physical and chemical changes; rate of reaction
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
physical change
easy to reverse
eg. changing state, making a mixture of substances, disolving solute in solvent
usually no colour change
no significant energy change
chemical change
difficult to reverse
always new chemical substances formed from original compounds
colour change
effervescence (fizzing)
other signs
light
smell
change in pH
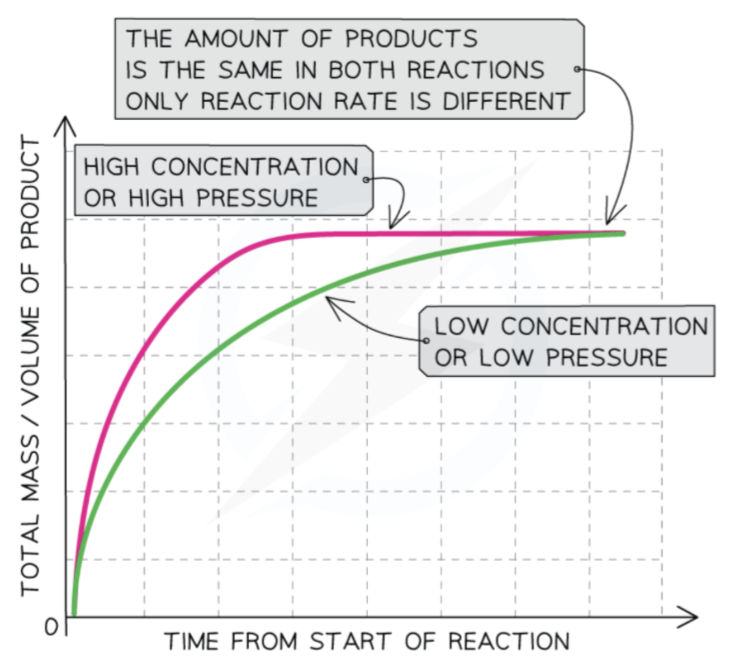
Increased concentration or pressure
increasing concentration/pressure → increased reaction rate
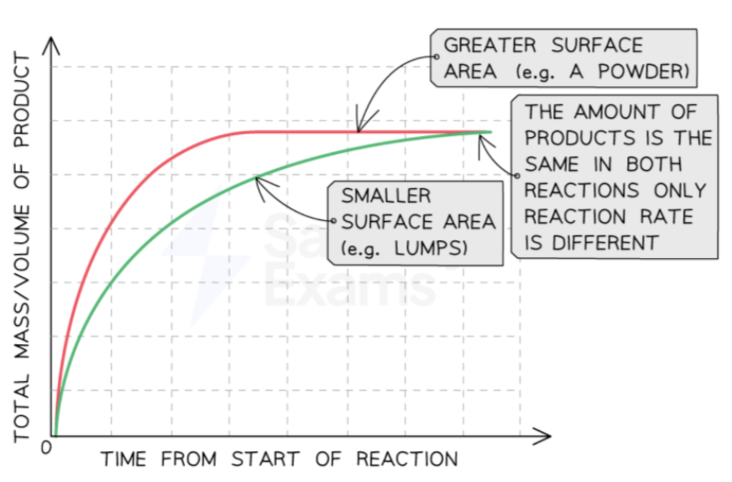
increased surface area
increasing surface area → increased reaction rate
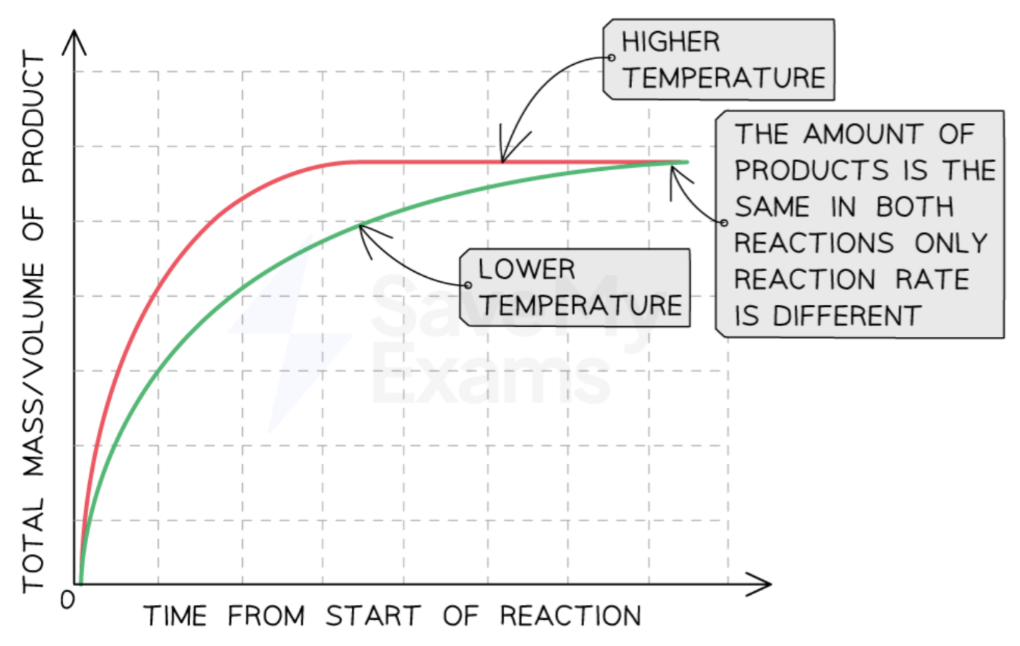
increased temperature
increased temperature → increases reaction rate
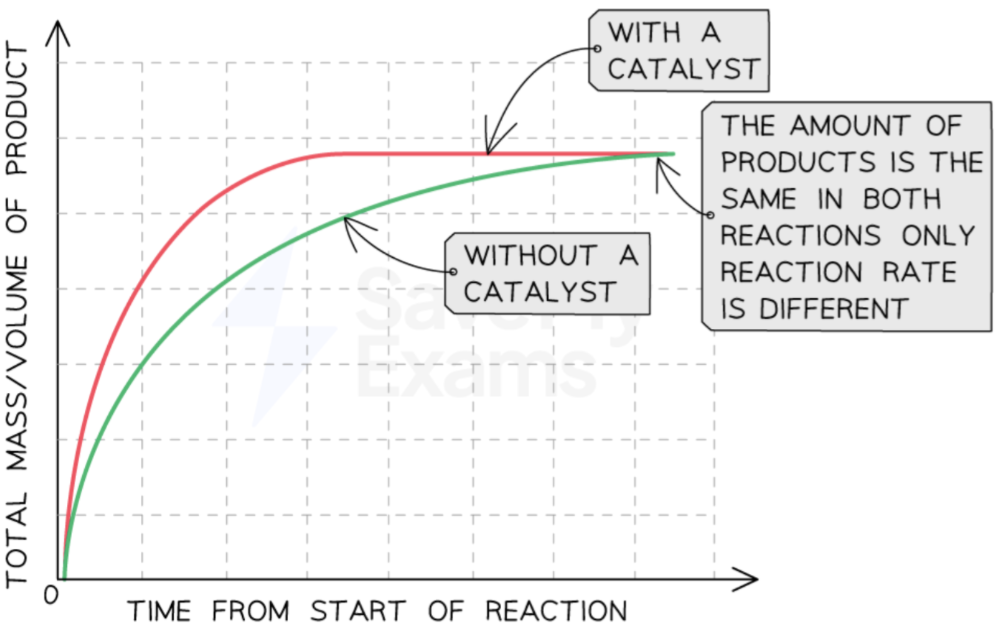
using a catalyst
presence of catalyst → increased reaction rate
the catalyst stays unchange during and after a reaction
collision theory
for a chemical reaction to happen, the reactant particles must collide successfully with each other
there must be enough activation energy