BIOC 3021 - Essay Exam 2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Asparagine basics
Neutral Polar, nonessential. (Asp, N)
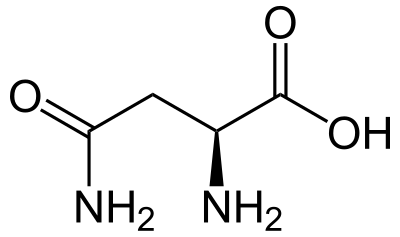
ASNS gene
what gene codes for asparagine synthase?
asparagine synthase function
converts aspartic acid into asparagine alongside glutamine, which gets converted into glutamic acid
thought to help maintain the normal balance of the four amino acids in the body
importance of asparagine synthase reaction
links nitrogen metabolism with energy metabolism
asparagine is a precursor for:
aspartate, an amino acid that transmits signals between neurons
blood-brain barrier
asparagine is unable to cross this, so the brain relies on asparagine synthase
what does nonessential mean?
can be synthesized by the human body, not required to be in our diet
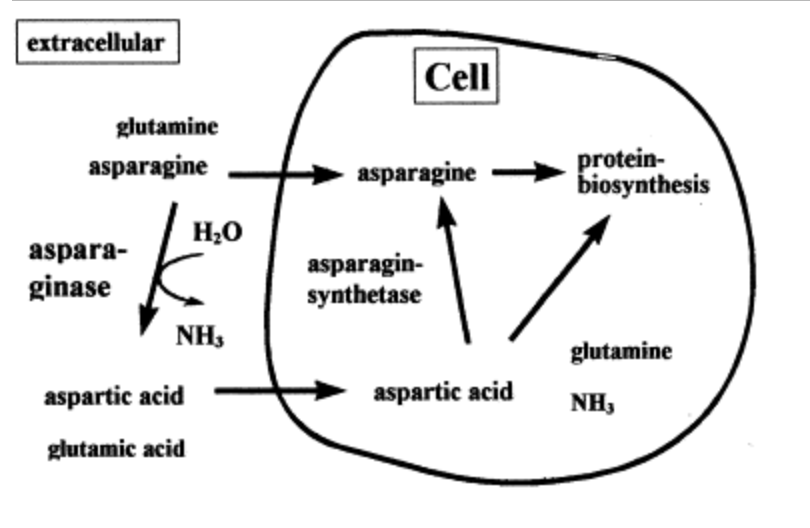
how is asparagine synthesized in humans?
through asparagine synthase, which converts aspartate and glutamine to asparagine and glutamate in an ATP-dependent amidotransferase reaction.
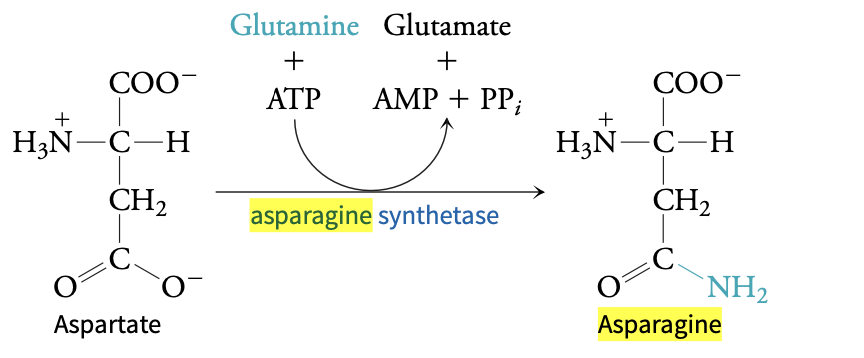
asparagine synthesis mechanism
Aspartate carboxyl is activated by an ATP-dependent process
Formation of β-aspartyl-AMP intermediate
Glutamine deamidation releases ammonia
Ammonia does nucleophilic attack on aspartyl, produces asparagine and glutamine
Features of R-group
amide, neutral polar (from carboxyamide), participates in hydrogen bond formation. In glycoproteins, the carbohydrates chain is often linked through this amide group.
asparagine role in body
Needed to produce many proteins as a precursor to other amino acids, break down toxic ammonia within cells, protein modification, and helps synthesize and release neurotransmitters
Synthesis and N-glucosylation of proteins
Nucleotide biosynthesis and ammonium metabolism
An amino exchange factor
asparagine location in protein structure
usually found near beginning of alpha helices as “asx turns and asx motifs” due to its ability to form H-bonds, or as amide groups in beta sheets.
thought to “cap” hydrogen bond interactions that would be otherwise “capped” by the polypeptide backbone
asparagine regulates the uptake of?
serine, arginine, and histidine
asparagine as an intermediate
breakdown produces malate, which can be oxidized in the citric acid cycle
can also be hydrolyzed by asparaginase back into aspartic acid, a precursor to other amino acids, and ammonia
asparagine as a precursor
for those fasting (when cells are starved for nutrients), asparagine and aspartic acid are utilized as precursors for de novo synthesis of glutamine and alanine in muscle
asparagine deficiency effect on brain
affects the growth of neural stem cells during development, could also cause increased cell death in post-mitotic neurons or gilal cells either due to the accumulation of substrates or a deficiency in its products. (research still inconclusive)
deficency may also lead to an accumulation of aspartate/glutamate in the brain, resulting in more neuronal damage
asparagine deficiency
caused by a mutation in the ASNS gene, causes neurological problems after birth. pathology includes
unusually small head size that worsens over time
developmental delays in mental and motor skills
exaggerated reflexes
weak muscle tone
epilepsy
blindness
when is asparagine essential?
necessary and sufficient to suppress glutamine deficiency apoptosis without restoring levels of other nonessential amino acids or TCA cycle intermediates, eg. when the body is deficient in glutamine
purpose of asparagine in proteins
provides key sites for N-linked glycosylation, can modify protein chain with addition of carbohydrate chains. essential for proper protein folding, stability, and cell signaling
mechanism of asparagine deficiency
leads to reduced DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis, inhibition of cell growth, and activation of apoptotic cell-death mechanisms
what role does glutamine play in asparagine synthesis?
glutamine acts as a amide donor, transferring the amino group to aspartate and resulting in asparagine and glutamate.