Physics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Base Quantities
The basic quantities that are used to define all quantities of the system. Length, mass, and time.
Derived Quantities
Quantities that can be expressed as algebraic combinations of base quantities.
SI standard of time is based on what
Vibration of atoms of Cesium-133
Is there an SI base unit for area
Area can be expressed in terms of square meters
SI standard of length is based on what
The speed of light
The SI base units
Meter (L), Kilogram (M), Second ( T)
Vector Quantity
A quantity with both magnitude (how large) and direction to be specified
Scalar Quantity
A quantity that only needs magnitude to be specified.
Representation of Vectors
A statement providing its magnitude and direction
Using a variable name with a little arrow
Representing a vector graphically
Vector A and B lie in the x-y plane. A = B if:
Ax = Bx and Ay = By
Let A = 2î + 6j - 3k and B = 4î + 2j + k. How is A . B found?
Combine like terms.
The value of k x(j x î)
0
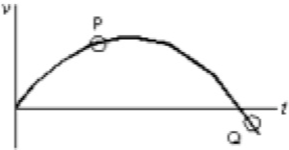
The diagram above shows a velocity-time graph for a car moving in a straight line. At point Q the car must be:
moving with zero acceleration
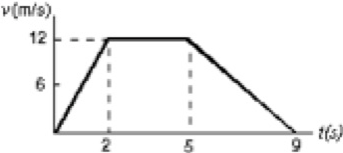
The diagram represents the straight line motion of a car.
The car accelerates at 6 m/s2 for the first 2 s
The position-time graph of an object is a straight line with a positive slope. The object has
constant velocity
Position
Its location with respect to the origin of the reference
Initial
When we start observing the object
Final
When we stopped observing the object
Equation for average speed
Distance traveled/ time of travel
Displacement
Change in position
Average Velocity
Displacement/time (final - initial)
Unit of acceleration
Velocity (m/s) divided by time (s)