Topic 3: Alleles and Inheritance (g-i)
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Define a gene
A section of DNA that codes for the production of a protein
Define an allele
Different form of the same gene
Define phenotype
The feature that results from a genotype (the observable characteristic)
Define a genotype
The allele each cell has for a certain feature
Homozygous meaning
Two copies of the same allele (e.g TT or tt)
Heterozygous meaning
Two different alleles (e.g Tt)
Dominant meaning
The allele that is always expressed, even in a heterozygous state and is represented by a capital letter
Recessive meaning
Is only expressed when there are two copies of the allele present, shown as lower case of the same letter
Define a gamate
A haploid sex cell
What is a zygote?
The cell formed when gamete’s fuze together in fertilisation
Codominant meaning
When two alleles are expressed in the same phenotype
What are all our features controlled by?
Genes which are found on chromosomes
When two different alleles are in the same cell, which one is expressed?
The dominant one
What is monohybrid inheritance?
This is the inheritance of a single characteristic.
It can be represented in a single diagram, called a punnet square
What is a punnet square?
It shows a first generation/ set of offspring or second generation of offspring, where two individuals from the first generation are bred together
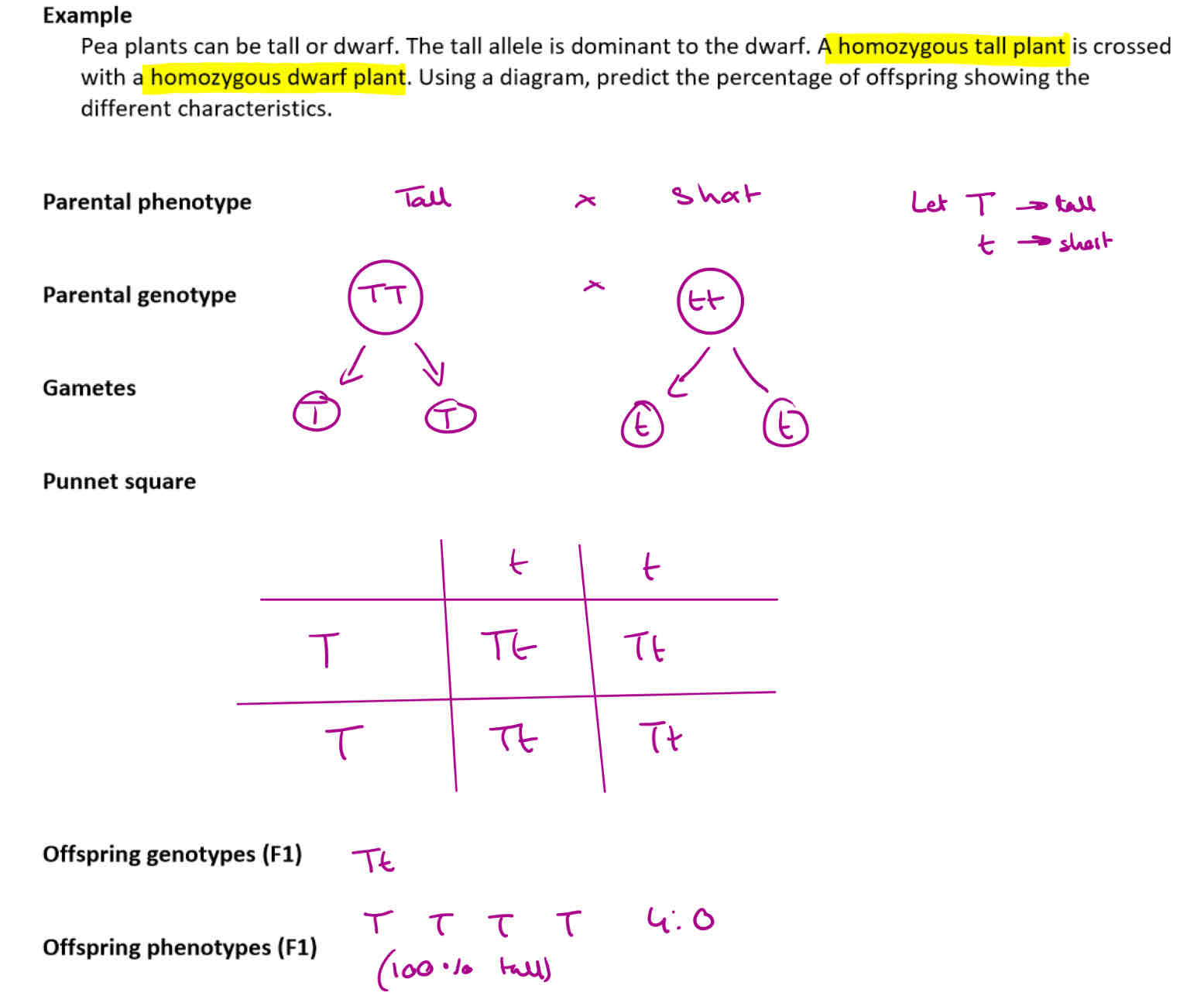
Question: Pea plants can be tall or dwarf. The tall allele is dominant to the dwarf. A homozygous tall plant is crowded with a homozygous dwarf plant. Using a diagram, predict the percentage of offspring showing the different characteristics
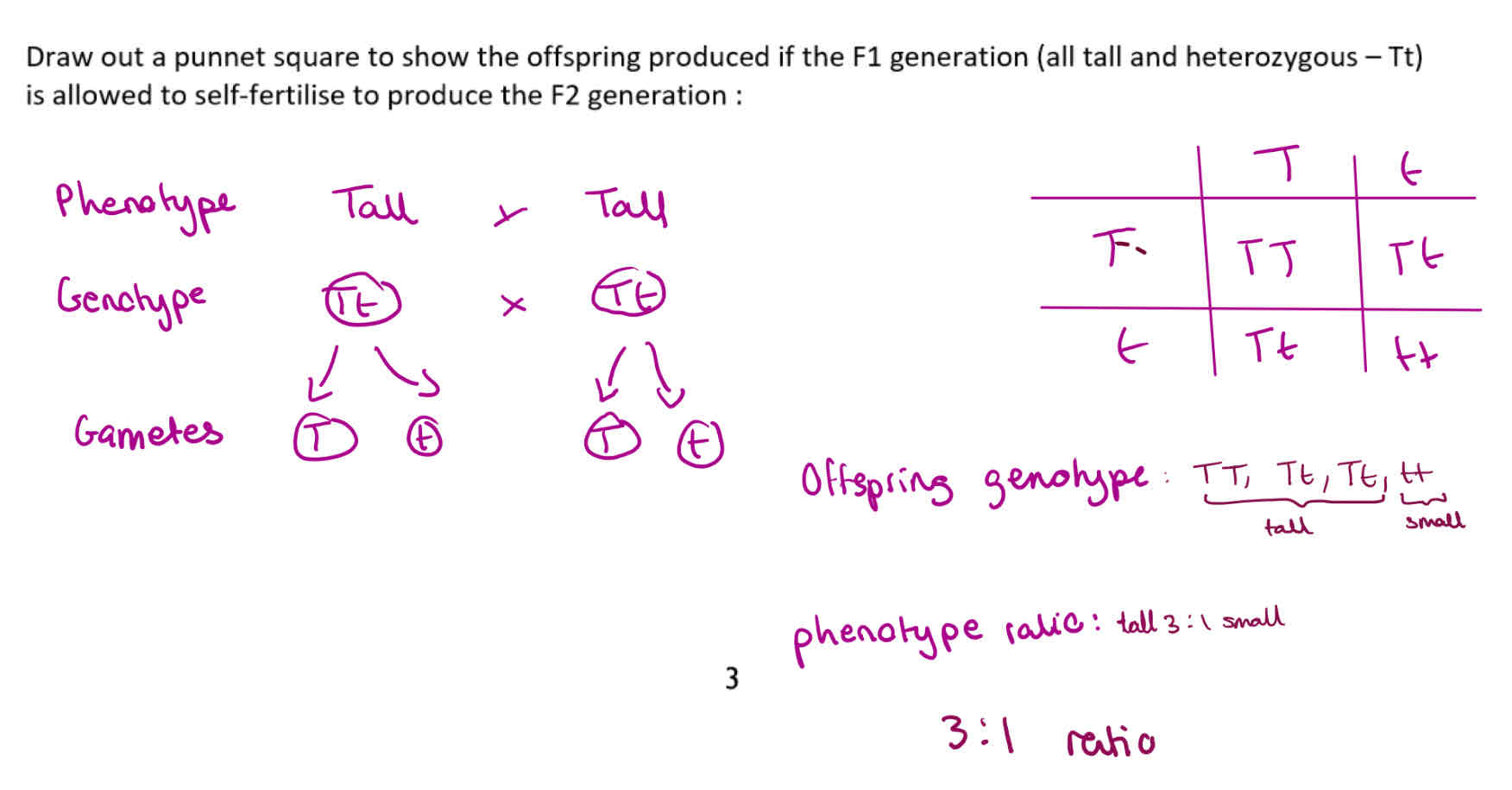
Question: Draw out a punnet square to show the offspring produced if the first generation (all tall and heterozygous- Tt) is allowed to self-fertilise to produce the second generation
What are pedigree charts?
diagrams which show how genotypes and their resulting phenotypes are inherited in families
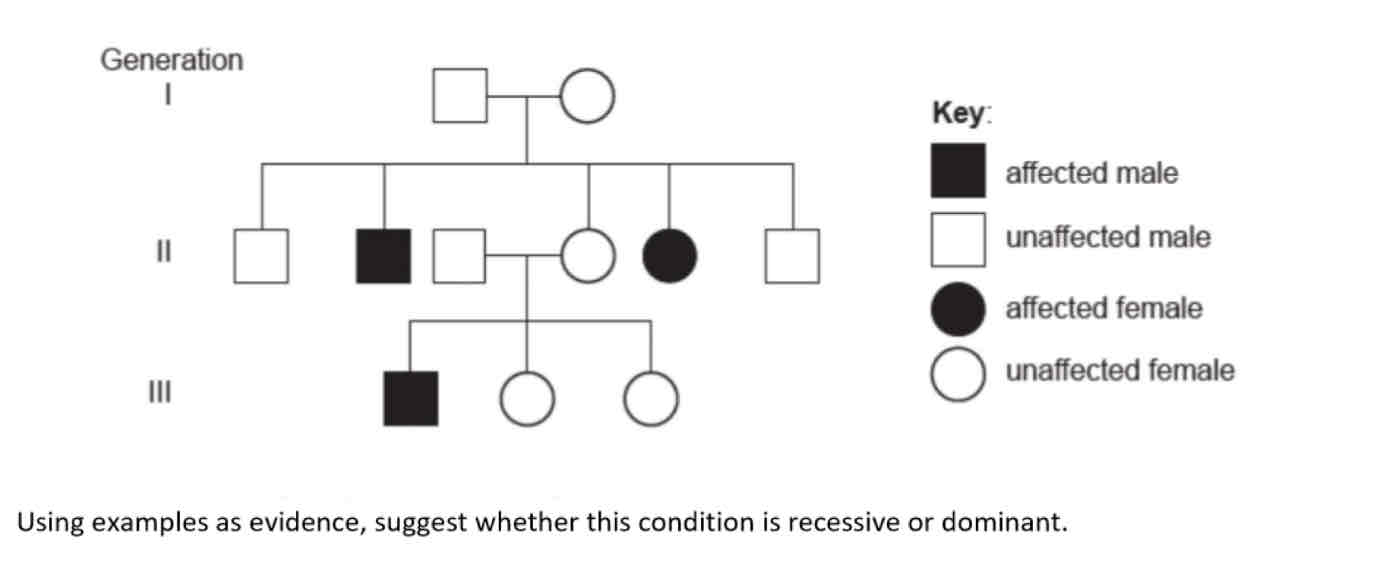
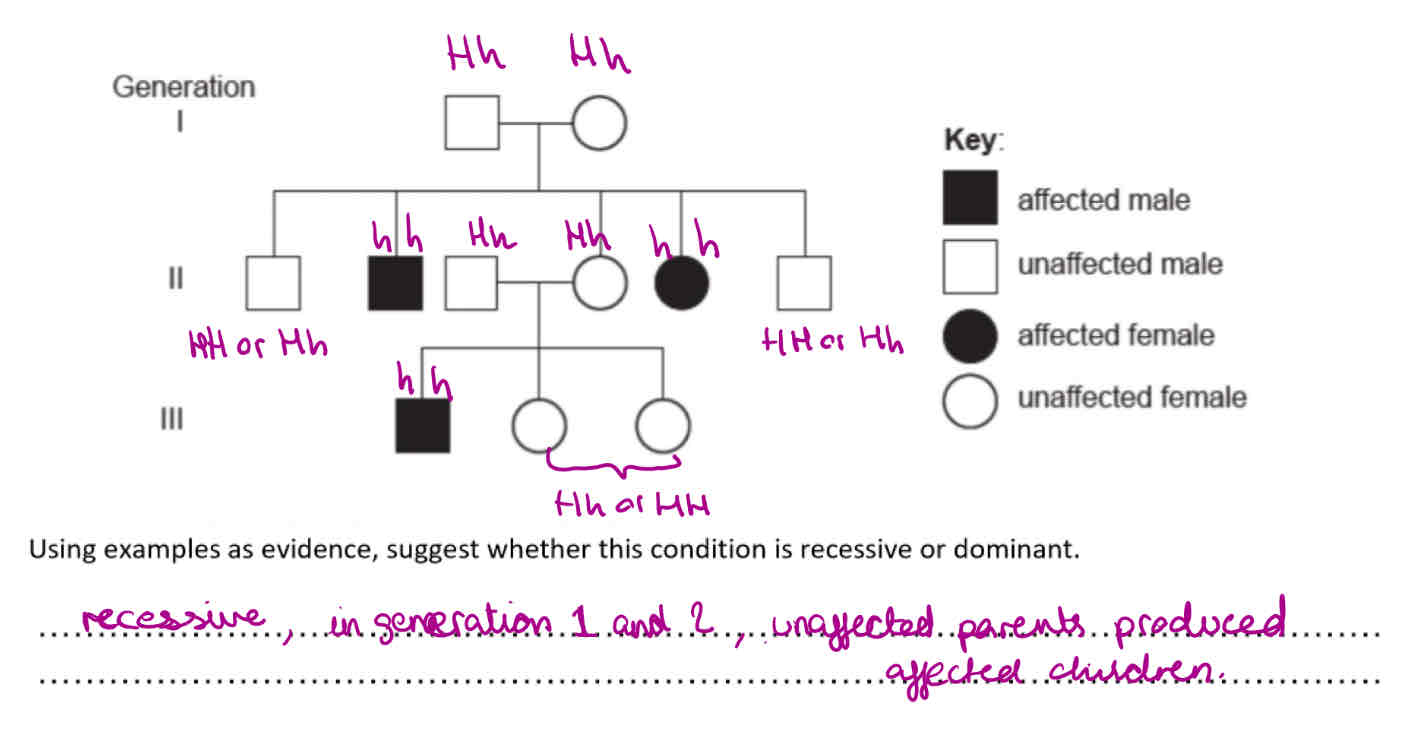
What is the genotype of the affected boy’s father?
Aa
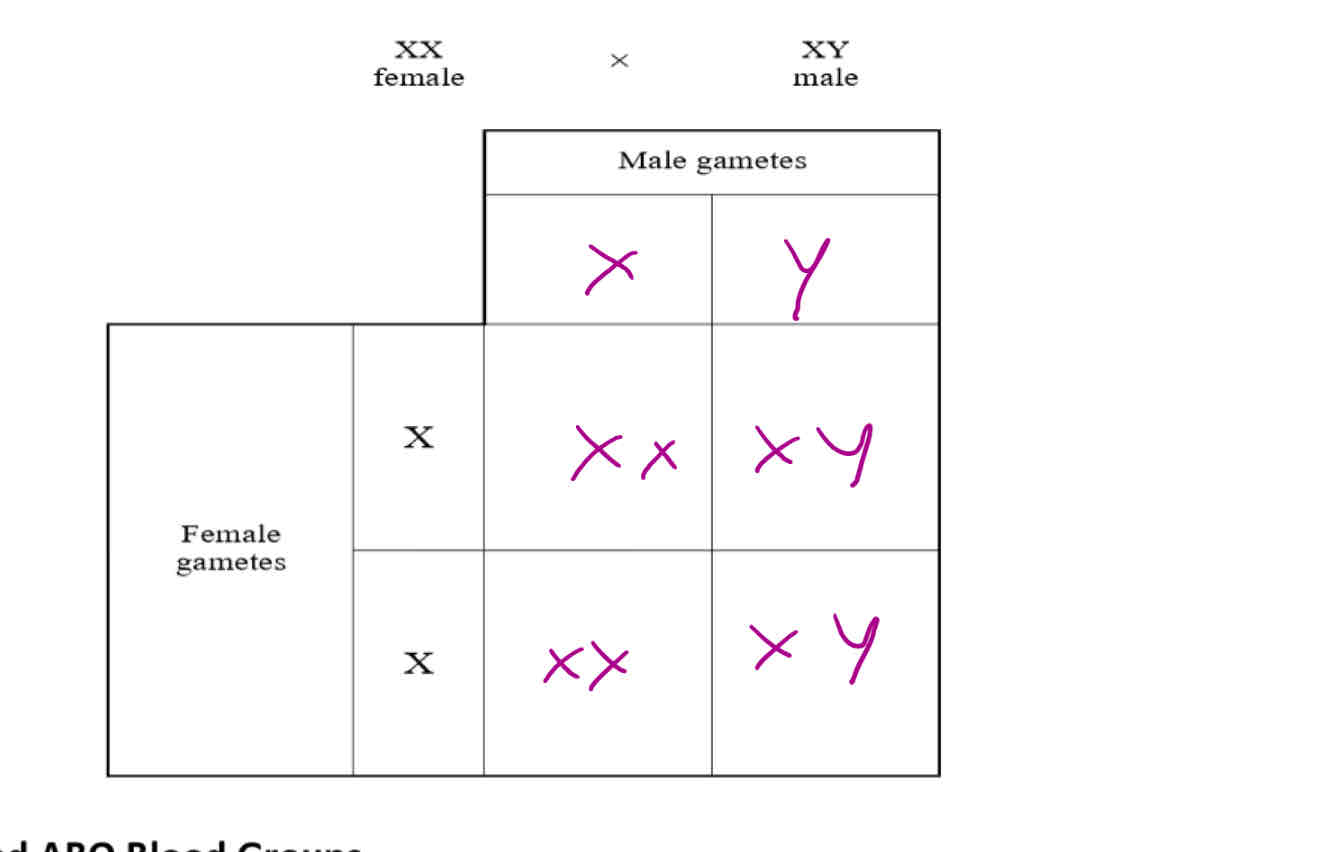
What is sex determination?
Sex is not controlled by a single gene, but by the presence or absence of the Y chromosome. Males have XY chromosomes, females have XX chromosomes
What are the sex chromosomes of males?
Males are XY, female are XX
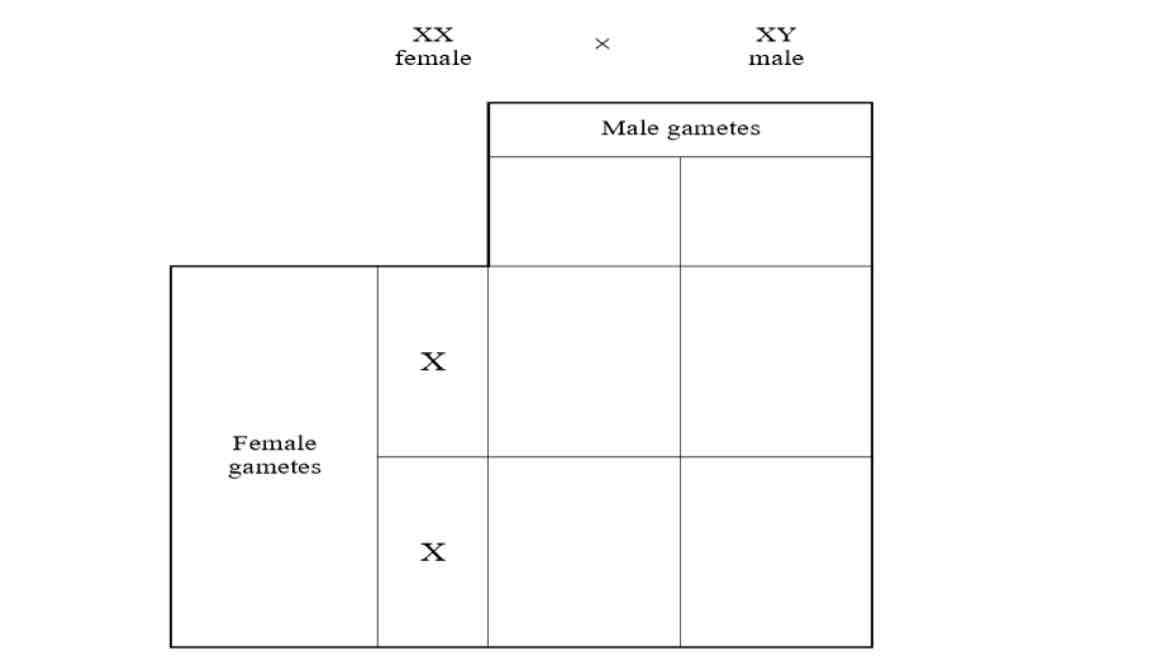
Complete the punnet square to show the sex determination in humans
What is codominance?
If two alleles are expressed in the same phenotype, they are called codominant.
A letter is chosen to represent the gene and then superscript letters are used to illustrate the alleles
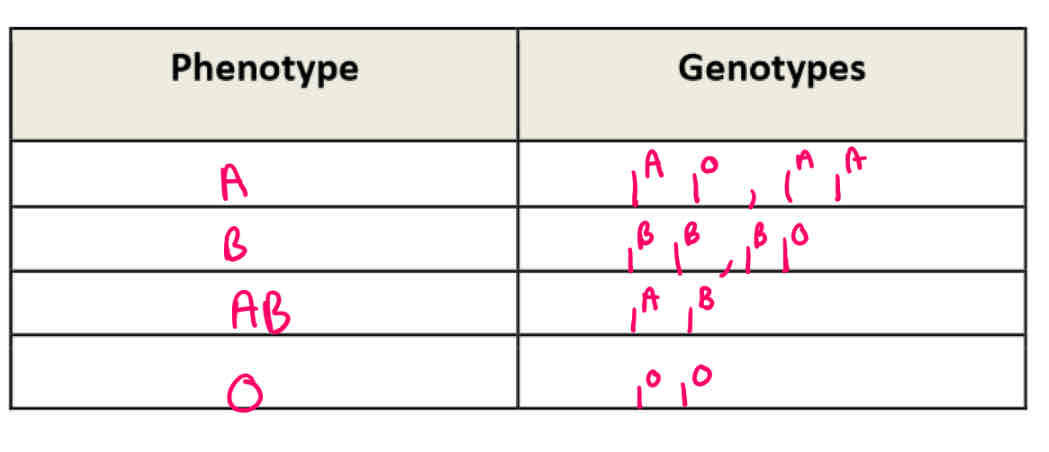
What are the 3 alleles for the gene for blood groups?
I^A, I^B, i^O
Which of the blood group alleles are dominant?
I^A and I^B
Which of the alleles for blood groups is recessive?
I^O
Complete this table with the possible phenotypes and genotypes of the 3 alleles
What is meant by sex-linked gened?
Genes/ alleles that are present of the X (or Y) chromosome
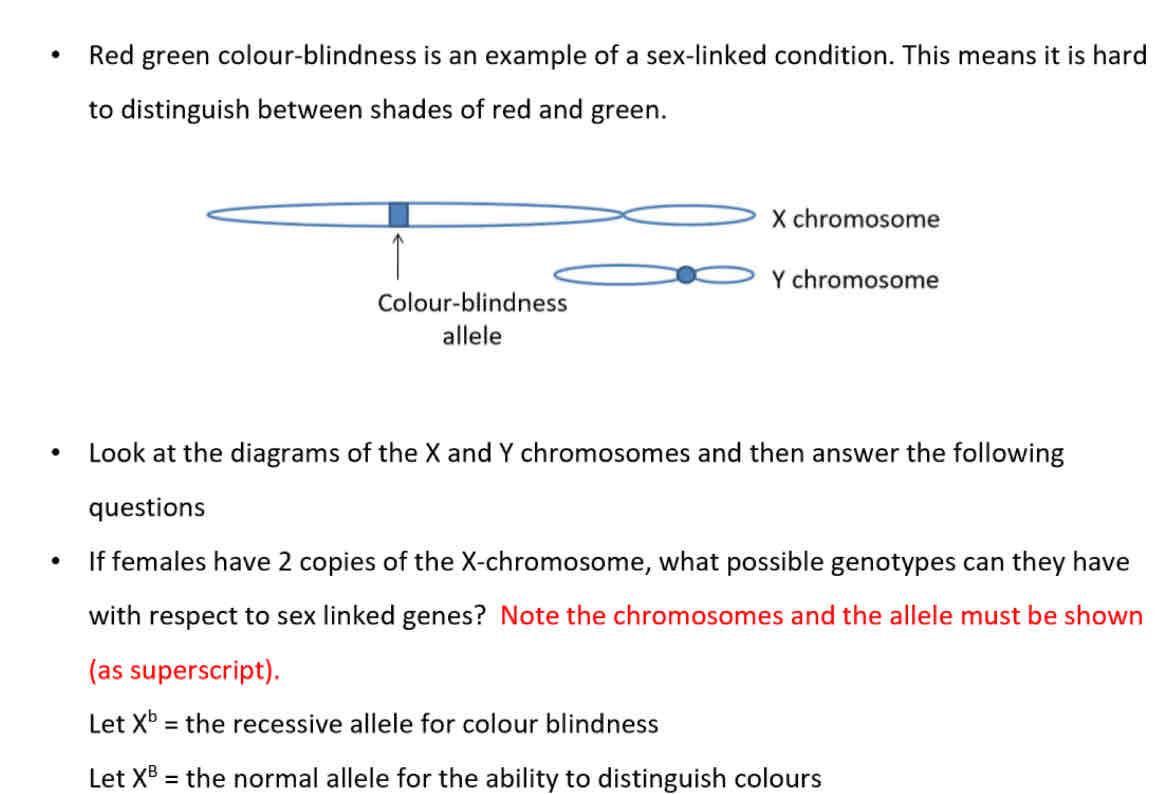
Because males only have one copy of the X-chromosomes, how many copies of the sex-linked genes will they normally have?
One genotype: X^B Y, X^b Y
If a recessive condition is caused by a gene on the X chromosome, then which sex is most likely to be affected?
Males, because females have a second recessive allele of the other X chromosome so the recessive condition is not expressed
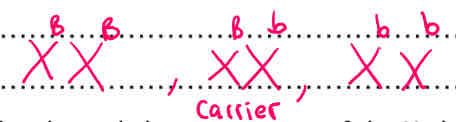
What is meant by a carrier of a disease?
How can females be carriers?
*When the condition is not shown in the phenotype but the excessive allele for the condition is on one of the X chromosomes , X^BX^b.
Females can be carrie because they have to X chromosomes so can express two different alleles. Therefore one may have the recessive condition and the other doesn’t, so they are a carrier as they have the allele for it but do not show it in their genotype

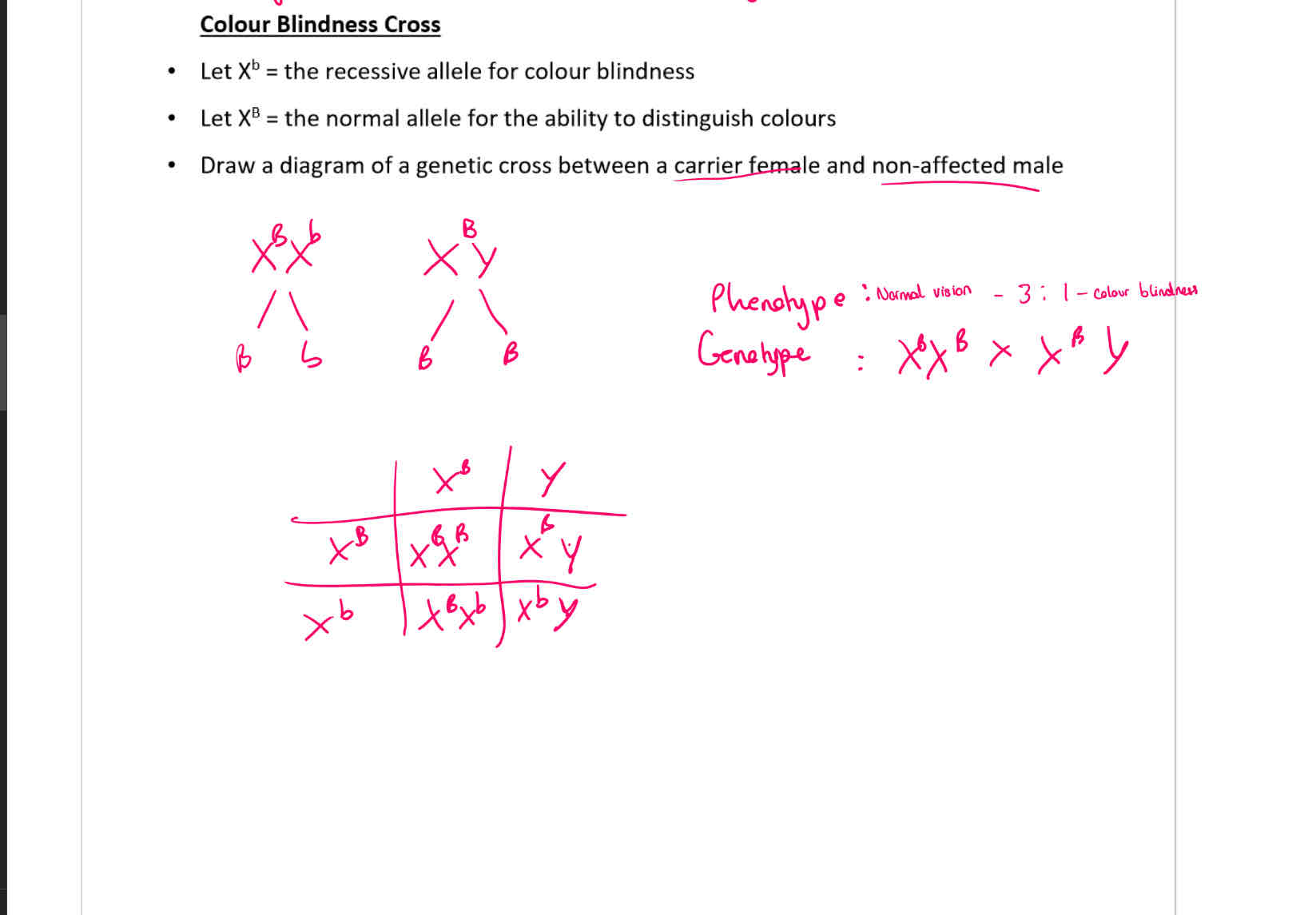
What is haemophilia?
A recessive, sex-linked condition carried on the X chromosome. It causes a longer than normal blood clotting time
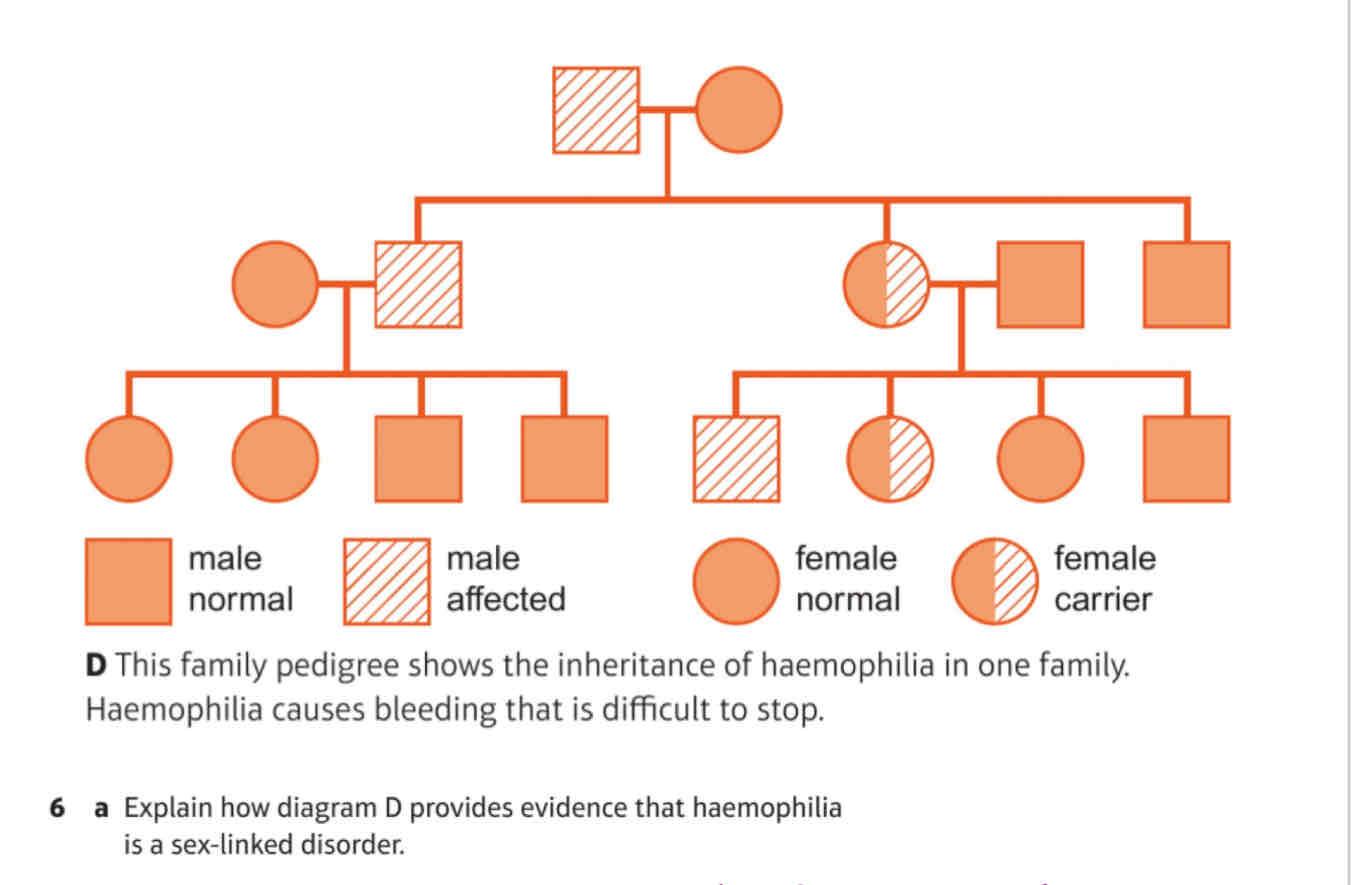
A) Explain how diagram D provides evidence that haemophilia is a sex-linked disorder.
B) Explain why a female carrier of the haemophilia allele does not suffer from the disorder
A) Because no female have the disorder, it is only in some males. Females are carriers
B) Because they have another X chromosome so the recessive condition is not expressed
What is Testcross?
It is used to determine the genotype of the unknown organism.
How can you use testcross to find out an unknown allele?
You cross the unknown with homozygous recessive alleles and if there is a recessive allele is in the offspring, the unknown was heterozygous
