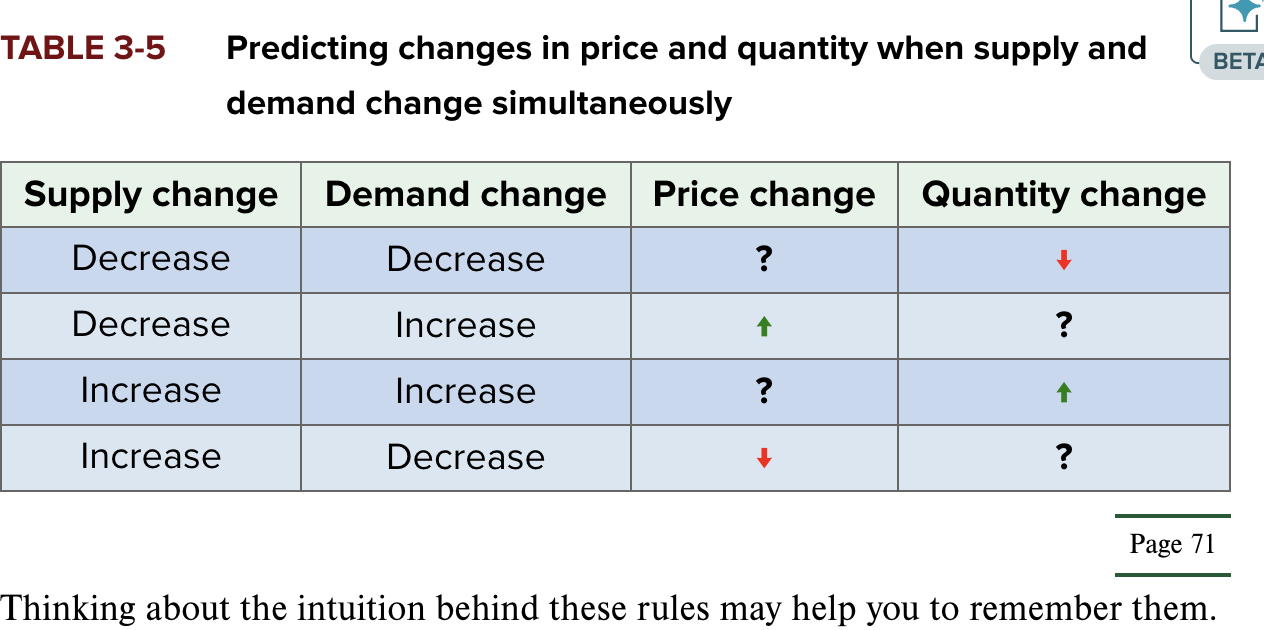
what happens when demand increases and supply decreases
buyers r willing to pay more for the same quanity and sellers r willing to supply the same qauntitty only if they recieve a higher price. OTHER WORDS: they can AGREE on a higher price at any quanityt, and the eq. price will RISE
what happebs when demand decreases and supply increases
buyers r willing to buy same amount for lower price, and seller are willing to supply the same quantity for a lower price too (bc now production costs r lower, meaning they’re still making a profit) → eq price goes down
utility
a measure of the amount of satisfaction a person derives from something
increases utility
doing things you like