Body Size & Weight
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Describe LBM
Skeletal muscles, water, bone and essential fat in internal organs, bone marrow and nerve tissues. Higher in men than women, increases with exercise, decreases with age. Major determinant of RMR, water makes up 60-65%
Describe Essential Body Fat
Necessary for physiologic function and makes up about 3% of BW in men and 12% in women
Describe Storage Body Fat
The energy reserve under the skin and around internal organs to protect them from trauma. Primarily triglycerides in adipose tissue and most considered expendable
WHO definiiton of obesity
Abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that impairs health classified as BMI >30
When is obesity considered a disease?
Patient has excessive body fat, assessed by reliable measures
Causes of excessive body fat
Genetic or developmental errors
Infections
Hypothalamic injury
Adverse reactions to medications
Nutritional/energy balance
Unfavourable environmental factors
What does excessive body fat result in?
Pathogeneic structural or functional abnormalities and increased patient morbity and mortality
What contributes to adiposopathy or “sick fat” disease
Multiple pathogenic adipocyte and/or adipose tissue
Endrocrine and immune dysfunctions
Endocrine/metabolic consequences of adiposopathy or “sick fat” disease
Elevated blood glucose
Elevated blood pressure
Dyslipidaemia
Other metabolic diseases
What contributes to fat mass disease?
Multiple pathogenci physicla forces from excessive body fat causing stress damage to other body tissues
Biochemical/structural consequences of fat mass disease
Stress on weight bearing joints
Immobility
Tissue compression (e.g. sleep apnoea, GI refluc, high BP)
Tissue friction (e.g. intertrigo)
Worldwide prevalence of overweight/obesity
650 million people
BMI nearly triple between 1975 and 2016
65% population killed by more overweight and obesity than underweight
5th leading cause for global deaths
Overweight/obesity prevalence in NZ
1 in 3 adults obese
Pacific and Maori most likely
x1.5 more likely in deprived neighbourhoods
13.5% children (Maori & Pacific highest)
2nd highest prevalence in the world
Medical complications of obesity
Idiopathic intracrancial hypertension
Stroke
Cataracts
Pulmonary disease
abnormal fucntion
obstructive sleep apnea
hypoventilation syndrome
Coronary heart disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
steatosis
steatohepatitis
cirrhosis
Diabetes
Dyslipidemia
Hypertension
Severe pancreatitis
Gallbladder disease
Cancer
breast
uterus
cervix
colon
esophagus
pancreas
kidney
prostate
Gynecologic abnormalities
abnormal menses
infertility
PCOS
Osteoarthritis
Phlebitis
venous stasis
Skin
Gout
Female specific manifestations
Hyoerandrogenaemia
Hirsutism
Acne
PCOS
Menstrual disorders
Infertility
Gestational diabetes
Pre eclampsia
Thrombosis
Male specific manifestations
Hypoangrogenemia
Hyperestrogenemia
Erectile dysfunction
Low sperm count
Infertility
Etiology of obesity - physiological mediators
Energy intake & energy expenditure
How does energy intake impact etiology of obesity?
Loss of autoregulation
Underreporting of intake
Appetite control impacted by CNS that controls eating behaviour
Macronuterient selection
Sensory preferecnes
Eating frequency
How does energy expenditure impact the etiology of obesity?
Greater body mass reuslting in higher BMR and higher energy expenditure
DIT remains at 10%
Total higher energy expenditure due to increase in body size
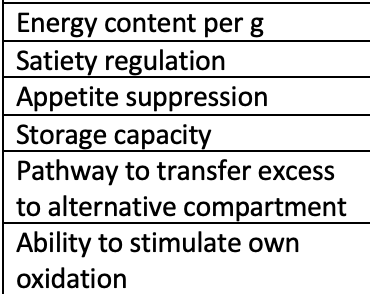
Answer for Protein
4kcal
High
High
Low
Yes
Excellent

Answer for Carbohydrate
4kcal
Moderate
High
Low
Yes
Excellent

Asnwer for Fat
9kcal
Low
Low
High
No
Poor
Etiology of obesity - lifestyle, environemental, genetic factors
Genetcis
Taste, satiety portion sizes
Sleep, stress cardiac rhythms
Psychological
Physcial inactivity
Environment
Gut microflora
Medication
Endocrine disrupting chemicals
Viruses & pathogens
General principles of weight loss
Calorie deficit of 500kcal/day, 3500kcal/week roughly equivalent to 0.45kg of fat tissue.
Limit highly processed foods of minimal nutritional value, energy dense beverages, potential non nutrititive sweeteners
Encourage consumption of healthy proteins & fats, vegetables, leafy greens, fruits, berries, nuts, legumes, whole grains, complex carbs over simple sugars and high fibre foods
What does a low calorie diet look like?
1,200 - 1,800 kcal/day
Restricted fat (low <30%, very low <10%)
Restricted carbohydrate (low GI, low 50-150g, very low <50g)
What does a very low calorie diet look like?
<800 kcal/day
Under medical supervision
Short term
Full meal replacement programs
What does a balanced, resricted energy nutrition therapy look like?
500 kcal deficit
Healthy eating
Regular excersie
Support
Pharmacological agents used in weight management
Xenical
Duromine
Saxenda
Contrave
Classes of obesity
Class III : >40
Class II: 35-39
Class I: 30-34
Obese: >30
Pre Obese: 25-29
Overweight: >25
Waist circumference cut offs
Increased risk
Women >80cm
Men > 94cm
Substantially increased risk
Women >88cm
Men >102cm
5 principles of the non-diet paradigm
Accepting and respecting body shape diversity
Acknowledging that health is more than body size and involvs cultural, physical, social, spiritual, occupational, emotion and psychological inputs
Enjoyment of food and movement
Acknowledgement of individual responses to eating, hunger and satiety
Role of the dietitian in patient centered care
Support a person to improve health and wellbeing
Support a person to identify and make changes to the bheaviours and practices in a patient centred manner
(if needed) provide practical advice and effective strategies to help manage food and behaviours
Describe weight bias
The negative attitudes towards and beliefs about others because of their weight
Describe weight stigma and internalised effects
The discriminatory acts and idealogies targeted towards individuals because of their weight and size. The effect of interalised weight stigma is self judgement and negative self esteem leading to body shame feeling judges, sterotyped and negative self esteem which has an impact on psychological and physical well being
Risk of intentional weight loss
Fat women who intentionally lost 15%+ of their BW were x2 greater risk of death comapred to fat women who remained weight stable
Increased risk of dying from CVD in people who lose weight, risk increased lineraly with amount of weight lost
Describe the weight neutral model
Supporting all people to engage with midful, self compassionate care across lifestyle behaviours (nutrition, movement, mental and social wellbeing)
Describe HAES
Offers alternative to a weight centric approach to health care, pursuing health should not be a moral imperative, nor an individual obligation, health status should never be used to judge, oppress or determine the value of an individual. Seeks to promote health equity, end weight discrimiantion and improve acces to quality healthcare regardless of a persons size
Principles of intuitive eating
Reject the diet mentality
Honour your hunger
Make peace with food
Challenge the food police
Respect your fullness
Discover satisfaction factor
Honour your feelings without using food
Respect your body
Enjoy movement
Honour your health
Describe the mindful eating cycle
Why do I eat?
When do I want to eat?
What do I eat?
How do I eat?
How much do I eat?
Where do I invest my energy?
Benefits of mindful eating
Directed by person not clinician
Increases awareness of behaviours, thoughts, feelings and emotions
Opportunity to stop automatic reactions (reduce/change habit reactions)
Allow a new path to be taken, learn new ways to respond
Increase confidence around food