Chapter 2 - Kaplan MCAT Gen Chem Review
1/57
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
periods of periodic table
rows
groups of periodic table
columns
groups of periodic table have similar
chemical properties
valence electrons determine
chemical reactivity and properties of element
roman numeral represents the
number of valence electrons in neutral state
periodic table groups roman numerals from left to right
IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIIIB VIIIB VIIIB IB IIB IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA
/
1A 2A 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 8B 8B 8B 1B 2B 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A
2 rows of periodic table separated
lanthanides and actinides
A elements
-representative elements
-valence electrons in s or p
B elements
-nonrepresentative elements
-transition elements: valence electrons in s and d
-lanthanide or actinide series: valence electrons in s and f
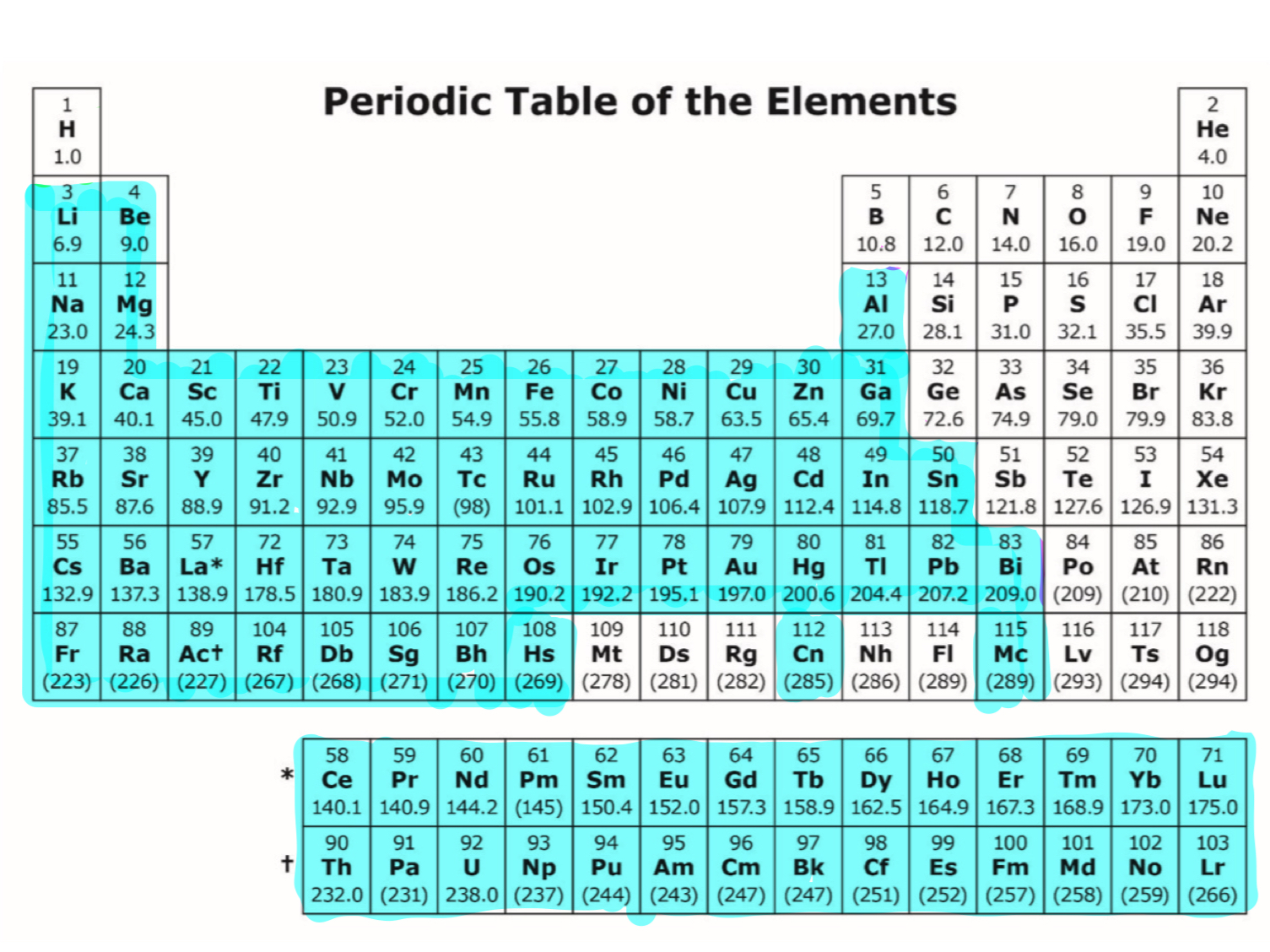
metals
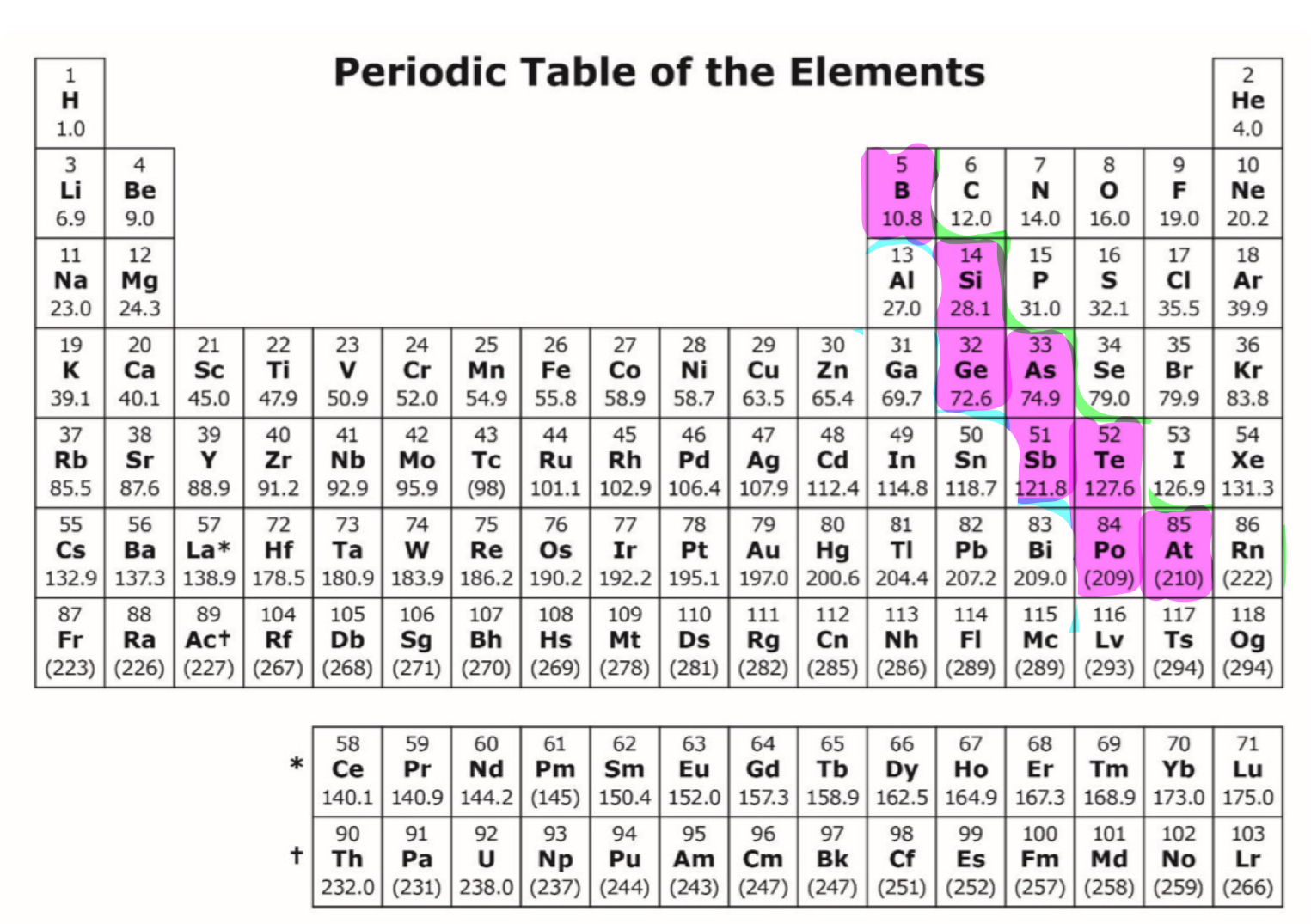
metalloids
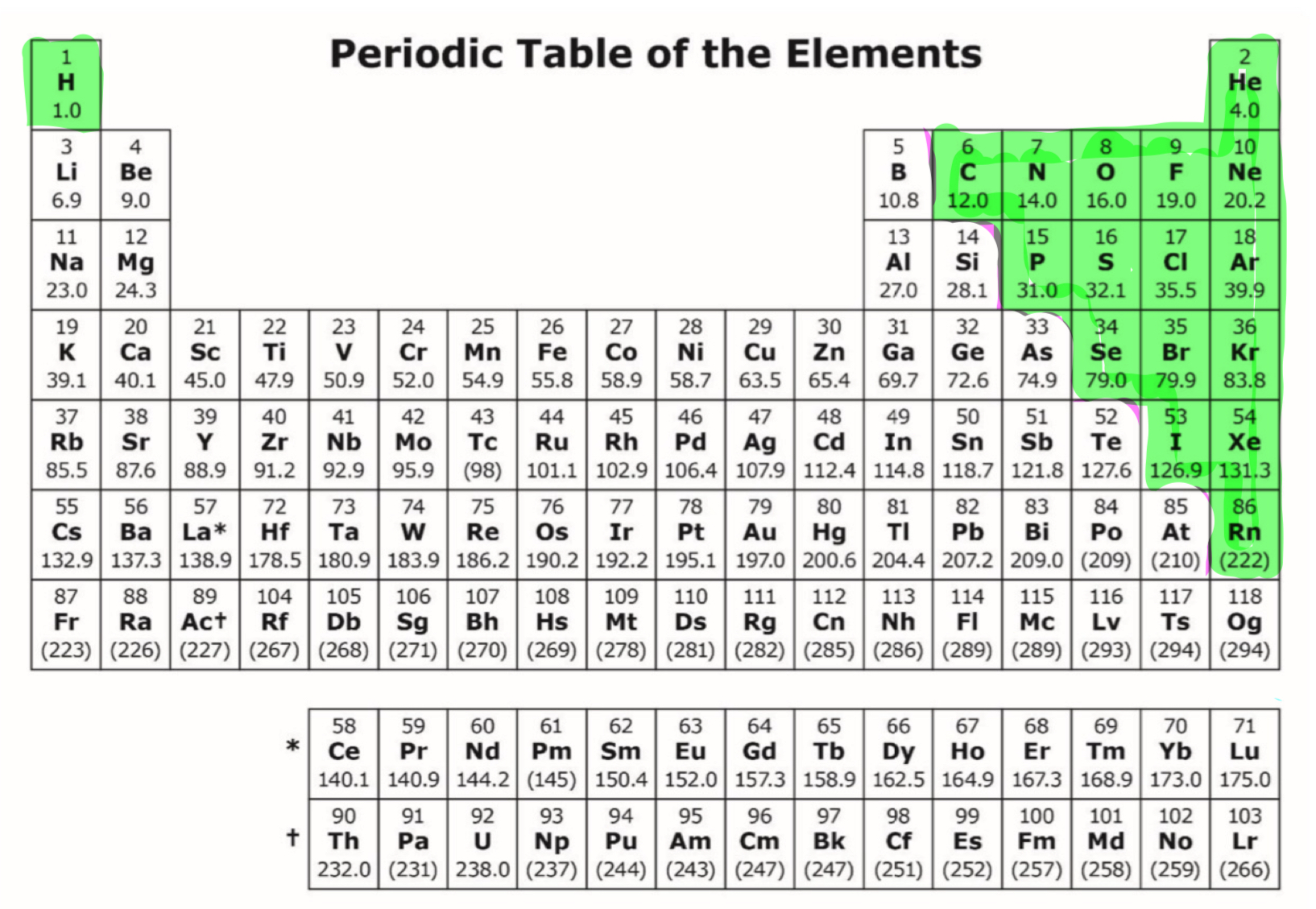
nonmetals
metals are good conductors bc
valence electrons are free to move
metals
-low effective nuclear charge
-low electrogegativity
-large atomic radius
-small ionic radius
-low ionization energy
-low electron affinity
nonmetals
-high electronegativity
-small atomic radius
-large ionic radius
-high ionization energy
-high electron affinity
metalloids
-electronegativities and ionization energies lie between metals and nonmetals
-varying physical properties
Z_eff
-effective nuclear charge
-electrostatic attraction between the valence shell electrons and the nucleus
Z_eff ____ from left to right in a period
increases
Z_eff ___ within a group
is somewhat constant
as principal quantum number increases, outermost electrons…
are held less tight
atomic radius
one half the distance between the centers of 2 atoms of an element that are briefly in contact with each other
atomic radius ____ from left to right across a period
decreases
atomic radius ___ down a group
increases
2 generalizations about ionic radii
1. metals lose electrons and become positive
2. nonmetals gain electrons and become negative
nonmetals close to metalloid line have ____ ionic radius
larger (gain electrons while nucleus keeps same charge)
metals closer to metalloid line have _____ ionic radius
smaller (have more electrons to lose)
ionization potential / ionization energy
the energy required to move an electron from a gaseous species
IE
ionization energy
endothermic
input of heat
the greater the Z_eff, or closer the valence electrons to nucleus…
the more tightly bound they are
ionization energy ____ left to right across a period
increases
ionization energy ____ down a group
decreases
first ionization energy
-the energy necessary to remove the first electron
-then there’s second ionization, and so on
active metals
-elements in group IA and IIA
-low ionization energies
-always found as ionic compounds minerals or ores
exothermic
expel energy in form of heat
electron affinity
the energy dissipated by a gaseous species when it gains an electron
delta H_rxn is (negative/positive)
negative
electron affinity is (negative/positive)
positive
electron affinity ____ left to right across a period
increases
electron affinity _____ down a group
decreases
noble gases have electron affinities to the order of ___
zero
electronegativity
measure of the attractive force that an atom will exert on an electron in a chemical bond
greater the electronegativity, the more…
it attracts electrons within a bond
electronegativity correlates to
ionization energy (lower ionization energy, lower electronegativity)
first 3 noble gases are exceptions
pauling electronegativity scale
ranges from .7 to 4.0
electronegativity _____ left to right across a period
increases
electronegativity _____ down a group
increases
alkali metals
-group IA
-lower densities than other metals
-low Z_eff
-easily lose one electron
-react readily w nonmetals
low Z_eff
-large atomic radius
-low ionization energies
-low electron affinity
-low electronegativity
alkaline earth metals
-group IIA
-share most characteristics of alkali metals (higher effective nuclear charges=smaller atomic radii)
-easily lose 2 electrons
chalcogens
-group VIA
-nonmetals and metalloids
-smaller atomic radii, large ionic radii
-toxic/damaging at high concentrations
halogens
-group VIIA
-highly reactive nonmetals
-often gain 1 electron
-range from gas to liquid to solid
-high electronegativity, high electron affinity especially to IA and IIA
-found as halides (ions) (diatomic molecules)
noble gases
-VIIIA
-inert gases
-minimal chemical reactivity
-high ionization energy, no electronegativity
-low boiling point, gas at room temp
transition metals
-group B
-low electron affinities, low ionization energies, low electronegativities
-hard, high melting+boiling points
-malleable, good conductors
-oxidation states
-associate in solution w molecules of water or w nonmetals
why are transition metals good conductors
loosely held electrons
oxidation states
different possible charged forms, often correlated to different colors
formation of hydration complexes causes
d-orbitals to split into 2 energy sub levels
if an object absorbs a given color of light and reflects all others, our brain mixes these ____ and we perceive the complimentary color of the frequency that was absorbed
subtraction frequencies