Chapter 11-Commerce 1MA3 (Marketing)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Importance of price in the marketing mix
Price is a top factor in buying decisions
It’s the only part of marketing that brings in money
It’s the hardest of the 4Ps to manage
Managers often misunderstand it
Company objectives (orietntation
Profit oriented
Sales oriented
Competitor orientation:Competitive parity
Customer orientation
Profit oriented
Target profit pricing: sets price to reach a specific sales level and profit per unit. Make a specific amount of total profit.
Sets price to hit a sales goal with a set profit per unit.
Maximizing profits: uses a detailed math model to find the price that gives the highest total profit
Target return pricing means setting a price to earn a set profit based on how much money the company spent.
Example: If they spend $100, they might want to make $20 back — so they price to get that 20% profit. Earn a certain % return on the money invested.
Sales oriented
The company aims to grow sales, believing it's more helpful than just boosting profits.
Competitor orientation:Competitive parity
Focus on beating or matching competitors.
Competitive parity: Set prices similar to competitors’ prices.
Customer orientation
It focuses on value and customer satisfaction, setting prices to align with consumer expectations.
5C’s of pricing
company objectives
customers
costs
competition
channel members
customers
Understanding consumers reactions to different prices
Demand curves: Price vs. quantity demanded
Price elasticity: How demand changes with price
Income effect: How income changes buying habits
Substitution effect: Switching products due to price changes
Complementary products: Products that go together, affecting each other's demand
Cross price elasticity: How price change in one product affects demand for another
Costs
Variable costs: Costs that change with production level
Fixed costs: Costs that stay the same regardless of production
Total costs: The sum of variable and fixed costs
Break-even analysis: A calculation to determine when total revenue equals total costs.
Break-even analysis formula
Fixed costs/ (sales revenue-varaible costs)
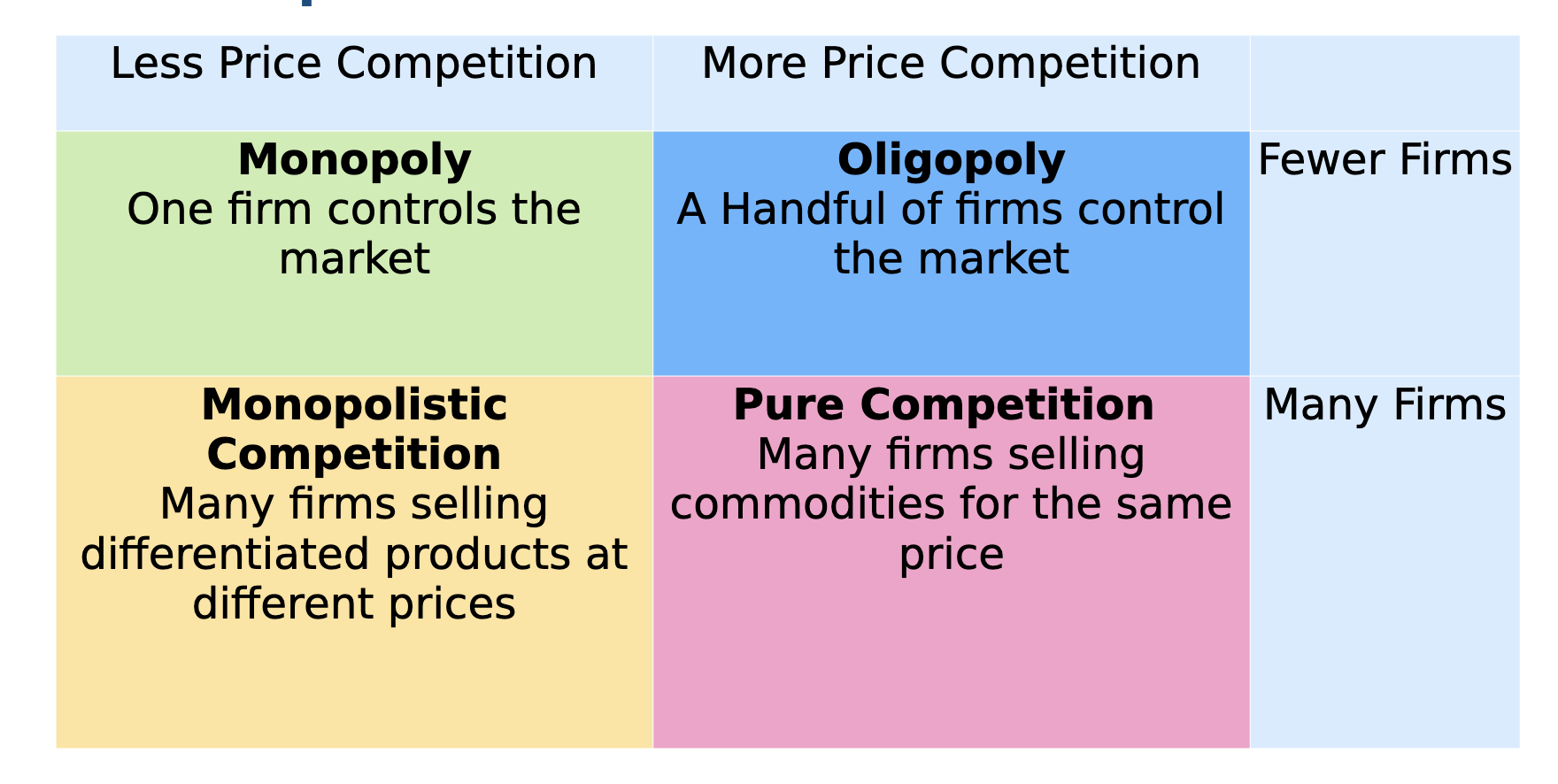
competition graph
different firms price differently
channel members
Different pricing goals can lead to grey-market sales, where products are legally sold through unofficial sellers at lower prices, so brands warn that warranties don’t count unless bought from approved dealers.
Pricing Methods
Cost based pricing:
Competitor based pricing:
Value based pricing:
Improvement value:
Cost of ownership method:
Cost based pricing:
Sets the final price by starting with the cost of making the product, ignoring consumer demand or competitor prices.
Competitor based pricing:
Sets prices based on how the firm wants consumers to view its product compared to competitors.
Setting the price based on how you want your product to look compared to others — cheaper, same, or more expensive.
Value based pricing
Sets prices based on how much the customer believes the product is worth.
Example of value-based pricing:
Apple prices the iPhone high because customers see it as a premium product with strong brand value, design, and features—even if it costs less to make.
Improvement value:
How much more customers are willing to pay for a product because it’s better than similar ones.
estimate of how much more consumers are willing to pay for a product relative to other comparable products
Example: Customers may pay more for a vacuum with stronger suction and longer battery life than cheaper models.
Cost of ownership method:
Cost of ownership method: setting prices that determines the total cost of owning the product over its useful life

cost
compeitior
value
nON SENSE
Cost-based pricing starts with the cost per unit and assumes costs don't change with production levels.
NON SENSE
Sets high prices to show that a product is superior to competitors.
premium pricing
non sense
Value-based pricing: Sets prices based on how consumers perceive the overall value of the product.
Psychological Factors Affecting Value-Based Pricing
Strategies
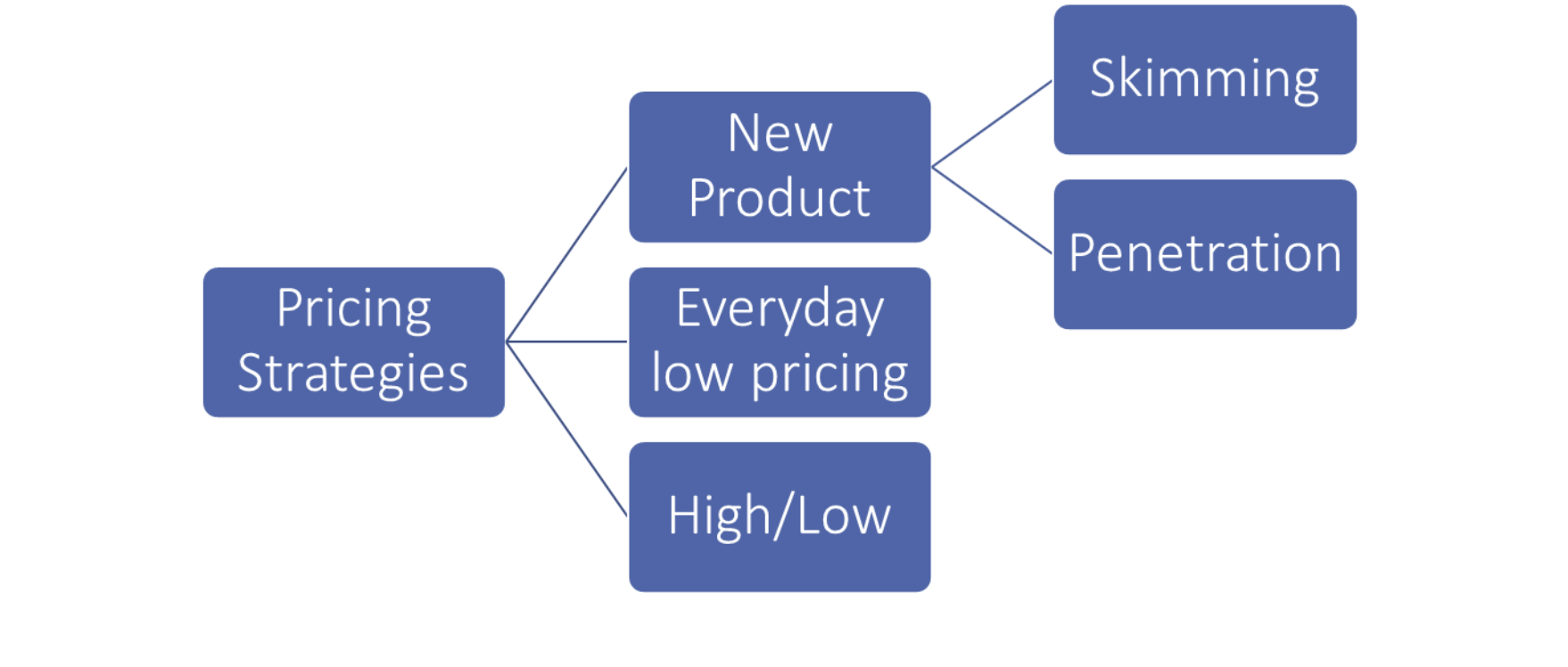
Everyday low pricing (EDLP)
Setting prices consistently lower than regular prices but higher than discounts to offer better value than competitors.
high/low pricing
Temporarily lowering prices to encourage more purchases.
Price skimming:
Selling a new product at a high price initially, then lowering it over time to attract more price-sensitive customers as the market saturates.
Market penetration:
Setting a low initial price to quickly gain sales, market share, and profits.
Experience curve effect:
As sales increase, unit costs decrease, allowing for further price reductions.
Shrinkflation
decrease food package sizes while leaving prices unchanged
what are some Price Tactics- CONSUMER
Price lining:
Price bundling:
Leader pricing:
what is pricing tactics
short term methods used to focus on company objectives
Price lining:
Setting a price floor and ceiling for a group of similar products to create a clear range of prices within the product line
Price bundling:
Pricing multiple products together at a single, lower price.
MCDONALDS MEAL
Leader pricing:
Selling an item at a low price to attract customers, hoping they'll buy more.
Consumer Price Reductions
Markdowns:
Coupon:
Rebate: manufactuerur issues discount in which a portion of the purchase price is returned to the buyer in cash
Rebate:
A discount where the manufacturer returns a portion of the purchase price to the buyer in cash.
Business-to-business Pricing Tactics:
Seasonal discounts:
Cash discounts:
Allowances:
Advertising allowances:
Listing allowances:
Quantity discounts:
Seasonal discounts:
An additional discount offered to retailers as an incentive to order merchandise before the usual buying season.
Example of preseason discount: A shoe manufacturer offers retailers a 15% discount on sneakers if they order them before the back-to-school season starts, encouraging early purchases.
Cash discounts:
Cash discount: An additional reduction in price offered to buyers who pay their invoice before the discount period ends.
Example: A supplier offers a 5% discount if the retailer pays the invoice within 10 days.
Allowances:
allowances offered in return to specific behaviors
Discounts given for doing something specific (like early orders or advertising the product).
Advertising allowances: Discounts for featuring the product in ads.
Listing allowances: Payments to get products on shelves or more shelf space.
Quantity discounts
Offering a lower price based on the amount purchased.
Example of quantity discount: A supplier offers a 10% discount if a retailer buys 100 or more units of a product.
Unethical Tactics
Loss leader pricing:
Bait and switch:
Predatory pricing:
Price discrimination:
Price fixing:
Loss leader pricing:
Loss leader: Selling a product at a loss to attract customers, hoping they will buy more profitable items.
Example: A store sells a printer at a very low price, hoping customers will buy ink and paper, which have higher profit margins
Bait and switch:
Attracts customers with a low-priced item, then pressures them to buy a higher-priced item by criticizing the cheaper one.
Predatory pricing:
Setting a low price to drive competitors out of business.
Price discrimination:
Selling the same product to different resellers at different prices.
Price fixing:
Working with other firms to control prices.