Rise & Spread of Islam
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Umayyad Dynasty
(661-750 CE)
-1st Islamic caliphate established after the death of Muhammad; established by Mu'awiya
-Moved capital to Damascus, closer to trade routes
-Spread the empire across N. Africa, into Spain,
-Arabic official lang., built Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
-Fell to the Abbasids, continued presence in Spain later on.
-Caliph: The civil and religious leader of a Muslim state considered to be a representative of Allah on earth
-Established 3 tiered tax system (Muslim Arabs paid Zakat converts paid more, dhimmi (people of the book, non-Muslim) paid highest, jizya: tax paid by Christians, Jews allowing them to practice their own religion.
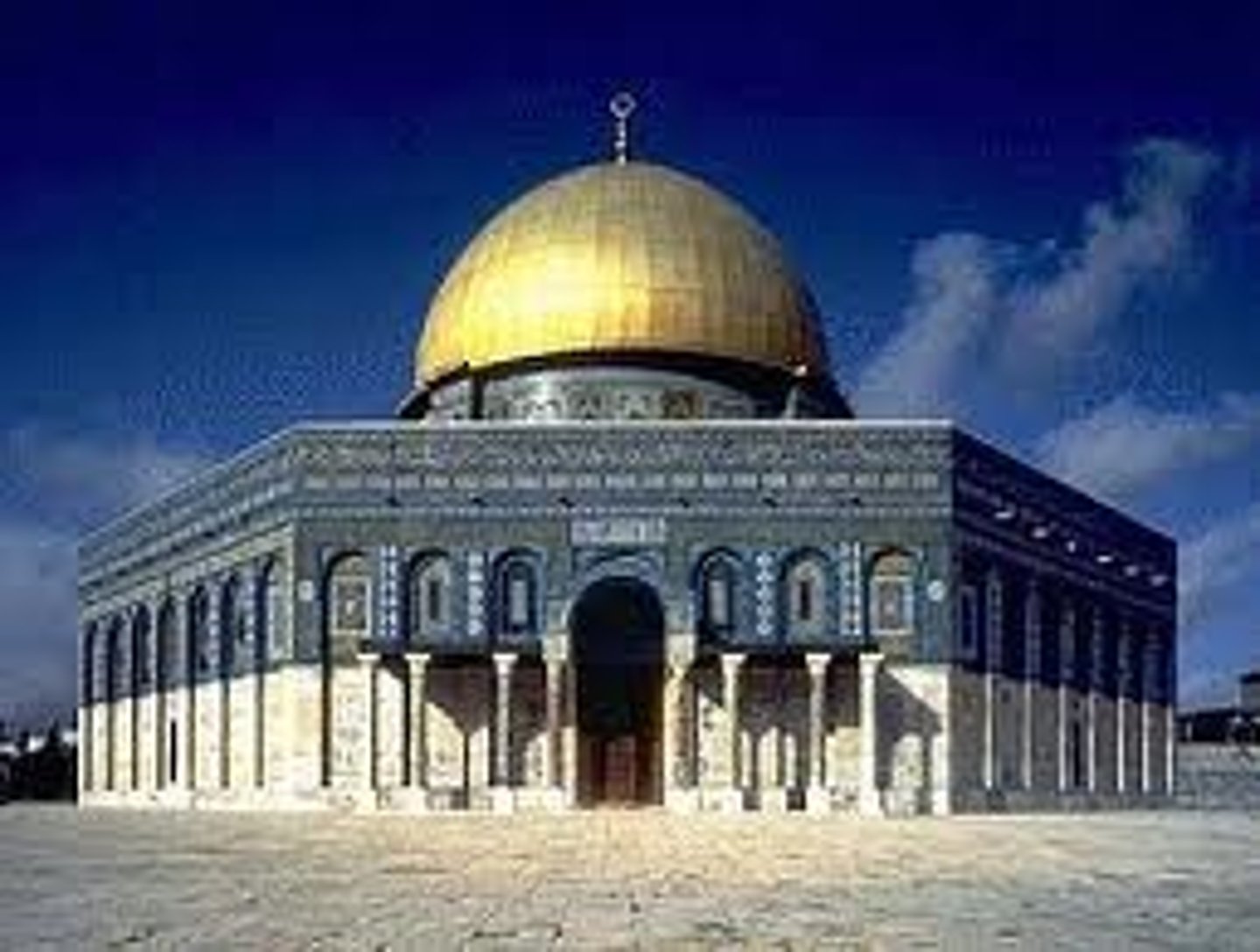

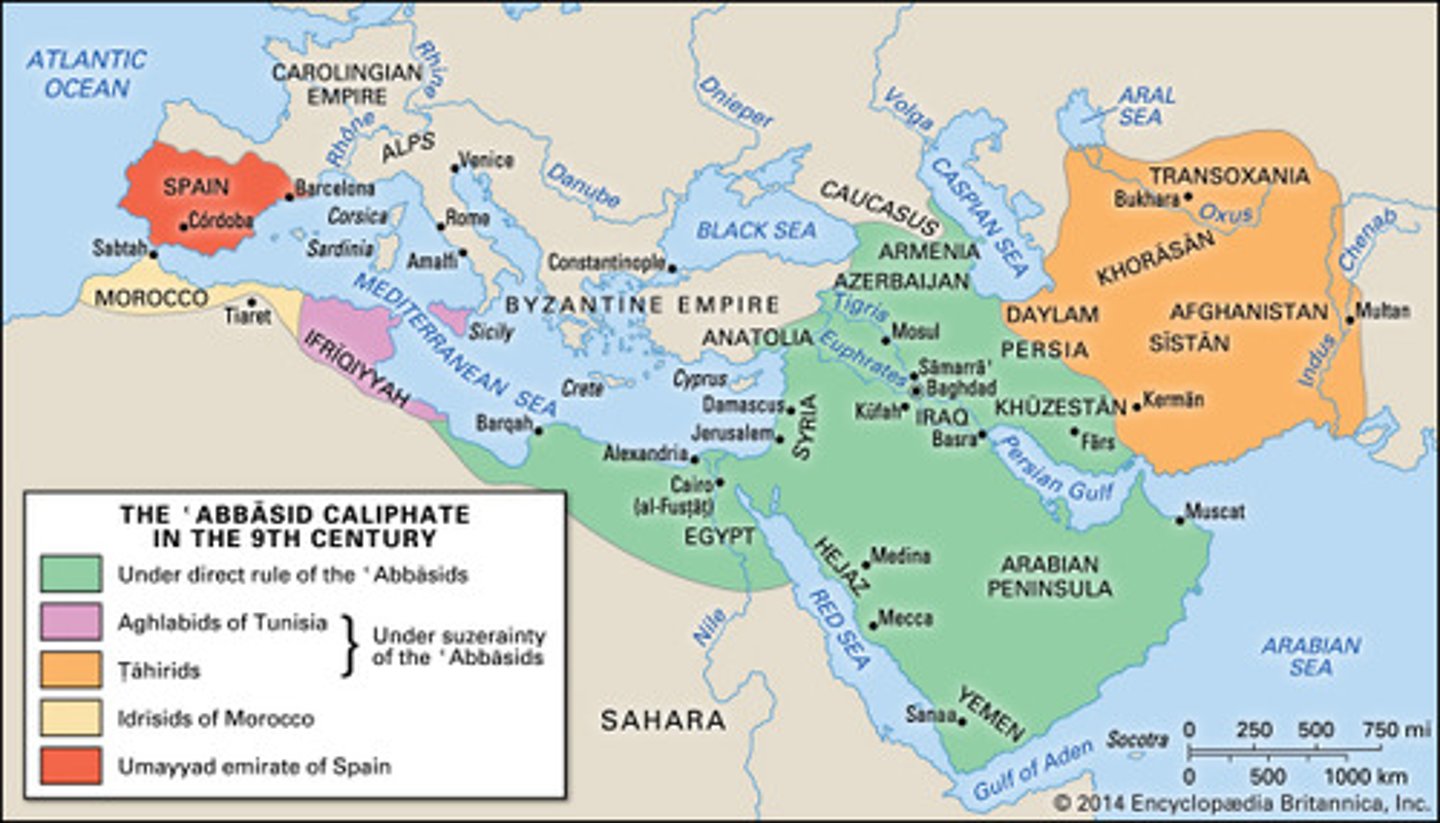
Abbasid Dynasty
(750-1258 CE)
-2nd caliphate succeeding the Umayyad, focused more on administration and centralization (strong bureaucracy) than conquering and expansion.
-Moved capital to Baghdad (House of Wisdom: "university" established in the 800's, served as a learning and education center for the empire, many Greek and Persian texts were translated into Arabic)
-Madrasa: colleges for higher instruction in the teachings of Islam as well as in secular subjects, founded throughout the Islamic world; helped preserve western European traditions and literature
-Persian descent, were considered Mawali (Non-Arab converts to Islam); granted full acceptance in the community of believers.
-Paper-making, "Arabic" numerals, the astrolabe, literature (1001 Arabian Nights)
-Suffered invasions (Seljuk Turks, European Crusades, the MONGOLS 1258)
Seljuk Turks
-Nomadic Turks from Asia who conquered Baghdad in 1055 and allowed the caliph to remain only as a religious leader; they governed strictly
-Staunch Sunnis
-Defeated the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert (1071), triggering the crusades
-Let agricultural lands fall into disrepair, pop. declines

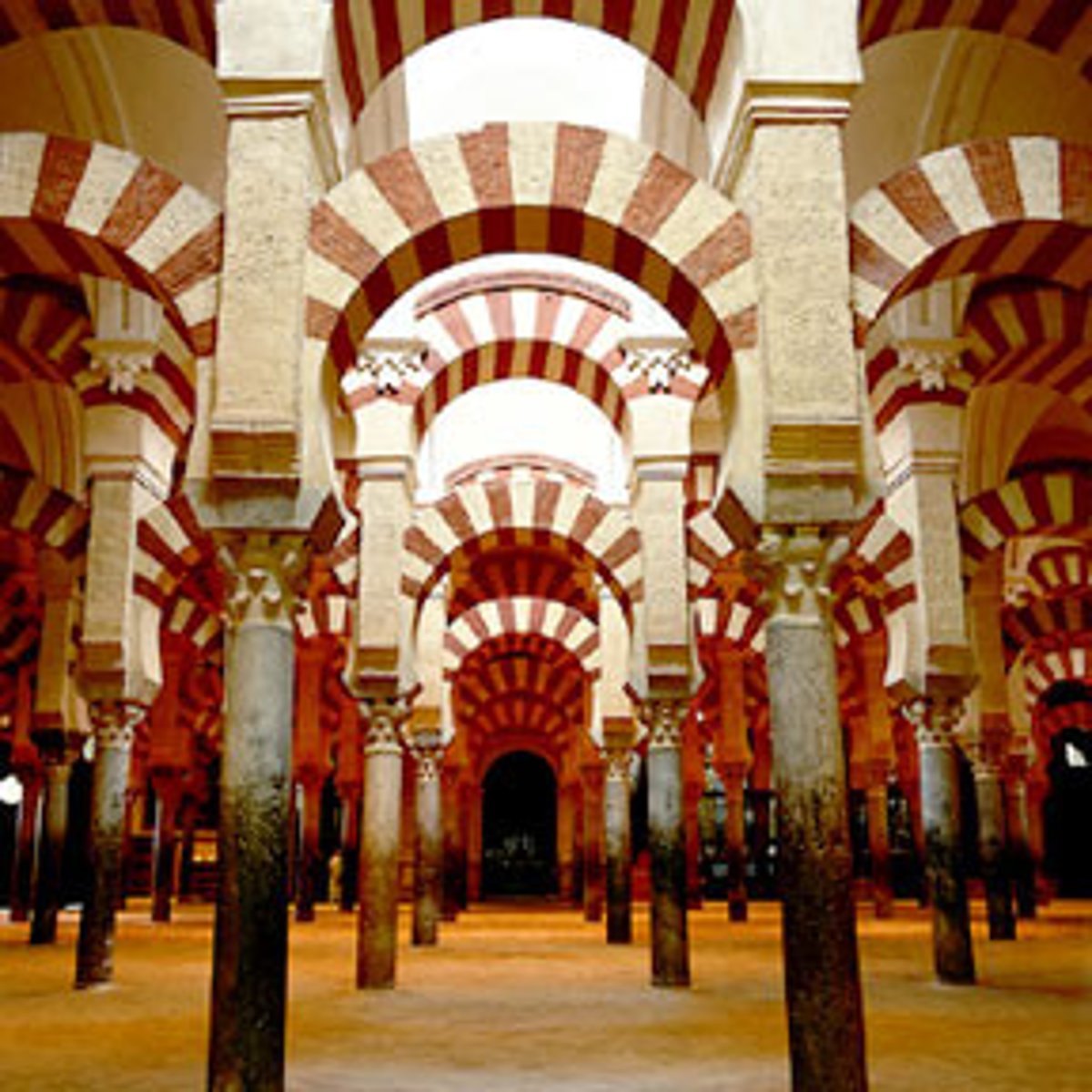
Cordoba
-Umayyad caliphate in Spain, flourished 711-1492
-Center for learning and intellectual life b/c of its libraries & universities, also widely tolerant of dhimmi peoples ("the people of the book" applied as inclusive term to Jews and Christians in Islamic territories; later extended to Zoroastrians and even Hindus).
-the Great Mosque: built on the ruins of a ruined Christian Church, famous for its horseshoe arches, it provides a striking example of the sophistication provided by the fusion of Jewish, Muslim and Christian art.

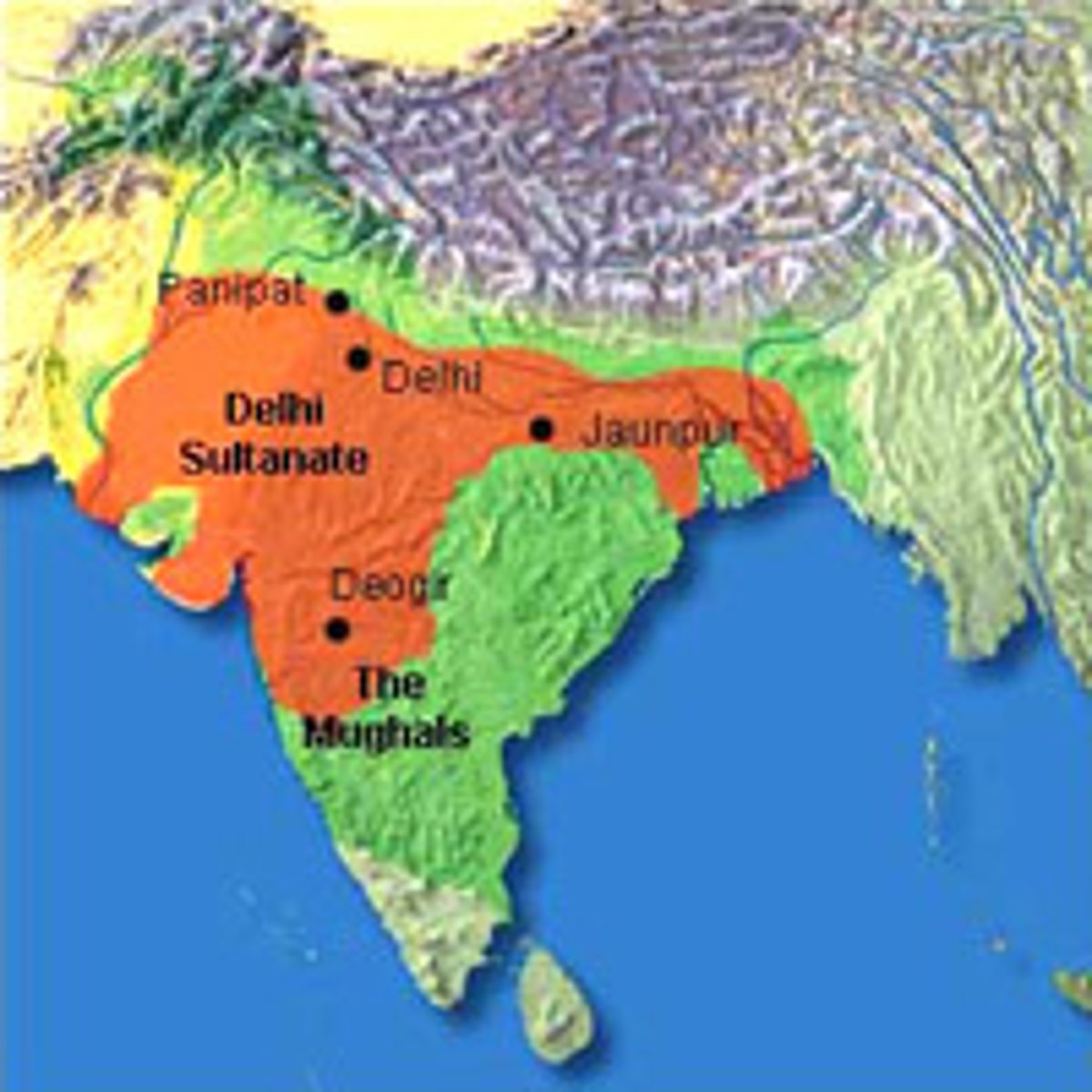
Delhi Sultanate
(1206-1526)
synthesis of Indian & Islamic civilization; integration of the Indian subcontinent into a growing world system and wider international networks spanning large parts of Afro-Eurasia; responsible for repelling the Mongol invasions; caused destruction and desecration of politically important temples in South Asia.; conquered and succeeded by the Mughal Empire.
Crusades
(c. 1095-1270)
-Series of armed "pilgrimages" (holy wars) to the Holy Land by Christians determined to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule; western imperialism est. short-lived Crusader Kingdoms
-Saladin: powerful Muslim ruler, recaptured all of the Crusader cities, including Jerusalem in 1187
-Brought an end to western Europe's centuries of intellectual and cultural isolation.
-Important cultural & technological exchange east to west

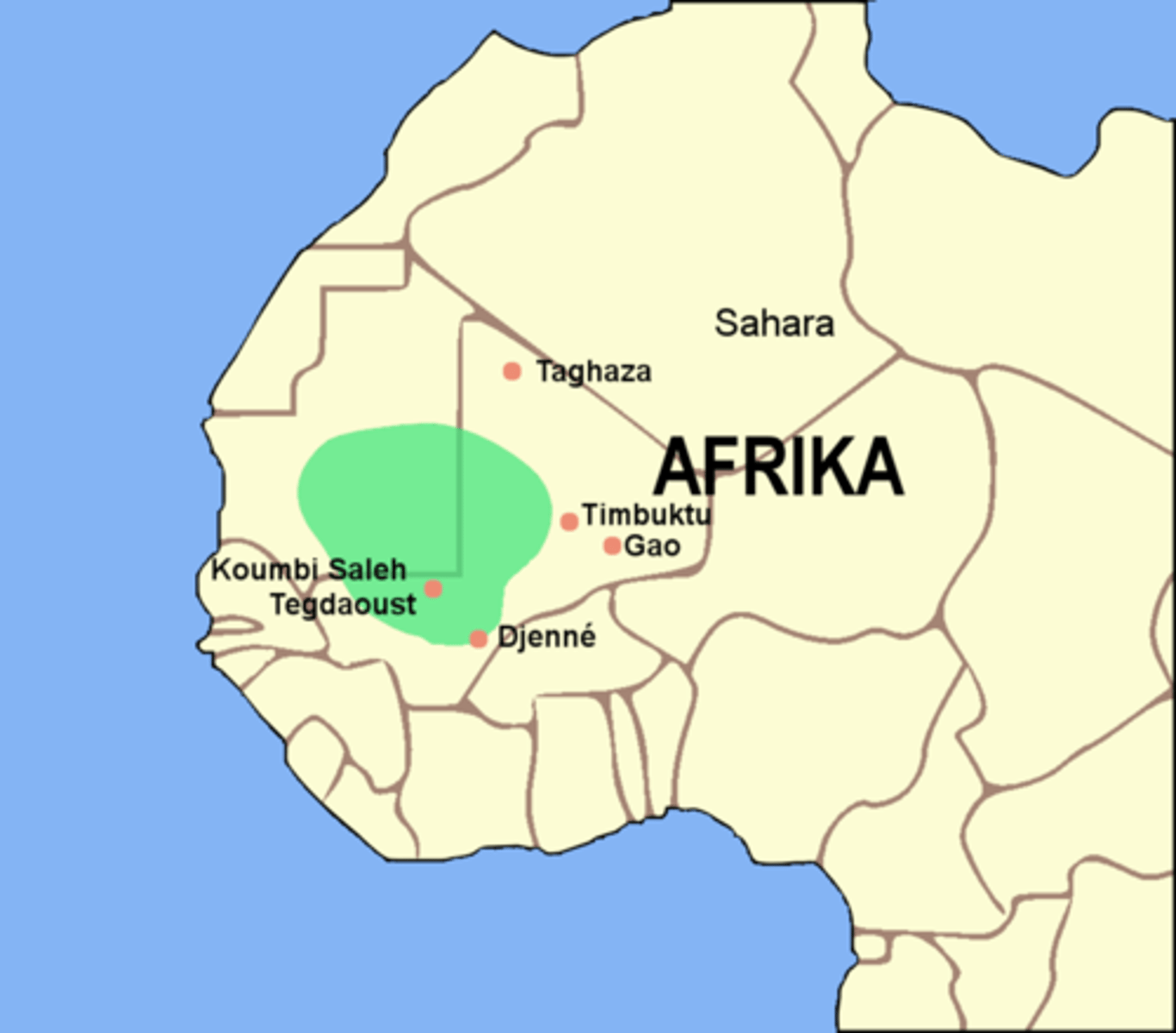
Ghana
(c. 300-c. 1200)
-1st known kingdom in sub-Saharan West Africa
-Involved in the Gold/Salt trade as early as the 200s
-Rulers converted to Islam, used it to reinforce the kingship, considered sacred/divine, so "ruler cults" developed, though relatively few subjects converted
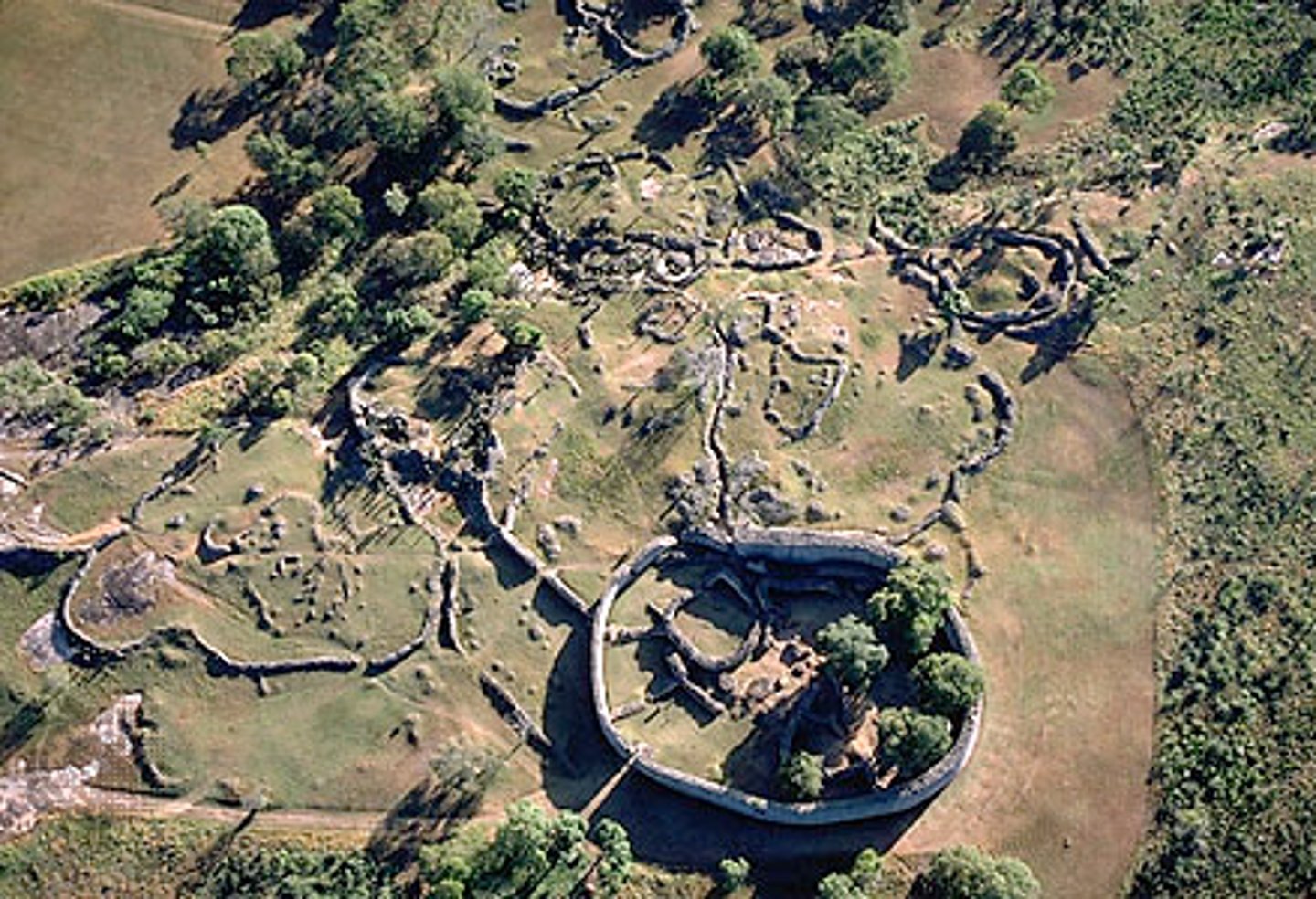
Great Zimbabwe
(c. 1000-c. 1400s)
-City, (in the modern African country of Zimbabwe), whose many stone structures were built between about 1250 and 1450, when it was a trading center and the capital of a large state.
-served as middleman between gold miners, ivory hunters in southern Africa, traders on coast

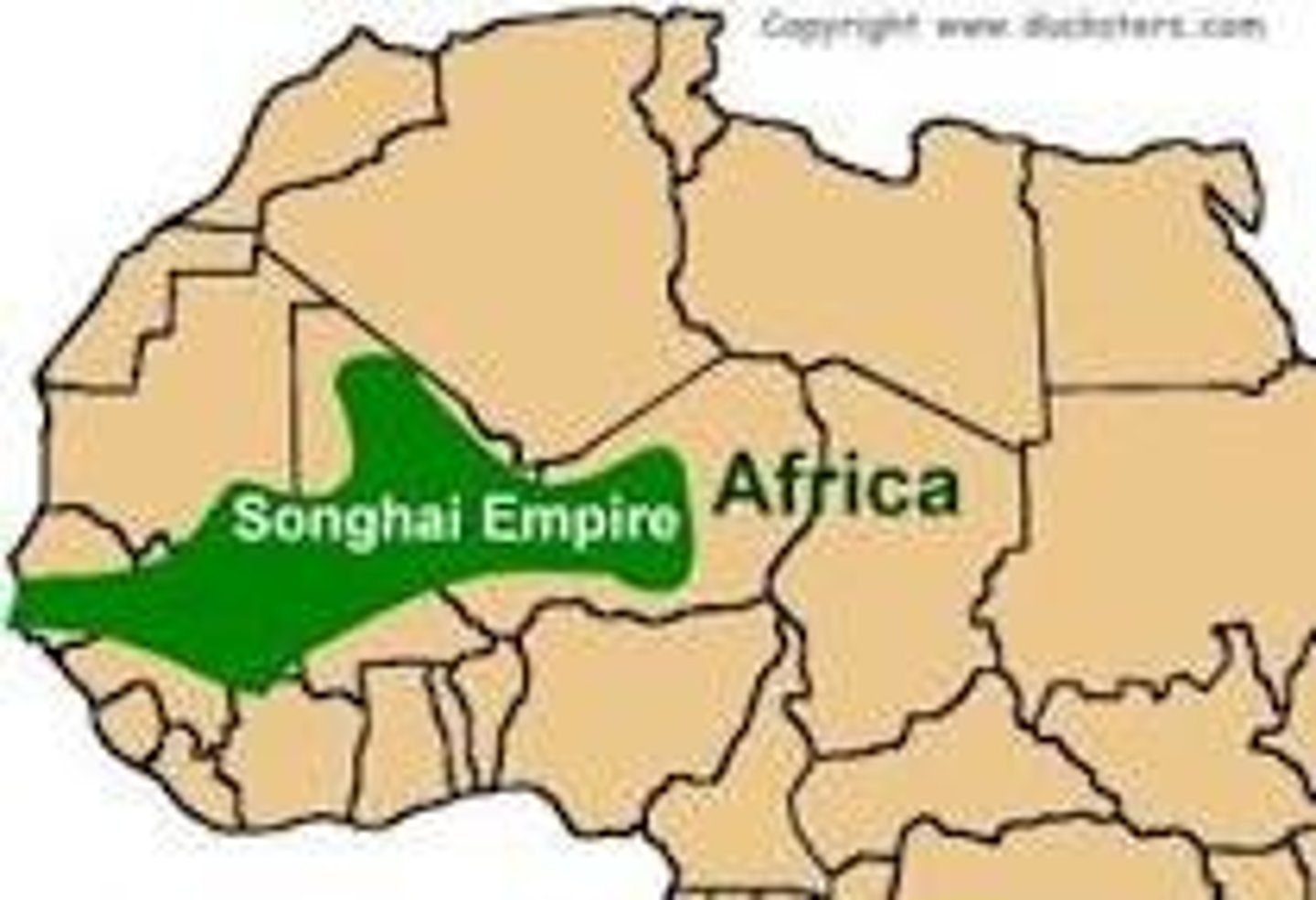
Songhay
(1464-1591)
-Successor state to Mali; dominated middle reaches of Niger valley; reached imperial status under Sunni Ali
-Trans-Saharan trade that had slowed after fall of Mali resumed once again
-Re-established Timbuktu as a center of culture, Islamic scholarship
-Blended traditional West African beliefs and the religion of Islam.
-Began to weaken due to internal strife and civil war mid-1500's; 1591, a Moroccan army invaded and captured the cities of Timbuktu and Gao with the aid of guns
-Hausa kingdoms: Peoples of northern Nigeria; formed states following the demise of Songhay Empire that combined Muslim and pagan traditions
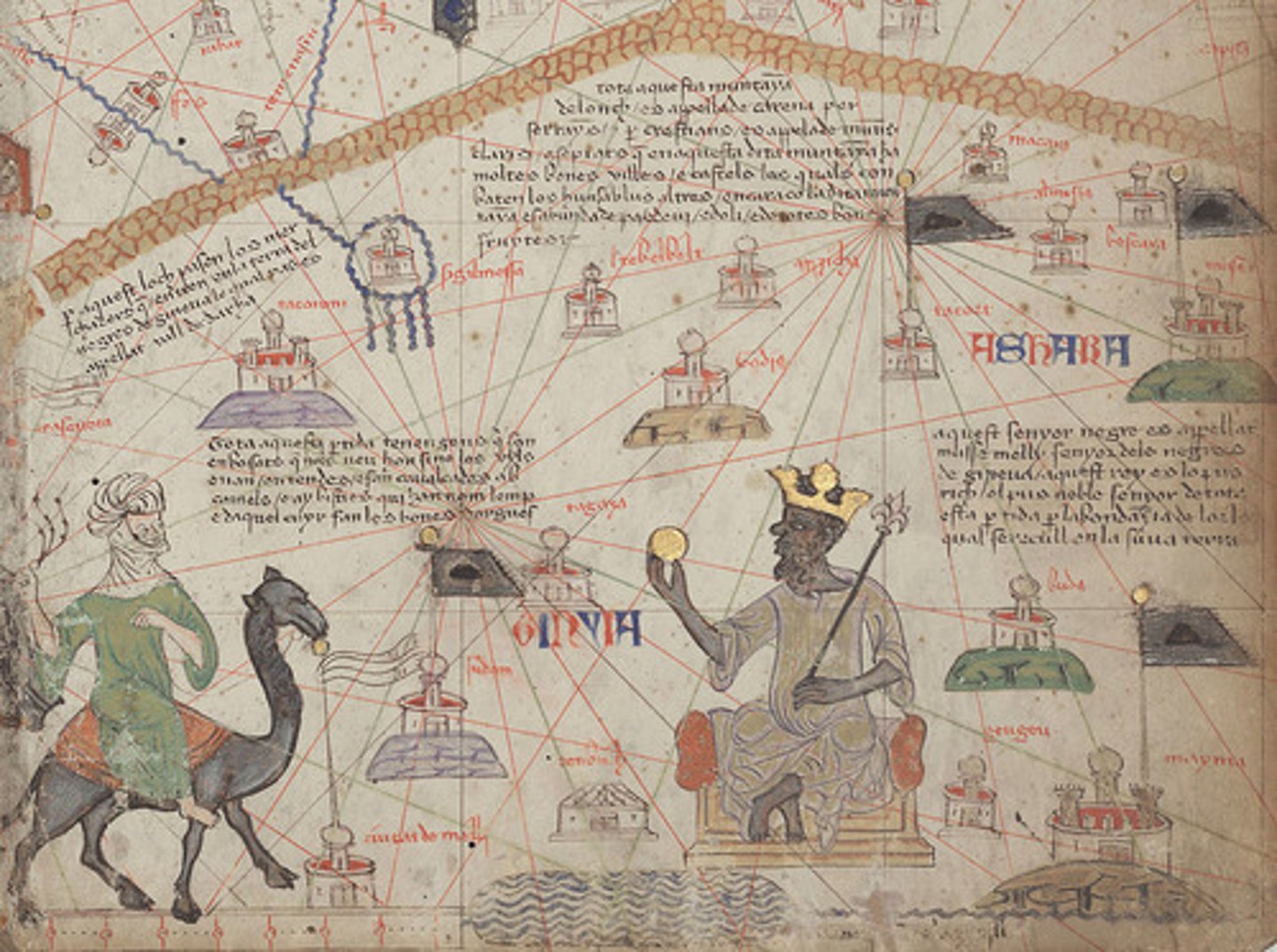
Mali
(c. 1235-1600)
-Empire created by indigenous Muslims in western Sudan of West Africa; wealthy due to trans-Saharan gold trade.
- rise to power due to Sundiata; used alliances helped unify, Islam played an important part in the government and many of the government administrators were Muslim scribes
-Mansa Musa: (r 1312 -1337); made pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) that drew the Islamic world's attention; brought back architects, artists, & holy men; crippled Egyptian economy for 20 years
-Timbuktu: became a major major terminus of the trans-Saharan trade and a center of Islamic learning.
Griots: storytellers/oral historians in Africa, important part of the culture and social life of the village; advisors to kings

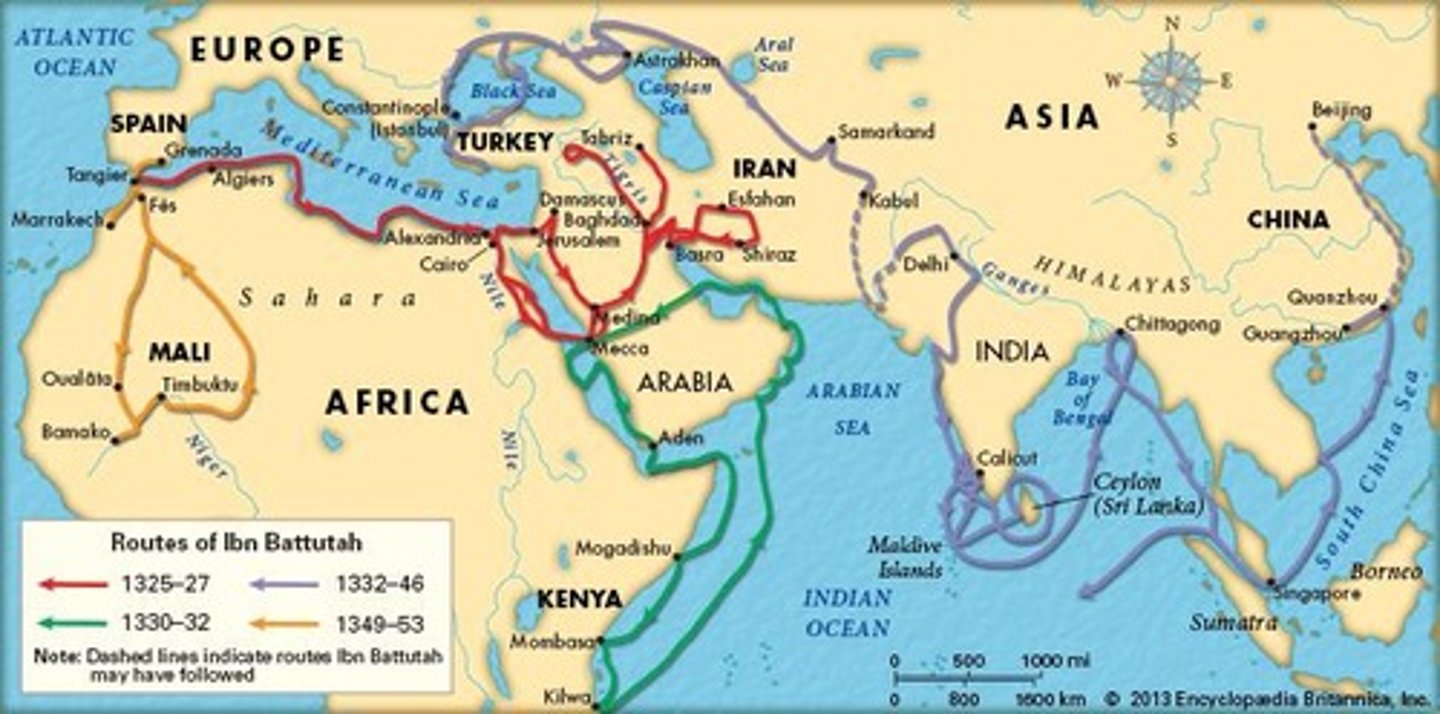
Ibn Battuta
(1304-1369)
- Muslim traveler who described societies and cultures in his travel records, providing historians with much information about the Saharan trade; widely traveled individual of his time.
Dhows/Junks
- Arab sailing vessels with triangular or lateen sails; strongly influenced European ship design, helped them spread their trade empire and sufi missionaries, which lead to the massive expansion of their religion.
-Chinese ships, particularly from the 1400s, are often called these. It was a sturdy Chinese ship design and the largest of its kind were treasures ships that could carry a thousand tons of cargo.
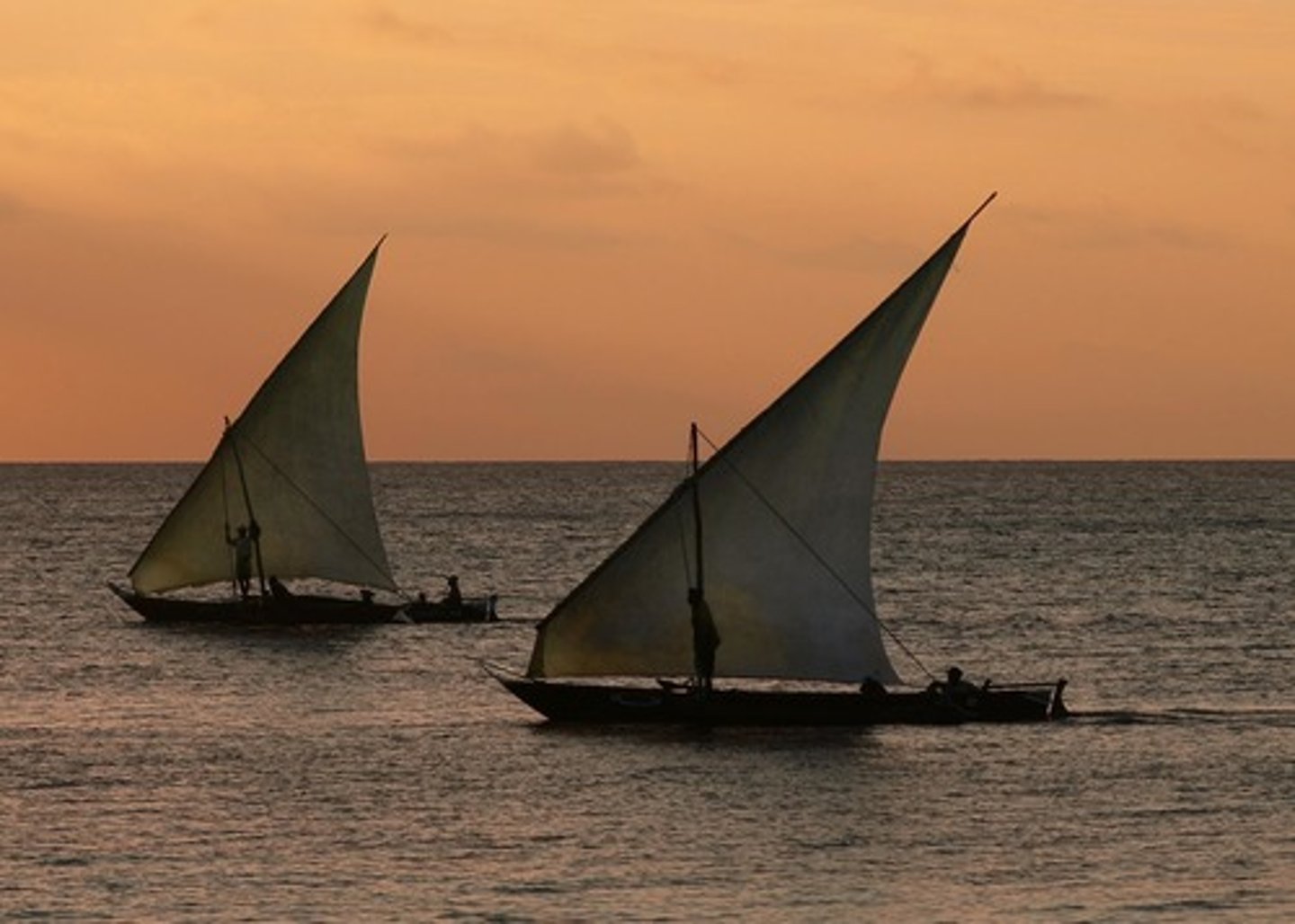

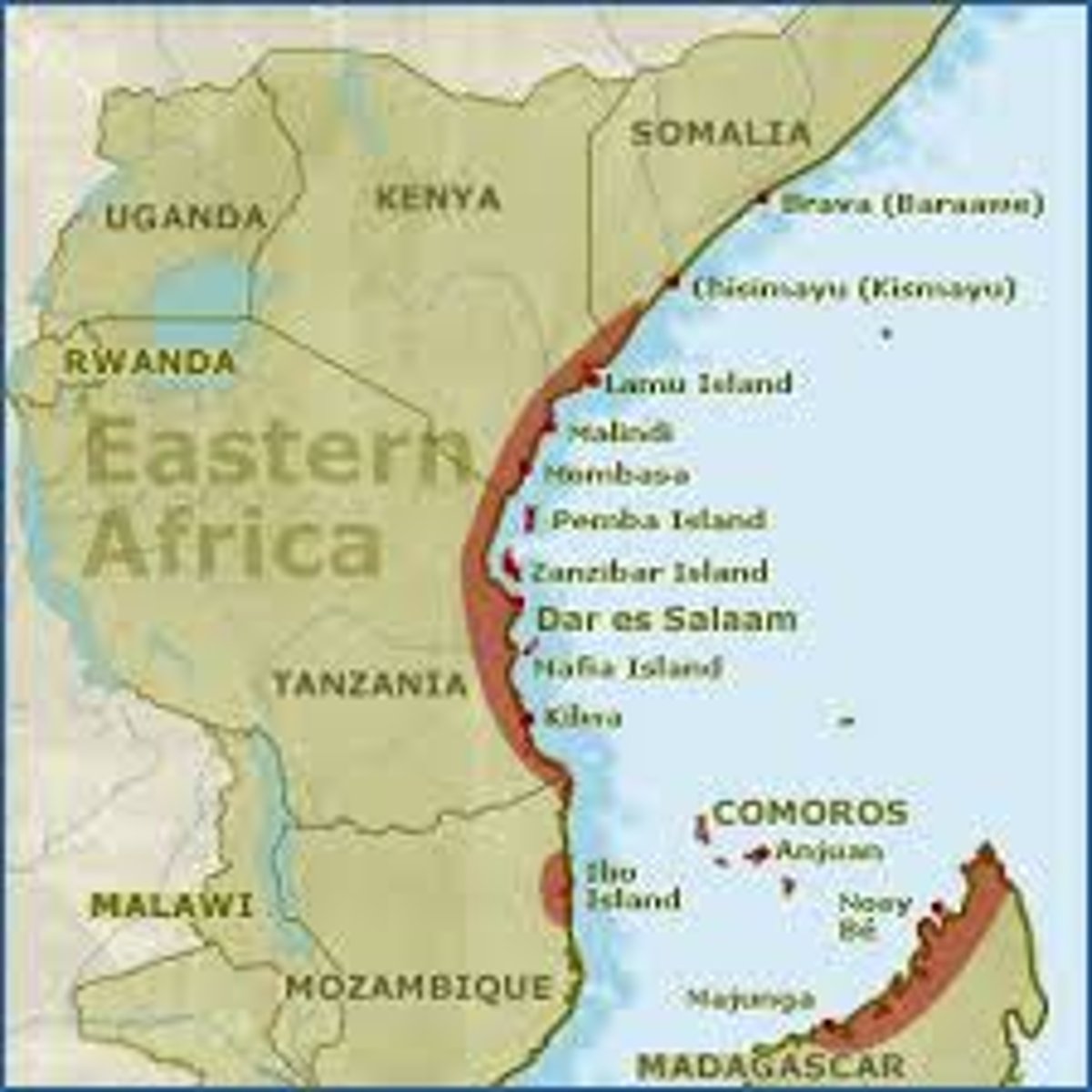
Swahili Coast
-Trade centers in eastern Africa; growth was due largely to the increase in trade along the Indian Ocean Basin.
-Bantu settlers on the coast and Arab merchants who traded along the east African coast interacted to create city-states such as Mogadishu, Sofala, and Kilwa.
-Swahili is a language that blends Bantu and Arabic. Merchants traded gold, slaves and ivory for pottery, glassware, and textiles from Persia, India and China; wealthy merchants often converted to Islam, but did not give up their own religions or traditions.
-Zanj: black slaves from swahili coast; several failed attempts at revolt
Muhammad
(570-632)
-Founder of Islam, prophet of God.
-Came into contact with other peoples via trade; in 610 began meditating at night in the mountains, had a vision of Gabriel who gave him a message from Allah (the Koran: basis of Islam)
-Hadith: a tradition based on reports of the sayings and activities of Muhammad and his companions; est. a principle based on Muhammad's life
-5 Pillars: basic acts of worship of Islam (shahada: profession of faith, salat: prayer, sawm: fasting during the holy month of Ramadan, zakat: a religious tax required of all believers, hajj: pilgrimage to Mecca)

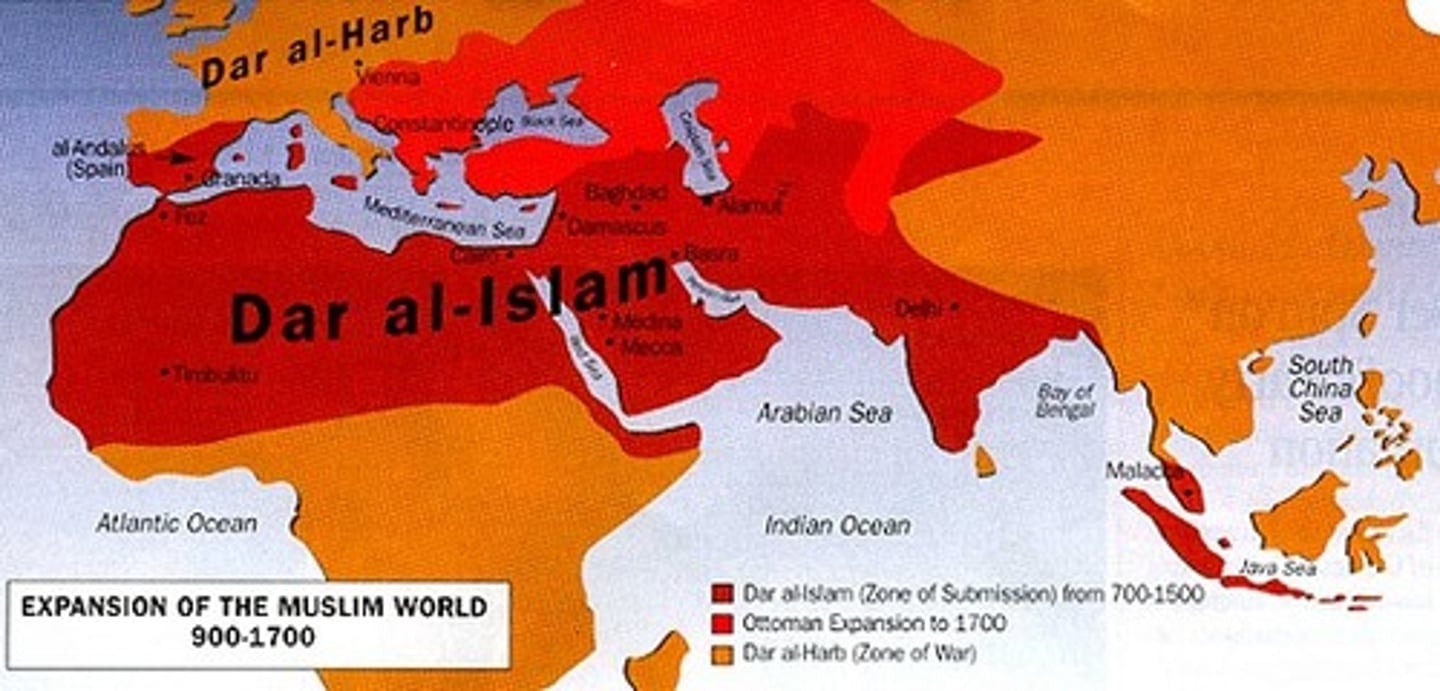
Dar al-Islam
-The world as belonging either to Muslim or non-Muslim territory, exists within Islam
-Allowed for expeditions from other countries to be facilitated; culturally unified different peoples and lands
-Umma: -The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a community.
Mecca/Medina
-Holy city in Islam, home to Muhammad
-Located in the mountainous region along the Red Sea in Arabian Peninsula; founded by Umayyad clan of Quraysh; location of chief religious pilgrimage point in Islam, because it has the Ka'ba (most revered religious shrine in Pre-Islamic Arabia; home to the gods, later incorporated as important Shrine in Islam.)
-Medina: City in western Saudi Arabia to where Muhammad had fled (Hejira: 622, beginning of Muslim calendar, considered to mark the beginning of the Islamic faith); 1st Muslim city, 1st mosque
-Bedouin: Nomadic, polytheistic pastoralists (goats, sheep, camels) of the Arabian peninsula; early converts to Islam; the key towns (Mecca, Medina) found in Arabia were as much an extension of these groups culture

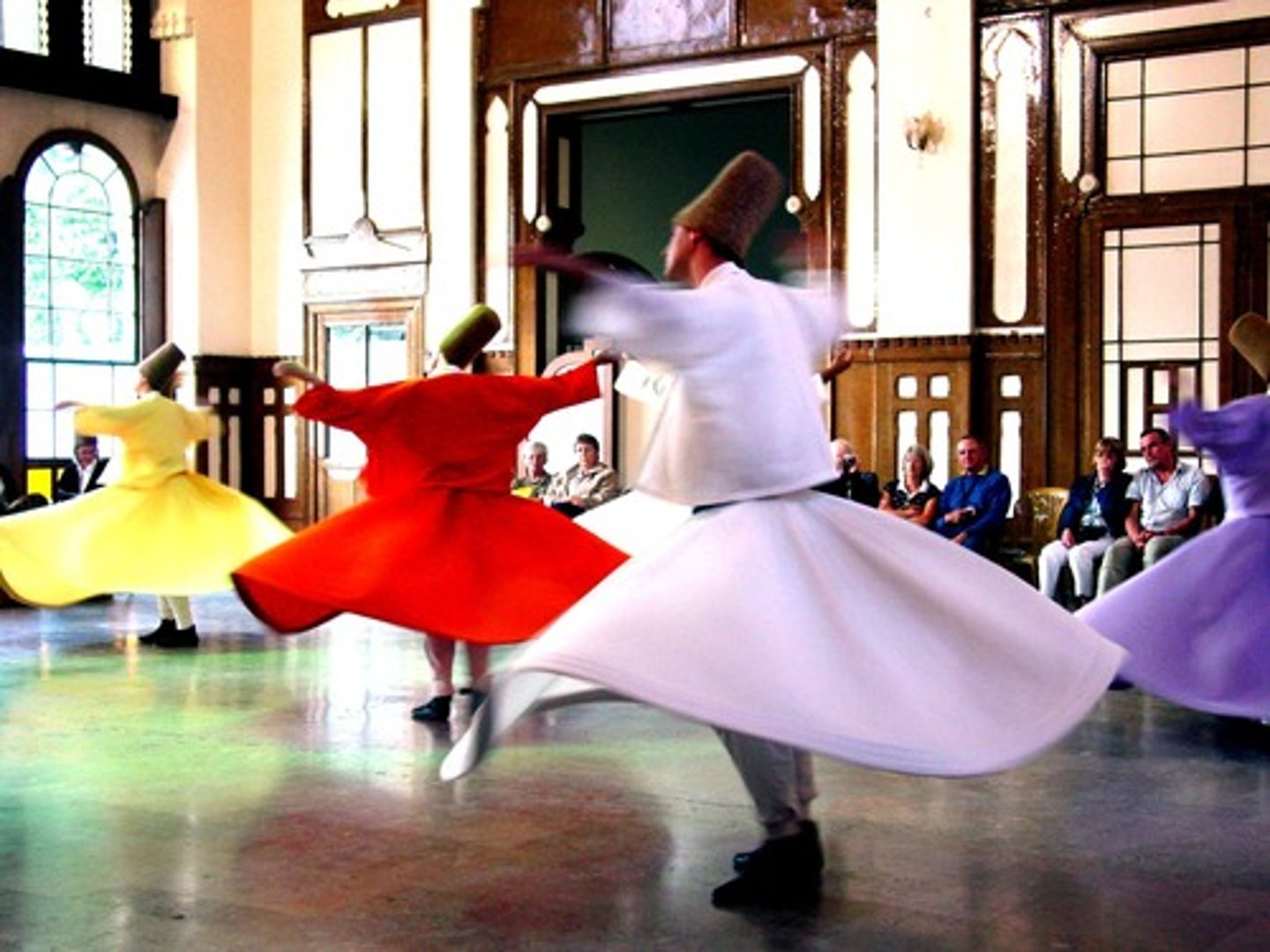
Sufis
-Mystical Muslim group that believed they could draw closer to God through prayer and an ascetic routine (denial of physical desire to gain a spiritual goal)
-Most successful missionaries, helped spread the faith to India & SE Asia

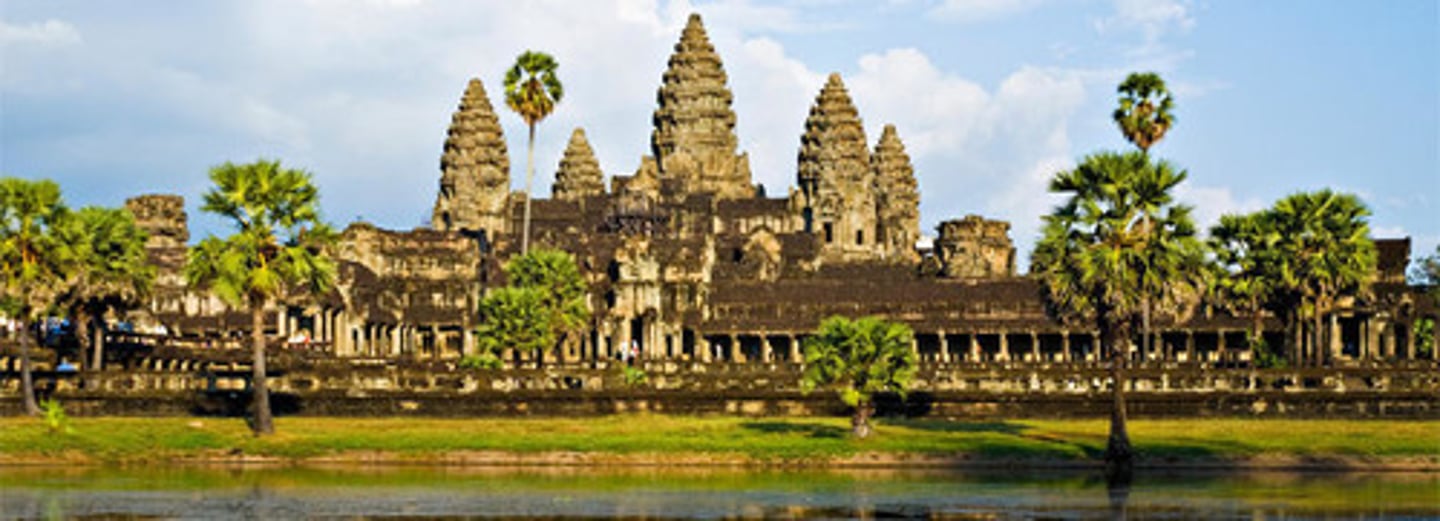
Khmer Empire
(802-1369)
- powerful and long-lasting kingdom on the mainland of SE Asia, centering in what is today Cambodia; reflected strong Indian influence, adopted Hindu, Buddhist beliefs; grew prosperous from rice farming
• Angkor Wat: largest Hindu temple in the world complex dedicated to Vishnu, only took 30 years to build, strong central govt./wealth
• Indianization: spread and diffusion of Indian culture, through Asia especially, through trade across Indian ocean

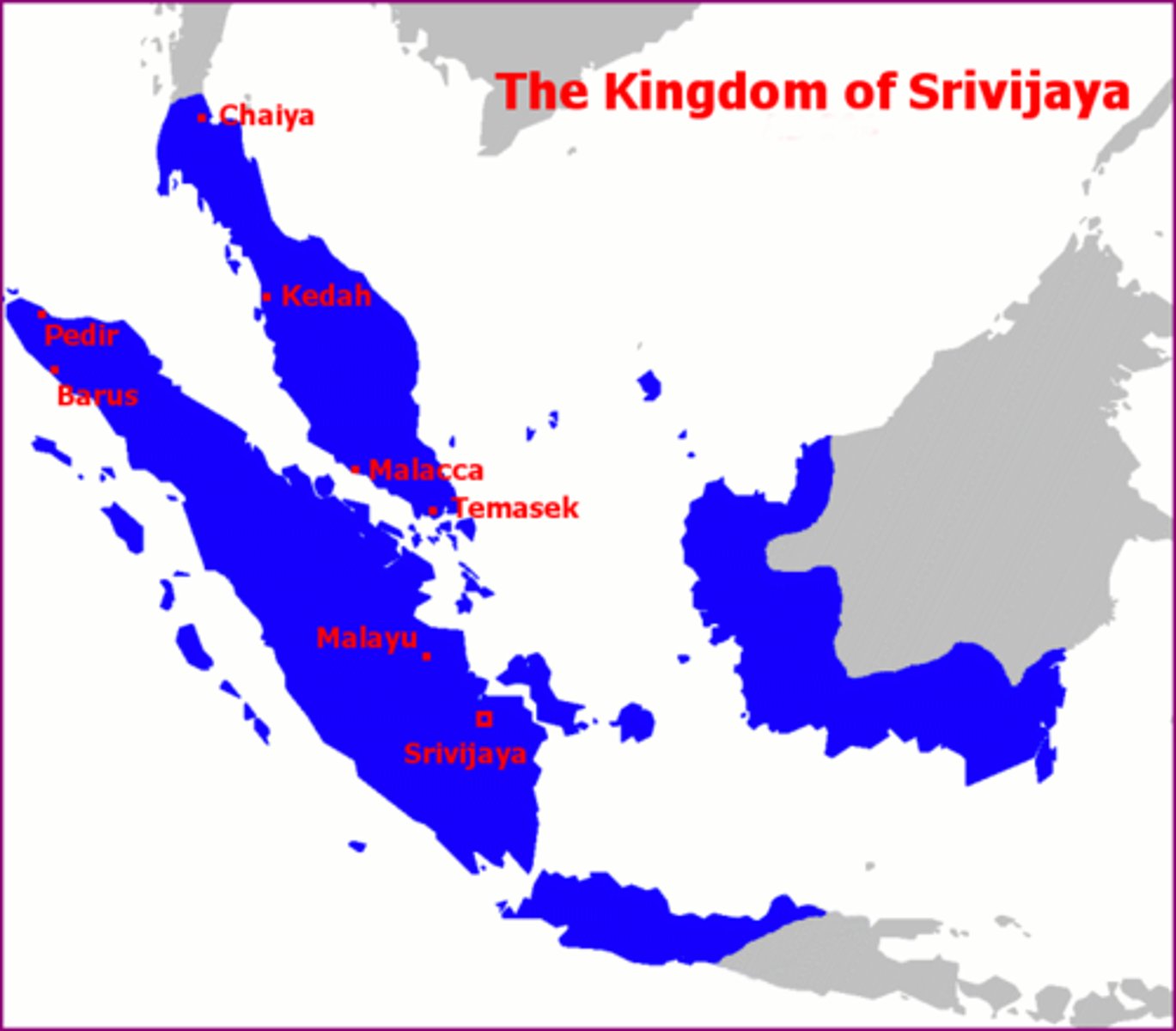
Srivijaya
(650-1377)
-Center of trade; established monopoly over trade from China to India, controlled the Malacca (Melaka) Strait (main shipping channel between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean; geographic choke-point, helped control spice trade)
Palembang became center for Buddhist & Sanskrit culture with large university & library; attracted pilgrims & students from East Asia; constructed Borobudur (largest Buddhism monument anywhere in the world; cultural exchange and syncretism); controlled by Chola in the 11th century; resistant to Muslim missionaries, fall opened up SE Asia to Muslim conversion.
Bhakti
-In some ways gap between the two religions narrowed during post classical era with the sufis often using Hindu ways such as acting as an Indian guru to attract followers
-Both drew on long established/long observed cultural traditions
-Development of bhakti movement, a cult of love and devotion that sought to erase distinction between Hinduism and Islam
-Came from southern India in 12th century

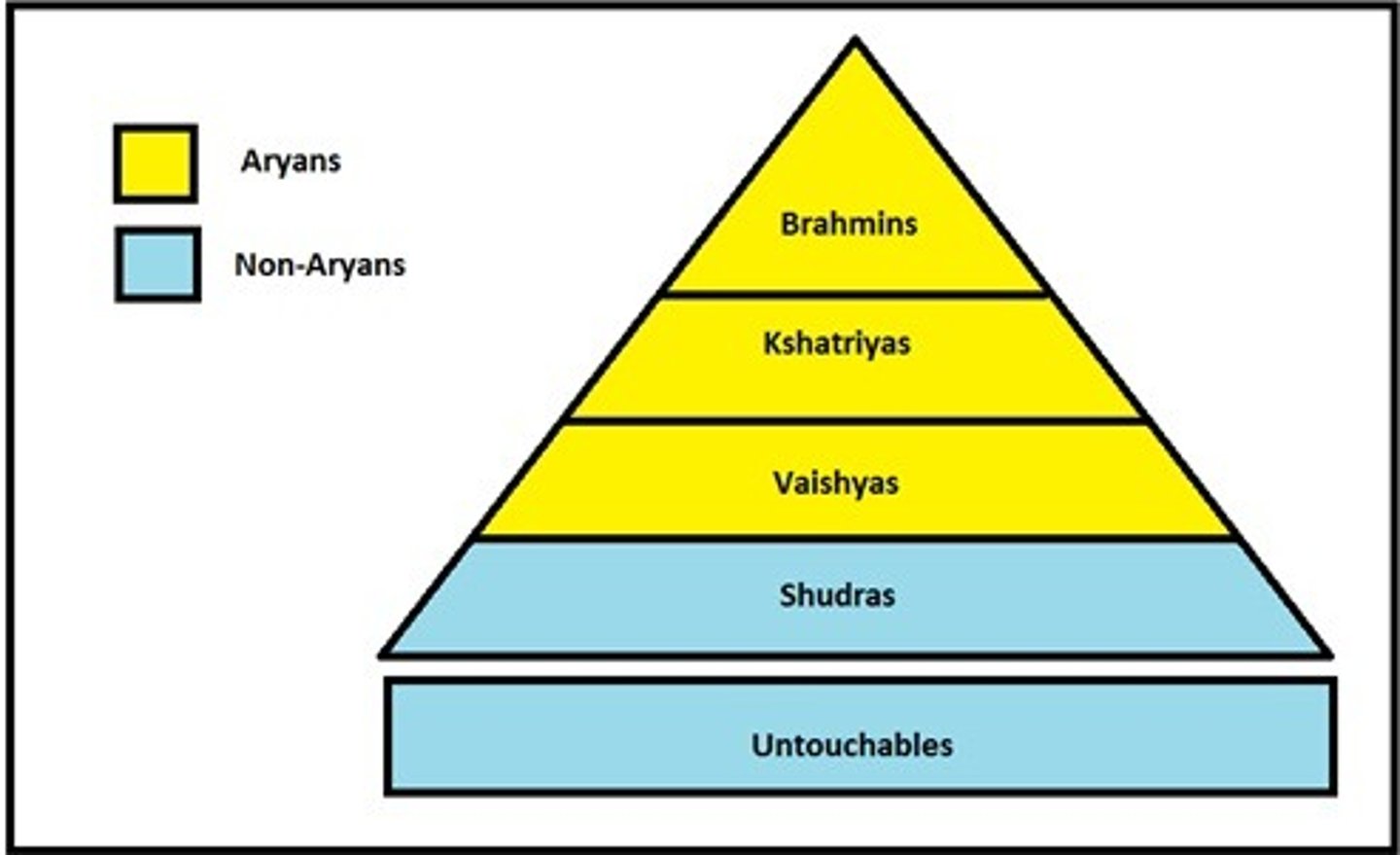
Caste System
-rigid system of social classification introduced by Aryans, originally based on race (varna); very little social mobility-brahmans (priests), kshtriyas (warriors), vaishya (merchants), sudras (peasants), dalits (untouchables, outcastes)-Jati: subcastes where people did the same jobs, similar to guilds
Emporia
-Multicultural Indian port cities that were involved in maritime trade in the Indian Ocean Basin.
-India was a natural site for warehouses, became cosmopolitan centers
-Diasporic communities: merchant communities that introduced their own cultures into other areas
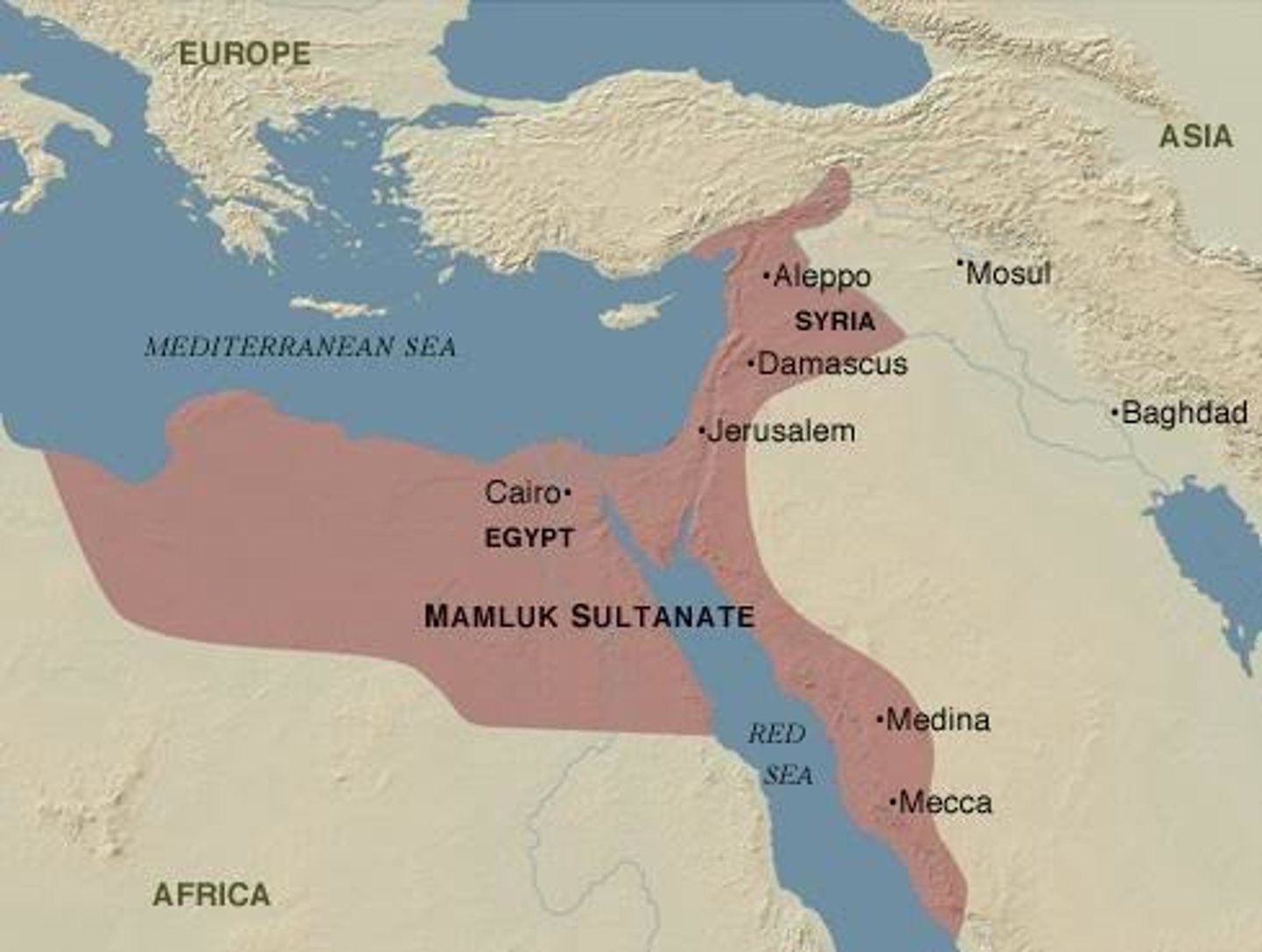
Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt
-(1250-1517) Under the Islamic system of military slavery, Turkic military slaves who formed an important part of the armed forces of the Abbasid Caliphate
-Mamluks seized control of Egyptian government; prospered by facilitating trade in cotton and sugar between Islamic world and Europe
Malacca Sultanate
-(1400-1511) Muslim sultanate that became wealthy by building a navy and imposing fees on ships that passed through it which caused the sultan to become powerful enough to expand the state into Sumatra and the Southern Malay Peninsula; sultanate of this location when the Portuguese invaded the city in 1511
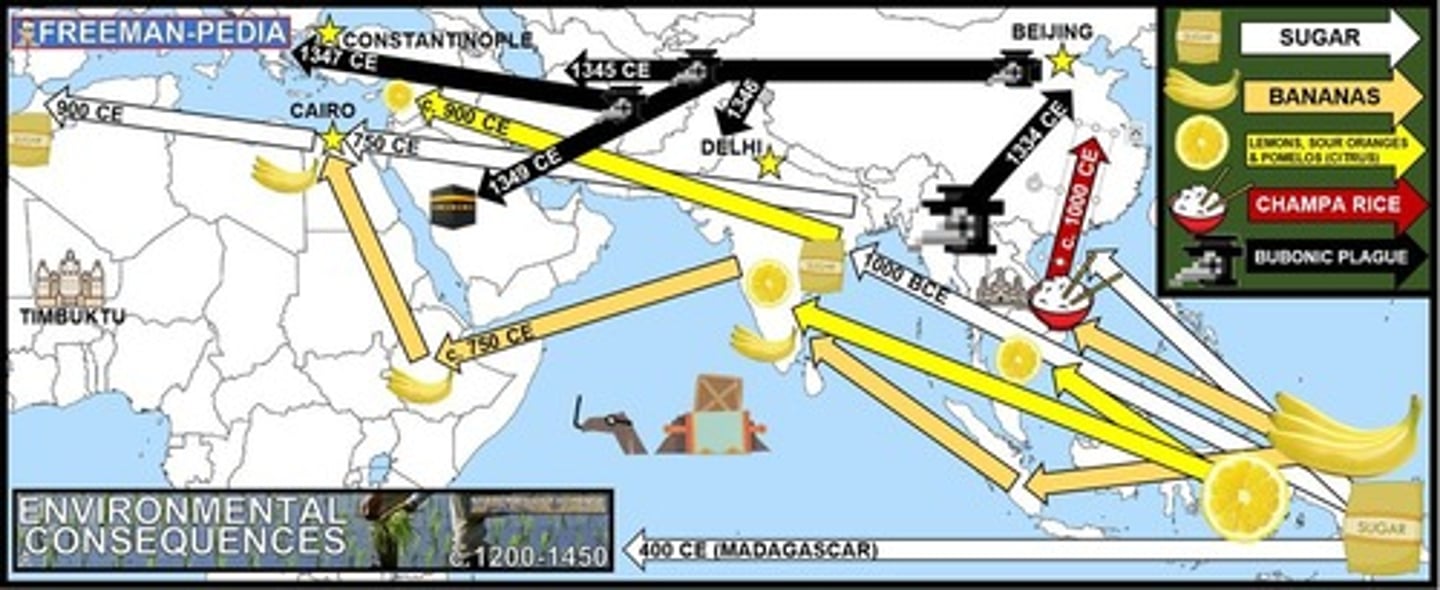
Muslim Agricultural Revolution
-This period of agricultural innovation from the 8th to the 13th century led to the diffusion throughout the Islamic world of many new farming and irrigation techniques, as well as new goods including coffee, sugarcane, and citrus fruits; overall population growth