Analyzing Populations
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Identify and describe the three ways to analyze population size
Counting = Works well for large visible relatively stationary organisms
Population Sampling = Grid out square meters randomly thought field, find average number of plants per square meter and multiply by square meter of field
Mark-Recapture Method = Set traps, count/mark/tag what you caught, release them, come back later and recapture
Population Growth Rate Equation
Change in population size over change in times equals birth rate minus death rate (add immigration and subtract emigration)
dN = change in population size
dt = change in time
B = birth rate
D = death rate
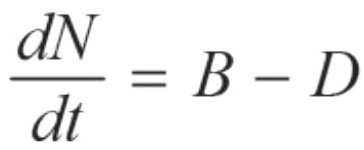
Survivorship Curve I
Most losses occur at older ages; most fatality for elderly; K-selected
Traits of K-Selected Species
In Survivorship Curve I
Longer life span
Fewer offspring
Iteroparity = multiple reproductions
Parental care
Larger sized animals
Survivorship Curve II
Equal chance of death at any time
Survivorship Curve III
Lots of offspring though most dies; those that survive live long; r-selected species
Traits of r-Selected Species
Lots of offspring
Semelparity = single reproduction
No parental care
Shorter life span
Exponential Growth
Slow initial growth (lag phase) then rapid increase of growth and will either experience a population crash or develop logistic growth
R-selected species
Survivorship Curve III
Does not go on forever - will eventually hit a limiting factor
Intrinsic rate of increase = maximum rate of reproduction
Conditions for Exponential Growth
Ideal conditions for population
All needed resources in abundance (food, water space)
No predators, competition, disease, natural disaster
Exponential Growth Equation
Change in population size over change in time equals the maximum per Capita growth rate of a population times population size
dN = change in population size
dt = change in time
rmax = maximum per Capita growth rate of population
N = population size
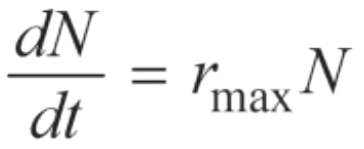
Cull the herd
Remove the weak, keeping remaining healthy and strong
Carrying Capacity (K)
The maximum number of organisms the population can sustain