7th Grade ELA Test Prep
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
setting
where and when the story takes place.

conflict
the problem in the story

main idea
what a piece of writing is mainly about

theme
the overall message of the story

chronological order
in the time order in which events happened

persuasive
used to convice the reader of the writer's point of view

myth
a fictional tale that explains the actions of gods or the causes of natural phenomena
autobiography
the story of a person's life written by that person in first person point of view

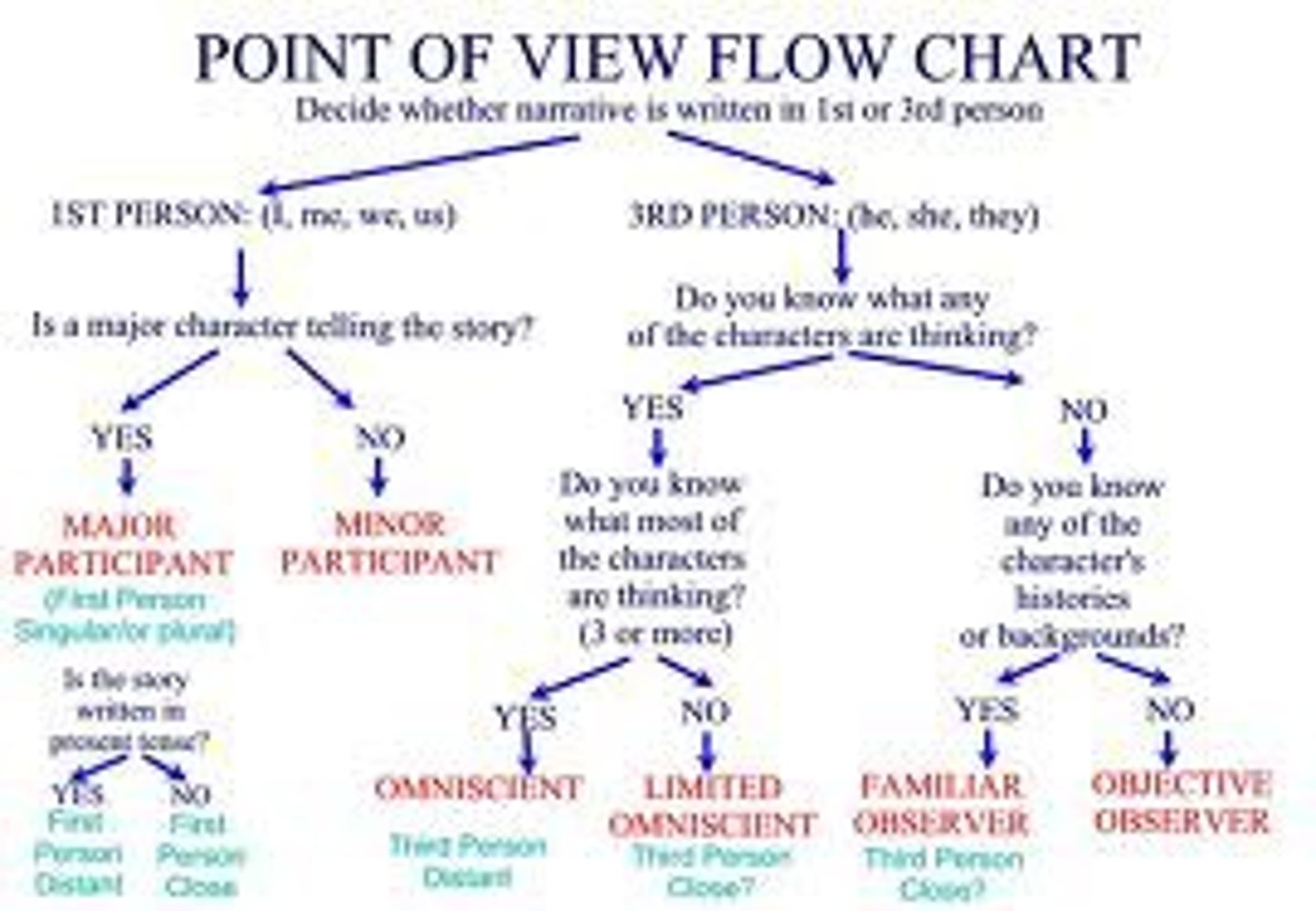
point of view
the perspective from which a story is told
alliteration
the repetition of consonant SOUNDS at the beginning of words. For example, Sally sells seashells by the sea shore.
personification
giving human qualities to non-human things

simile
comparison using like or as. Clue: You "smile" when you see someone you like." Example: The car was as cold as ice.

idiom
an expression with a meaning different from the literal meaning of the individual words

flashback
when a portion of the story goes back in time

foreshadow
The use of clues to suggest events that will happen later in the plot

inference/infer
to draw a reasonable conclusion from the information presented

justify / prove
to demonstrate that something is right; to defend with reasons

genre
a type of literature

dialogue
a conversation between two persons
"Let's go!" mom yelled.

captions
small text found near a picture that provides important information about the picture

diagrams
A drawing that shows or explains something...usually includes labels and captions.
fiction
a literary work based on the imagination and not necessarily on fact.
nonfiction
Writing that tells about real-life, people, places, things, ideas, or events.

onomatopoeia
the use of words that represent sounds
rhyme scheme
the pattern of rhyme in a poem (ex. ABAB)
contradict
to disagree; to say the opposite

mislead
Give the wrong idea; to deceive; to lead someone in the wrong direction.
cause
the reason why something happens

narrator
the person who is telling the story; the speaker

comparison
Shows how two things are alike/different or how one is better than the other ("This blanket is like a fluffy cloud.") (Commercials might show how one product is better or cheaper than other brands. Politicians might show how their policies or positions are better than their opponents.)
exaggerate
Sometimes authors overstate the facts leading to a false of importance. (We will all be doomed if we don't take a stand now!) (This is a one-time offer. You can't get this price after today.) Key words: always, never, everyone

metaphor
a comparison or two unlike things without using like or as

hyperbole
elaborate exaggeration

imagery
a collection of word pictures that appeal to the reader; uses devices such as metaphor, simile, etc.
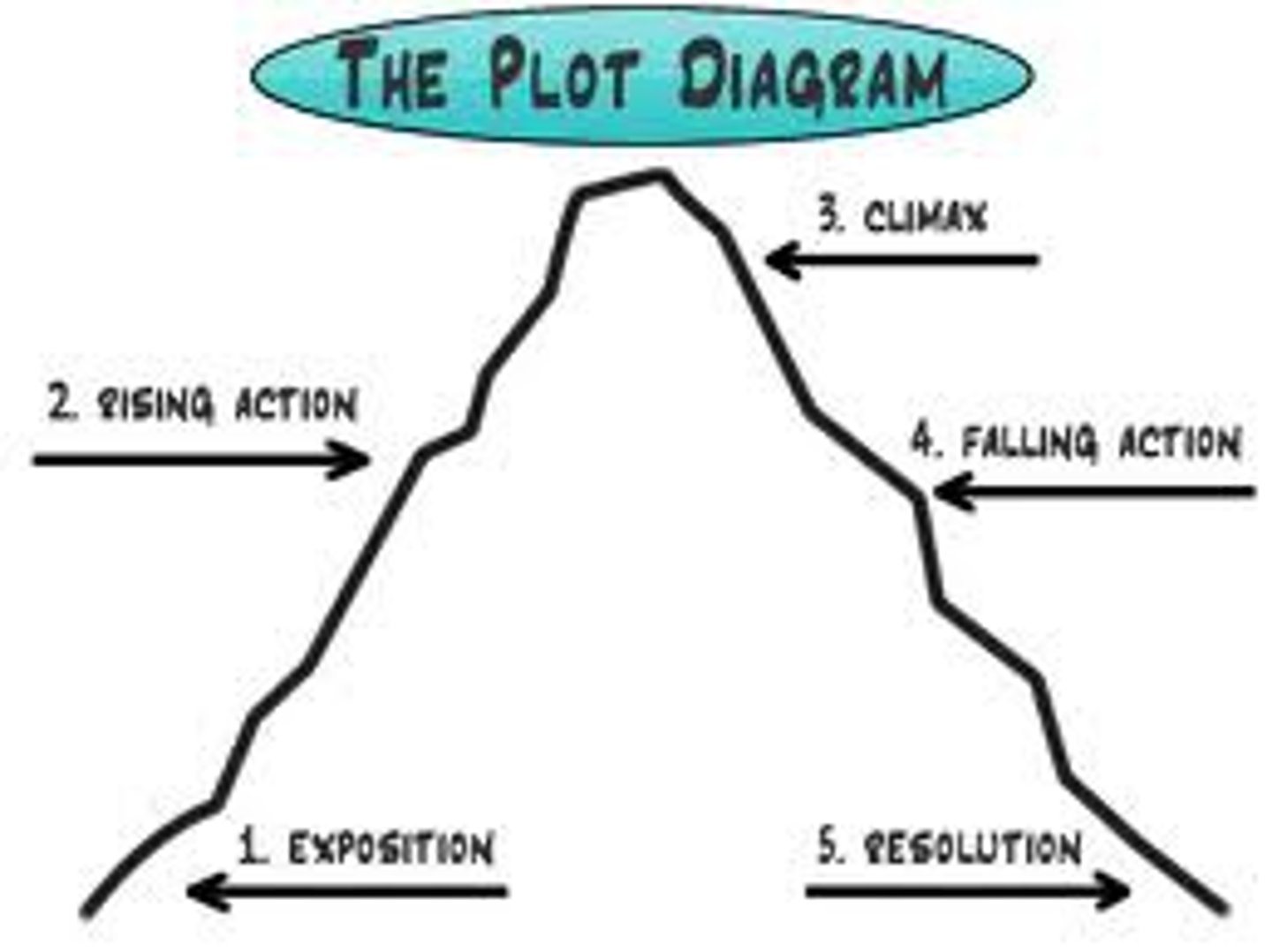
exposition
the part of a story (usually the beginning) which explains the background and setting of the story. The characters are often introduced.

rising action
the central part of a story during which various problems arise, leading up to the climax

climax
the turning point in the action of a story--the problem is solved
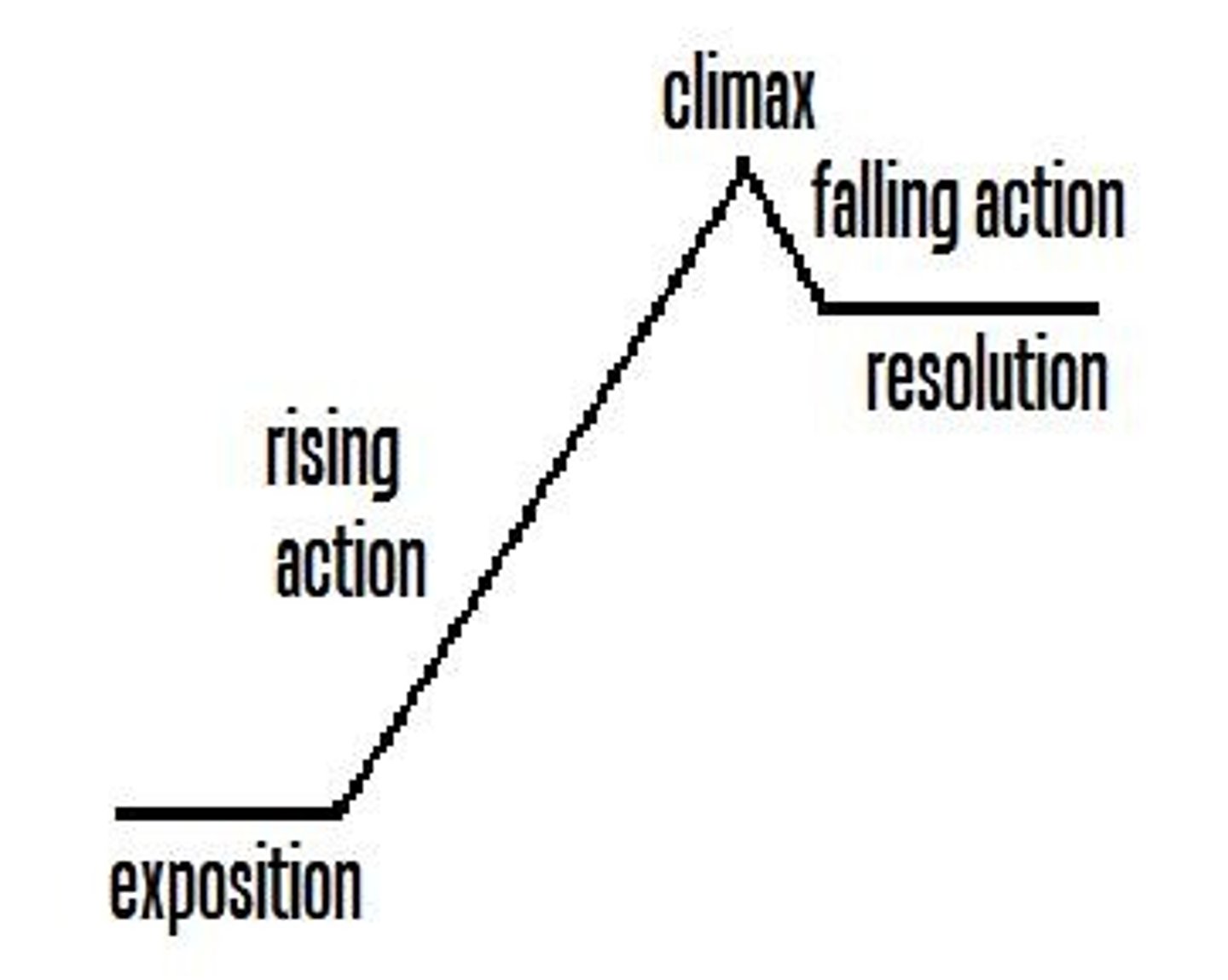
falling action
the part of a story which follows the climax or turning point
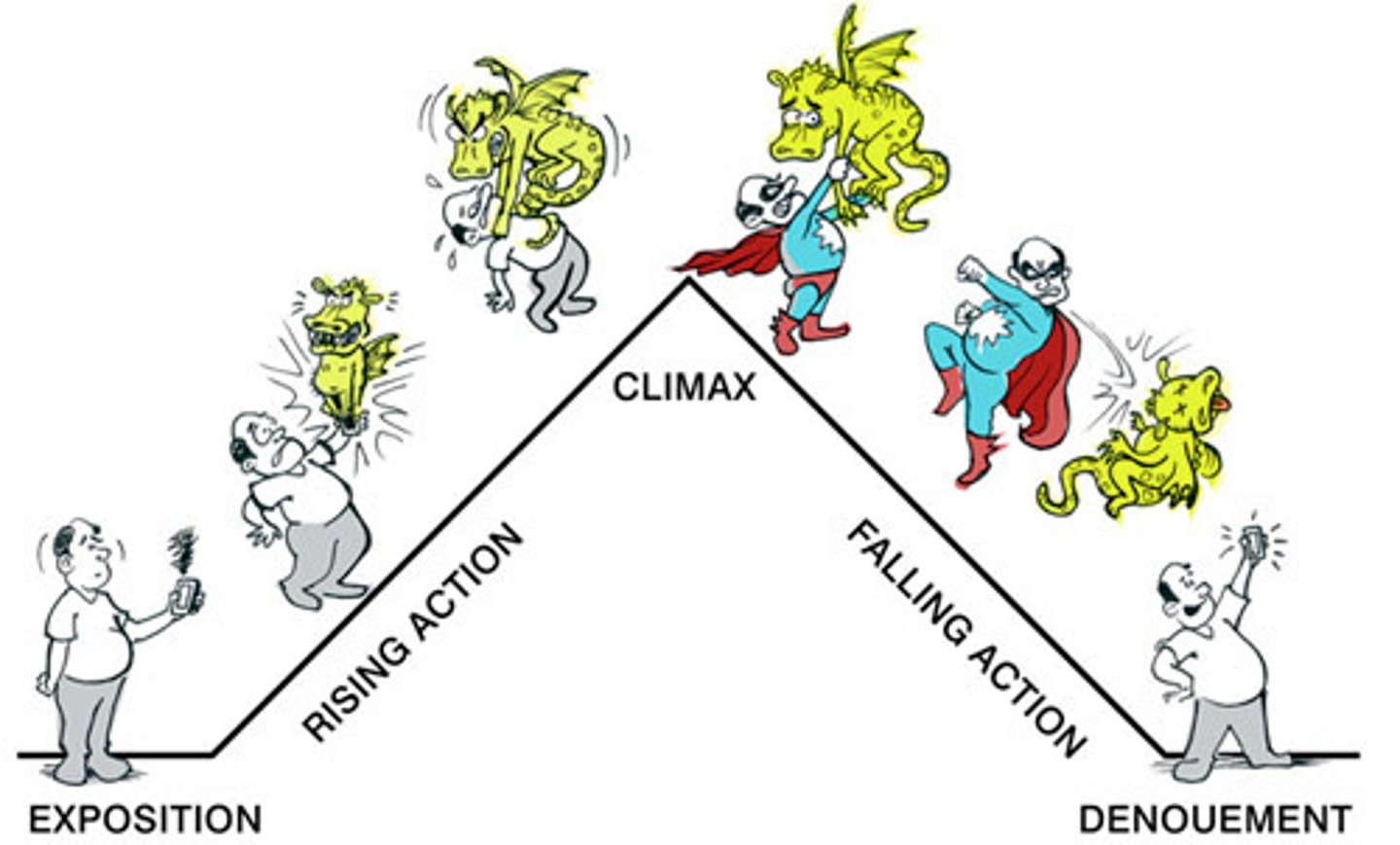
resolution
the ending or final outcome of a story

drawing conclusions
combining several pieces of information to make an inference

figurative language
language that means more than what it says on the surface; usually gives us a feeling about its subject

plot
the events that make up a story
prefix
a word part that can be added at the beginning of a word to make a new word

suffix
a word part that can be added at the end of a word to make up a new word

text features
the parts of a text that stand out (diagram, table of contents, index, etc)
affect
to influence
role
the actions and activities assigned to or required or expected of a person or group

impact
influencing strongly
convey
make known
playwright
The person who wrote the play/drama.

author's purpose
The reason an author writes the text--to persuade, inform, explain and entertain

motivation
the reason the character says or does something
audience
Who the piece of text was originally written for. Example: in a letter, look at who the letter is addressed to (Dear Mom)
stanza
similar to a paragraph but in a poem
line
similar to a sentence but in a poem
result
the outcome of an experiment or problem

related
connected
source
Where information comes from.
message
The theme or central idea of a work, the insight it offers into life

character traits
qualities that characters possess (honesty)
tone
the attitude, or feeling that the author has about the subject
mood
the feeling or emotion the reader gets when reading a passage

symbolism
a person, place, or thing that represents something beyond its literal meaning. (ex. A heart might represent love.)

details
the bits and pieces of information that support the main idea

text structure
the way an author arranges/organizes text (organizational pattern)
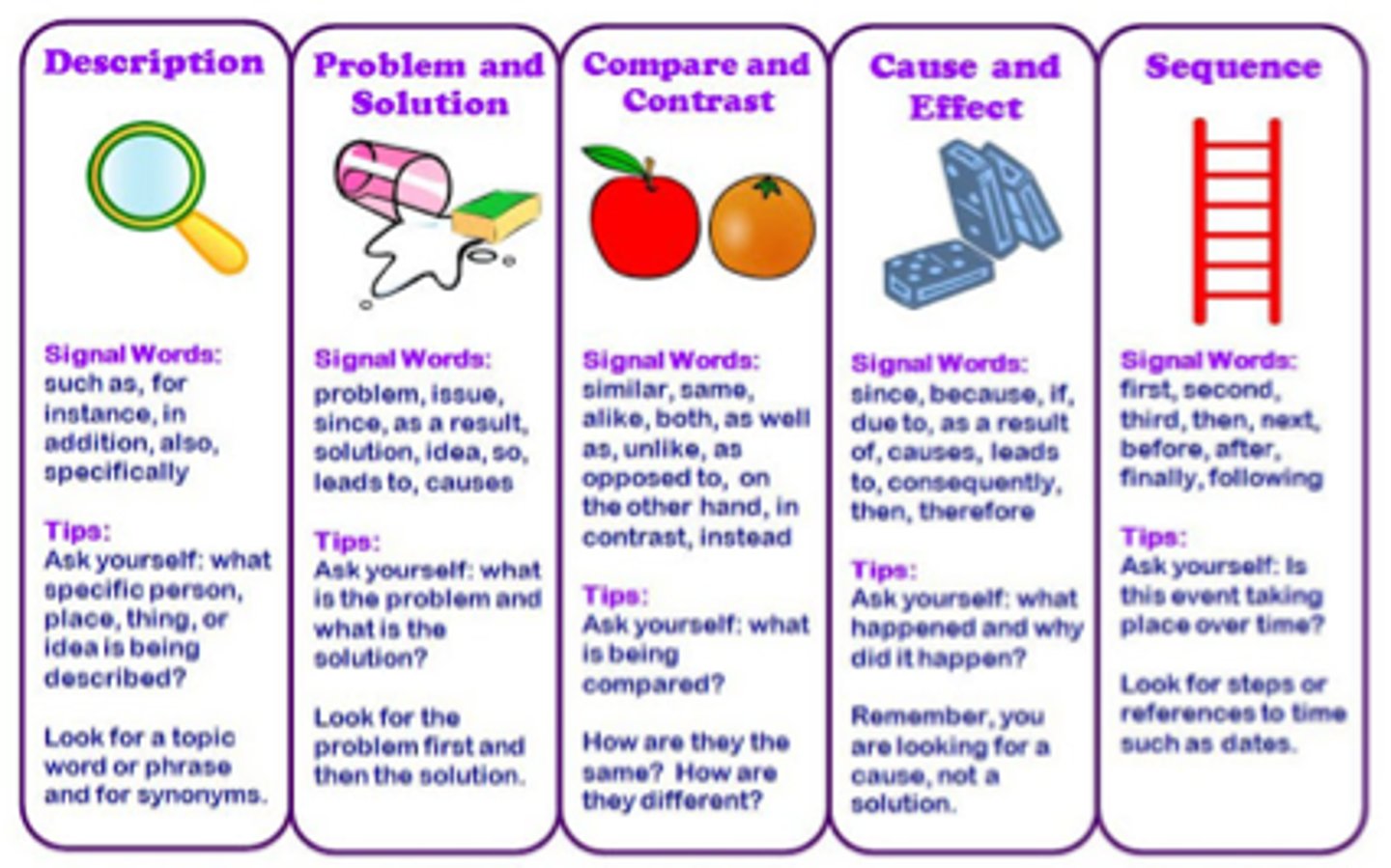
effect
what happens as a result of an event or action (what happens after)
fact
a statement that can be proved by experts, looking up information in a book, etc.

opinion
a personal belief or judgement that can not be proven

speaker
the person that narrates the poem
synonym
words that have the same meaning

antonym
words that are opposites

act
part of a play
scene
part of an act in a play
selection
another name for a reading passage
emphasize
to stress upon; something that is important

omni-
Greek root meaning, "all"
chron/o
Greek root meaning, "time"
auto
Greek root meaning, "self"
bio
Greek root meaning, "life"
graph
Greek root meaning, "write"
photo
Greek root meaning, "light"
re-
Latin prefix meaning, "again"
pre-
Latin prefix meaning, "before"
mono
Greek root meaning, "one"
bi-
Greek root meaning, "two"
tri-
Greek root meaning, "three"
omni-
all