Natural Moral Law- Aquinas (Normative Ethical Theories Topic pt1): AQA A Level Religious Studies
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Revision cards for Natural Moral Law by Aquinas, part 1 of 3 for revision cards on Normative Ethical Theories
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is a normative ethical theory?
The idea that we must look at what makes an action morally good or bad
What is absolute morality?
Everything is inherently right or wrong, this doesn’t change based on the situation
What is relative morality?
There is no inherit right or wrong, it depends on the situation
What is the Deontological Normative ethical theory?
This is absolutist (true for every situation).
It is concerned with duty, rules and rights. eg. Aquinas’ Natural Law
What is the Teleological Normative ethical theory?
This relates to the telos or goal/aim of something.
It is consequentialist, because it looks at the consequences. eg Fletchers situation ethics
What is the character based Normative ethical theory?
This is more concerned with “what kind of person should I be?” rather than “what should I do?”. The idea is that a good person will know what good actions are eg. Aristotles Virtue Ethics
What did Aqunias say about God?
God is immutable (changeless).
God is good and the purpose of creation was to reflect that.
The laws of nature reflect God’s nature and regulate the world.
What is eudemonia?
Everything has a final goal and humanity’s is eudemonia (complete happiness/wellbeing), which comes in two parts:
The earthly part relates to humans.
The final goal is the beatific vision (the ultimate, direct, self communication of God to humanity).
What is the “fourfold division of law”?
Eternal law: God’s blueprint for the natural and moral order of things
Divine Law: God’s special revelation disclosed to humanity in the Bible and in the teachings of the church.
Natural Moral Law: God’s eternal law revealed through nature and interpreted by reason.
Human law: the system of laws implemented by humanity
What did Cicero say?
“True law is correct reason congruent with nature… There will not be one law at Rome, another at Athens, one now, another later, but one law both everlasting and unchangeable will encompass all nations and for all time”
What was said in the Summa Theologica about good and evil?
“The first principle of practical reason is one founded on the notion of good. Viz. that ‘good is that which all things seek after’. Hence this is the first precept of law, that ‘good is to be done and pursued, and evil is to be avoided’. All other precepts of the natural moral law are based upon this”
What are the primary precepts? (WORLD)
W= worship God
O= ordered society
R= reproduce
L= learning'
D= defend the innocent
What are some examples of secondary precenps?
W= worship God —> attend church
O= ordered society —> don’t steal
R= reproduce —→ have children
L= learning —> build schools
D= defend the innocent —> have police
What did Aquinas say about the secondary precepts?
“The natural law is altogether unchangeable in its first principles: but in its secondary principles… it may be changed in some particular cases of rare occurrence, through some special causes hindering the observance of such precepts”
– Summa Theologica
What did Aquinas say about repaying a debt?
“goods entrusted to another should be restores to their owner… but it may happen in a particular case that it would be injurious, and therefore unreasonable… for instance, if they are claimed for the purpose of fighting against one’s country”
- Summa Theologica
What are the “cardinal” virtues?
Prudence
Justice
Fortitude
Temperence
What are the theological virtues?
Love
Hope
Faith
“these three remain: faith, hope and love. But the greatest of these is love”. - 1 Corinthians 13:13
“[love] binds everything together in perfect harmony”- Colossians 3:14 (St Paul’s letter)
“the theological virtues are the foundation of Christian moral activity… They are infused by God into the souls of the faithful”
- Catechism of the Catholic Church
What is a example of a good exterior act and a bad interior act?
-Helping an old lady cross the road (external good)
-Only doing it to impress someone (bad external act)
What is the principle of double effect?
Condition | Explanation | Example |
The nature of the act (condition) | The morality of the proposed action must be good or at the very least neutral. | Intentionally killing an innocent person could never be okay. |
The means–end (condition) | The bad effect of the action must not be the means by which the good effect is achieved. (You can’t do something bad to achieve something good). | Torturing someone to find out the location of a bomb wouldn’t be allowed. |
The good intention (condition) | The intention must be to achieve the good effect. The bad effect may be foreseen but it must not be intended. | A pregnant woman who has cancer having chemotherapy is acceptable because the medicine is to fight the cancer, not end the pregnancy. |
The proportionality (condition) | The good effect must be at least proportionate in its significance to the bad effect. | Giving morphine to someone at the end of their life is okay because the pain relief is proportionate to the fact it may hasten their death. |
What is proportinalism?
Proportionalism argues that where a proportionate reason exists, it would be right to ignore the rule in that situation.
e.g. Aquinas said it would be permissible for a starving man to steal in order to save his life
What did Aquinas say about lying?
“therefore it is not lawful to tell a lie in order to deliver another from any danger whatever. Nevertheless it is lawful to hide the truth prudently, by keeping it back…” -Summa Theologica
What are the evaluations of proportionalism?

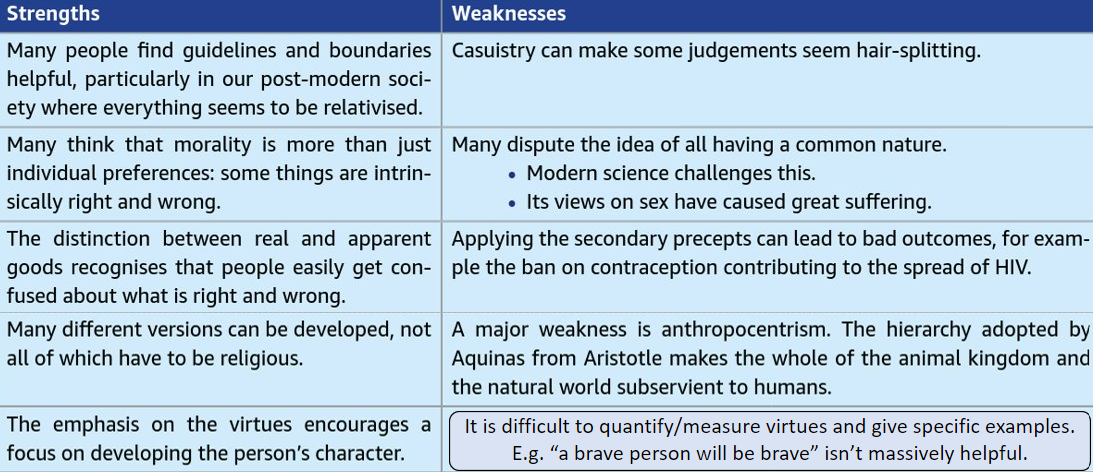
What are the evaluations of moral law?