4/5/6) Microscopy and light properties & petrographic microscope & observations in plane polarized light
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what are the goals of microscopy?
magnification: produce a magnified image
resolution: separate details in the image
use unique properties that arises from the interaction of light and the minerals
human eyes can see a minimum of what length?
100 um
what is index of refraction, example?
speed of light in a mineral must be lower than the speed of light in a vacuum. the ratio of this is the refractive index
a refractive index of 1.54 means ligth travels 1.54 slower through the medium than it travels through a vacuum
light bends towards the medium with ___?
higher n
what is snells law
n1sin@1 = n2sin@2
sin@1 / sin@2 = n2/n1
what is the critical angle
when the refracted ray is at 90• from vertical
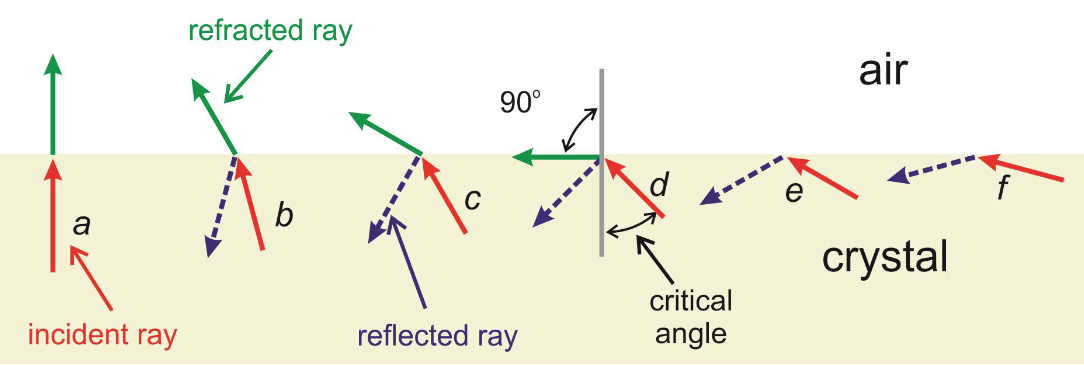
what is total internal reflection
when angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle and no light can get refracted out. it just reflects in the medium of origin
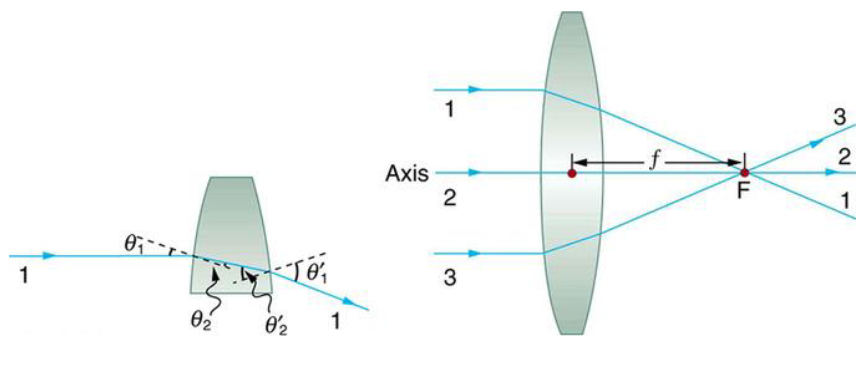
explain light through a biconvex lens, important?
rays entering the lens parallel to ground exit at an angle, rays entering at an angle exit parallel to ground parallel and the rays get refracted to the focal point and back out, all upside down
light entering the lens at the optic center will not be refracted
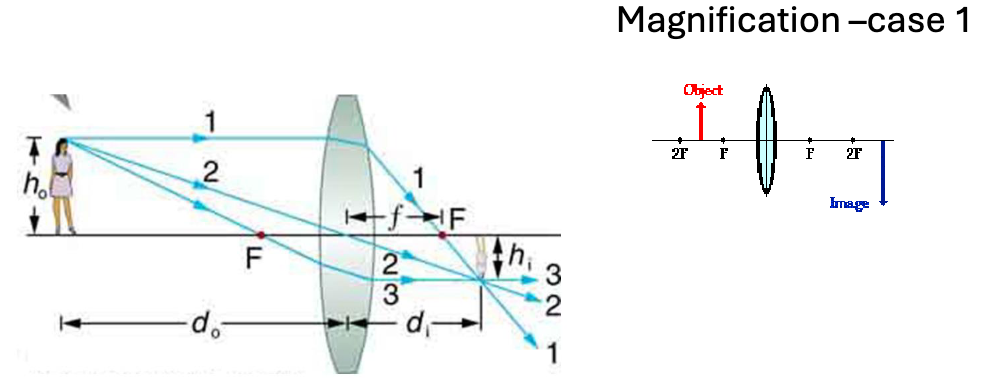
explain magnification case 1, d0, di, focal length (and eqn), magnification
d0 is distance between object and lens
di is distance from lens to where image forms
focal length is the distance from the center of lens to focal point
1/f = (1/d0) + (1/di)
magnification = m = (hi/h0) = (di/d0)
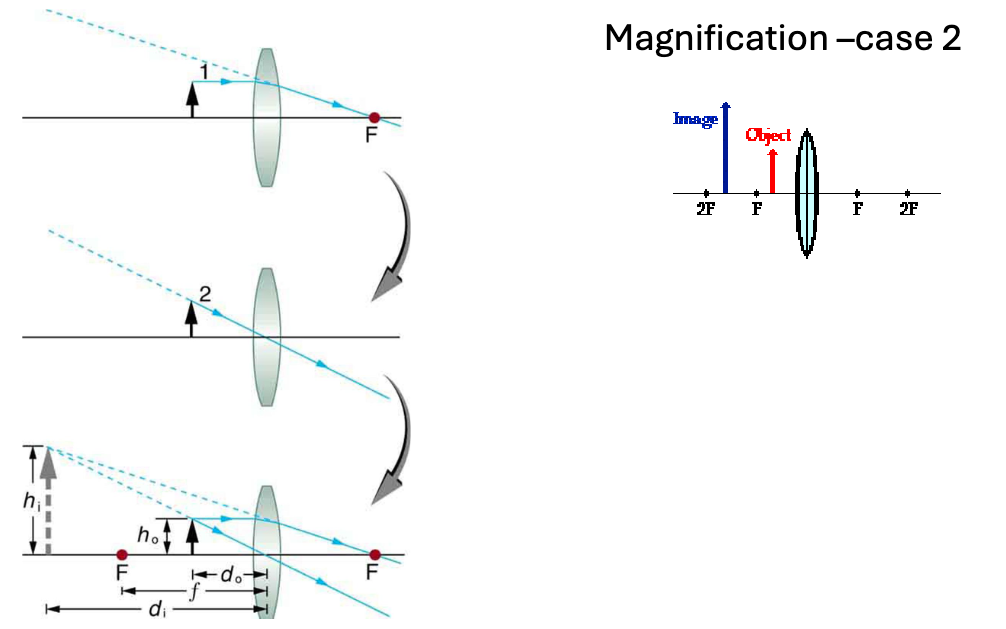
explain magnification case 2
ray coming from the top of object parallel to axis, ray goes through focal point, rays don’t intersect on the other side of the lens, instead they intersect on the same side of the lens
virtual image
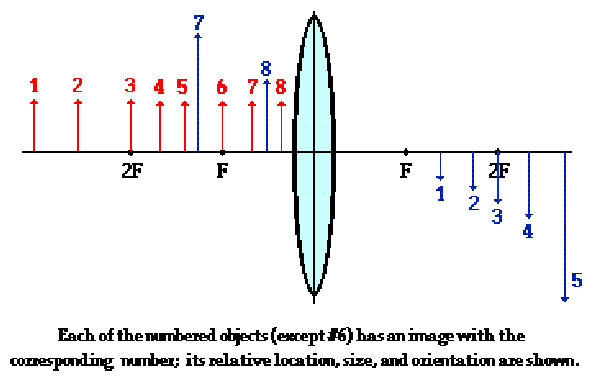
explain these numbers
1/2: object is farther than twice the focal distance = smaller
3: object is at twice the focal length = same size
4/5: object is between 2F and F = larger
6: object is at focal length = no image
7/8: object is between F and lens = virtual image appears and magnified
explain importants about polarized light (and unpolarized)
light vibrates in all directions (unpolarized)
polarizing filter causes vibration only in 2 directions (plane polarized light)
light that isn’t vibrating in that direction either gets resolved to fit or gets eliminated
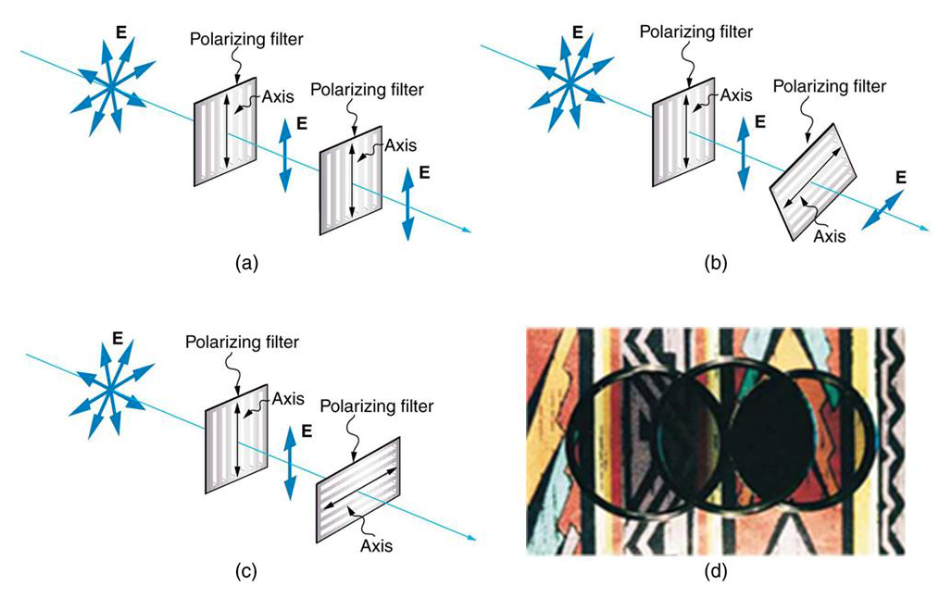
explain diagram abc
a: filters are same direction, light density doesn’t change
b: second filter is diagonal to first, light density decreases (li = licos@)
c: second filter is perp to first, light density becomes zero
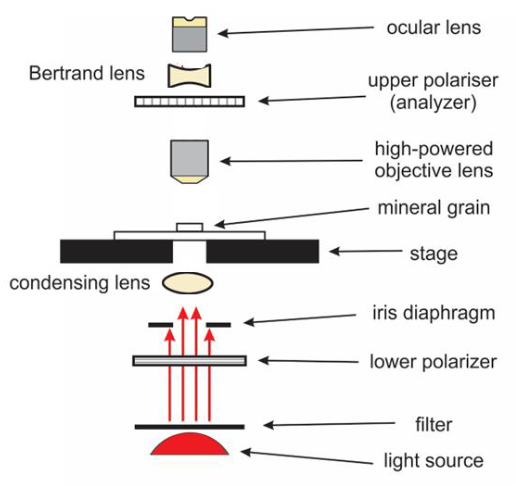
diagram of microscope
ocular lens
bertrand lens
upper polarizer / analyzer
high powered objective lens
stage
condensing lens
iris diaphragm
lower polarizer
filter
light source
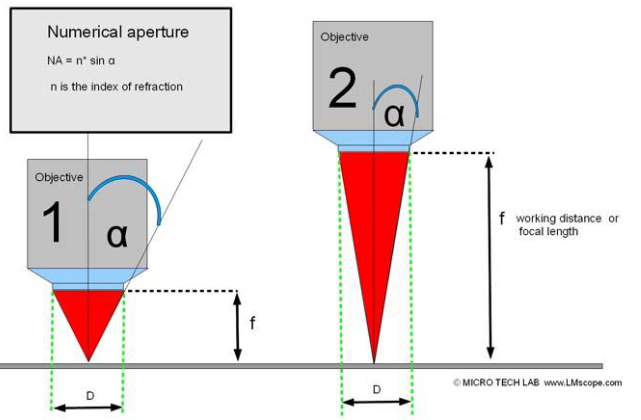
what is numerical aperature
measure of lens to gather light from object
NA = n*sin(a)
a: half of the angle of angular aperture of the cone of light OR angle between vertical and edge of light transmitted from focal point
what is resolution? example?
R = (lambda / 2)*NA
lambda = wavelength of light (white light avg of 550nm)
2 lenses can have the same magnification but different numerical aperature and hence different resolutions
Plane polarized light vibrates in ___
E-W direction
standard thickness of thin section?
30µm
list optical properties
opacity, grain size/shape, colour, pleochroism, cleavage, refractive index (relief)
opaqueness?
mineral does not transmit light even at 30 microns thick
most oxides and sulfides are opaque (magnetite, hematite, pyrite)
what are the grain shapes?
equant
acicular
tabular/platy
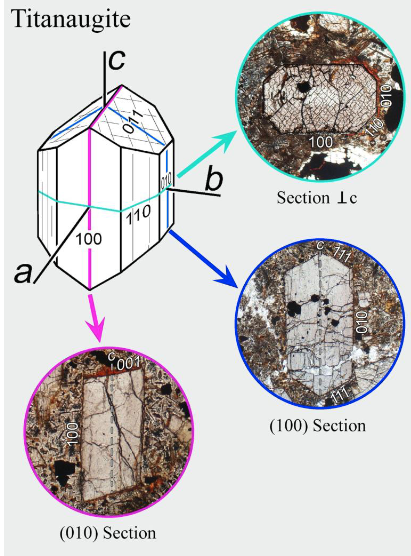
explain longitudinal sections, example (monoclinic)
shapes of crystal can vary based on the orientation of the crystal under microscope, and how you cut the thin section
A axis is angled, inclined a bit
B axis is perp to C axis, transverse
C axis is perp to A and par to b and C, tabular
what is relief? high relief means?
how well the boundary of the crystal stands out compared to the surrounding crystal or mounting medium
depends on the difference in refractive index of the mineral and surroundings
*high relief if RI is much different because light gets refracted more extremely away from boundary*
positive and negative relief
RI grain > RI Mmed = (+)
RI grain < RI Mmed = (–)
becke lines bend towards the medium with the ___, and?
higher refractive index
light converges on one spot causing the bright spot