C4: Chemical calculations
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Mass of products =
Mass of reactants
Law of conservation of mass
No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction so mass of the products = mass of the reactants
When are ionic compounds formed?
When metals react w non-metals
Ions
Charged atoms
What ions do metals form?
Positive

Rules for ions (metals)
Charge on ion = group no in periodic table
What ions do transition metals form?
Positive- but can form diff ions


State the formula for these non metal ions

Which non-metal ions are diff compared to others and why?
Form positive ions, not -

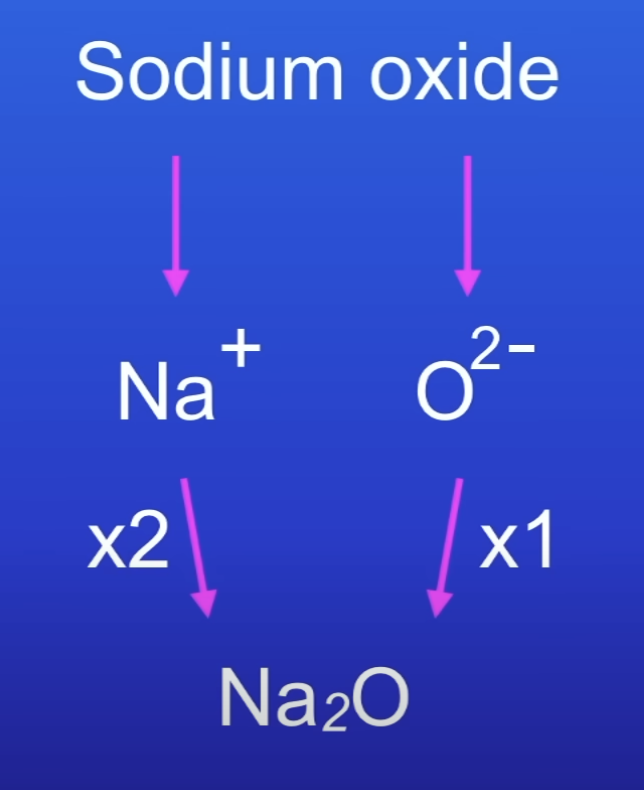
Formula of ionic compounds
Charges on ionic compounds cancel out → overall charge is 0
Overall charge on ionic compounds
0
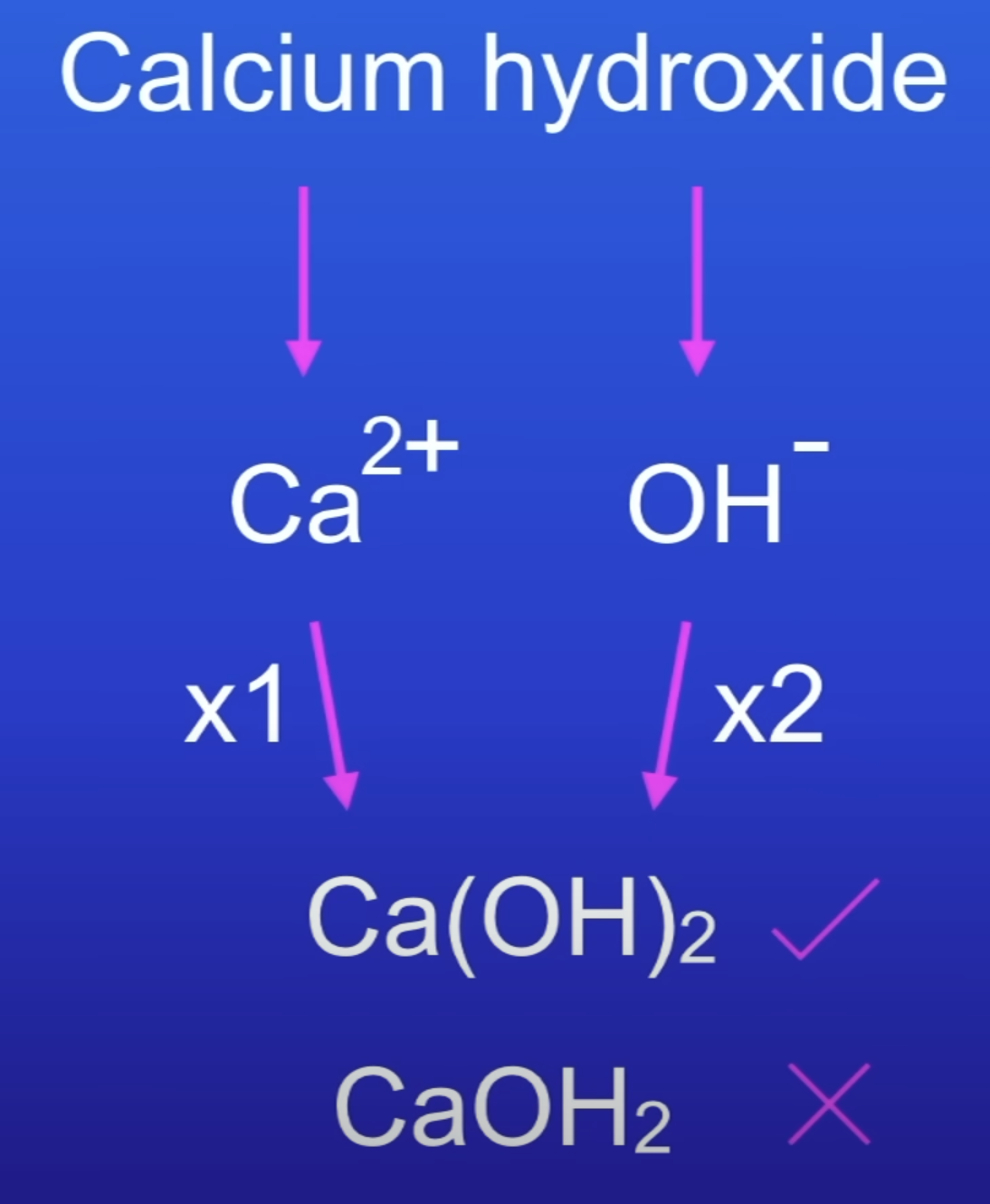
How to work out the charges of ions in an ionic compound?
Drop and swap method
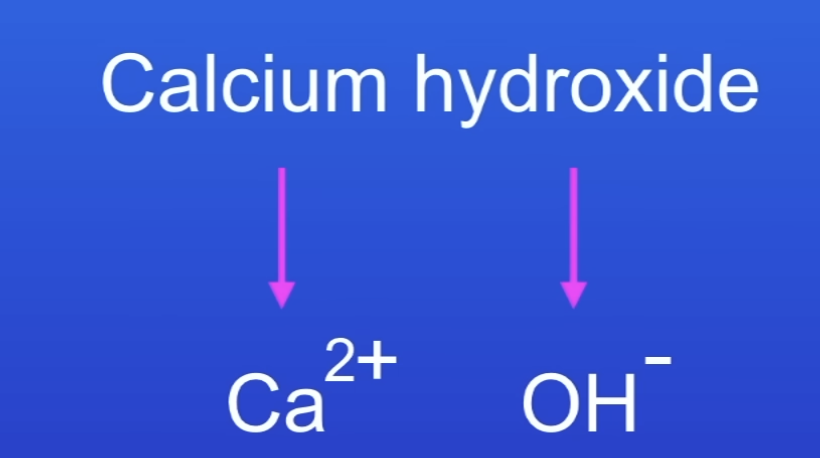
Calcium hydroxide formula
Balanced chemical equation
No. of atoms on LHS = RHS
Relative atomic mass
The average mass of the isotopes of that element weighted to take into account the abundance of each isotopes
Abundance
How common an isotope is
Formula for Ar (based on percentage abundance of isotopes)
((mass no of isotope 1 x percentage abundance of isotope 1) + (mass no of isotope 2 x percentage abundance of isotope 2)) / 100
Relative formula mass (Mr)
Sum of relative atomic masses of the atoms in the no.s shown in the formula
Key facts about relative formula mass (Mr)
No units
Doesn’t involve big numbers
In a balanced chemical equation, sum of the Mr of reactants =
Sum of Mr products
Percentage by mass
Shows what % of Mr is due to 1 of the elements in a compound
Percentage by mass equation

Relative atomic mass (Ar) of any element in grams =
1 mole of that atoms of that element
What are chemical amounts measured in?
Moles (mol)
1 mole of a substance contains?
The same no. of particles / atoms / molecules / ions as 1 mole of any other substance
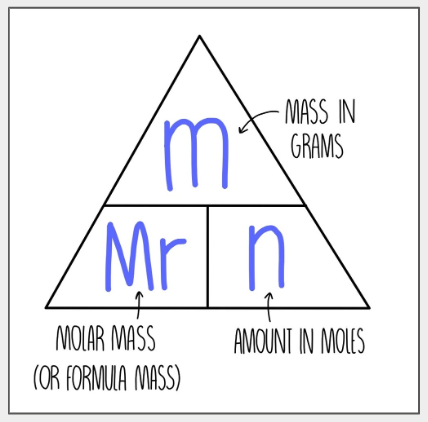
Number of moles equation
Mr mol carries mass

Number of moles of a compound equation

How to balance an equation using moles?
Calc no. of moles of each
Write mole no. in front of the respective chemical
Simplest ratio → divide all mole no.s by the smallest no.

Balance this equation

The no of … in 1 mole of C is the as the no of … in 1 mole of CO2
Atoms
Molecules
Avogadro’s constant
No. of atoms, molecules or ions in a mole of a given substance
Value of Avogadro’s constant
6.02 × 1023 per mole

Calc no of moles of atoms in 1 molecule of H2O
3 moles of atoms
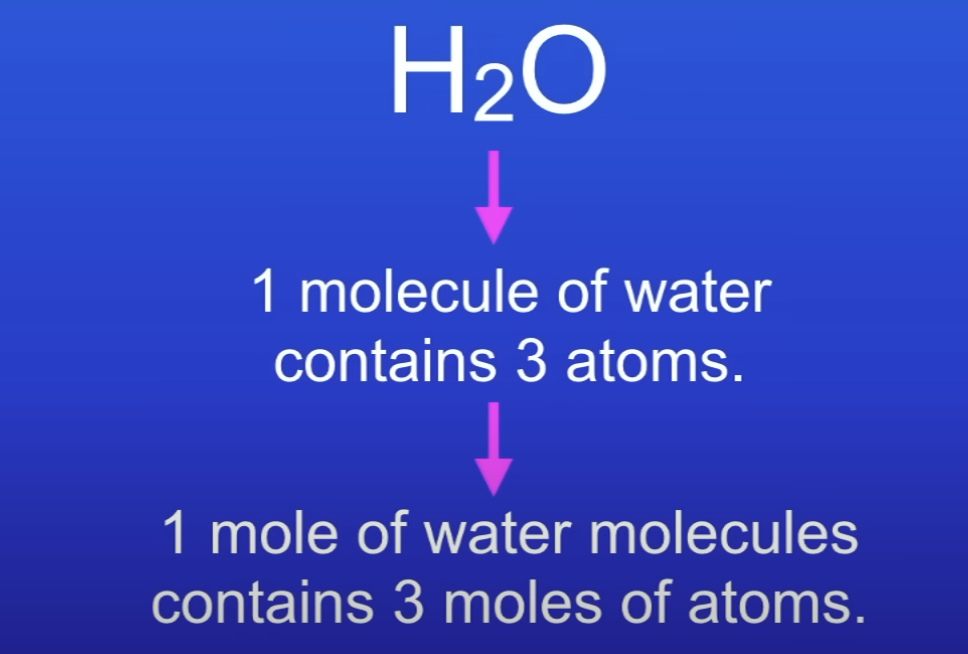
How to calculate no. of atoms in a compound?
Calc no. of moles
Multiply by 6.02 × 10²³

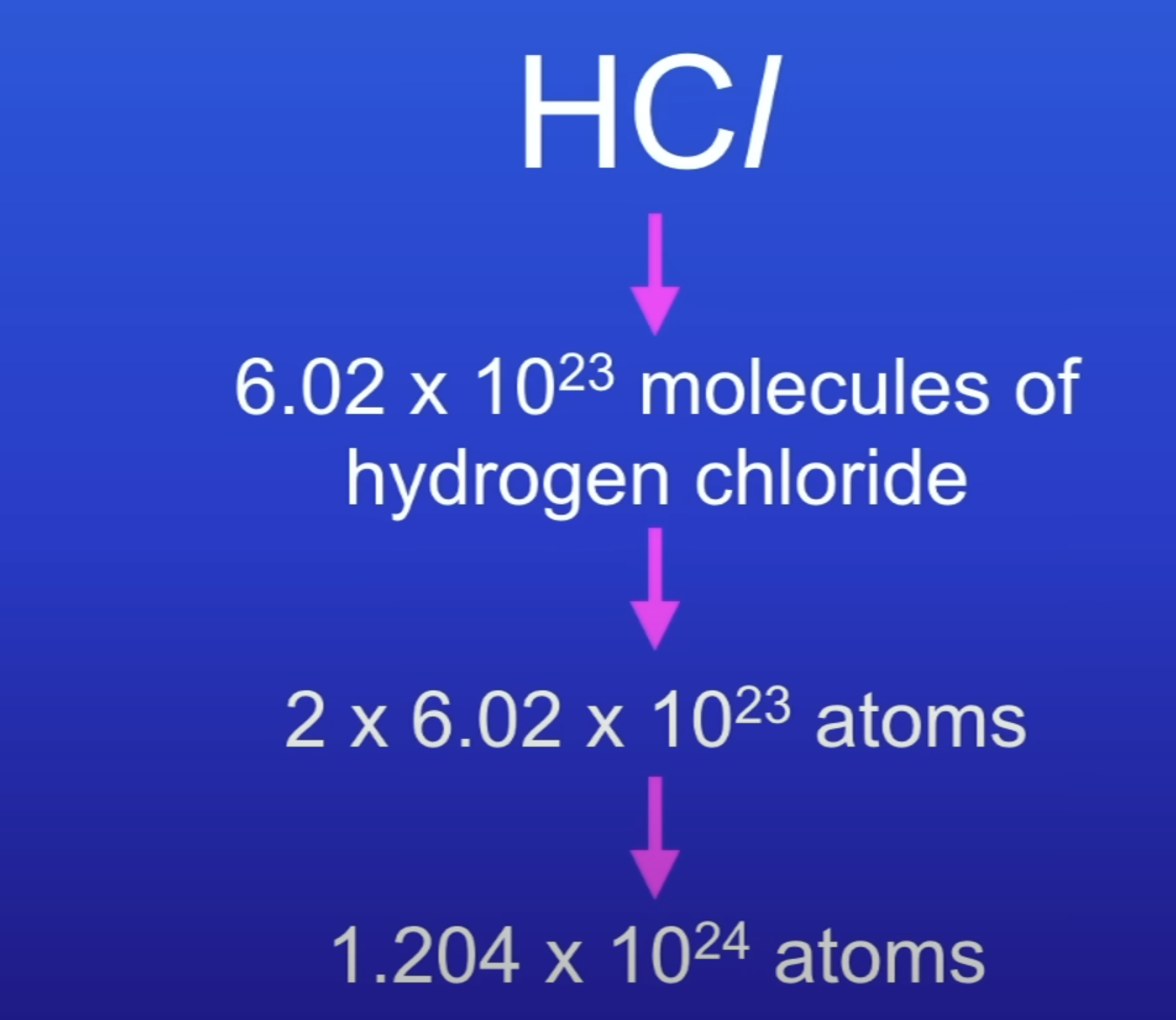
Calc no of atoms in 1 mole of HCl
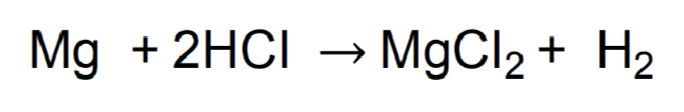
What does this equation show?
1 mole of Mg reacts w 2 moles of HCl to make 1 mole of MgCl2 + 1 mole of H2

Calc no. of atoms in 28g of Lithium
Ar of Li = 7
Calc moles- 28 / 7 = 4
4 × 6.02 × 10²³
2.408 × 1024
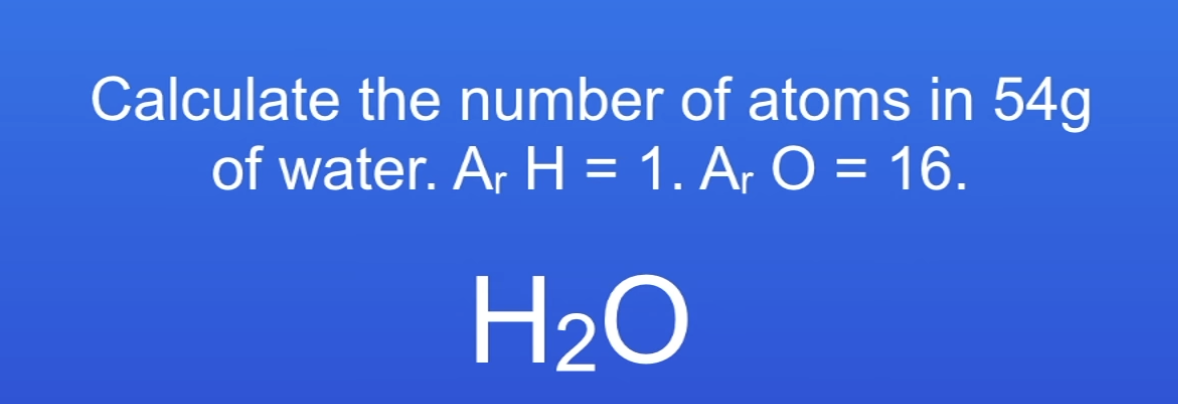
Calc no. of atoms in 54g of H2O

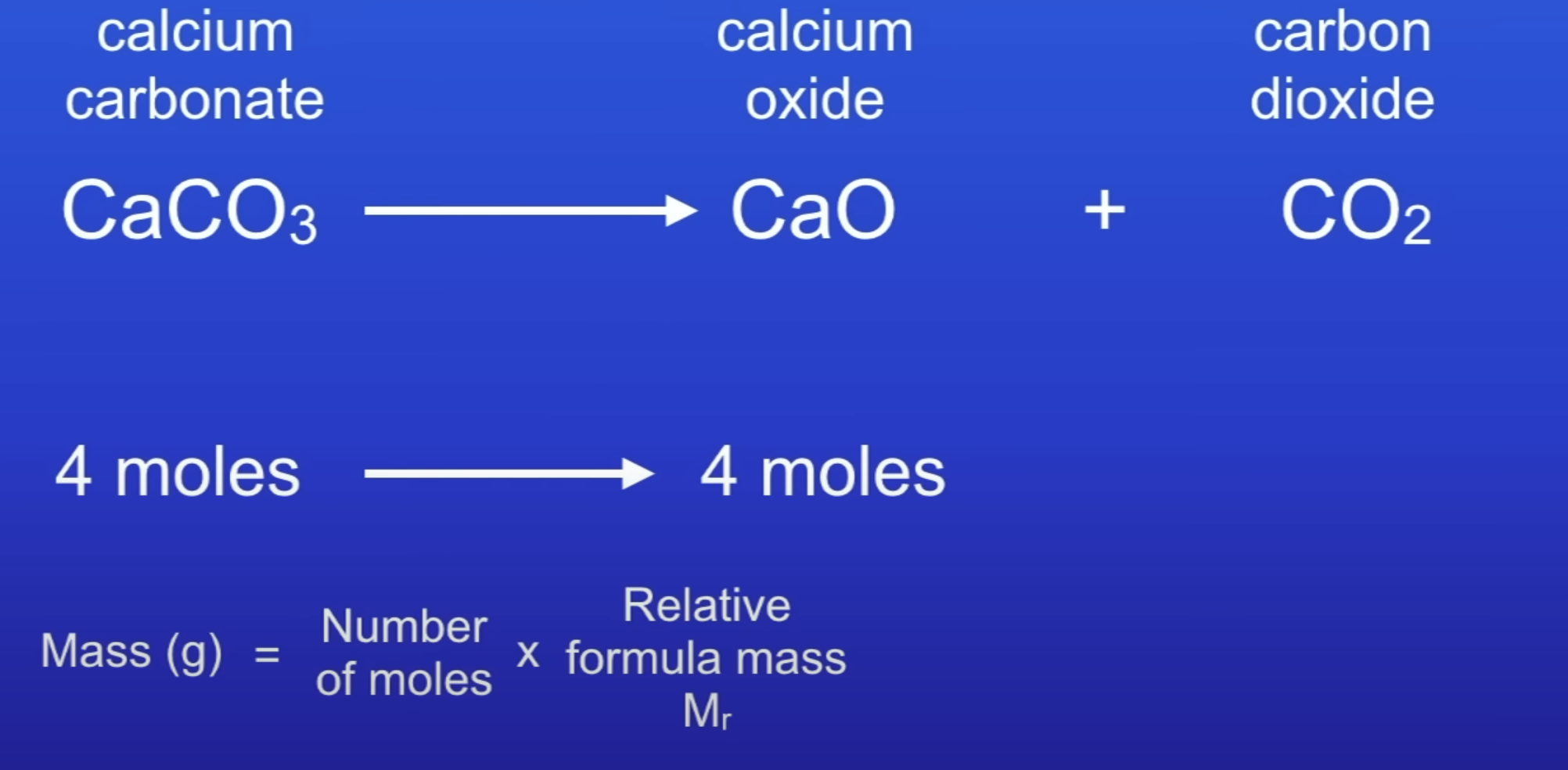
How to calc masses of reactants + products in chemical reactions?
Balance equation
Calc moles
Use molar ratio to find mass

4 × 100 = 400
Limiting reactant
Reactant that is completely used up
Why is it called the limiting reactant?
It limits the amount of products formed
Excess reactant
Reactant not fully used up
In chemical reactions why is an excess of 1 reactant used, rather than exact amounts?
To ensure all the other reactant is used
If solid → can filter excess
How to find the limiting reactant?
Calc no of moles
Find molar ratio
Compare to balanced equation
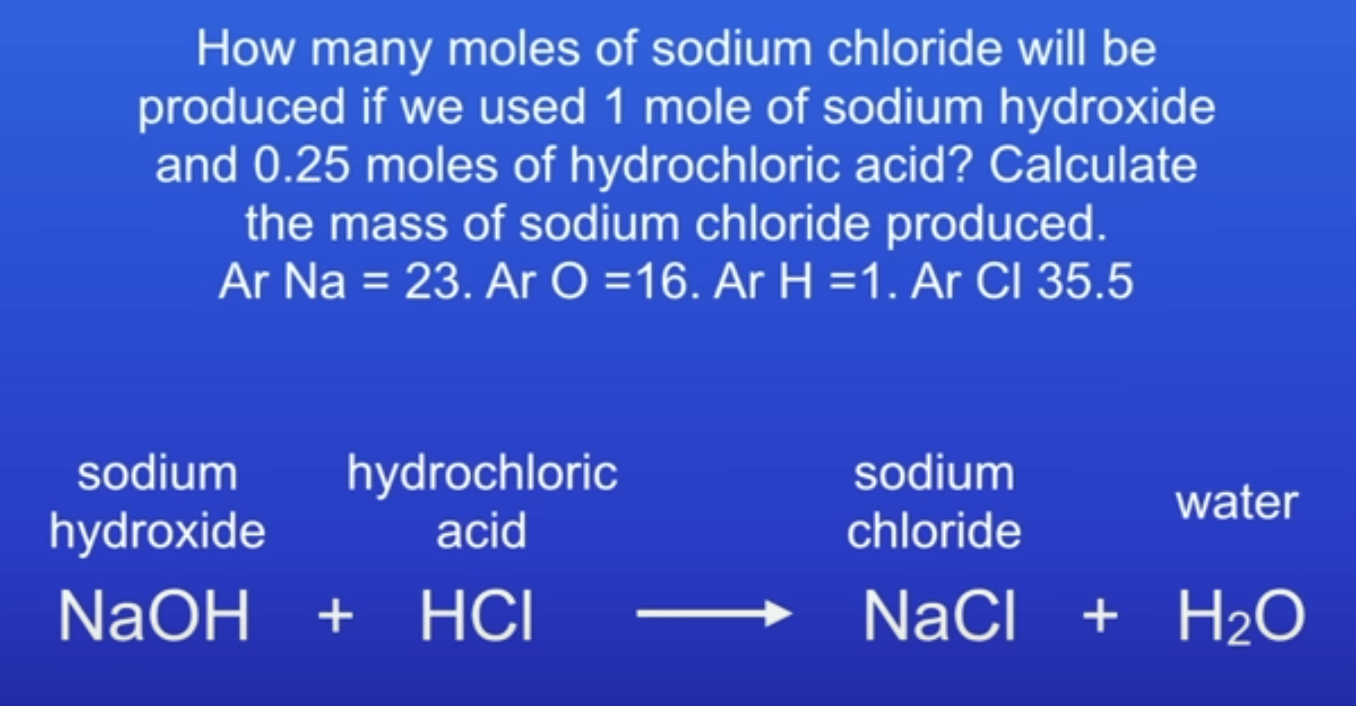
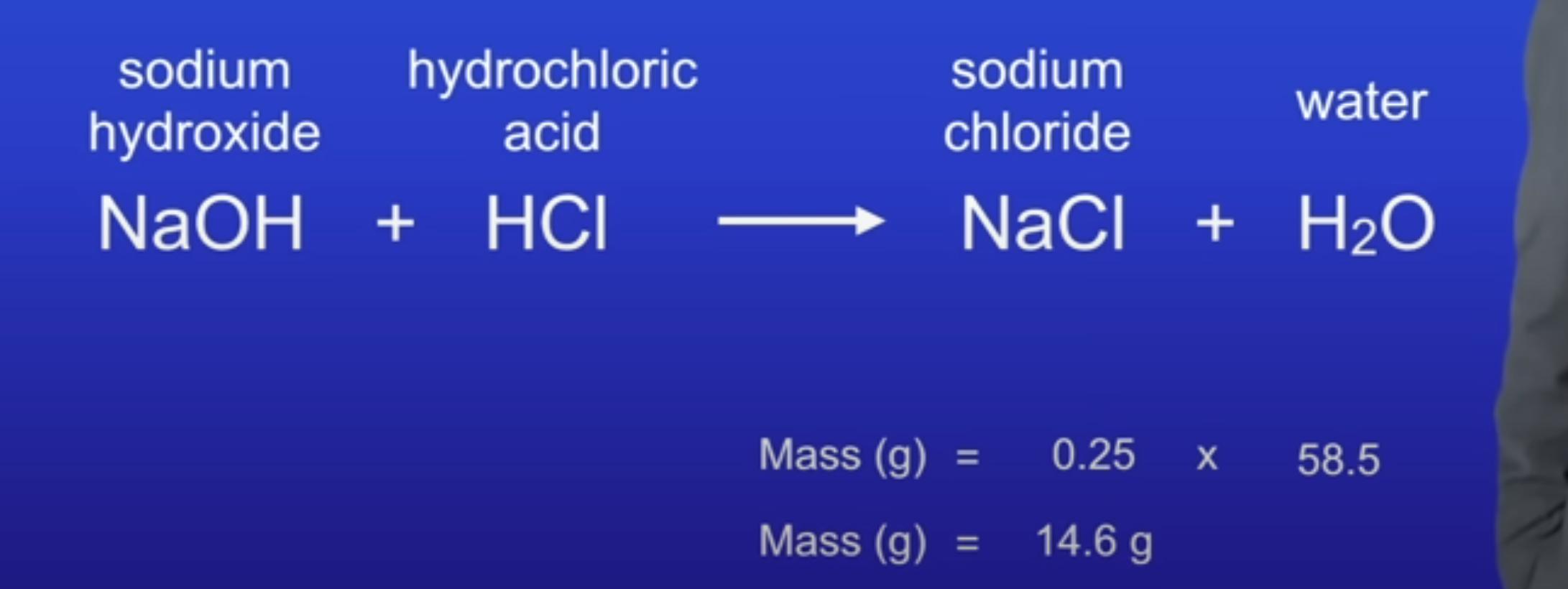
Find the limiting reactant
LR = HCl
1:1 ratio of reactants
1 mol : 0.25 mol
Concentration
Mass of a solute in a given volume of solution
Solute
Chemical dissolved in a solvent
Unit of concentration
g/dm3
mol/dm3
Decimeter
Litre (1000ml)
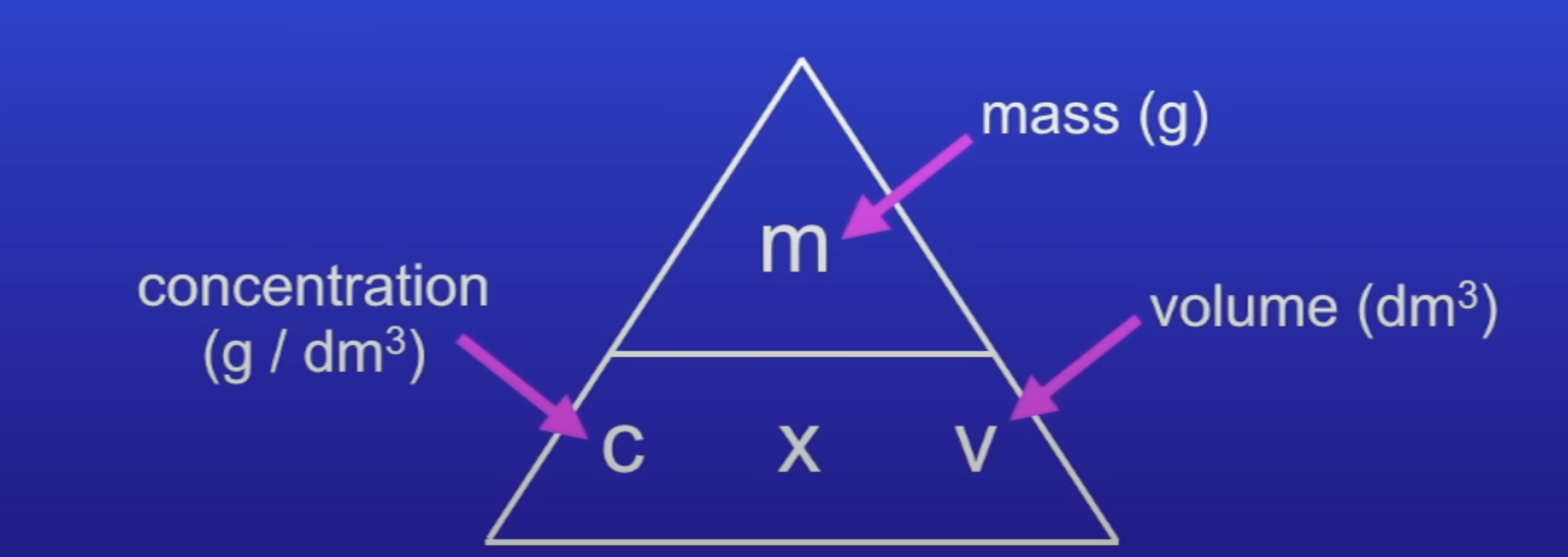
Concentration equation
conc = mass / vol
conc = mol / vol
How to increase conc of a solution?
Increase mass of solute, same vol of solution
Same mass of solute, decrease vol of solution
How do you get from cm^3 to dm^3
cm3 divide 1000 = dm3
Yield
Amount of product obtained from a chemical reaction
Why isn’t it always possible to achieve a 100% yield
Reversible reaction doesn’t go to completion
Some product lost when it is separated from the reaction mixture
Some reactants react in ways diff to the expected reaction
Percentage yield equation

100% yield
All reactants end up as products
Percentage yield
Actual yield compared with the max theoretical amount as a %
Can a yield greater than 100% be achieved- why / why not?
No
Can’t create atoms
Due to law of conservation of mass
Percentage yield can’t be?
Greater than 100%

Calculate % yield
20%
Theoretical yield
Max amt of product expected from the reaction
Actual yield
Amt of product actually obtained from the reaction
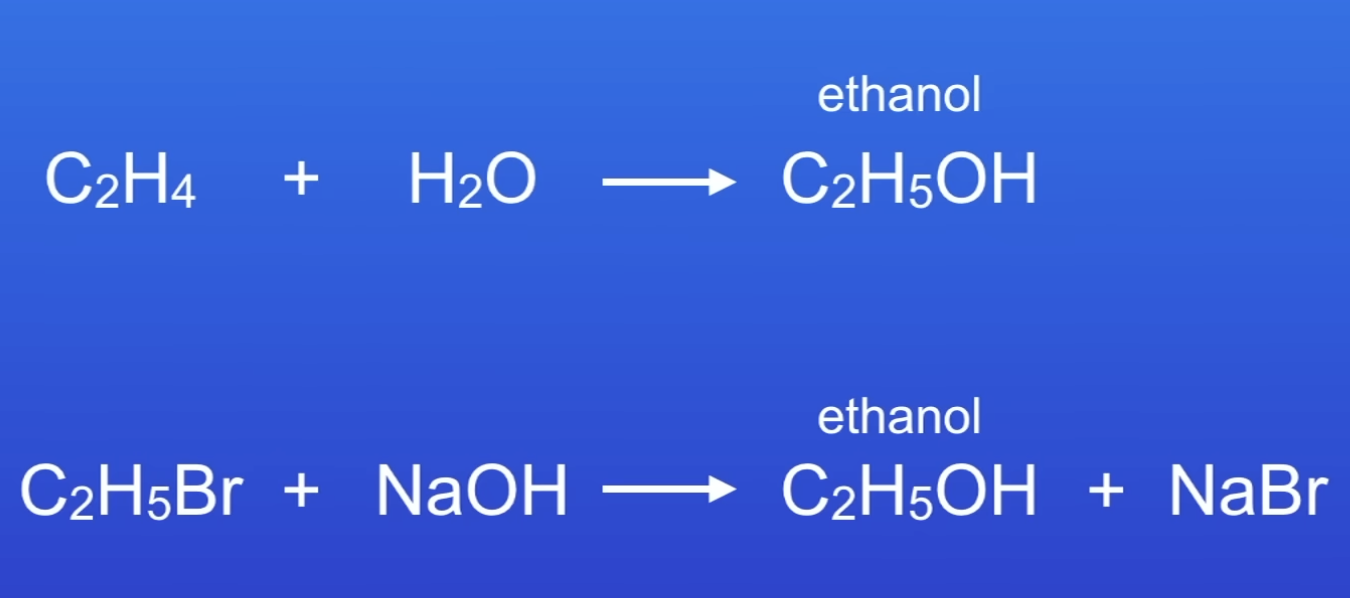
Which reaction should be chosen to make ethanol and why?
1st → efficient, high atom economy
All products in reactant end up as useful product
No waste products
Atom economy (utilisation)
A measure of the amt of starting materials that end up as useful products
Determines efficiency of a reaction
Why is it important to use reactions with high atom economy?
Sustainable development
Economic reasons
How do reactions with high atom economy increase sustainability?
Resources not wasted
How are reactions with high atom economy economical?
Minimize production of unwanted products → money saved
Atom economy equation
Mr of desired products (FE) / Sum of Mr of all reactants (FE)
FE = from equation

Key feature of atom economy
Big numbers count
Can atom economy be greater than 100%- why / why not?
No
Can’t create atoms
Law of conservation of mass
Mass of reactants = mass of products
What do reactions often produce + why is this bad?
Unwanted side products
Waste of money
What do scientists do with unwanted side products?
Find a use for them
Eg in other reactions → money not wasted
Factors affecting if a particular reaction pathway is chosen to produce a product?
Atom economy
Yield
Rate
Equilibrium position
Usefulness of by-products
Concentration (moles)
No. of moles in a given vol of solution
How to get conc (g/dm3) from conc (mol/dm3)
Conc (g/dm3) = Conc (mol/dm3) x Mr
How to use the conc of 1 solution to determine the conc of another?
Use moles
CNV


0.71 (2dp)
Equal amounts of moles of gas occupy?
The same volume under the same conditions of temp + pressure
Volume of 1 mole of any gas at room temp + pressure
24 dm3
Room temp + room pressure
20°C
1 atmosphere
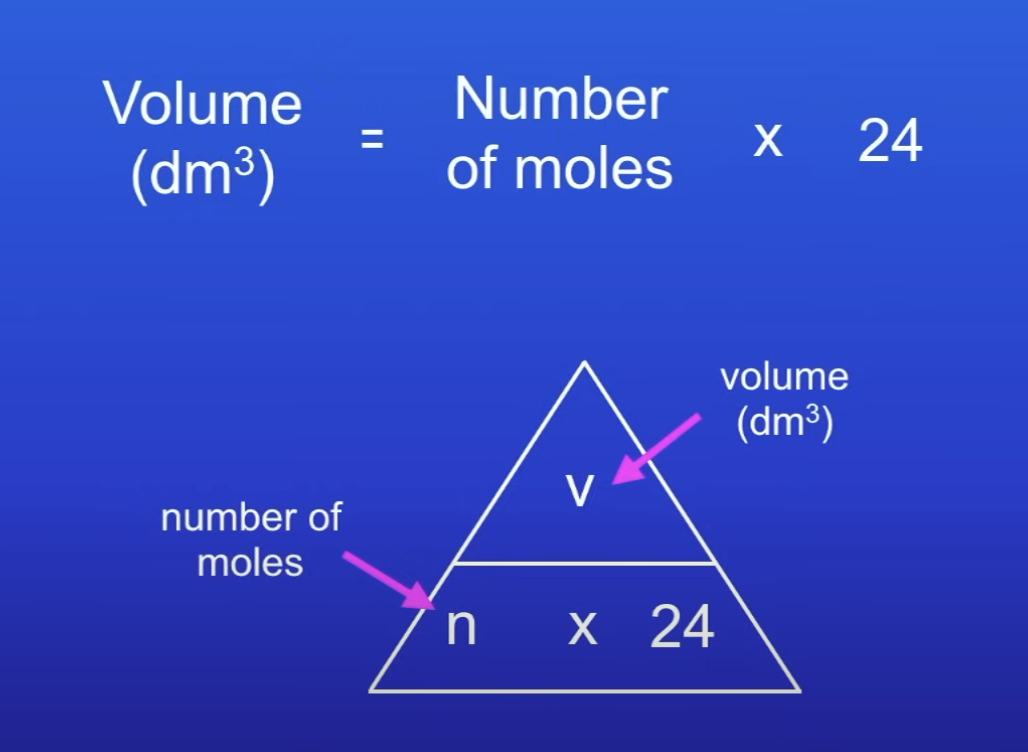
Volume of gas equation
No. of moles x 24 = vol of gas
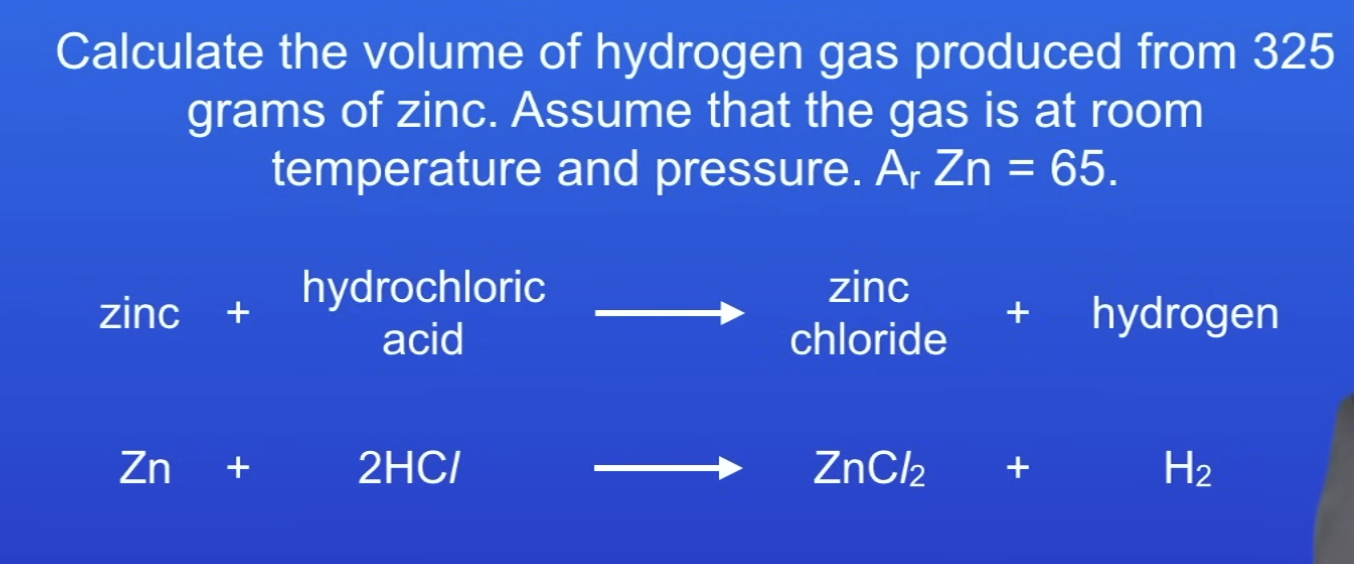
120 dm³

Why may some reactions involving a gas appear to break the law of conservation of mass?
Reaction in conical flask
Gas produced → gas escapes into air
So mass reading of products less than reactants
Examples of reactions that appear the break the law of conservation of mass?
Metal react w O2
Mass metal oxide greater than mass of the metal
Thermal decompositions of metal carbonates
CO2 produced + escapes into atmosphere
So metal oxide only solid product