Abrasives polishing
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not done yet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
surface irregularities can include fine surface roughness, this means
inherent particle size of investment
fine surface roughness have a high W/P ratio that _________ (inc/dec) surface roughness
inc
fine surface roughness with a low W/P ratio that _________ (inc/dec) investment adaptation or flow
dec
when thinking about fine surface roughness, what can encourage investment decomposition
prolonged burnout and overheating alloy
when thinking about fine surface roughness, what encourages rxn w investment
overheating alloy
definition of finishing
to put a final surface on; the refinement of form prior to polishing
definition of polishing
to make smooth and glossy, usually by abrasion
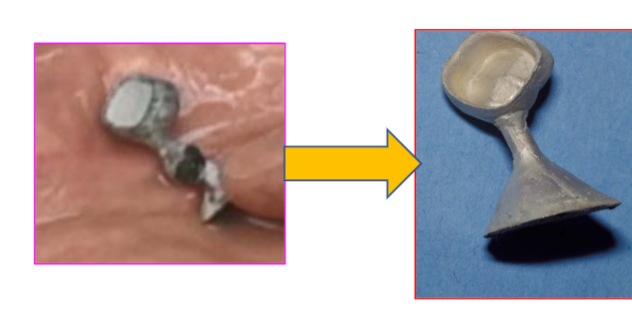
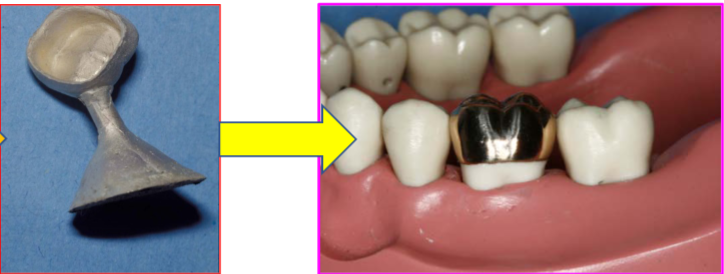
w an interim prothesis, would you do finishing or polishing
finishing
w a definitive prosthesis, would you do finishing or polishing
polishing
what are the general steps of “the direct restoration armamentarium” (12)
diagnostic
tissue management
isolation
decay removal
cavity preparation
sectional matrix
lingual matrix
bonding
composite
placing, shaping, bending, and curing
finishing
procedure systems
polishing
what is the diagnostic step of direct restoration armamentarium
where dentistry and tx begin using high quality hand-instruments, x-ray sensors, and headlight systems
what is the tissue management step of direct restoration armamentarium
a soft-tissue diode dental laser can make dentistry easier and more painless
what is the isolation step of direct restoration armamentarium
help control the oral environment of a procedure by isolating the effected tooth: a dental dam is commonly used to ensure protection from saliva, blood, and debri; can help clinician focus too
what is the decay removal step of direct restoration armamentarium
removing decay with high quality diamonds, carbides, and handpieces
what is the cavity preperation step of direct restoration armamentarium
using high-quality burs is essential for this step- preparation is key for restorative success
what is the sectional matrix step of direct restoration armamentarium
improves restorative success, an advanced sectional matrix system is used for CII composite restorations and provides a consistently tight posterior contact and delivers inc separation force to reduce flash
what is the lingual matrix step of direct restoration armamentarium
used to build up layers of composite during a CIV restoration; an effective fast set impression material can be used for anterior restorations that can lead to highly esthetic and efficient results
what is the bonding step of direct restoration armamentarium
bond to the enamel is the most important and determines the longevity of your restoration and the integrity of of the composite-enamel margin; the total etch technique provides the highest bond strength to enamel while demineralized the dentin and removing the smear layer
what is the composite step of direct restoration armamentarium
the right composite will provide pts w beautiful dental restorations that will last; an ideal composite will come in various shades and opacities and polish quickly while maintaining high gloss retention
what is the placing, shaping, blending , and curing step of direct restoration armamentarium
shaping and contouring before light-curing results in dec finishing time and equals efficiency and esthetically pleasing restorations
what is the finishing step of direct restoration armamentarium
trimming and finishing carbides and finishing diamonds are used to shape, strip, contour, and add texture to composite
what is the procedure systems step of direct restoration armamentarium
procedure kit can help w predictability, practicality, and repeatability in contouring, finishing, and polishing
what is the polishing step of direct restoration armamentarium
this can require a series of polishers, brushes, discs, strips, and paste
definition of abrasion
wear or material loss from a surface as a result of scratching or other mechanical means
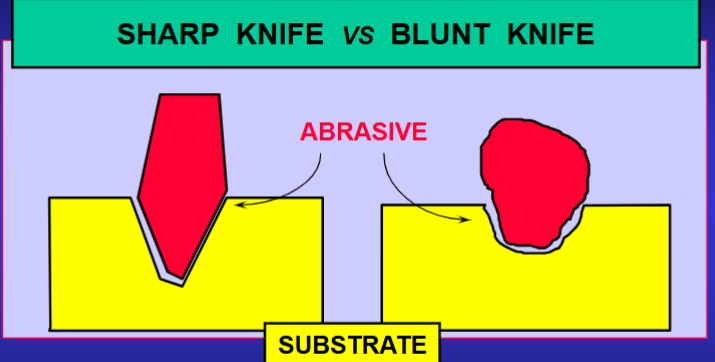
when thinking of dental abrasion, what is the substrate
material being abraded
when thinking about dental abrasion, what is the abrasive
material that causes wear
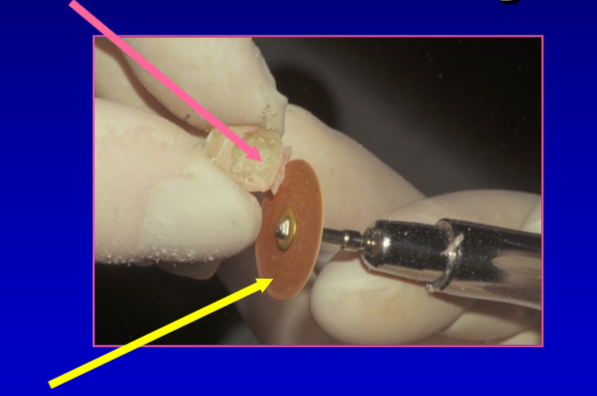
pink arrow
substrate
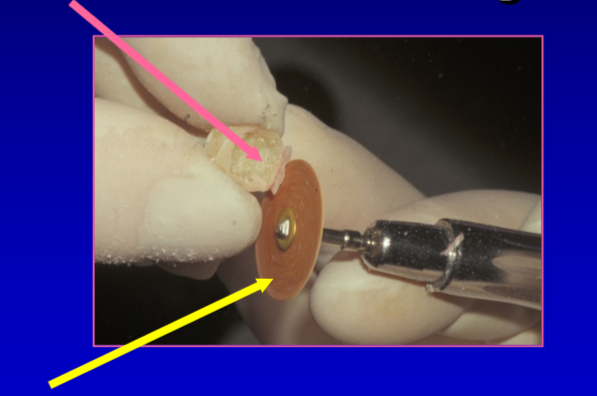
yellow arrow
abrasive
what are the three dental abrasion procedures
two-body abrasion
three-body abrasion
airborne particle abrasion
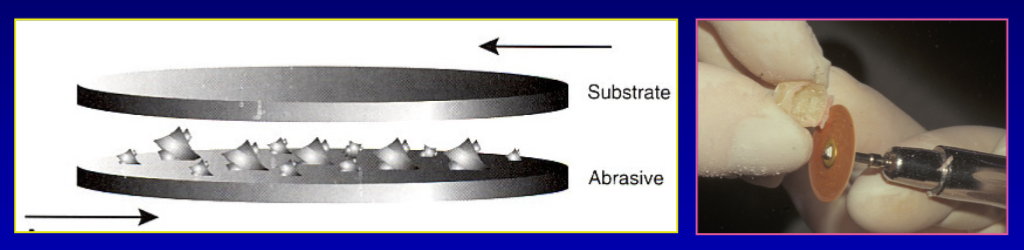
what is two-body abrasion
abrasive particles are tightly bonded to the abrasive instrument that is removing material from the substrate surface
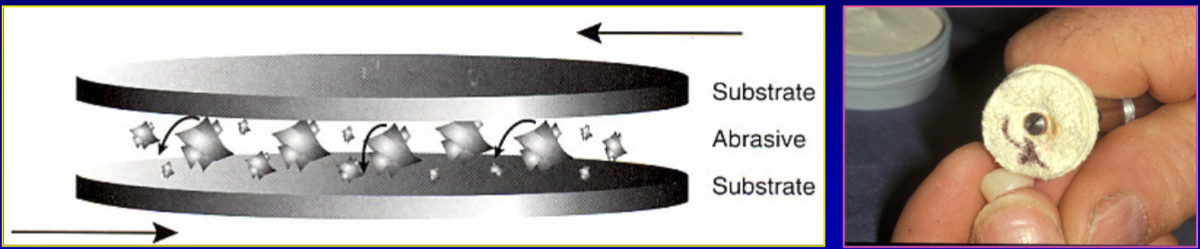
what is three-body abrasion
involves the use of non-bonded abrasives, abrasive particles are free to translate and rotate between two surfaces
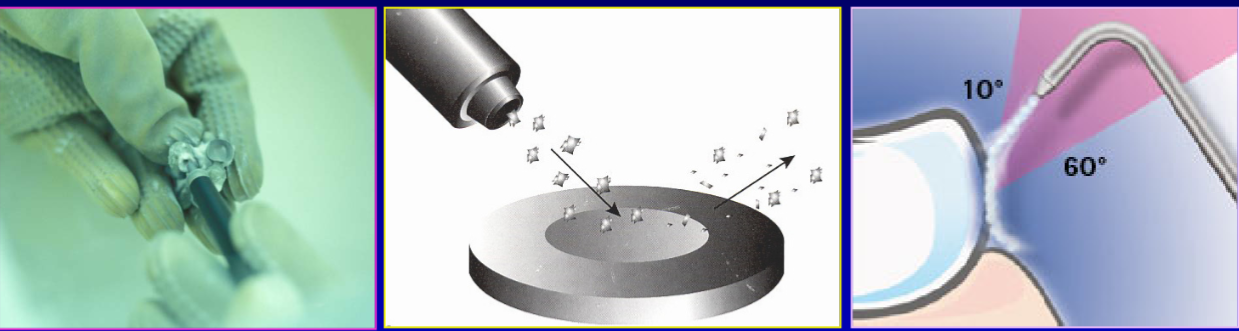
what is airborne particle abrasion
abrasive particles are propelled (sandblasted) against a substrate by air pressure to remove surface material
what are the 5 factors that affect the rate of abrasion
hardness between the abrasive and the substrate
particle size of abrasive
particle shape of abrasive
speed and pressure
lubrication
one of the factors that affect the rate of abrasion is hardness between the abrasive and the substrate, how can we assess hardness
the relative hardness of minerals using a scale established by Dr. Mohs (1812) and an indentation hardness test
what is the Mohs hardness test
the test compares the resistance of a mineral by scratching w ten reference minerals known as Mohs scale materials
what are the 10 materials used in Mohs hardness test
Talc
gypsum
calcite
fluorite
apatite
orthoclase
quartz
topaz
corundum
diamond

what is Mohs Hardness Scale
determined by scratching the surface of the tile w different mineral and subjectively assigning a “Mohs” number
pumice is created when…
super-heated, highly pressurized rock is violently ejected from a volcano
what is included in an indentation hardness test
test surface harness- Brinell, Knoop, Vickers hardness tests
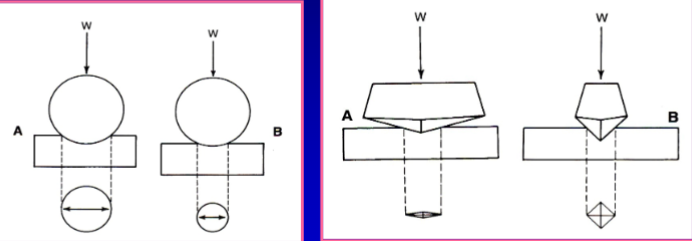
what is an indentation hardness test
the size or the depth of the indentation and the amount of force are used to calculate a hardness value
one of the factors that affect the rate of abrasion is particle size of abrasive, explain this between large and small particles
for the same applied pressure: larger particles leave larger scratches in the substrate while smaller particles leave smaller scratches in the substrate

what color is superfine
white

what color is fine
red

what color is medium
blue

what color is coarse
black
one of the factors that affect the rate of abrasion is particle shape of abrasive, explain the difference of a sharp vs rounder particle
a sharp particle produces a deeper abrasion than a rounder particle under the same applied force
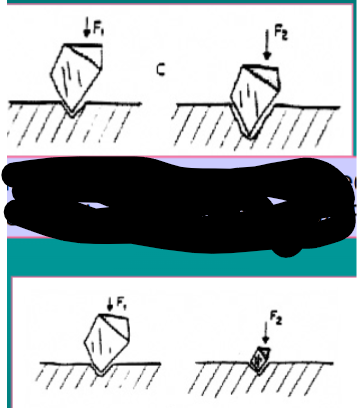
one of the factors that affect the rate of abrasion is abrasive speed and pressure, explain this
deeper and wider scratches are produced by inc the applied force, equivalent sized scratches can be produced by different size of particles by varying the applied pressure
one of the factors that affect the rate of abrasion is lubrication, explain this
reduce heat-buildup, to wash away debris to prevent clogging of the abrasive instrument (ex: wear in engines is reduced using oil or maintenance fluid as a lubricant→ stops metal to metal contact)
the most efficient abrasion occurs when the difference is __________ (larger or smaller) in hardness between the abrasive and substrate
larger

step-down approach to finishing and polishing
finishing: refinement procedure of substrate surface
polishing: makes smooth and glossy surface by abrasion
what are the three types of rotary grinding instruments
low speed, medium speed, high speed
a high speed rotary instrument is ______-driven
air

air turbine characteristics
balance between speed and torque, faster and consistent cutting and grinding
comparison or electric and air-driven handpieces
air-driven: faster, air turbine drive, less bur concentricity, louder sound, cheaper

what are the 5 finishing and polishing instruments
carbide burs, diamond burs, dental stones, rubber wheels, disks and strips
what are the three basic parts of a dental burs - carbide and diamond
the shank, the neck, and the head
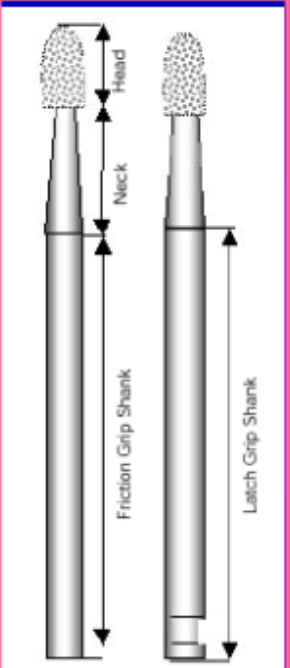
what are the two types of shanks in dental burs
friction grip (high speed) and latch-type (slow speed)
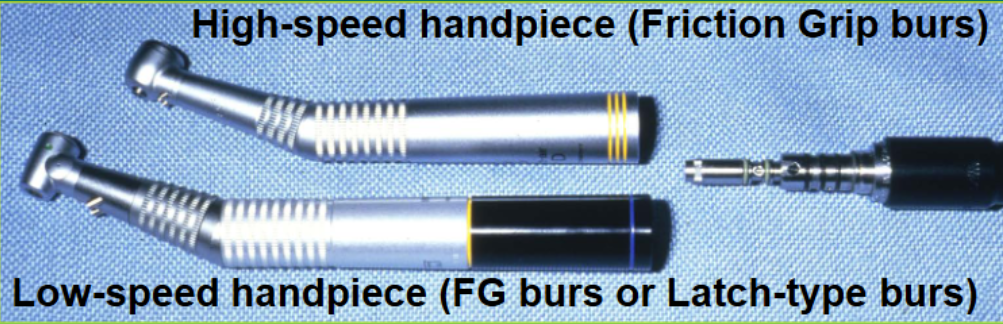
what is the purpose having different types of shanks in dental burs
to accommodate either contra-angles or straight handpieces
what are the different head types of carbide burs
barrel, cone, egg, taper, flame, cylinder

in carbide burs, the bur shank is made of ___________ while the cutting blades are made of ________________
stainless steel; tungsten carbide
carbide burs are primarily used for…
contouring and finishing
the most commonly used carbide burs range from 8 to 30 _________ blades which can be __________ or _________
fluted; straight or twisted
what is the straight blade design
one blade on tooth
what is the spiral blade design
several blades on the tooth
anatomy of a carbide bur
rake angle, rake, face clearance face
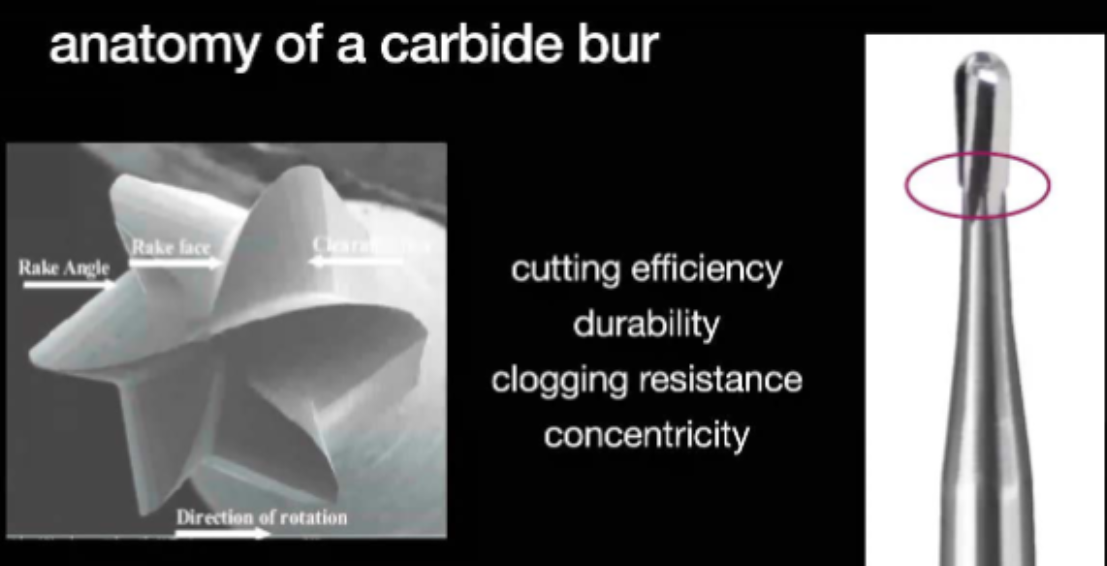
carbide bur blade design has ____ angles + ____ faces
3 angles, 2 faces
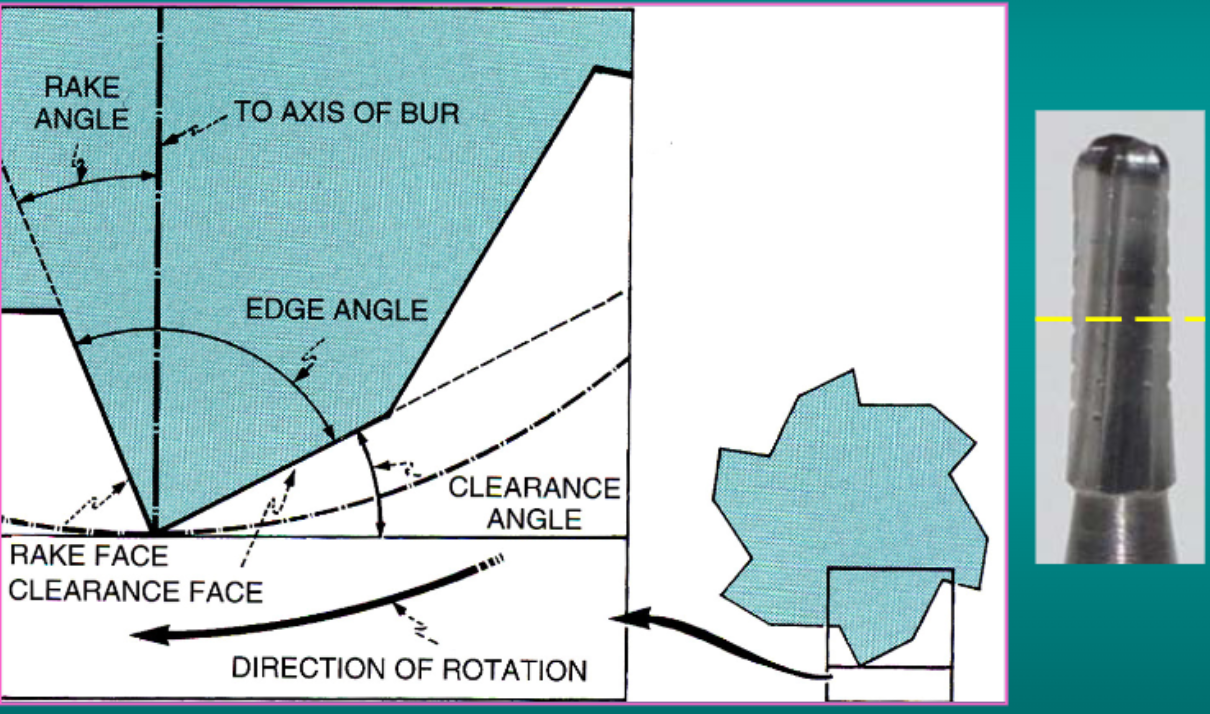
what is the rake angle
the angle made between the rake face and the line connecting the edge to the axis of the bur- cutting edge strength
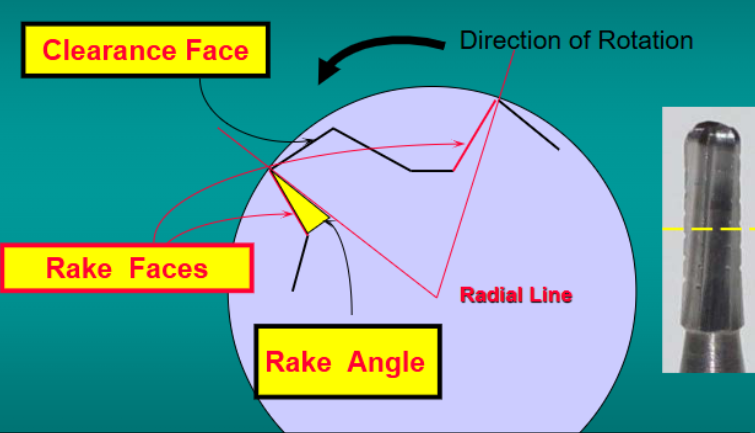

you want a positive rake angle for what type of materials
soft and weak materials

you want a negative rake angle for…
hard and brittle materials

what is a negative rake angle
the radial line lies behind the rake face and entirely within the blade

what is a positive rake angle
the radius lies outside the blade
the larger the rake angle means ____________ (higher/lower) strength of the cutting edge
lower
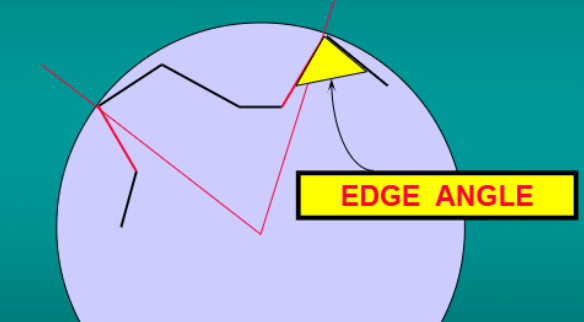
what is the edge angle
internal angle at the edge formed by the two faces of the bur blade, related to the resistance of the blade to fracture- blade strength
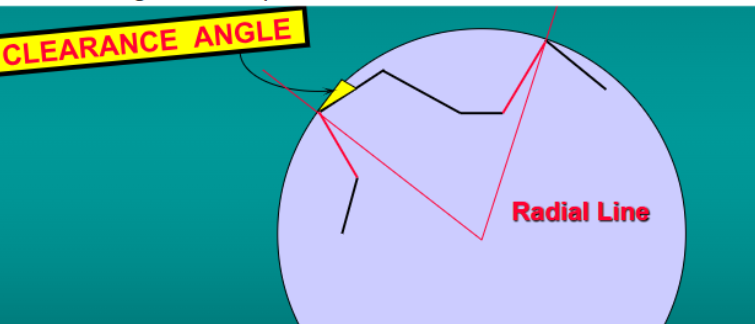
what is the clearance angle
angle between the clearance face immediately behind the edge and a tangent to the path of rotation- provides stop and space
the clearance angle helps eliminate…
rubbing friction of the clearance face of the blade against the new tooth surface
the clearance angle provides a stop to prevent…
the bur edge from digging into the tooth structure excessively
the clearance angle helps to provide an adequate clearance space for…
the chips formed ahead of the following blade
what are diamond instrument primarily used for
finishing ones are used for contour, adjust, and smooth composites or porcelain
diamond bur characteristics (3)
stainless steel shank
the powdered diamond abrasive
a metallic bonding material that holds diamond powder onto the shank
the diamond bur shank is made of…
stainless steel
the diamond bur cutting end is made of…
stainless steel with diamond particles cemented
diamond burs can also come in a disk form where the metal disk is made up of…
stainless steel w diamond particles cemented→ diamond grit
in most cases, diamond particle sizes are applied in a sequence, you start w a ________ (finer/coarser) grit and progress to a _________ (finer/coarser) grit
coarser; finer
diamond burs should always be utilized with…
water spray
polishing instruments, like rubber polishing instruments or pastes, will usually follow the use of…
diamonds
carbide burs are better for…
end-cutting procedures, they produce lower heat and have more blade edges for cutting
diamond burs are better for…
tooth preparation, braveling enamel margins and enameloplasty
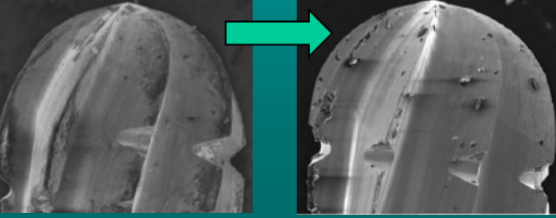
what is happening here
the left is an unused bur and the right is a used bur
what are the 5 cutting recommendations
using a contra-angle handpiece
air-water coolant system
high-operating speed
light pressure
a carbide bur or diamond bur
dental stones consists of what kind of particles
abrasive particles that have been sintered together or bound w an organic resin to form a cohesive mass
dental stones are available in what variety of grade
fine, medium, and coarse grades
what are the three types of dental stones
silicon carbide (carborundum)
aluminum oxide
diamond stone

what are dental stones primarily used for
contouring and finishing restorations, and where maximum abrasion is needed
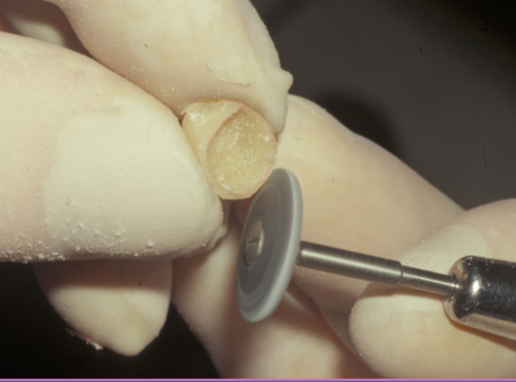
what are rubber wheels used for
fine grinding to remove coarse scratches from rough grinding
rubber wheels are made by…
molding the fine abrasives in a rubber matrix
what are the fine abrasives that are used in a rubber matrix to make rubber wheels
aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, chromium oxide

what are rubber polishers used for
for adjusting and polishing acrylic material

rubber polishers are often sold as kits, why
have a variety if shapes and grits since the wheel instruments are not flexible enough to reach all tooth surfaces
________ shape instruments are used for occlusal fine finishing and polishing
point

what do you not want to do when using rubber polishers
you do not want to apply heavy pressure, will produce excessive friction heat which can have a negative effect on the restoration, the rubber instrument, and the tooth itself