Exam 2: Clinical Avian Parasitology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
how is clinical assessment of avian parasites defined
history
PE
dx testing
direct fecal exam
fecal flotation
parasite PCR
adavanced molecular testing
specific treatment
what are the three major classes of mites
Dermanyssus
Ornithonyssus
Knemidokoptes
how is Dermanyssus gallinae defined
red mites
presents as weakness, anemia, excess preening
night feeders
tx= environmental cleaning, carbaryl pwder, frontline
how is Ornithonyssus sylviarum defined
fowl mite
remains on the bird
tx dust with pyrethrins, carbaryl
how are knemidokoptes spp defined
scaly leg and face mite
lesions on face, beak, vent and legs
tassel foot, break overgrowth
common in canaries, budgerigars
dx with skin scraping
tx with SQ ivermectin
how are lice described in birds
uncommon
nits (eggs attached to feathers)
dust, spray, pyrethrin or carbaryl
how are hippoboscid flies described
keds
flat
raptors and pigeons
anemia and death
keep wild birds away from aviary
what is the major trematode in birds
Clinostomum marginatum, aka yellow grub
how
how is Clnostomum marginatum describe in birds
seen in fish, frogs and birds
twi intermediate, one definitive host
eggs hatch, miracidium invades the foot of a snail
cercaria leaves the snail, encysting in the muscle of fish and frogs and then develops into the metacercaria
adult fund in the mouth and esophagus of herons and other fish eating birds
treated with removal and praziquantel
what are the major intestinal parasites in birds
giardia
helminths = capillaria, ascarids, spirurids, cestodes
how is giardia described in birds
budgies, cockatiels, toucan
cysts and adults in feces
wasting, chronic mucoid diarrhea, regurgitation, anorexia, feather picking
treat with metronidazole
how is trichomonosis described in birds
T. gallinae and T. stableri
sinuses, mouth, esphagous, liver, other
all birds affected but primarily doves and pigeons
birds may become infected by eating other birds
initially appear as small yellowish foci to coalescing lesions in mouth
contaminated water
infected birds lose weight and become listless
how is trichomonosis diagnosed in birds
histological exam
PCR
confirmation by microscopic examination of wet mount
culture of organisms in prepared culture media
how is trichomonosis treated
carnidazole
metroiazole
what is Capillaria
threadworms
direct or indirect (earthworm)
emaciation and diarrhea in peafowl
fecal float shows bipolar plug egg
treat with fenbendazole
how are cestodes described in birds
indirect life cycle
wasting
fecal proglottids
egg baskets or eggs in feces
Praiquatnel
how are ascarids described in birds
round worms
direct life cycle
nonspecific clinical signs
impaction, regurgitation, wasting weakness
tx with fenbedazole
what are the major respiratory tract parasites
tracheal mites
gapeworm
how are gapeworms described in birds
Sygamous trachea
couging dyspnea sneezing
tx with fenbendazole oral, ivermectin inj
Y shape- small male, large female
what is Cyathostoma bronchialis
respiratory parasite similar to gapeworm
chickens, water fowl, raties, and more
direct ingestion of 3rd stage larvae or indirect via earthworms
larynx, trachea, bronchi, air sacs
presenting signs
diagnose with eggs in feces/oral mucous, direct observation
treatment similar to gapeworm
how are tracheal mites described in birds
sternastoma tracheacolum
black spots in trachea and bronchi
air sacs at base of heart
treat with Ivermextin 200ug/kg, 5% sevin dust
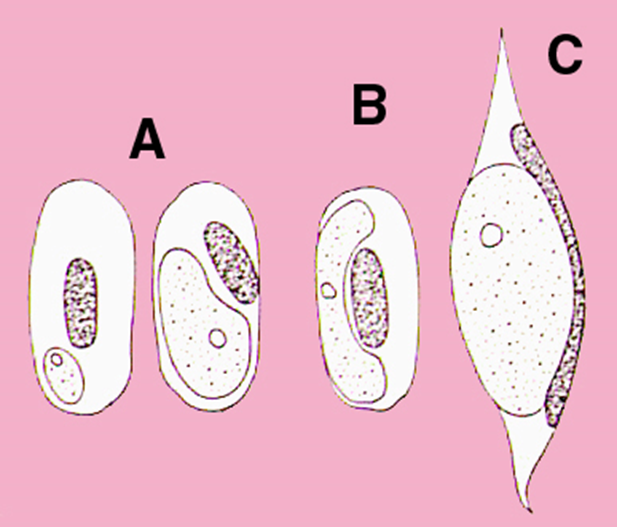
what blood parasite is A
Plasmodium, avian malaria
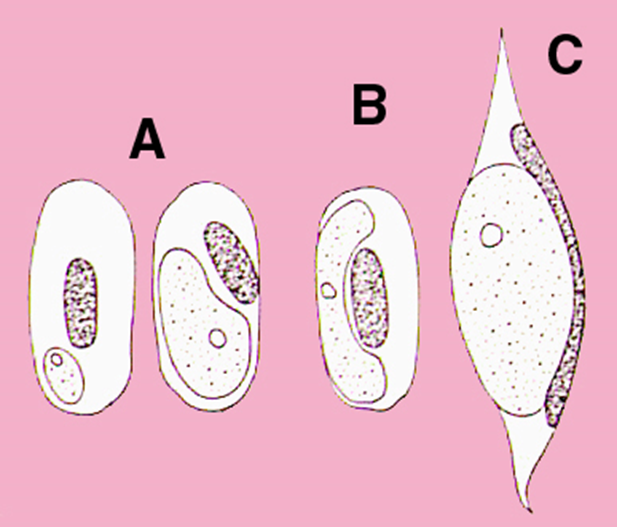
what blood parasite is B
hemoproteus
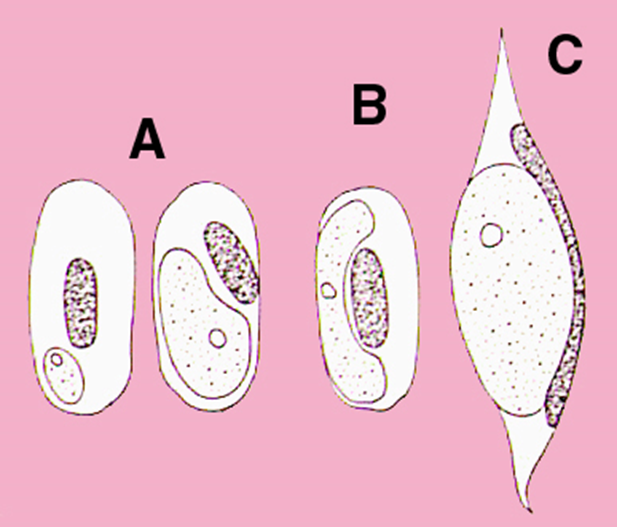
what blood parasite is C
leukocytozoon
how is plasmodium described in birds
RBC, extracellular
pathogenic in canaries, gryfalcons, chickens, ducks, pigens
hemolytc anemia, hemoglobinuria, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis
how is Haemoproteus or Parahaemoproteus described in birds
RBC
psittacine, BOP, pigeons, sea birds
present as anemia
nonpathogenic
treat with antimalarials but not recommended
vactors are hippoboscid flies (H) and Culicoids spp (P)
how is Leukocytozoon described in birds
RBC and WBC
ducks, geese, turkeys
hemolytic anemia
hemoglobinuria
treat with antimalarials?