The water cycle and water insecurity
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:38 AM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
What is the global hydrological cycle?
The closed system of all of earths water. It consists of many different stores, by which water is moved in and out of by solar and gravitational potential energy.
2
New cards
What is a store in the global hydrological cycle?
A place where water is held. Eg a reservoir or the atmosphere
3
New cards
What is a flow in the global hydrological cycle?
The movement of water between stores. Eg a river or rain
4
New cards
What is a process in relation to a flow?
A process is a physical mechanism that drives a flow. Eg gravitational pull drives a river
5
New cards
Name the flows in the global hydrological cycle
Surface runoff, infiltration and percolation, through flow and groundwater flow.
6
New cards
What is the difference between infiltration and percolation?
Infiltration is rainwater soaking into the soil, whereas percolation is the movement of water within the soil itself.
7
New cards
What is the difference between throughflow and groundwater flow?
Through flow is the downslope movement of water through the soil, roughly parallel to the ground surface whereas
Groundwater flow is the very slow horizontal movement of water through rock
Groundwater flow is the very slow horizontal movement of water through rock
8
New cards
What are the two different categories of water store?
Blue water- visible water such as rivers and lakes
Green water- non visible water in stored such as trees and soil
Green water- non visible water in stored such as trees and soil
9
New cards
What is residence time?
Average amount of time a water molecule stays in its store
10
New cards
What is a drainage basin?
The area of land drained by a a river and it tributaries.
11
New cards
What is a watershed?
The boundary of a drainage basin
12
New cards
What are the tree types of rainfall?
Orographic, frontal and conventional
13
New cards
What is orographic rainfall?
orographic rain is formed when air is forced to cool when it rises over relief features in the landscape such as hills or mountains. As it rises it cools, condenses and forms rain which falls on one side of the mountain, whereas the other side remains dry
14
New cards
What is frontal rainfall?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds. The clouds bring heavy rain.
15
New cards
What is conventional rainfall?
When the sun heats the earths surface, the air above it warms and rises. As it rises it cools and condenses to rainfall. This type of rainfall is common in tropical areas
16
New cards
What are the two outputs in the hydrological cycle?
Evaporation and transpiration. (Evapotranspiration EVT)
17
New cards
What is potential EVT?
The water loss that would occur if there was an unlimited supply of water in soil available for plants.
18
New cards
Name the physical factors the effect drainage basins
- The climate (eg the amount of precipitation and seasonal patters)
- vegetation (type and amount)
-the soil
- the geology of the area (permeable or impermeable)
- the relief
- vegetation (type and amount)
-the soil
- the geology of the area (permeable or impermeable)
- the relief
19
New cards
Name the human factors that effect drainage basins
- Reservoir creation
- deforestation (reduces interception so surface runoff increases)
- land use change (use of tarmac, which is impermeable, can cause flooding)
- deforestation (reduces interception so surface runoff increases)
- land use change (use of tarmac, which is impermeable, can cause flooding)
20
New cards
What is a water budget?
It is the annual balance between precipitation, evapotranspiration and runoff
21
New cards
What is the water budget equation and what does each character stand for?
P= Q + E +/- S
P= Precipitation
Q= Channel discharge
E= Evaporation
S= Change in store
P= Precipitation
Q= Channel discharge
E= Evaporation
S= Change in store
22
New cards
How can this equation show positive or negative water balance?
P>Q+E = +ive
P
P
23
New cards
What is a river regime?
The annual variation in discharge or flow of a river at a particular point or gauging station. Usually measured in cubic meters per second (cumecs)
24
New cards
Simple river regime
Where the river experiences seasonally high discharge followed by seasonally low discharge. Inputs typically depend on meltwater or storms.
Tends to be rivers in temperate and mountainous regions
Tends to be rivers in temperate and mountainous regions
25
New cards
Complex river regimes
Where larger rivers cross several different relief/climatic zones and so also experience different seasons + effects. Eg the river Ganges or the amazon
Human factory’s can also make river regimes more complex. Eg dams
Human factory’s can also make river regimes more complex. Eg dams
26
New cards
Other factors that impact river regimes
- Catchment size
- geology
- land use
- evaporation rate
- vegetation type
- geology
- land use
- evaporation rate
- vegetation type
27
New cards
What does a storm hydrograph show?
The variation in discharge of a river within a short period of time in response to input of precipitation
28
New cards
What are the two types of hydrograph?
Flat and flashy
29
New cards
What physical factors can effect the shape of a hydrograph?
- vol and duration of precipitation
- river size
- catchment area
- relief +geology
- vegetation cover
- river size
- catchment area
- relief +geology
- vegetation cover
30
New cards
What human factors can effect the shape of a hydrograph?
- deforestation (Vegetation cover)
- urbanisation (surface runoff)
- urbanisation (surface runoff)
31
New cards
What are the four types of drought?
- meteorological
- hydrological
- agricultural
- famine drought
- hydrological
- agricultural
- famine drought
32
New cards
What is meteorological drought?
Drought caused by lack of precipitation
33
New cards
What is hydrological drought
Drought caused by changes in the input and output of bodies of water
34
New cards
What is agricultural drought?
When water content of soil is low, causing plant biomass to decrease
35
New cards
What is famine drought?
A humanitarian crisis in which agricultural failure has lead fo wide spread food shortages
36
New cards
What are the natural causes of drought?
Short term-
- blocking anicyclones
Med term-
- ENSO (MAKE MORE NOTES ON THIS)
Long term-
-global atmospheric circulation (worldwide system of winds)
- blocking anicyclones
Med term-
- ENSO (MAKE MORE NOTES ON THIS)
Long term-
-global atmospheric circulation (worldwide system of winds)
37
New cards
What are human causes of drought?
- over abstraction of surface water
- deforestation
- climate change
- over extraction of ground water
- deforestation
- climate change
- over extraction of ground water
38
New cards
CASE STUDY
SAHAL AFRICA
39
New cards
CASE STUDY
AUSTRALIA
40
New cards
ENSO (El nino southern oscillation)
a variation in air circulation around the world that results in
* warmer whether to the Americas
* wet weather and flooding in Africa
happens ever 3-7 years
la nina is the opposite pattern
\
is being worsened by climate change
* more frequent
* more severe
* warmer whether to the Americas
* wet weather and flooding in Africa
happens ever 3-7 years
la nina is the opposite pattern
\
is being worsened by climate change
* more frequent
* more severe
41
New cards
What are the ecological impacts of drought on wetlands?
- very vulnerable when dry as organisms are adapted to wet environment
- soil dries up- can lead to easier erosion and oxidation of soil (which can real ease pollutants and nutrients in dangerously conc levels)
- some species such as birds may leave the area
- soil dries up- can lead to easier erosion and oxidation of soil (which can real ease pollutants and nutrients in dangerously conc levels)
- some species such as birds may leave the area
42
New cards
What are the ecological impacts of drought on forests?
- tree growth is slowed + leaves drop which can take up to 4 years to recover from
- tree death changes food chains as well as carbon cycle
- pests spread easier in dry conditions
- tree death changes food chains as well as carbon cycle
- pests spread easier in dry conditions
43
New cards
What are the types of flooding?
ground water, surface water flooding, flash flooding
44
New cards
What is ground water flooding?
occurs after ground is fully saturated and can no longer take in anymore water after prolonged heavy rain fall
45
New cards
What is surface water flooding?
when intense rainfall doesn’t have enough time to infiltrate and so flows over land
46
New cards
What is a flash flood?
A flood with a very short lag time (most dangerous)
47
New cards
Natural causes of flooding
* wet seasons/ too much rainfall
* impermeable rock type
* low-lying area
* area at the bottom of high relief
* impermeable rock type
* low-lying area
* area at the bottom of high relief
48
New cards
Human causes of flooding
- land use change (urbanisation- impermeable materials, deforestation- less interception)
- building over flood plains
- hard engineering such as straightening channels and dredging (increasing depth or river channels) while these may benefit some areas, down stream it can cause issues such as moor flooding .
- building over flood plains
- hard engineering such as straightening channels and dredging (increasing depth or river channels) while these may benefit some areas, down stream it can cause issues such as moor flooding .
49
New cards
How is spearman’s rank calculated?
* **Rs** = spearman’s rank coefficient
* **D** = difference in rank
* **n** = number of samples
* **D** = difference in rank
* **n** = number of samples
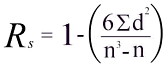
50
New cards
CASE STUDY
UK FLOODING 1953
51
New cards
CASE STUDY
Pakistan floods LIC (geofile)
52
New cards
What is eutrophication?
The process of farming chemicals such as fertilisers being carried into rivers by rain water.
53
New cards
Why is eutrophication bad?
- the nutrients carried into the river causes a huge dense growth of plants
- higher plants (eg algae) block light from reaching deeper parts of the river- causing plant death of underwater plants
- animal death occurs due to lack of photosynthesis by underwater plants leading to low O2 concentrations in water
- overall- decreasing the biodiversity of the river
- higher plants (eg algae) block light from reaching deeper parts of the river- causing plant death of underwater plants
- animal death occurs due to lack of photosynthesis by underwater plants leading to low O2 concentrations in water
- overall- decreasing the biodiversity of the river
54
New cards
water insecurity
when people do mot have enough quality water to sustain a quality life, as well as to support socio-economic development.
55
New cards
physical scarcity
the lack of available water sources such as surface and ground water
56
New cards
CASE STUDY- physical water scarcity
salt water encroachment- Kiribati?
57
New cards
economic scarcity
lack of ACCESS water due to lack of money or management
58
New cards
CASE STUDY- economic water scarcity
* Kathmandu Nepal
* Mexico city (also case study for water conflicts)
* cape town ?? (also case study for water conflicts)
* Mexico city (also case study for water conflicts)
* cape town ?? (also case study for water conflicts)
59
New cards
CASE STUDY- human water scarcity
aral sea
60
New cards
water poverty index
factors in Resources Access Capacity Use and Environment
\
and is a measure of TIME needed to collect a certain volume of water
\
and is a measure of TIME needed to collect a certain volume of water
61
New cards
factors that increase water demand
* population
* agriculture
* hot climate (climate change)
* standard of living (better life styles= need more water)
* agriculture
* hot climate (climate change)
* standard of living (better life styles= need more water)
62
New cards
factors that determine water supply
1. climate (precipitation levels)
2. topography (shape of land/ relief)
3. rock type (permeable or not)
4. river systems
5. pollution makes more water unusable)
6. urbanisation (causes more surface runoff)
63
New cards
CASE STUDY- water insecurity UK
the south of england is more water insecure to the the warmer climate. and as it is a small country there are fewer water sources.
most of Englands water comes form scotland which is a very water secure country
most of Englands water comes form scotland which is a very water secure country
64
New cards
CASE STUDY - conflicts over water
* the Nile
* mexico city
* cape town
* colorado river
* mexico city
* cape town
* colorado river
65
New cards
CASE STUDY- who is on control of the water (gov vs TNC)
Bolivia and the private water company Bechtel Corporation
66
New cards
CASE STUDY- solutions to water insecurity
UNICEF
67
New cards
IWRM
integrated water resources management
\
* a process which promotes co-ordinated development of water management between countries
\
* a process which promotes co-ordinated development of water management between countries
68
New cards
things that determine the price of water
* how hard water is to access
* demand
* level of infrastructure
* who is on control of the water (gov vs TNC)
* demand
* level of infrastructure
* who is on control of the water (gov vs TNC)
69
New cards
players in water distribution
* consumers
* company / gov in control / economy
* environment
* company / gov in control / economy
* environment
70
New cards
CASE STUDY- managing water supply
* three gorges dam china
* water transfer schemes china
* singapore holistic management
* desalination isreal
* IWRM
* UNs Helsinki rules
→ Colorado river
* water transfer schemes china
* singapore holistic management
* desalination isreal
* IWRM
* UNs Helsinki rules
→ Colorado river