BSC2086L E.5 Blood Vessels
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
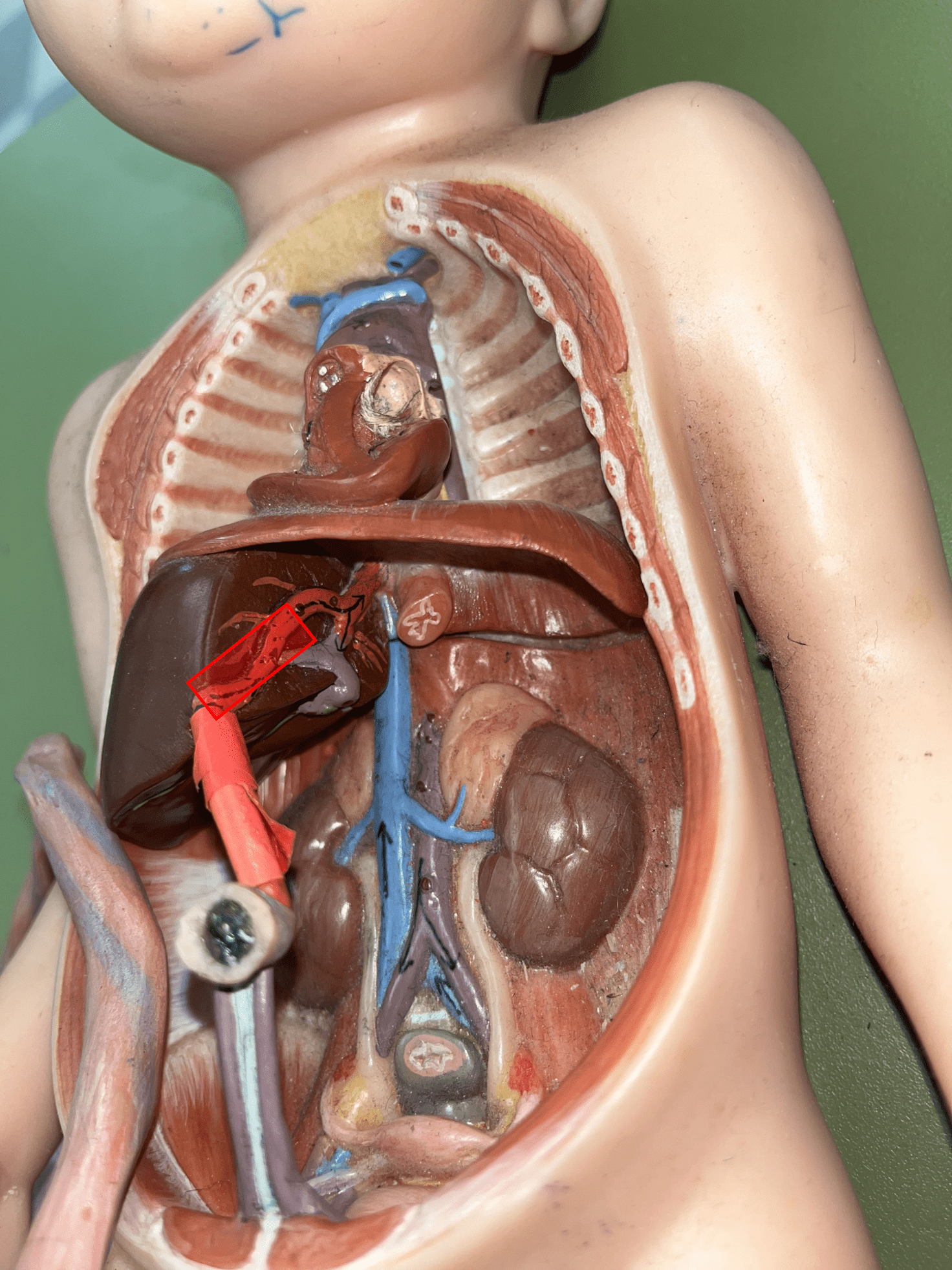
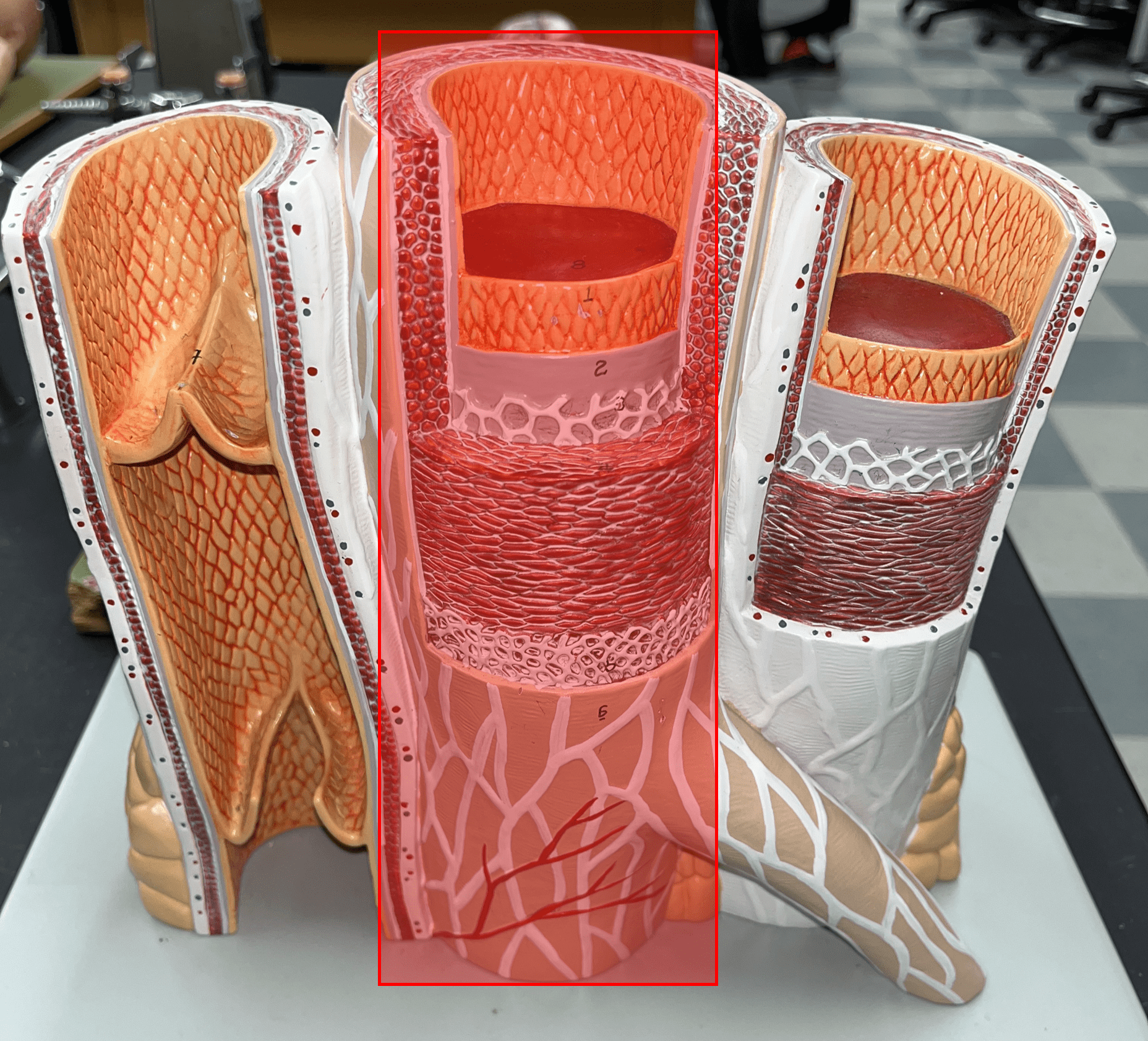
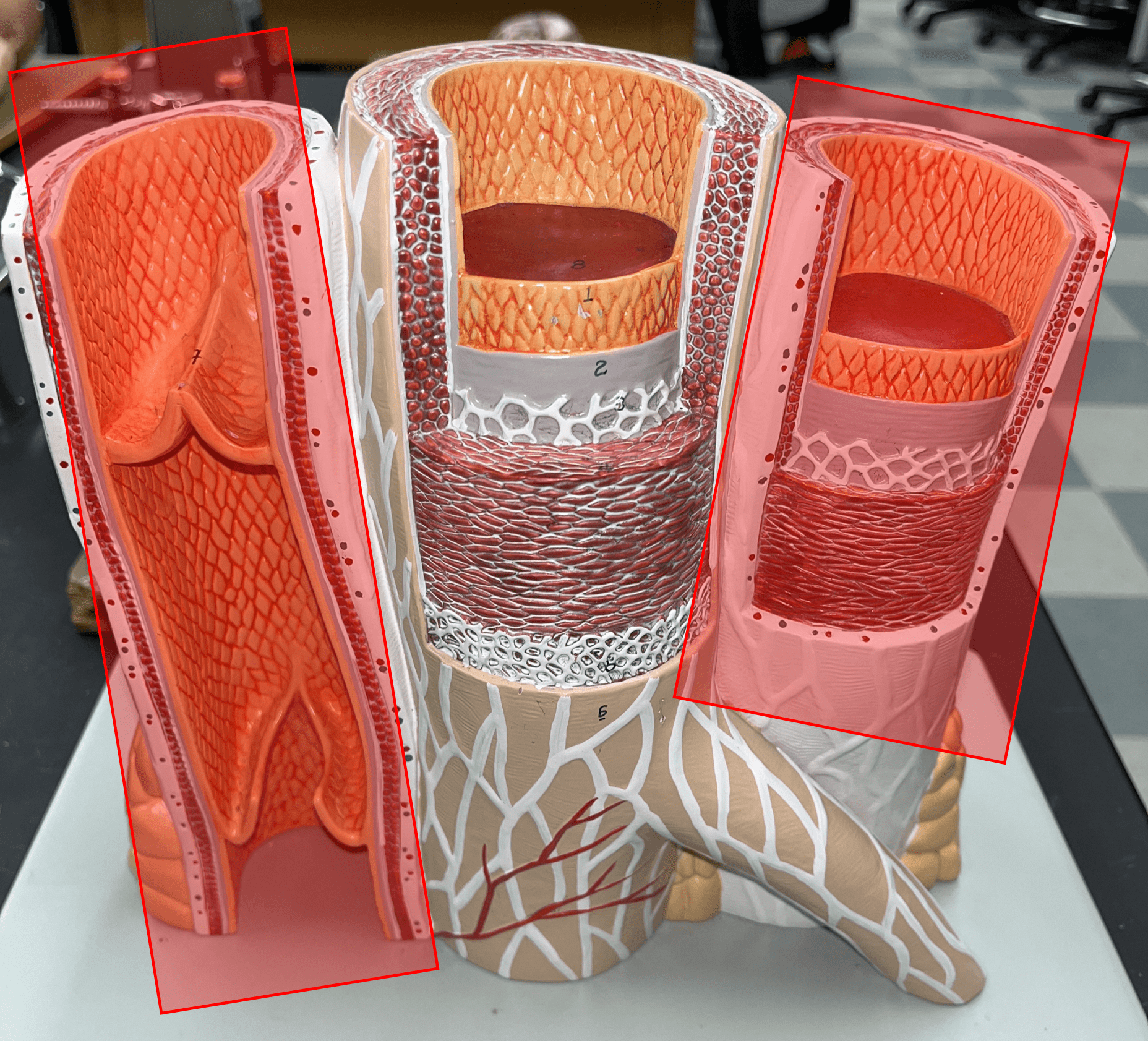
artery
• Transports blood away from the heart.
• Has the thickest tunica media.
• Also known as resistance or efferent vessels.
• Has the thickest tunica media.
• Also known as resistance or efferent vessels.
2
New cards
arteriole
A smaller branch of an artery.
3
New cards
capillary
• The smallest blood vessel.
• Consists of a single cell endothelium supported by a thin basement membrane.
• Allows the movement of small molecules and fluid between the blood and interstitial fluid.
• Consists of a single cell endothelium supported by a thin basement membrane.
• Allows the movement of small molecules and fluid between the blood and interstitial fluid.
4
New cards
vein
• Transports blood to the heart.
• Also known as capacitance or afferent vessels.
• Some contain valves.
• Also known as capacitance or afferent vessels.
• Some contain valves.
5
New cards
venule
A smaller branch converging to form a larger vein.
6
New cards
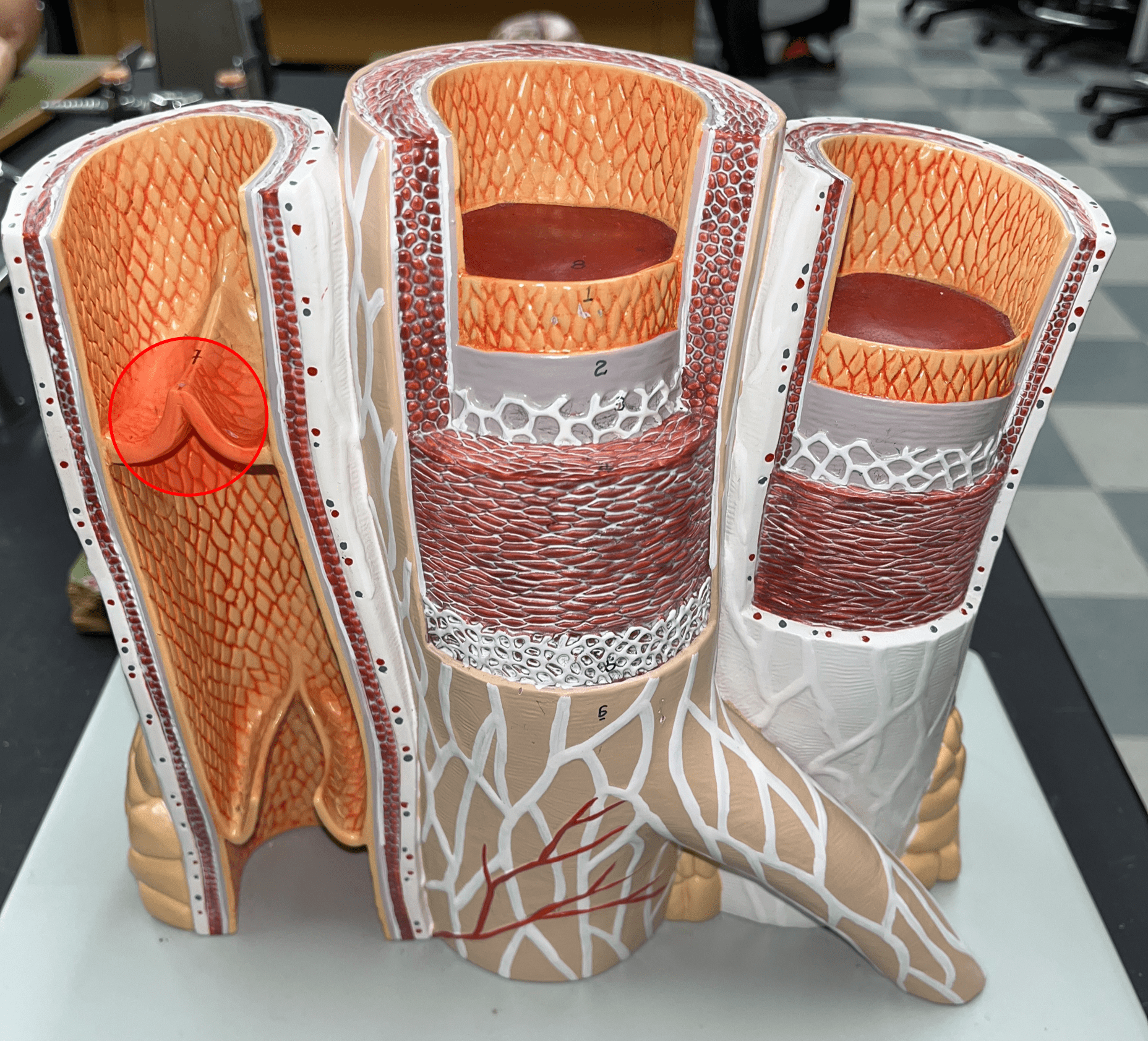
tunica externa
• The outermost layer of an artery wall.
• Composed of loose connective tissue and collagen fibers.
• Also known as the tunica adventitia.
• Composed of loose connective tissue and collagen fibers.
• Also known as the tunica adventitia.
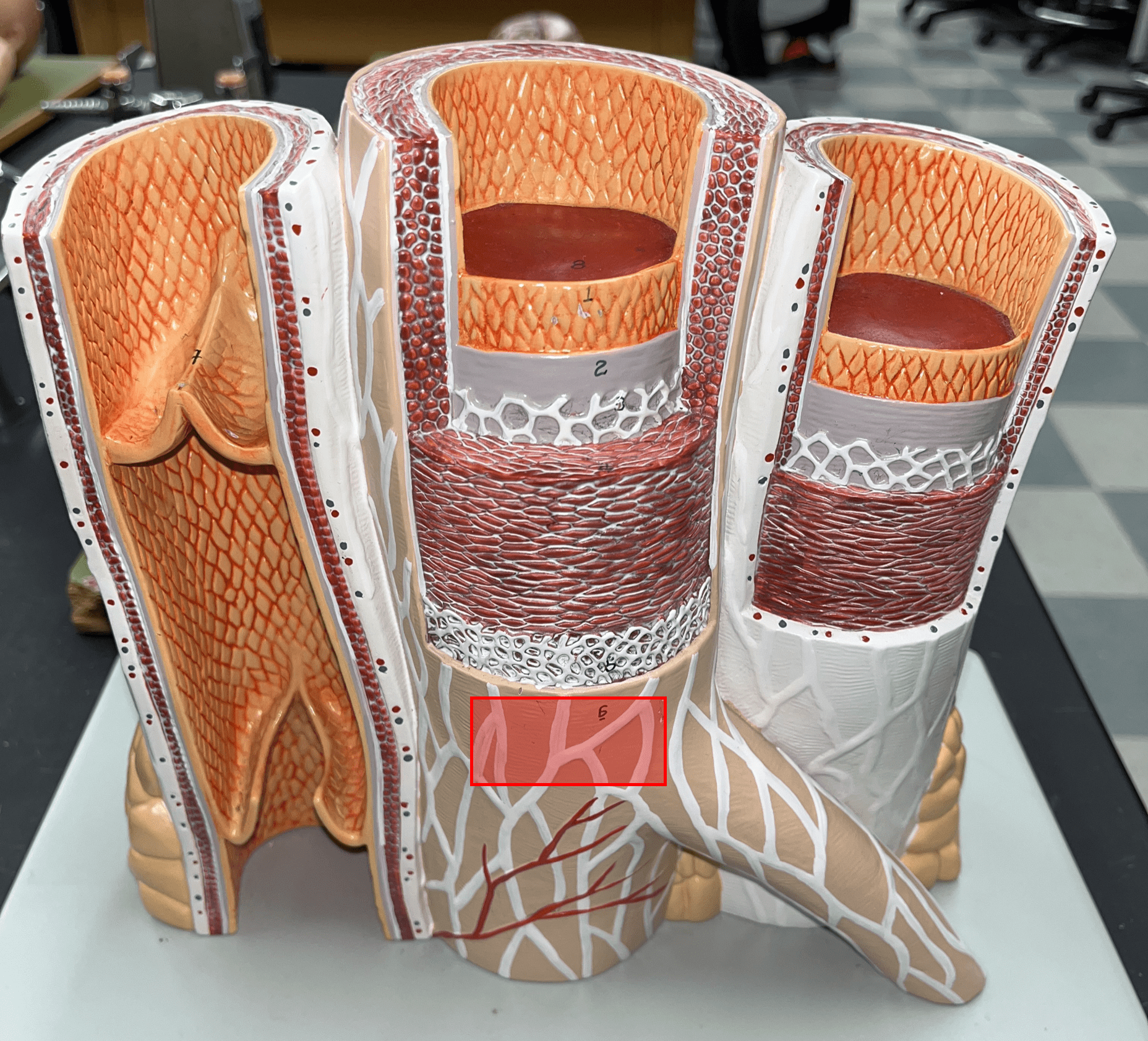

7
New cards
external elastic membrane
• A thin layer of elastic connective tissue.
• Found between the tunica externa and tunica media.
• Found between the tunica externa and tunica media.
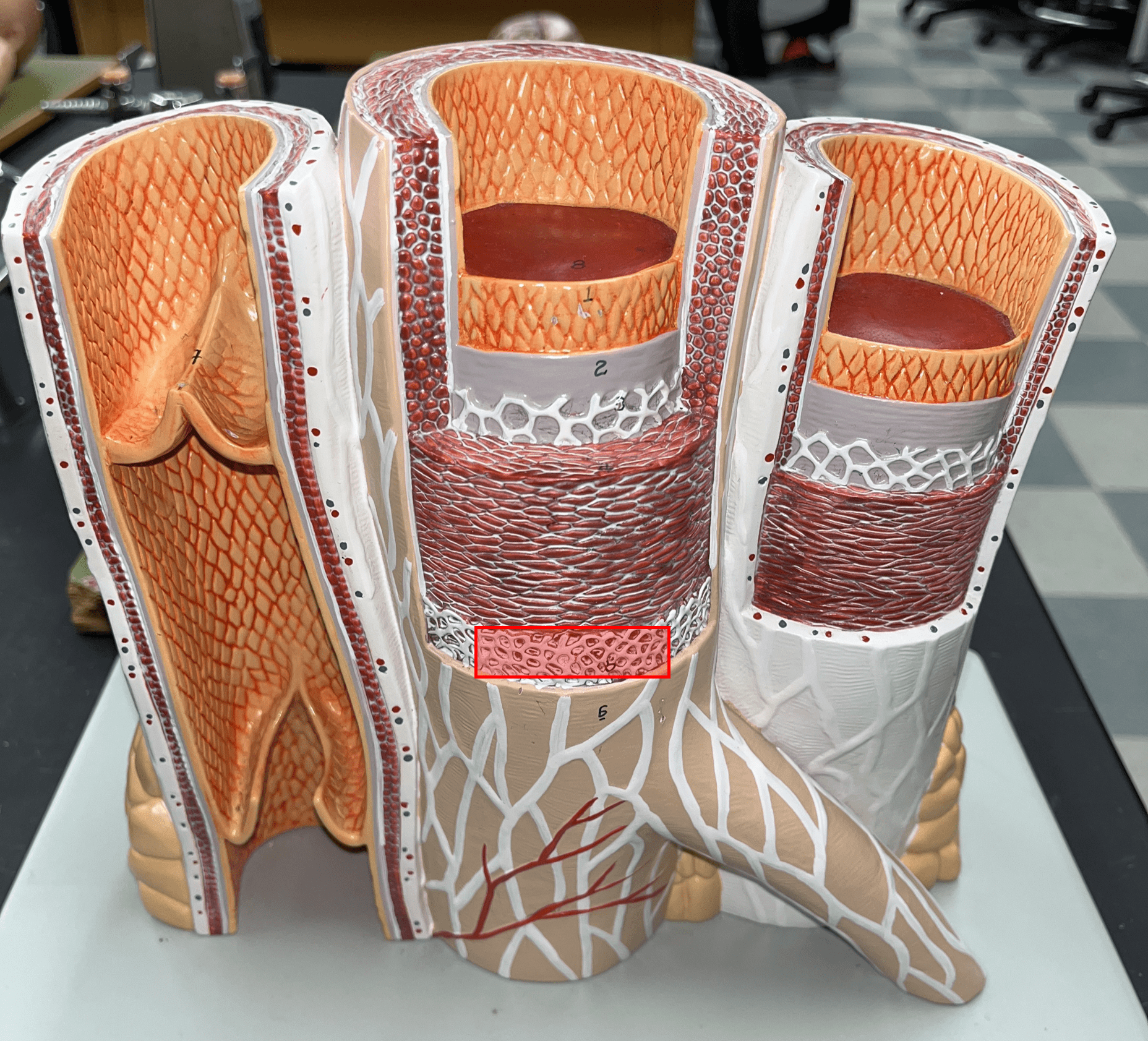

8
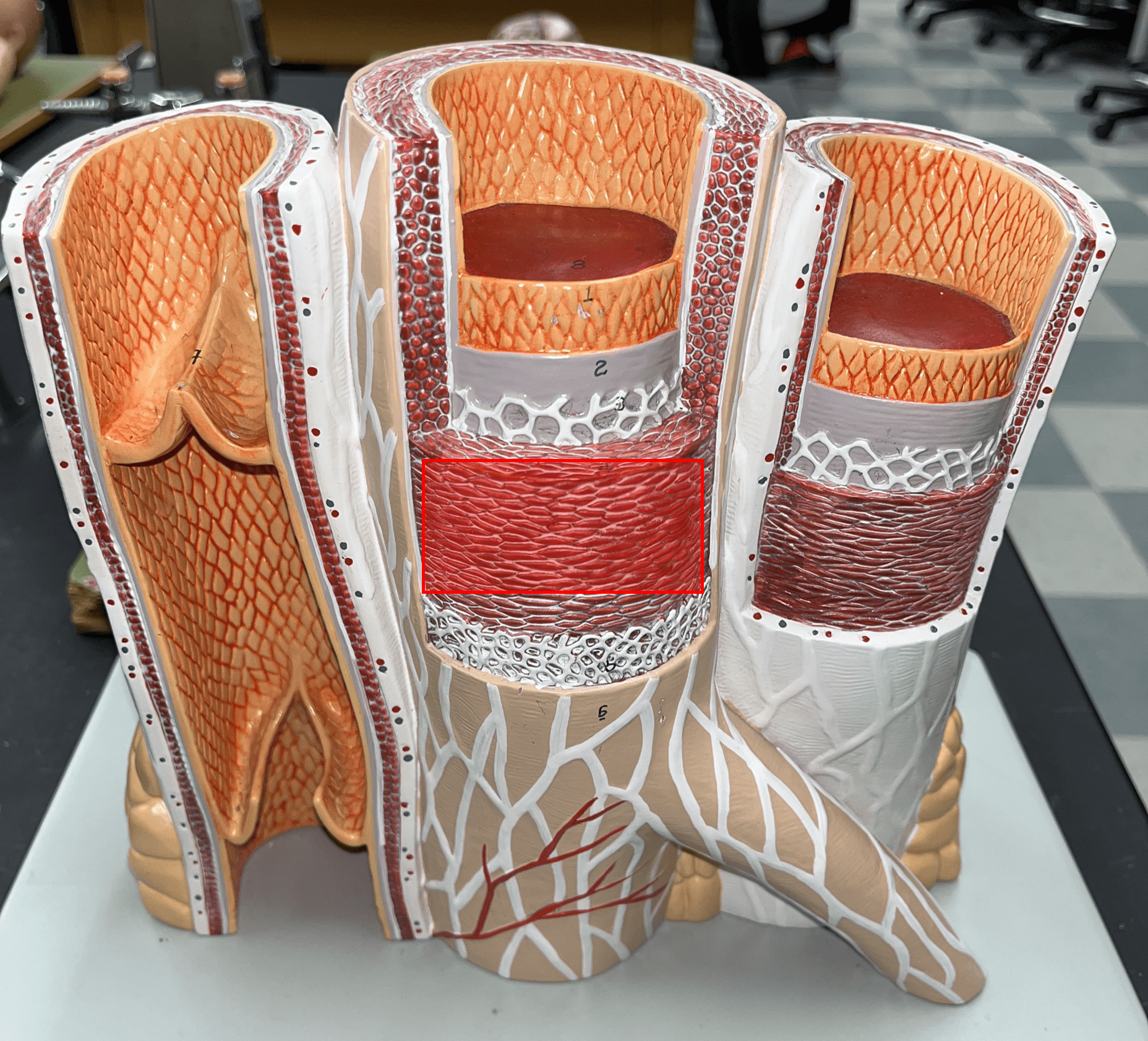
New cards
tunica media
• The middle layer of an artery wall.
• Composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
• The smooth muscle allows for vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
• Composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
• The smooth muscle allows for vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
9
New cards
internal elastic membrane
• A thin layer of elastic connective tissue.
• Found between the tunica media and tunica interna.
• Allows the lumen of a blood vessel to stretch.
• Found between the tunica media and tunica interna.
• Allows the lumen of a blood vessel to stretch.
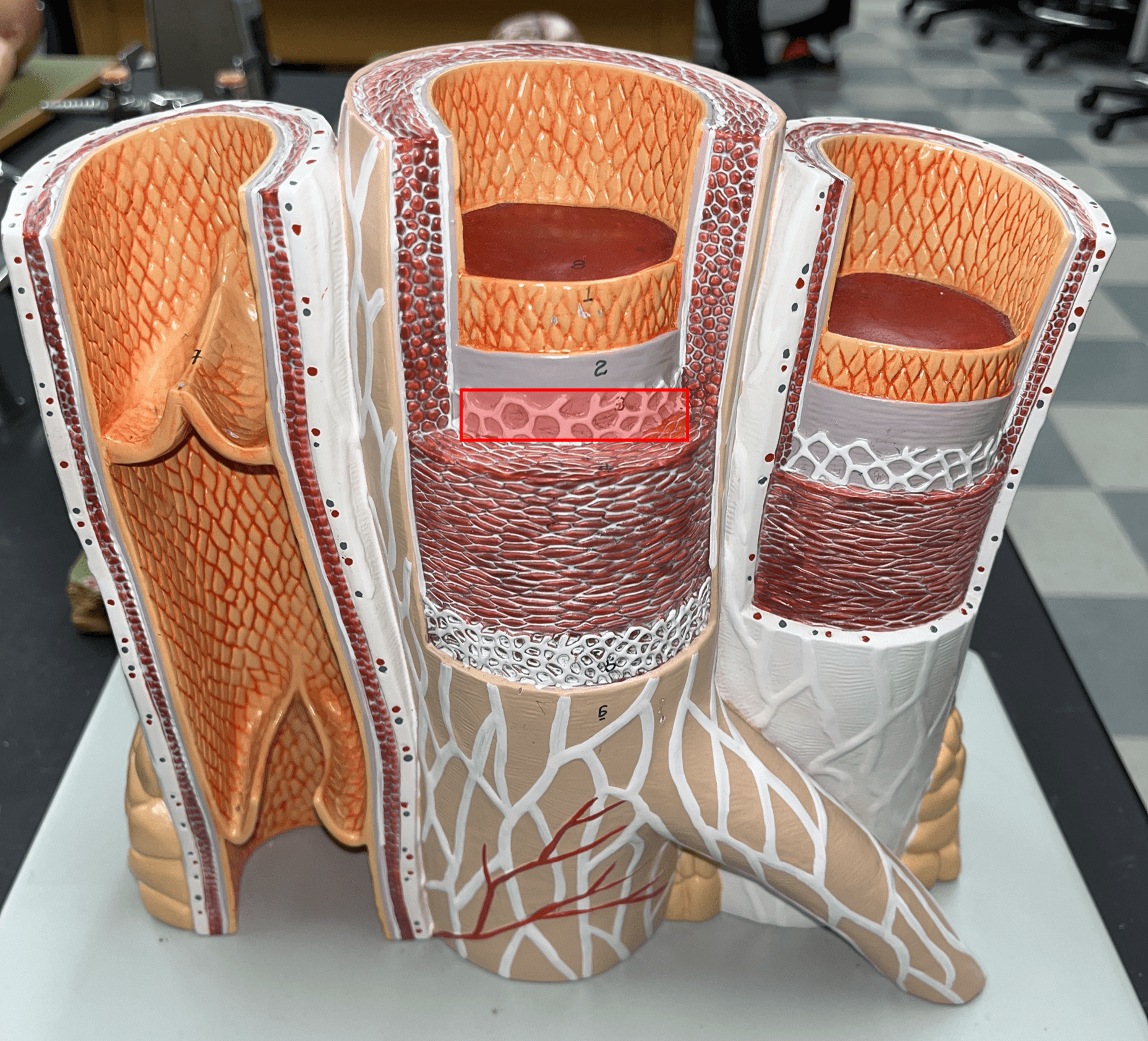

10
New cards
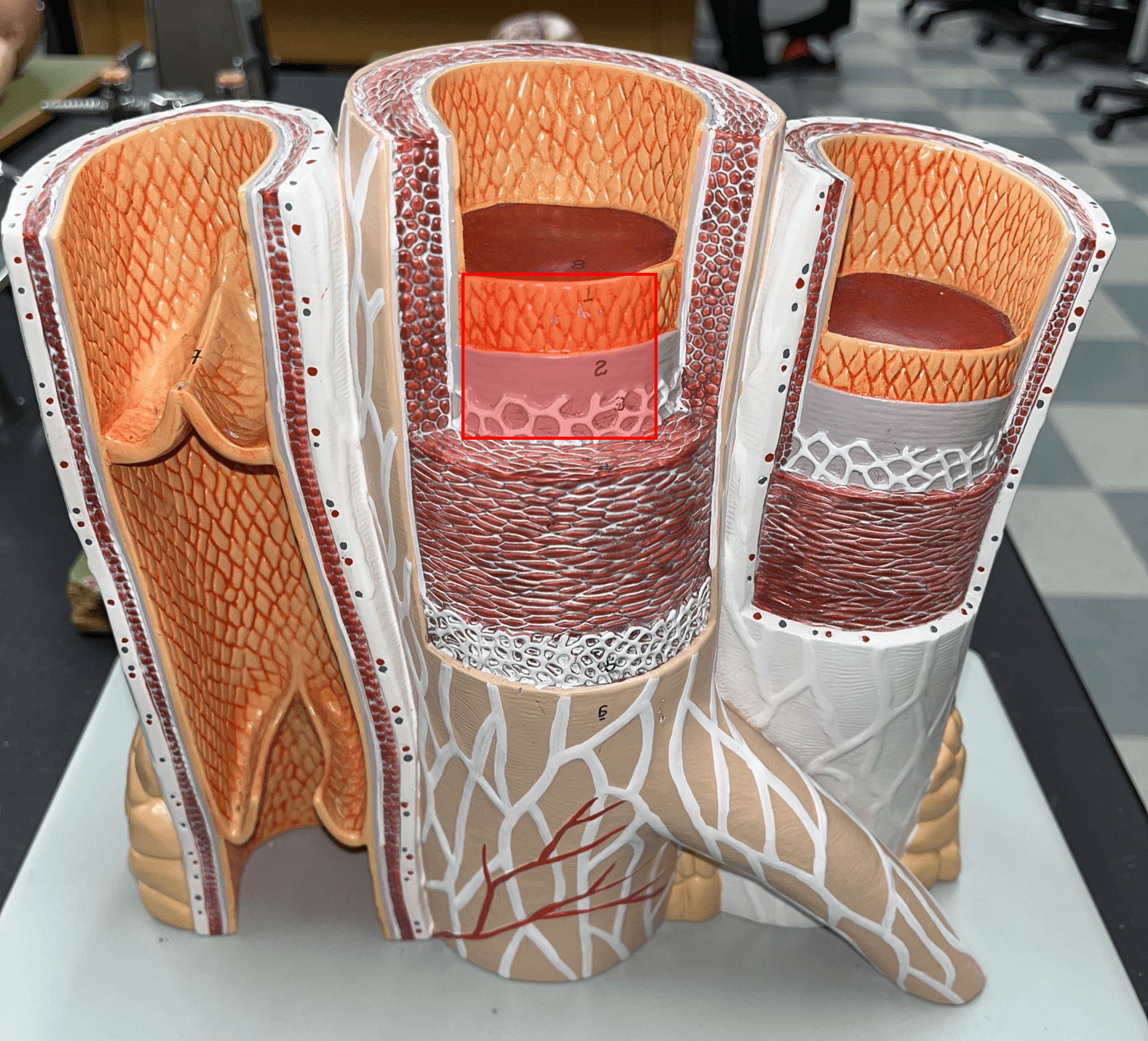
tunica interna
• The innermost layer of an artery.
• Consists of an inner endothelium and an outer basement membrane.
• Also known as the tunica intima.
• Consists of an inner endothelium and an outer basement membrane.
• Also known as the tunica intima.
11
New cards
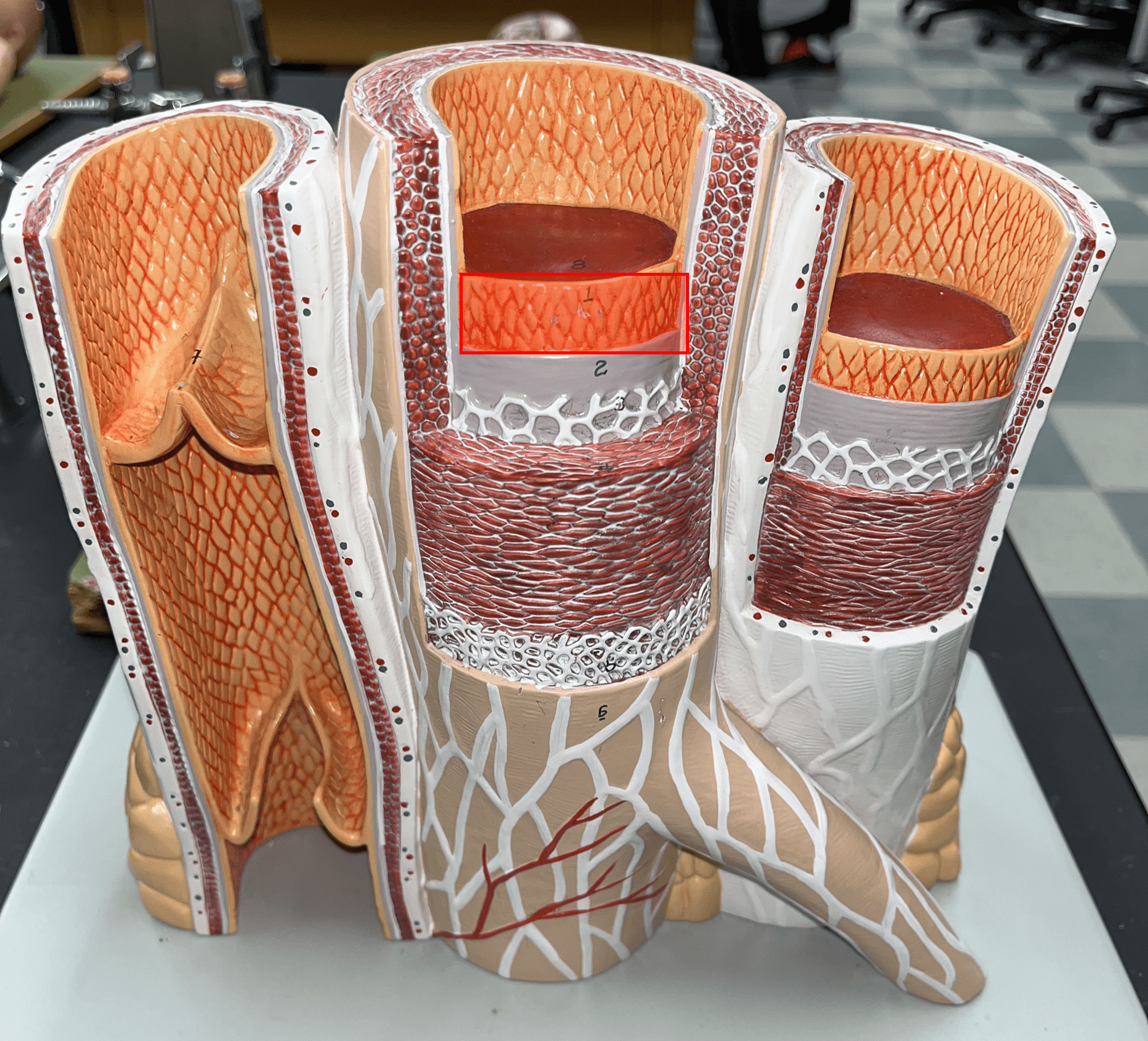
endothelium
• Part of the tunica interna.
• Composes a smooth inner surface of the vessel.
• Composes a smooth inner surface of the vessel.
12
New cards
valve
• Found in some veins.
• Establishes unidirectional flow of blood.
• Establishes unidirectional flow of blood.

13
New cards
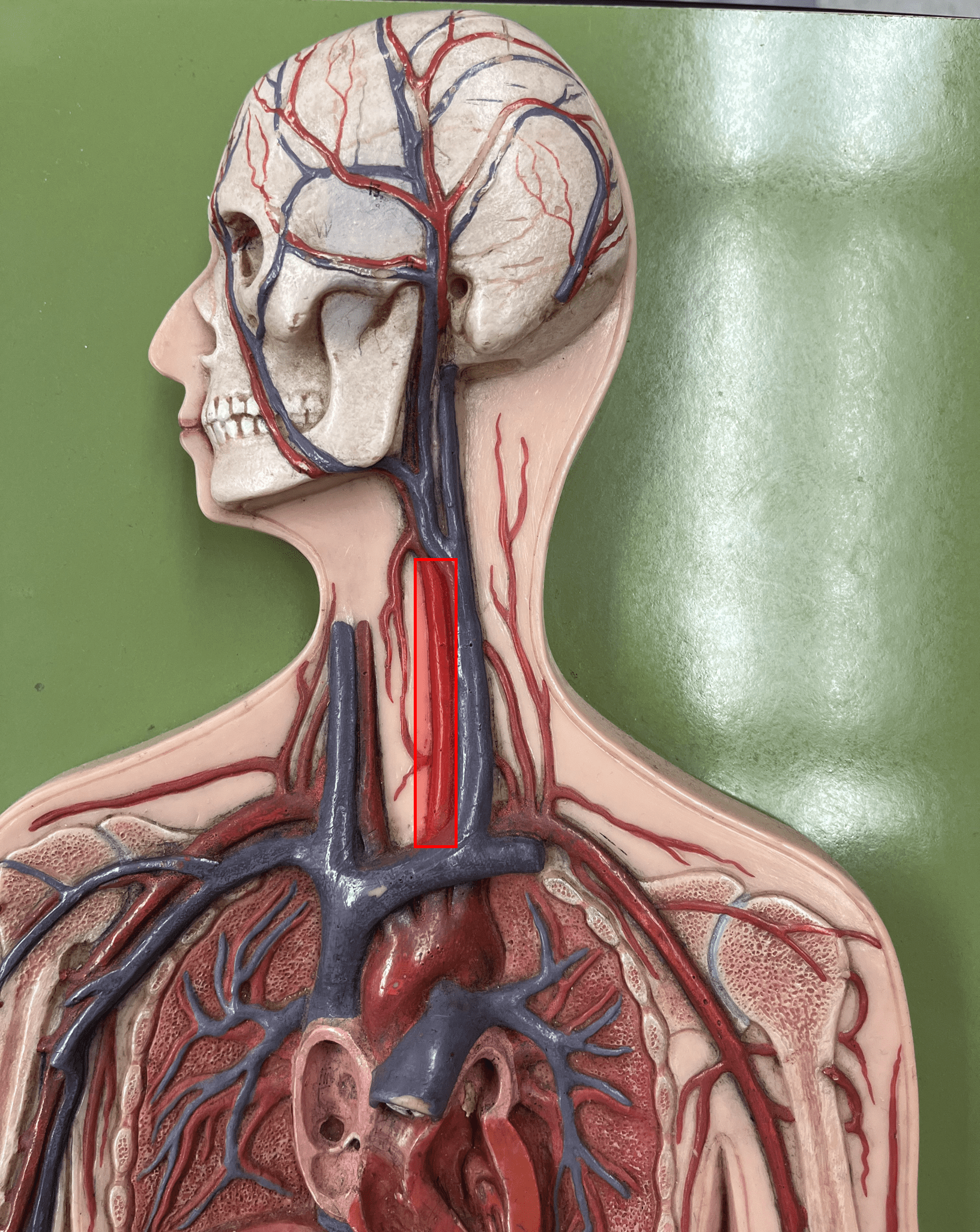
common carotid artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the brachiocephalic trunk (R.) or the aortic arch (L.).
• Supplies the head and neck through its branches.
• Originates from the brachiocephalic trunk (R.) or the aortic arch (L.).
• Supplies the head and neck through its branches.
14
New cards
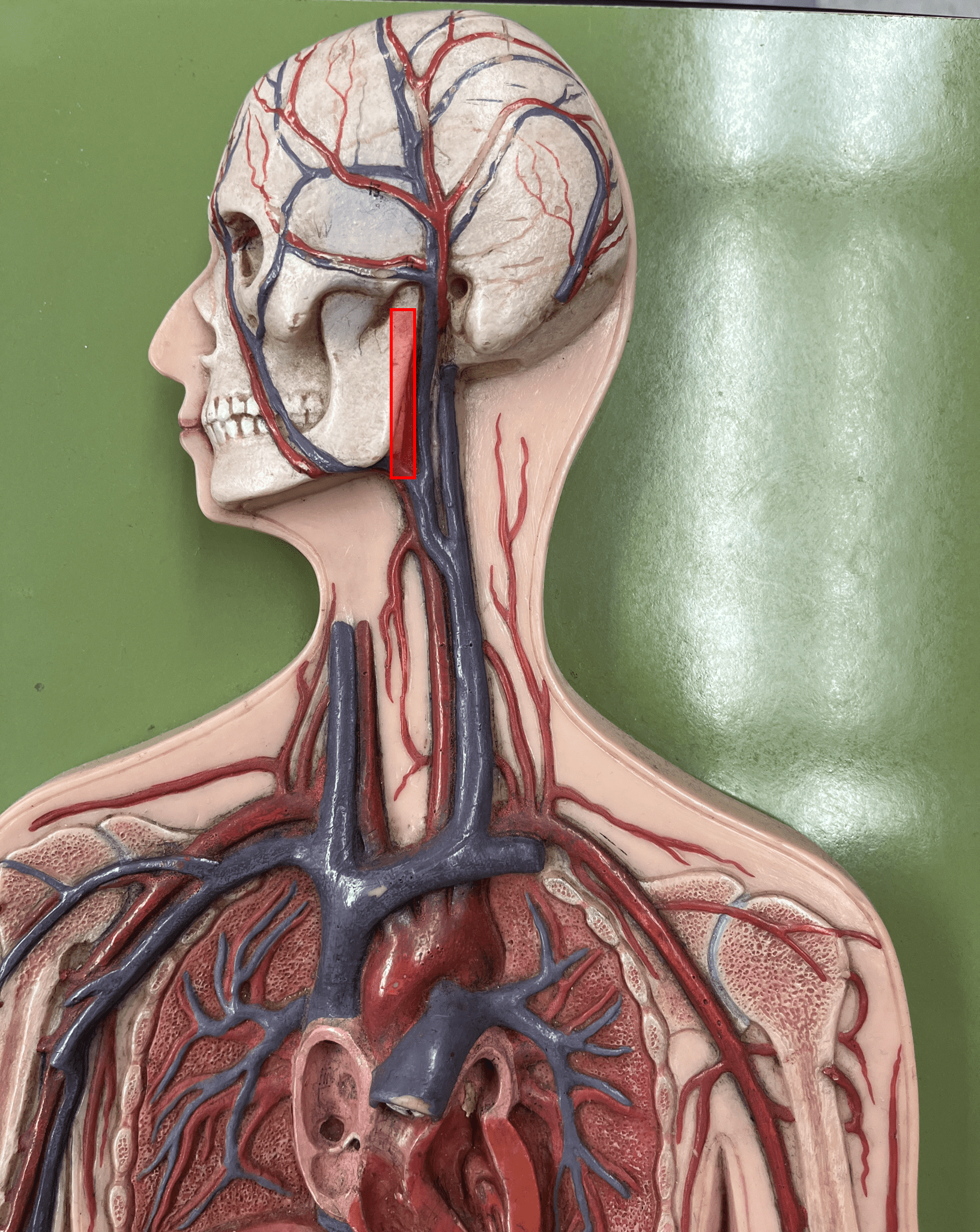
external carotid artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the common carotid artery.
• Supplies the extracranial structures through its branches.
• Laterally, the anteriormost artery of the neck.
• Originates from the common carotid artery.
• Supplies the extracranial structures through its branches.
• Laterally, the anteriormost artery of the neck.
15
New cards
facial artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the skin and muscles of the face.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the skin and muscles of the face.
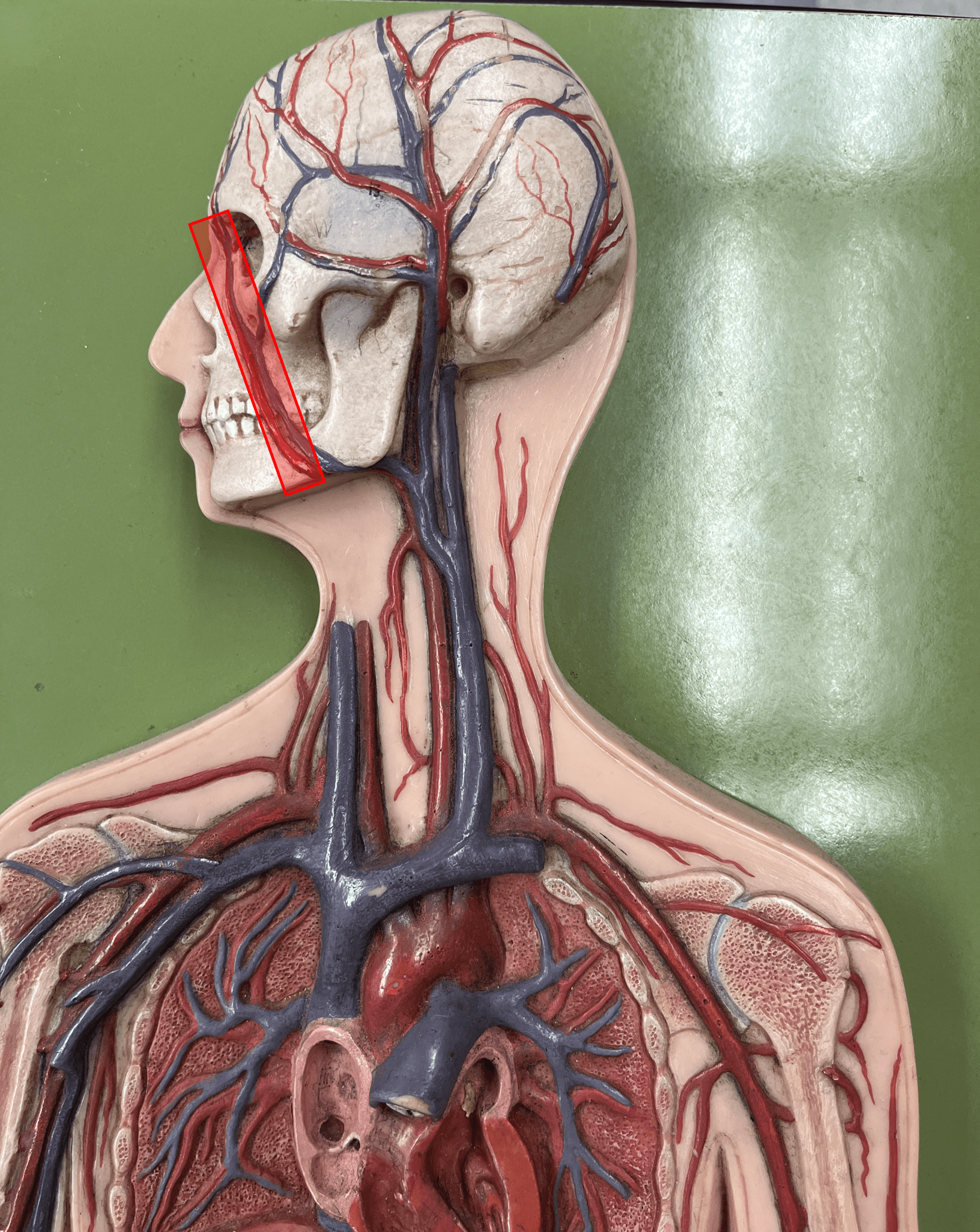
16
New cards
maxillary artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the teeth, maxilla, oral cavity, and external ear.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the teeth, maxilla, oral cavity, and external ear.
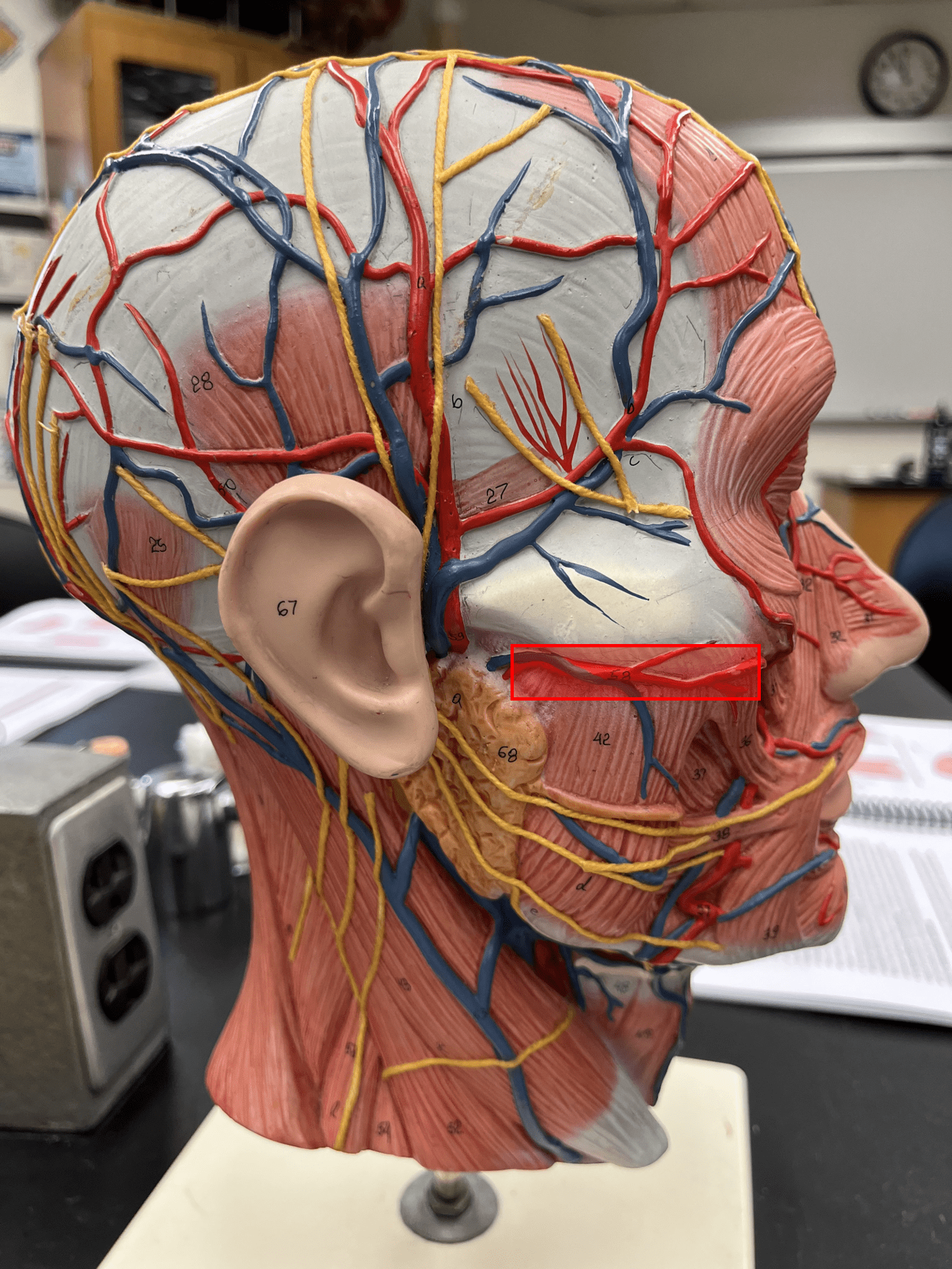
17
New cards
superficial temporal artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the chewing muscles, nasal cavity, lateral face and scalp, and dura mater.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the chewing muscles, nasal cavity, lateral face and scalp, and dura mater.
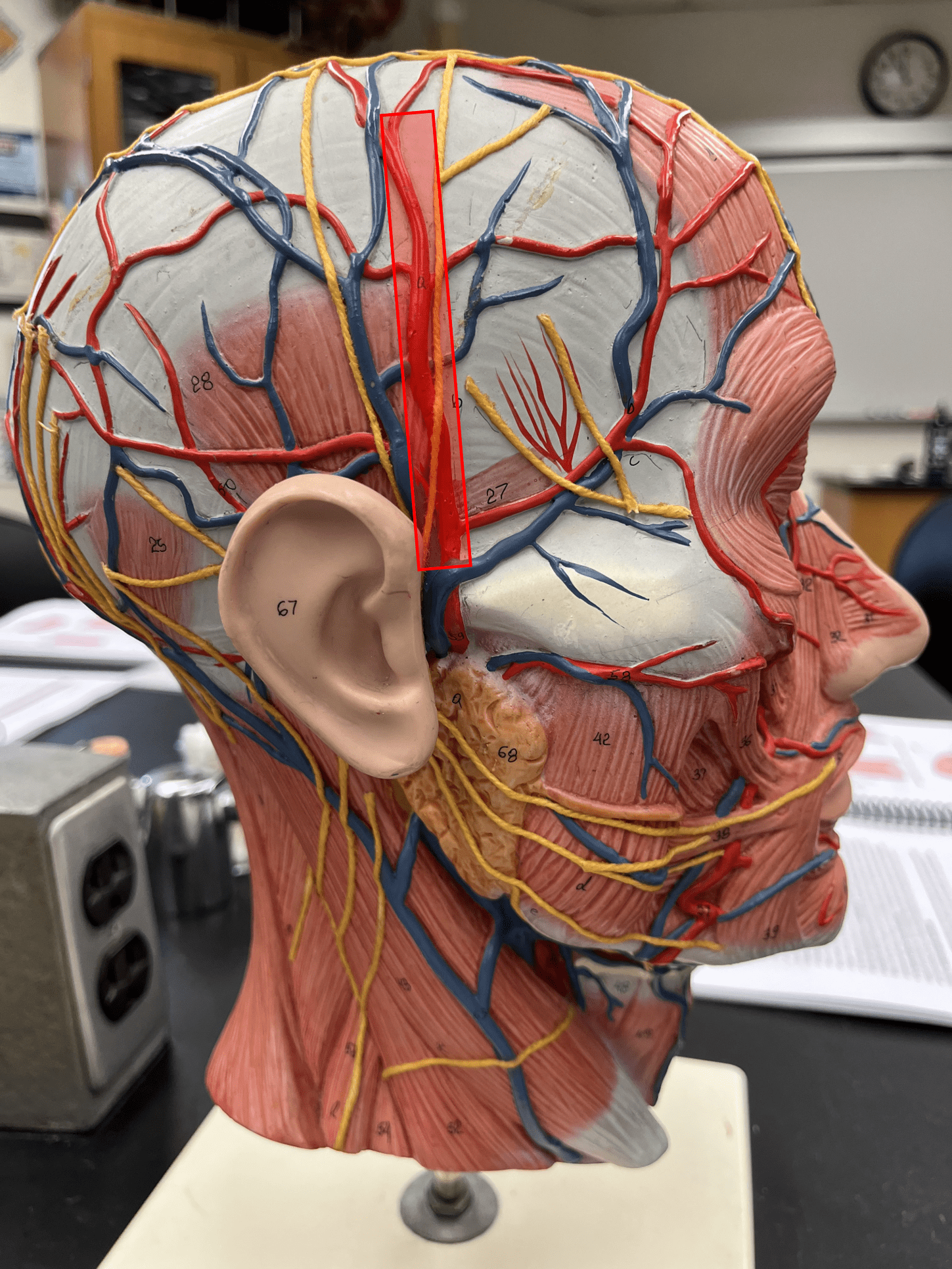
18
New cards
occipital artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the posterior scalp.
• Originates from the external carotid artery.
• Supplies the posterior scalp.
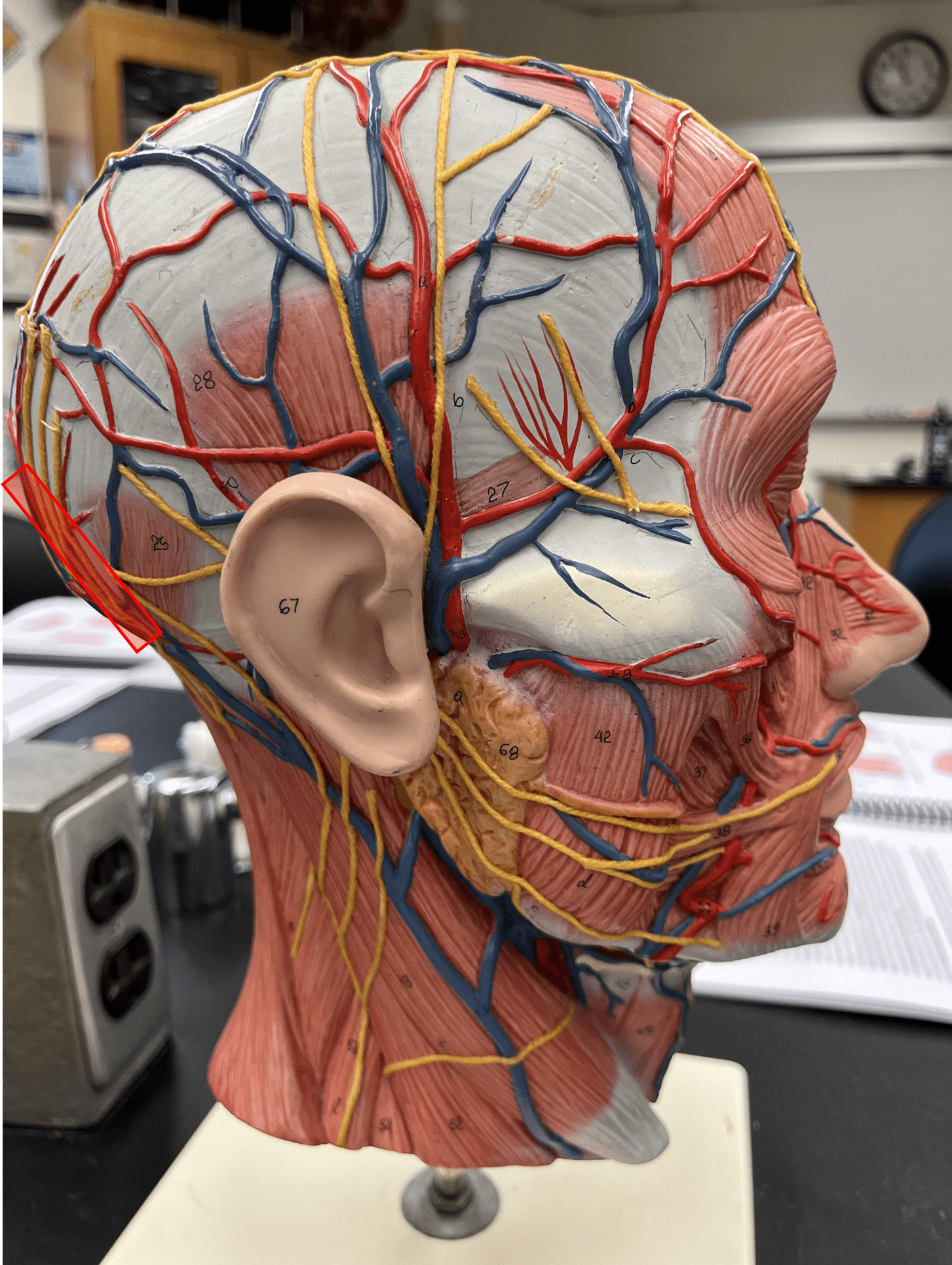
19
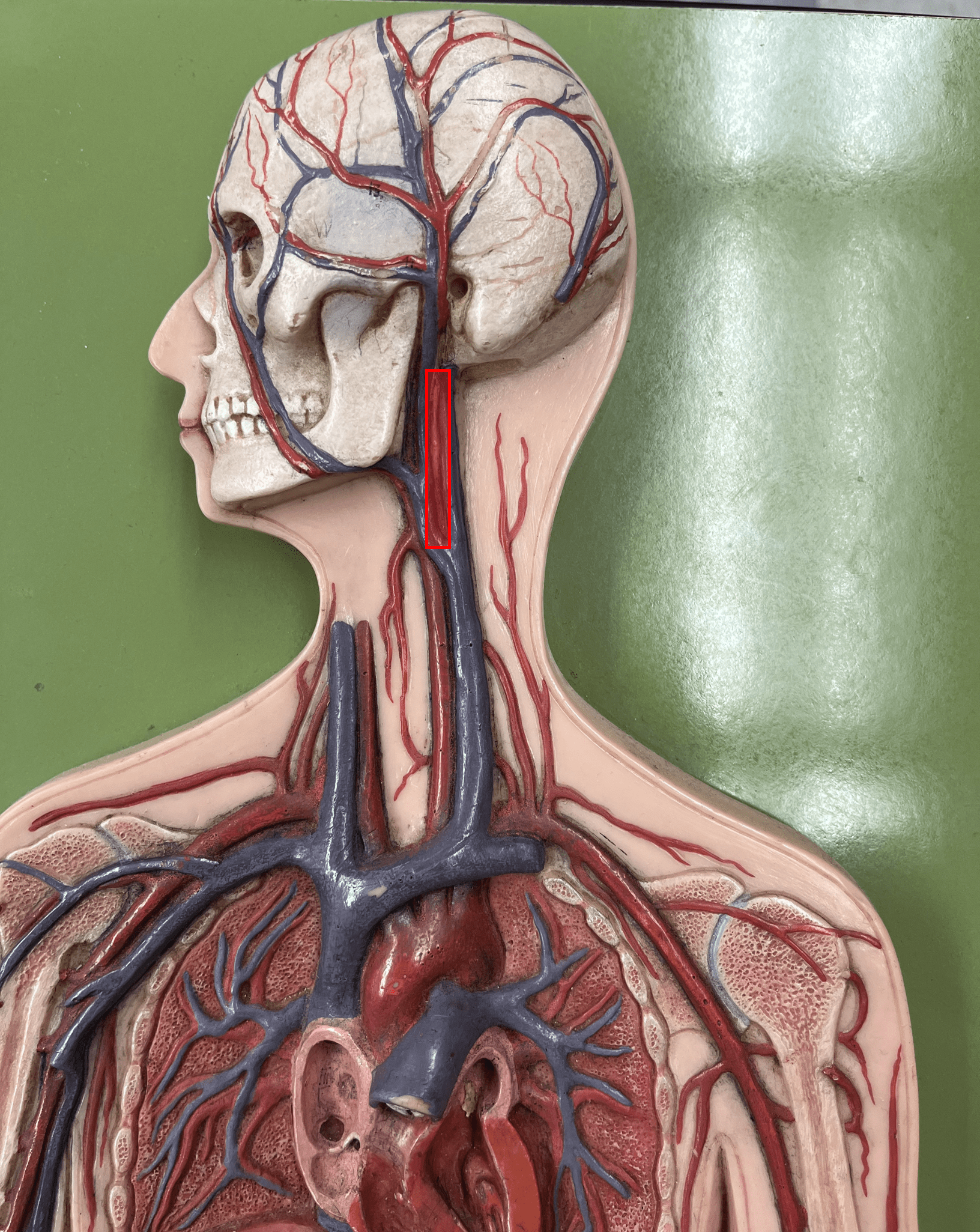
New cards
internal carotid artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the common carotid artery.
• Supplies the cerebrum through its branches.
• Laterally, the middle artery of the neck.
• Originates from the common carotid artery.
• Supplies the cerebrum through its branches.
• Laterally, the middle artery of the neck.
20
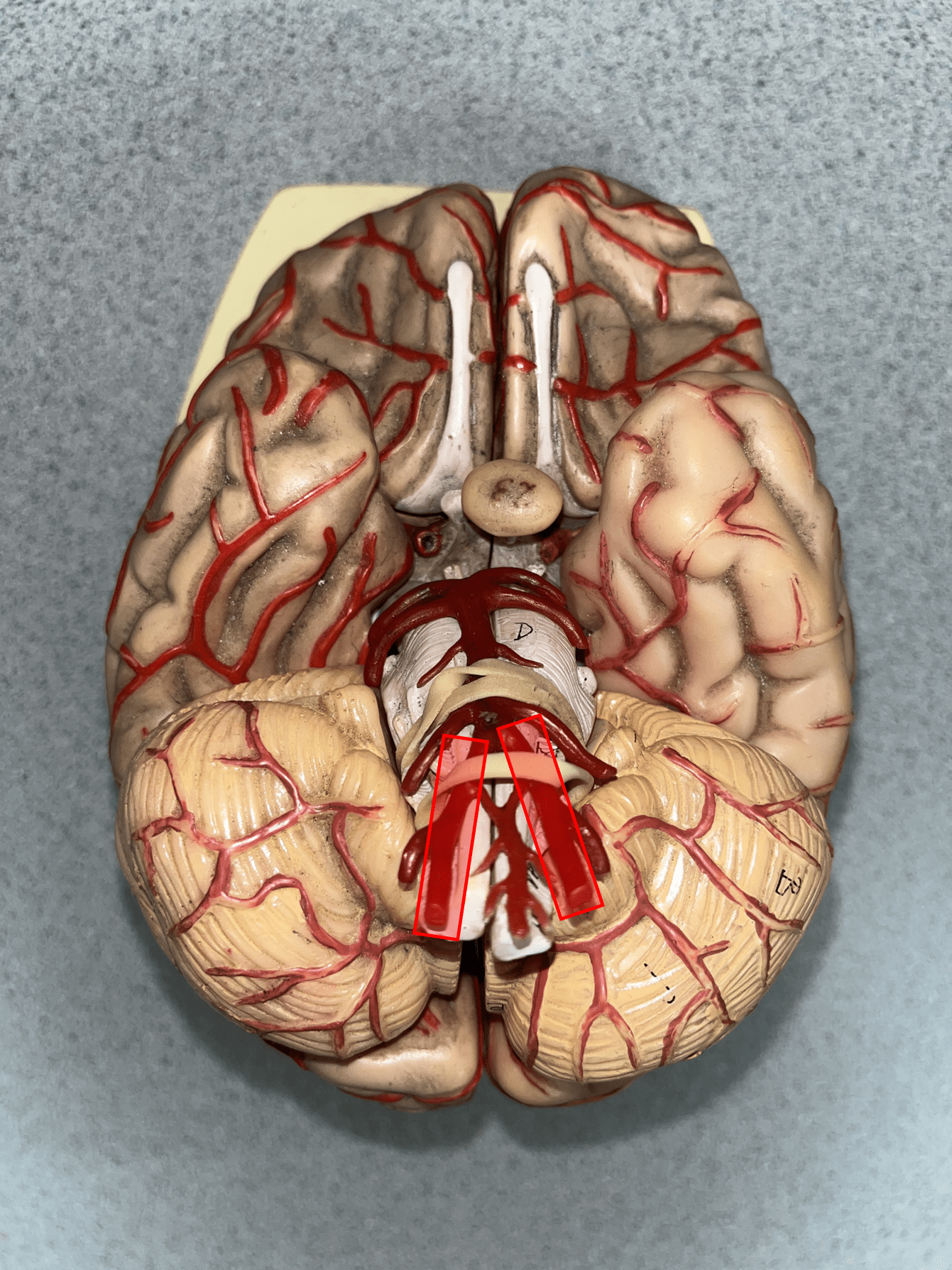
New cards
vertebral artery
• An artery of the head and neck.
• Originates from the subclavian artery.
• Supplies the spinal cord, meninges, and neck muscles.
• Laterally, the posteriormost artery of the neck.
• Originates from the subclavian artery.
• Supplies the spinal cord, meninges, and neck muscles.
• Laterally, the posteriormost artery of the neck.
21
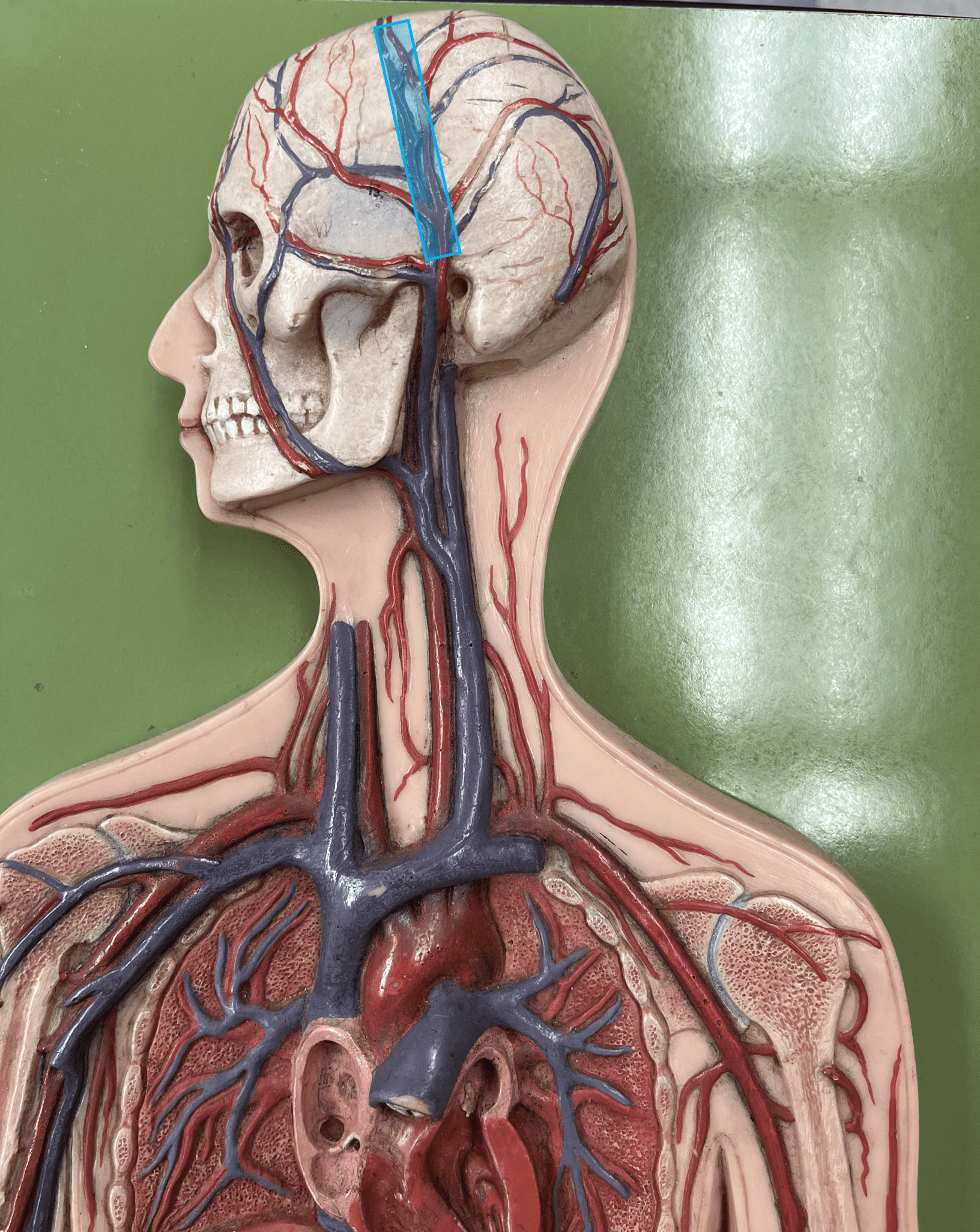
New cards
superficial temporal vein
• A vein of the head and neck.
• Drains the chewing muscles and scalp.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
• Drains the chewing muscles and scalp.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
22
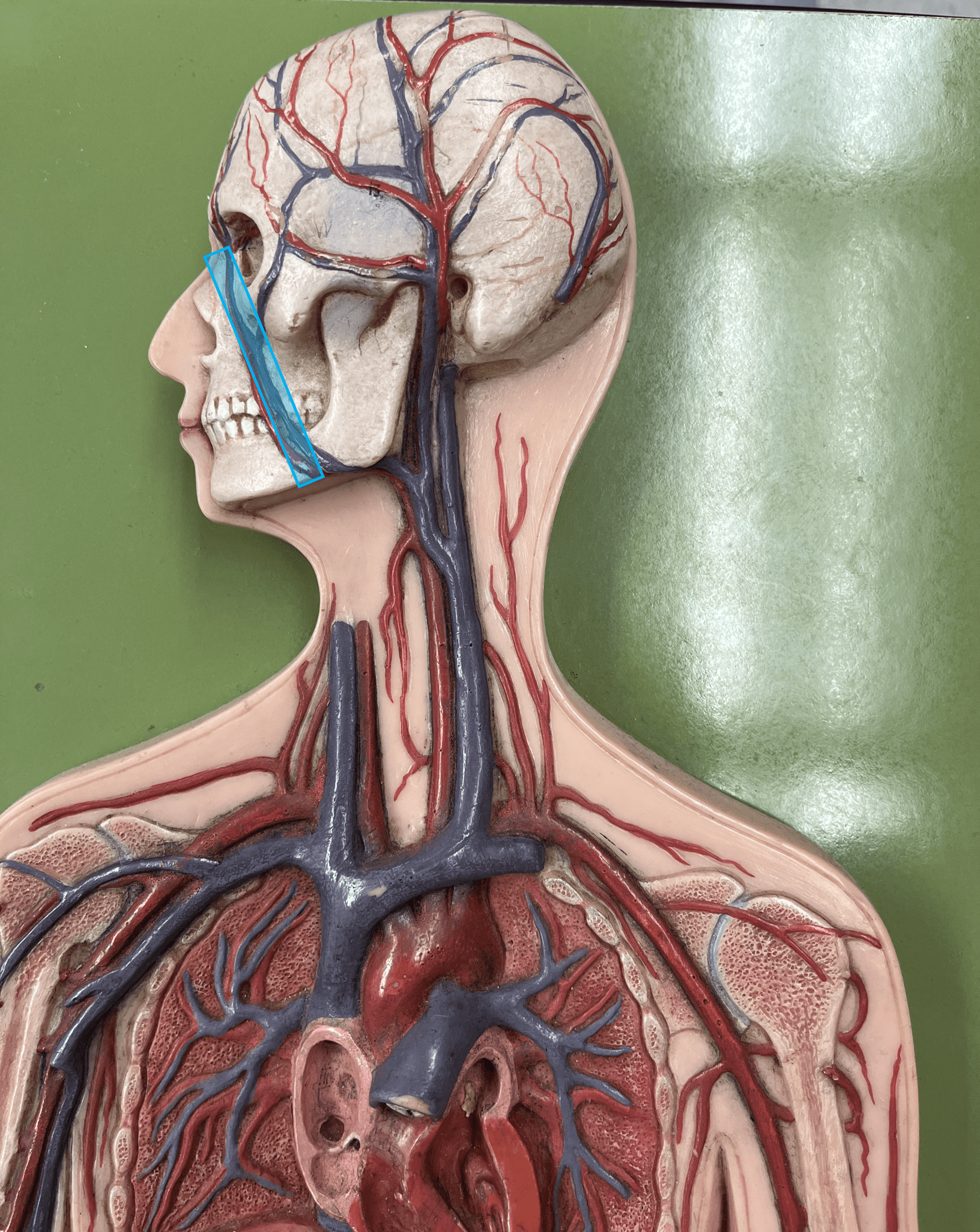
New cards
facial vein
• A vein of the head and neck.
• Drains the skin and muscles of the face.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
• Drains the skin and muscles of the face.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
23
New cards
occipital vein
• A vein of the head and neck.
• Drains the posterior scalp.
• Empties into the external jugular vein.
• Drains the posterior scalp.
• Empties into the external jugular vein.
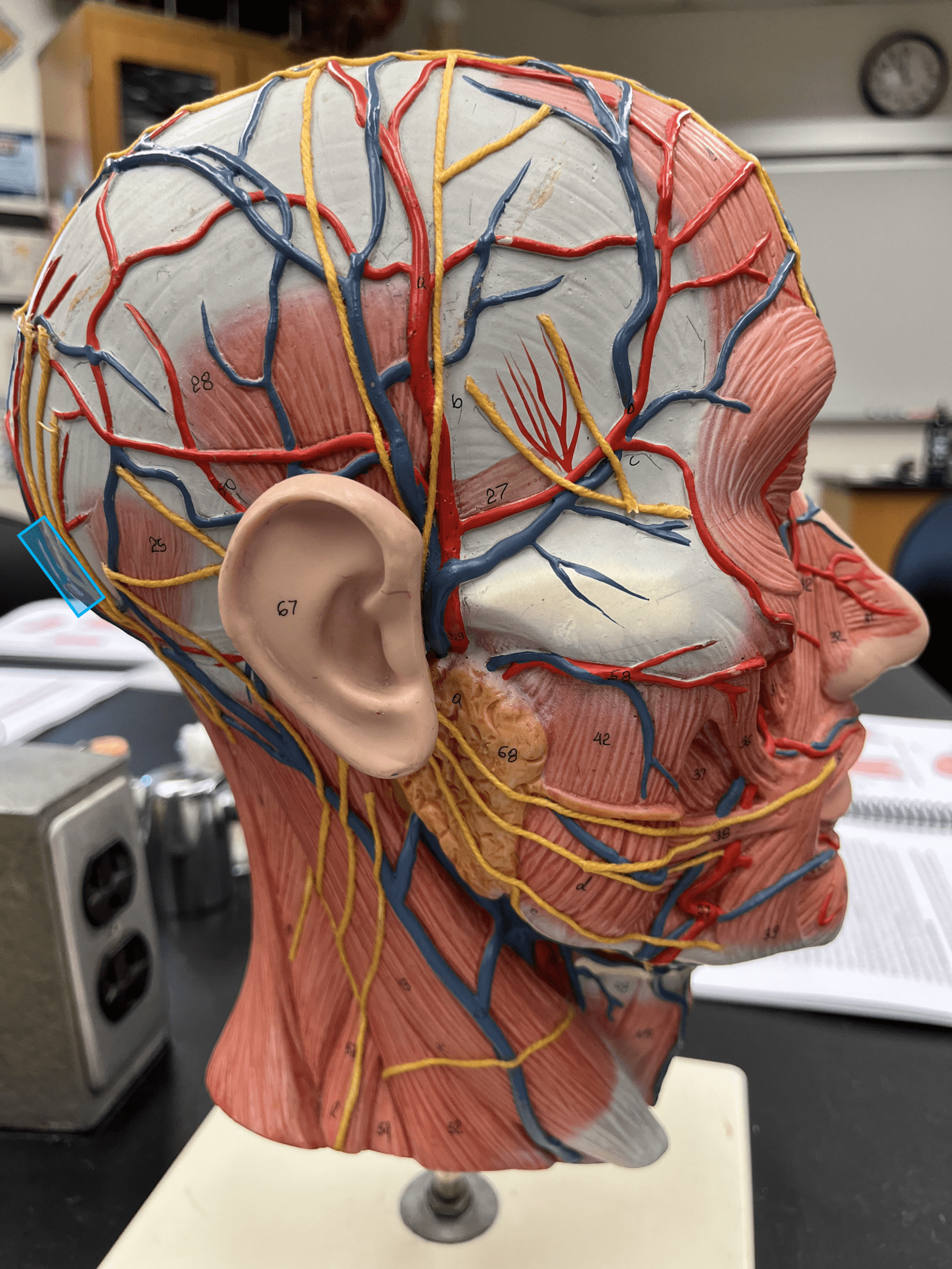
24
New cards
external jugular vein
• A vein of the head and neck.
• Drains the facial muscles and scalp.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the posteriormost vein of the neck.
• Drains the facial muscles and scalp.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the posteriormost vein of the neck.
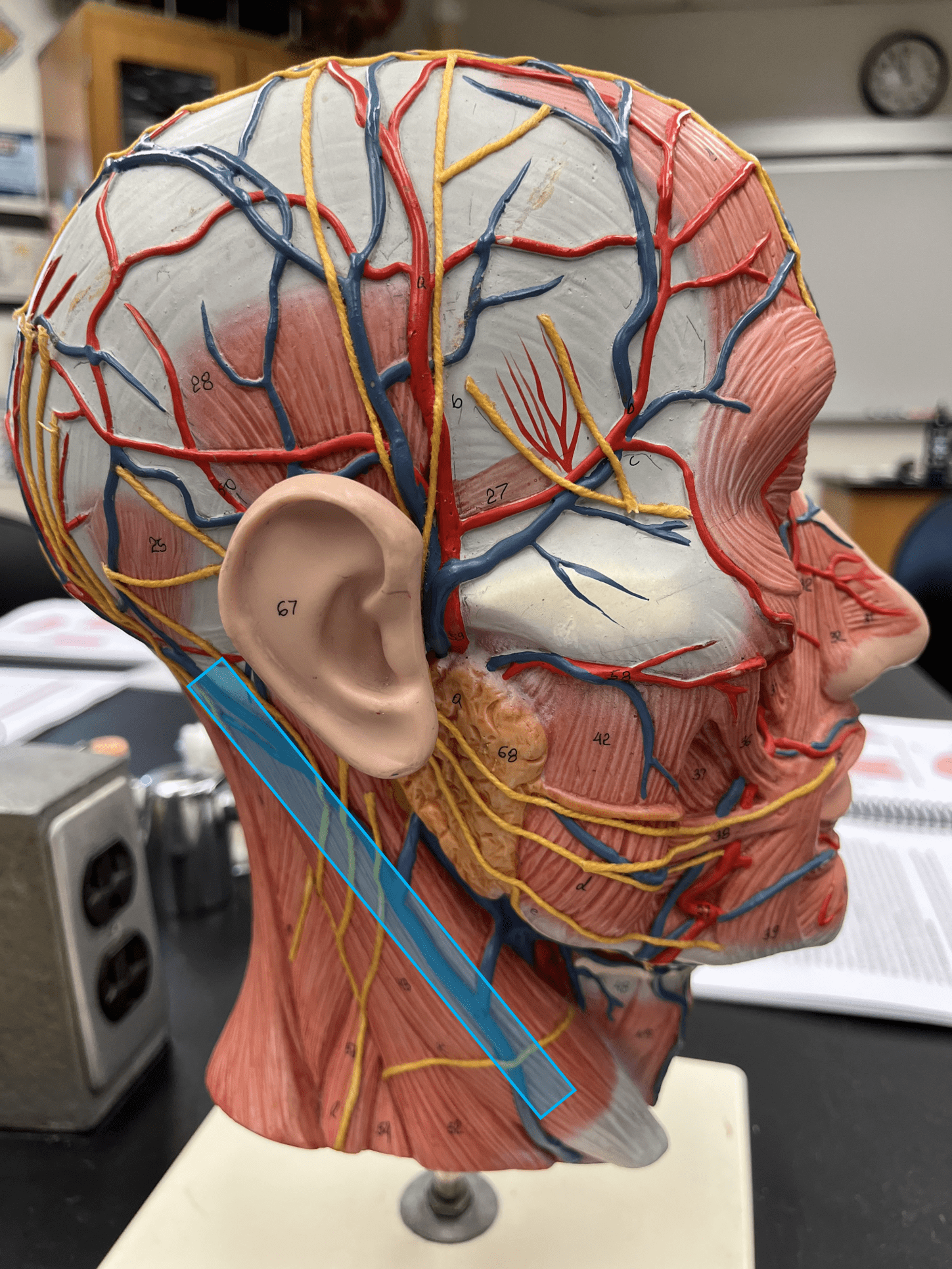
25
New cards
vertebral vein
• A vein of the head and neck (not shown).
• Drains the spinal cord and neck muscles.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the middle vein of the neck.
• Drains the spinal cord and neck muscles.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the middle vein of the neck.
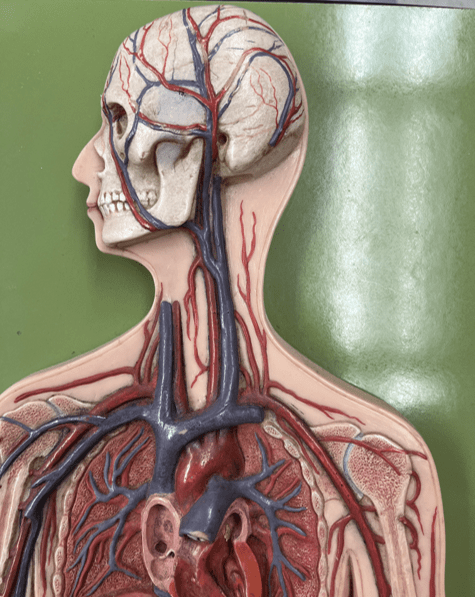
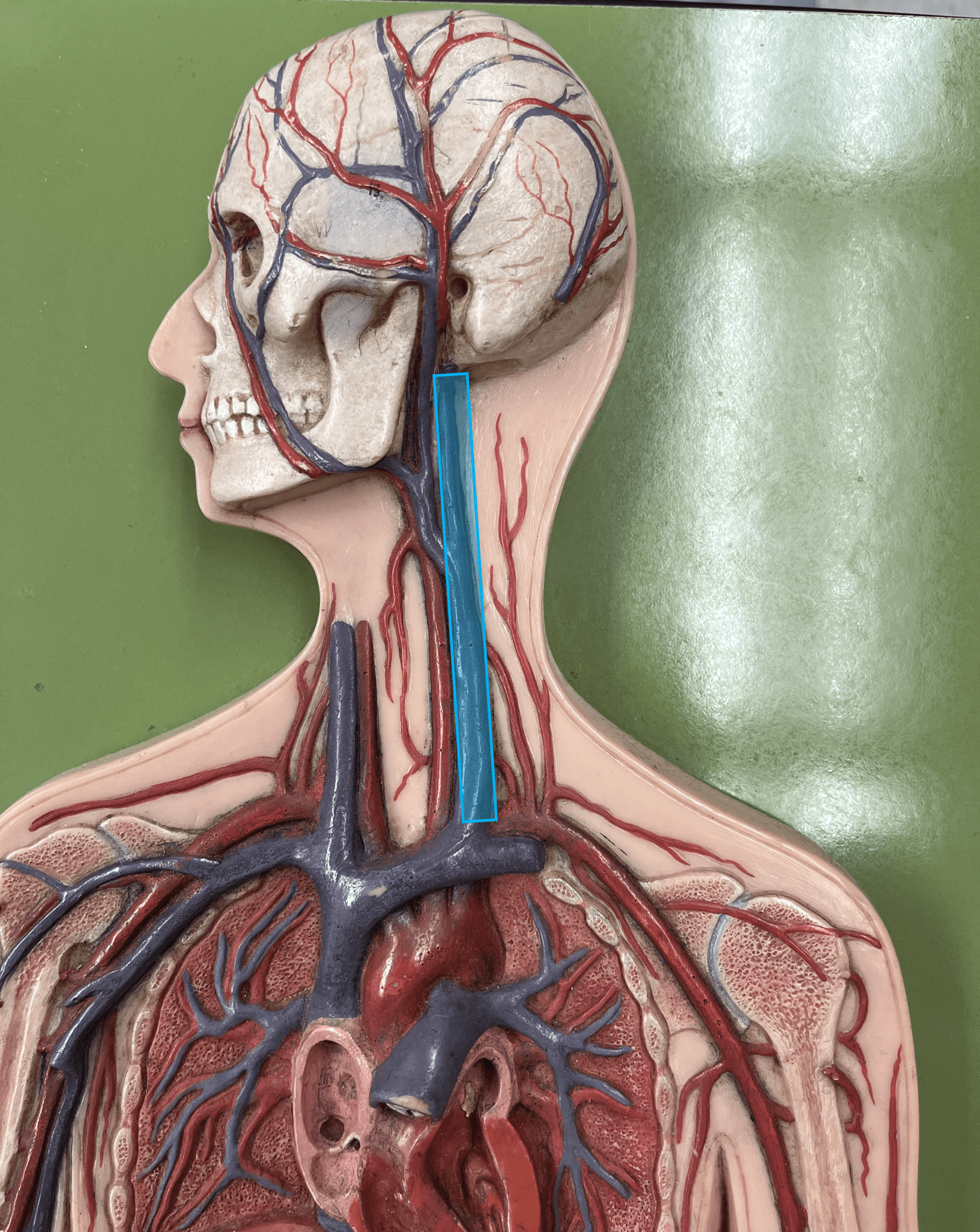
26
New cards
internal jugular vein
• A vein of the head and neck.
• Drains the brain, face, and neck.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the anteriormost vein of the neck.
• Drains the brain, face, and neck.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Laterally, the anteriormost vein of the neck.
27
New cards
anterior cerebral artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation.
• Originates from the internal carotid artery.
• Supplies the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain.
• Originates from the internal carotid artery.
• Supplies the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain.
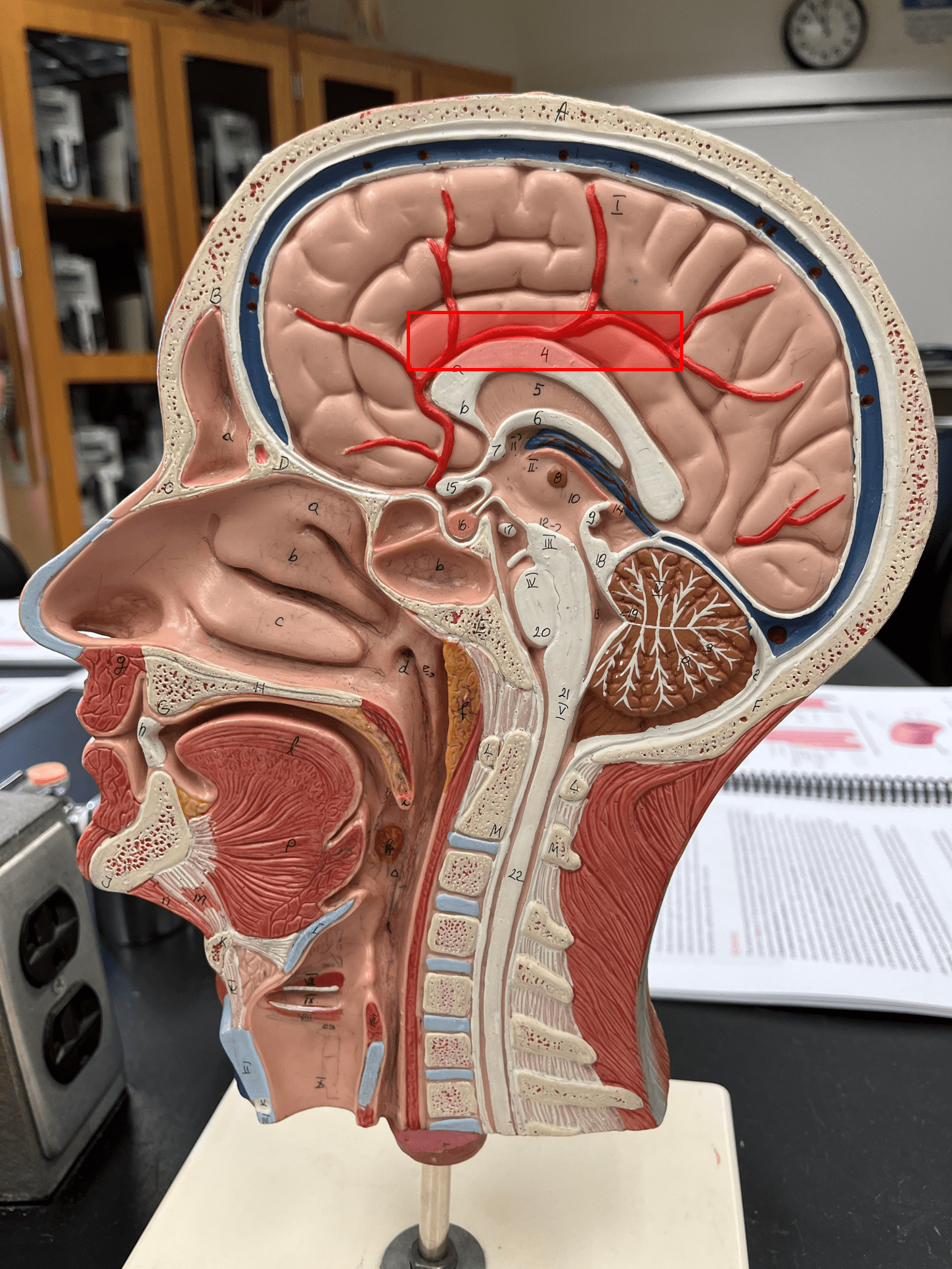
28
New cards
anterior communicating artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation (not shown).
• Connects the right and left anterior cerebral arteries.
• Connects the right and left anterior cerebral arteries.
29
New cards
posterior communicating artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation (not shown).
• Connects the posterior cerebral and internal carotid arteries.
• Connects the posterior cerebral and internal carotid arteries.
30
New cards
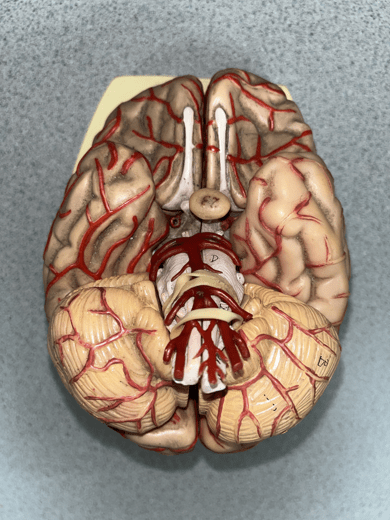
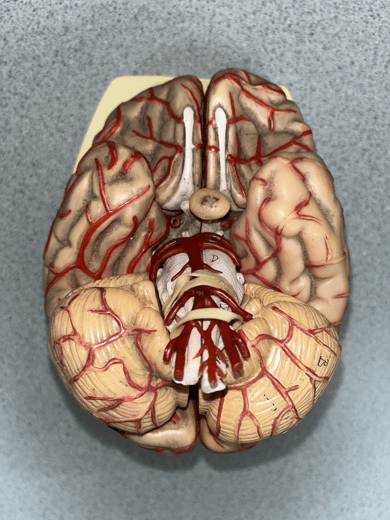
posterior cerebral artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation.
• Originates from the basilar artery.
• Supplies the temporal and occipital lobes, midbrain, and thalamus.
• Originates from the basilar artery.
• Supplies the temporal and occipital lobes, midbrain, and thalamus.
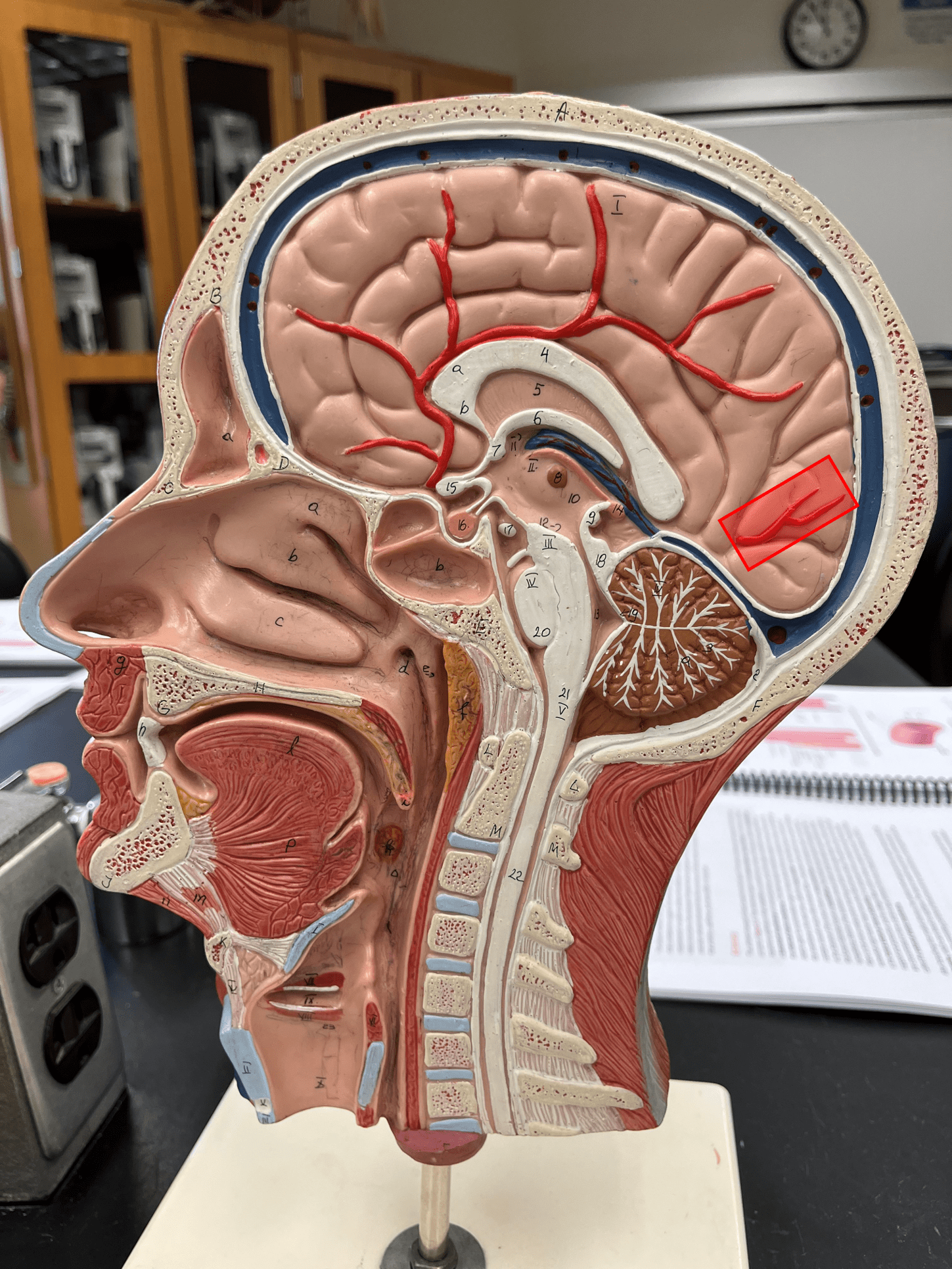
31
New cards
middle cerebral artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation (not shown).
• Originates from the internal carotid arteries.
• Supplies the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes.
• Originates from the internal carotid arteries.
• Supplies the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes.
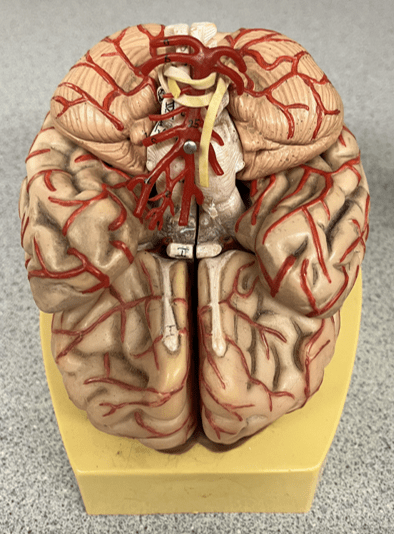
32
New cards
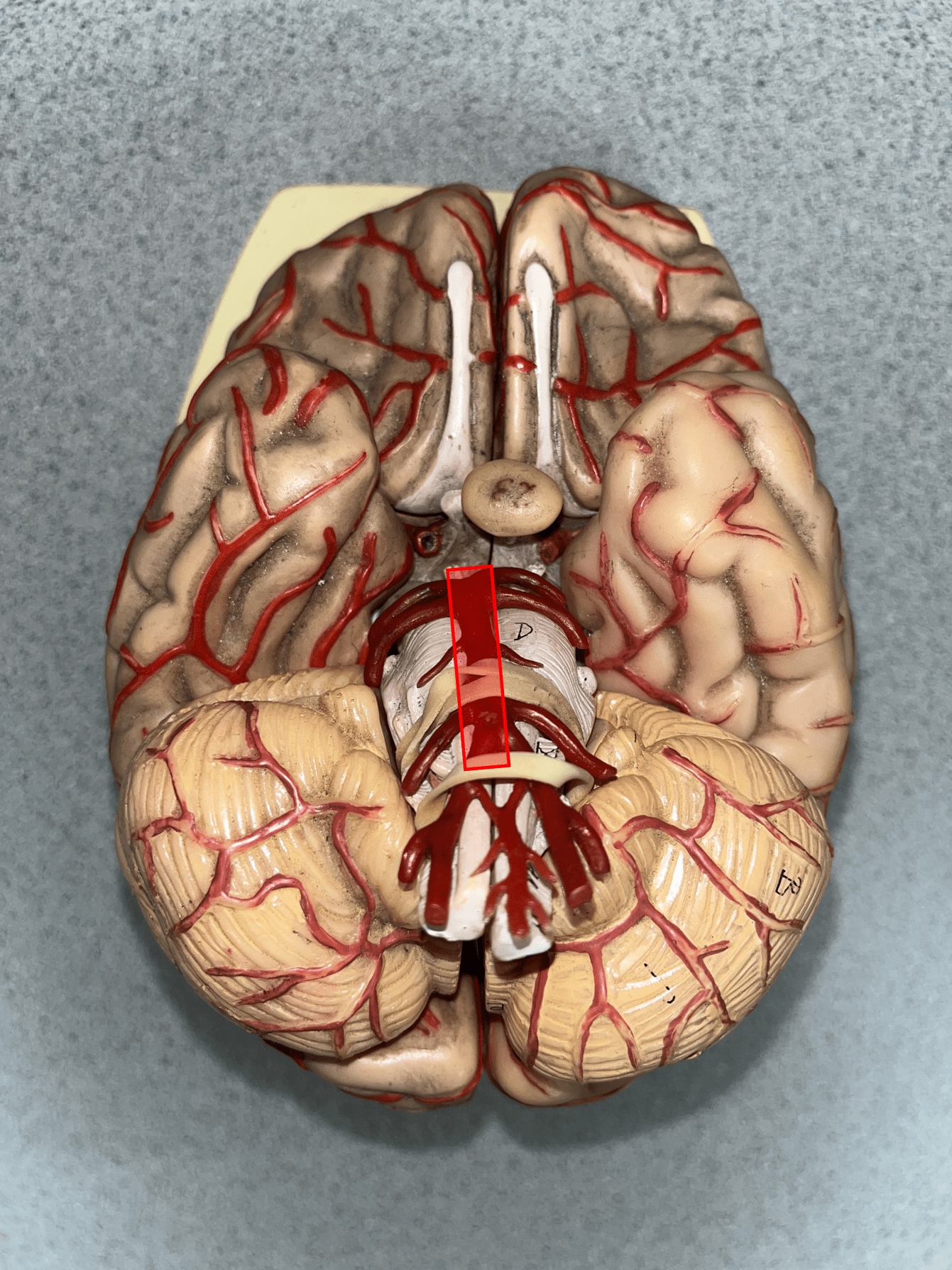
basilar artery
• An artery of the cerebral circulation.
• Originates from the convergence of the vertebral arteries.
• Supplies the cerebellum, pons, and inner ear through its branches.
• Originates from the convergence of the vertebral arteries.
• Supplies the cerebellum, pons, and inner ear through its branches.
33
New cards
superior sagittal sinus
• A vein of the cerebral circulation.
• Drains the superficial brain.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
• Drains the superficial brain.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
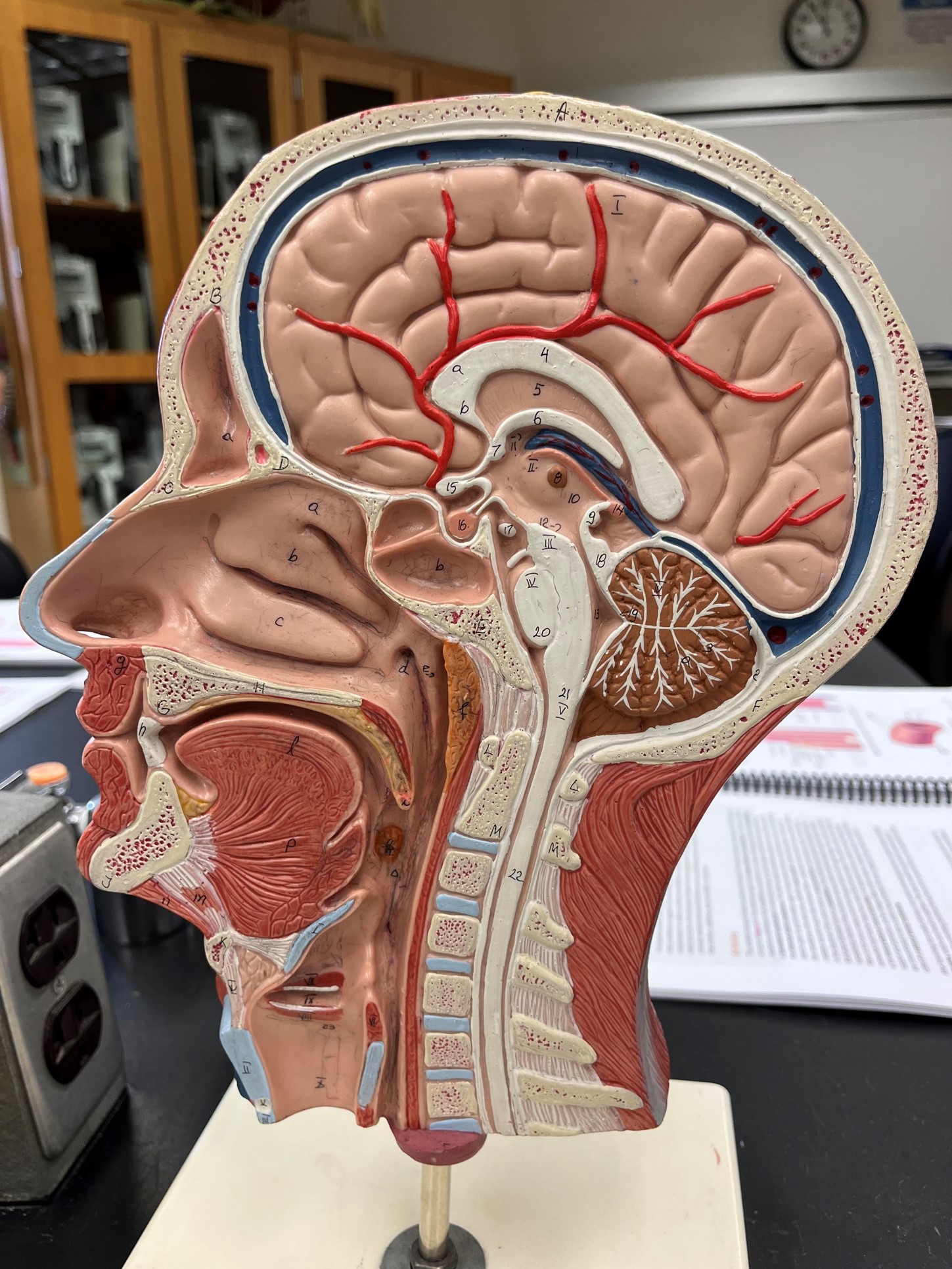
34
New cards
inferior sagittal sinus
• A vein of the cerebral circulation.
• Drains the deep brain.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
• Drains the deep brain.
• Empties into the internal jugular vein.
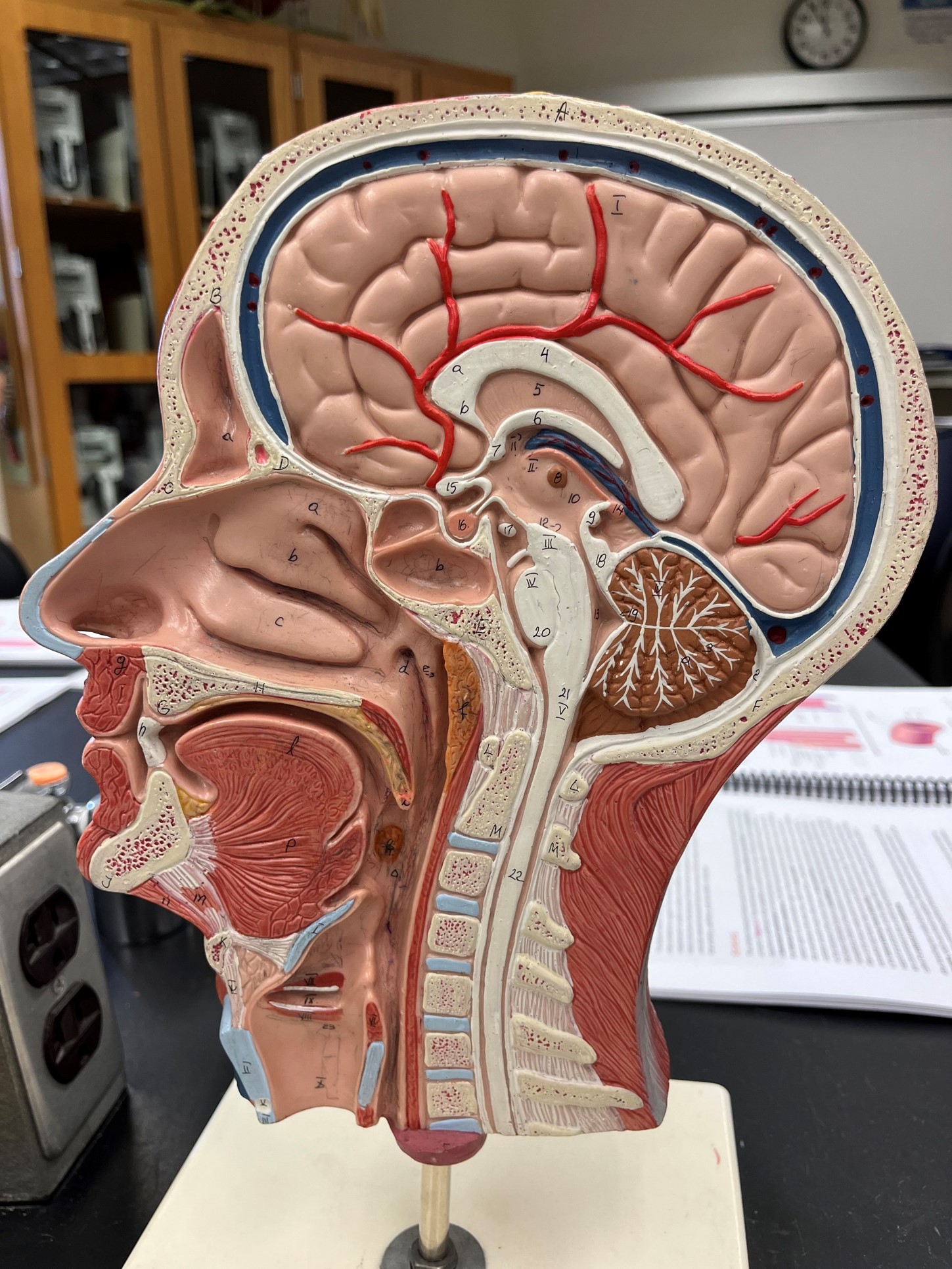
35
New cards
ascending aorta
• An artery of the thorax.
• Originates from the left ventricle of the heart.
• Supplies its branches.
• Originates from the left ventricle of the heart.
• Supplies its branches.
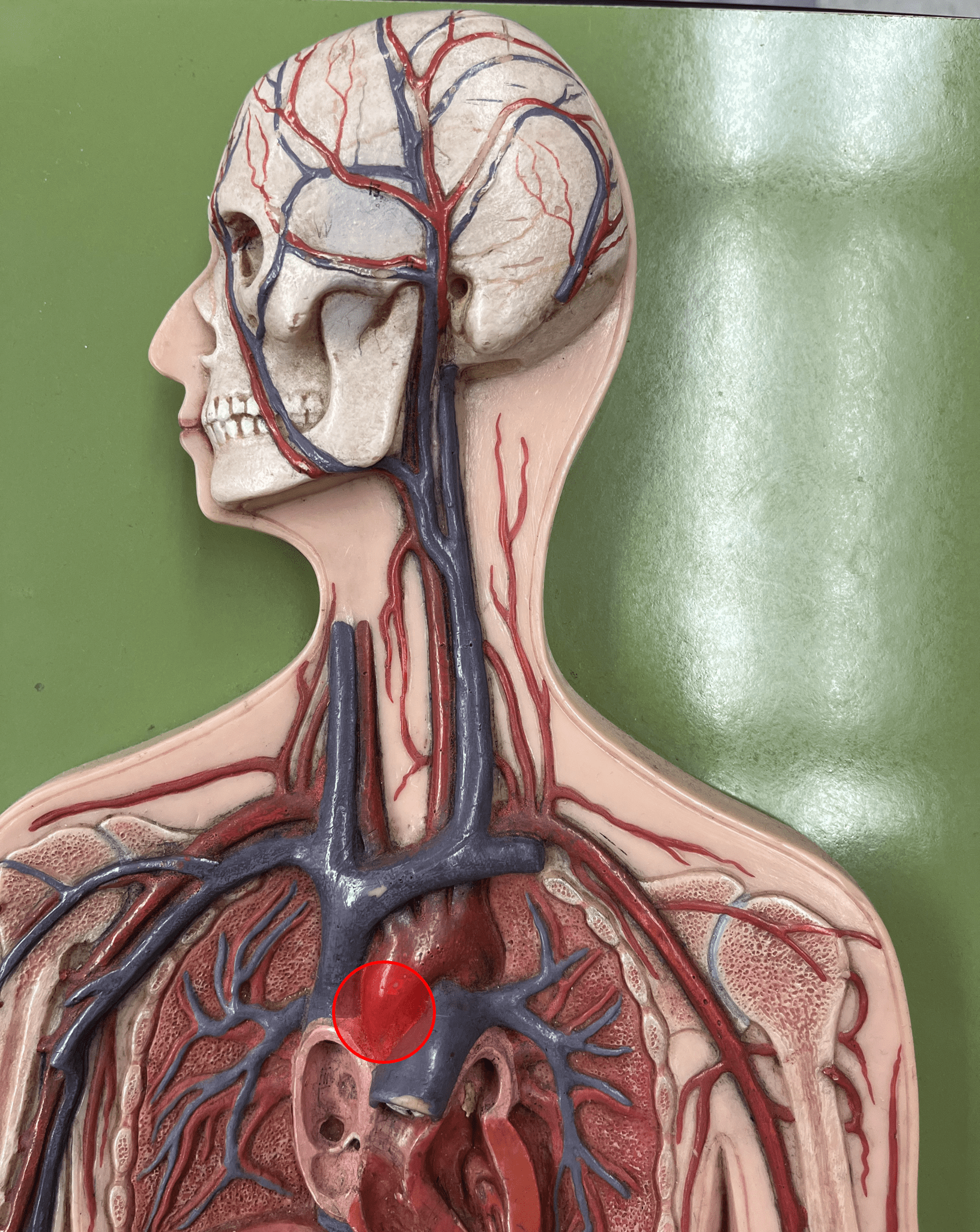
36
New cards
aortic arch
• An artery of the thorax.
• Originates as the continuation of the ascending aorta.
• Supplies its branches: the brachiocephalic trunk, L. subclavian artery, and L. common carotid artery.
• Originates as the continuation of the ascending aorta.
• Supplies its branches: the brachiocephalic trunk, L. subclavian artery, and L. common carotid artery.
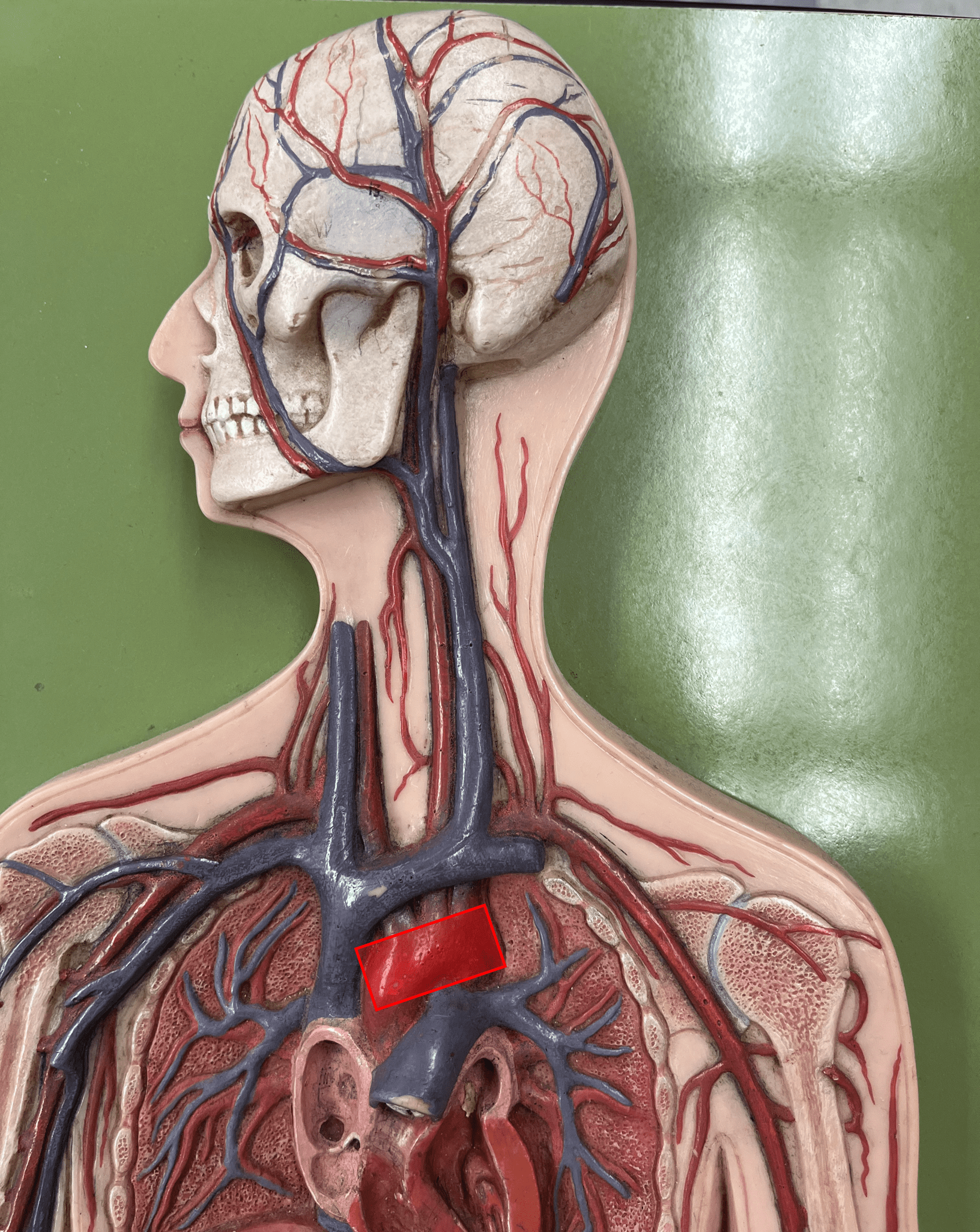
37
New cards
brachiocephalic trunk
• An artery of the thorax.
• Originates from the aortic arch.
• Supplies its branches: the R. subclavian and R. common carotid arteries.
• Originates from the aortic arch.
• Supplies its branches: the R. subclavian and R. common carotid arteries.
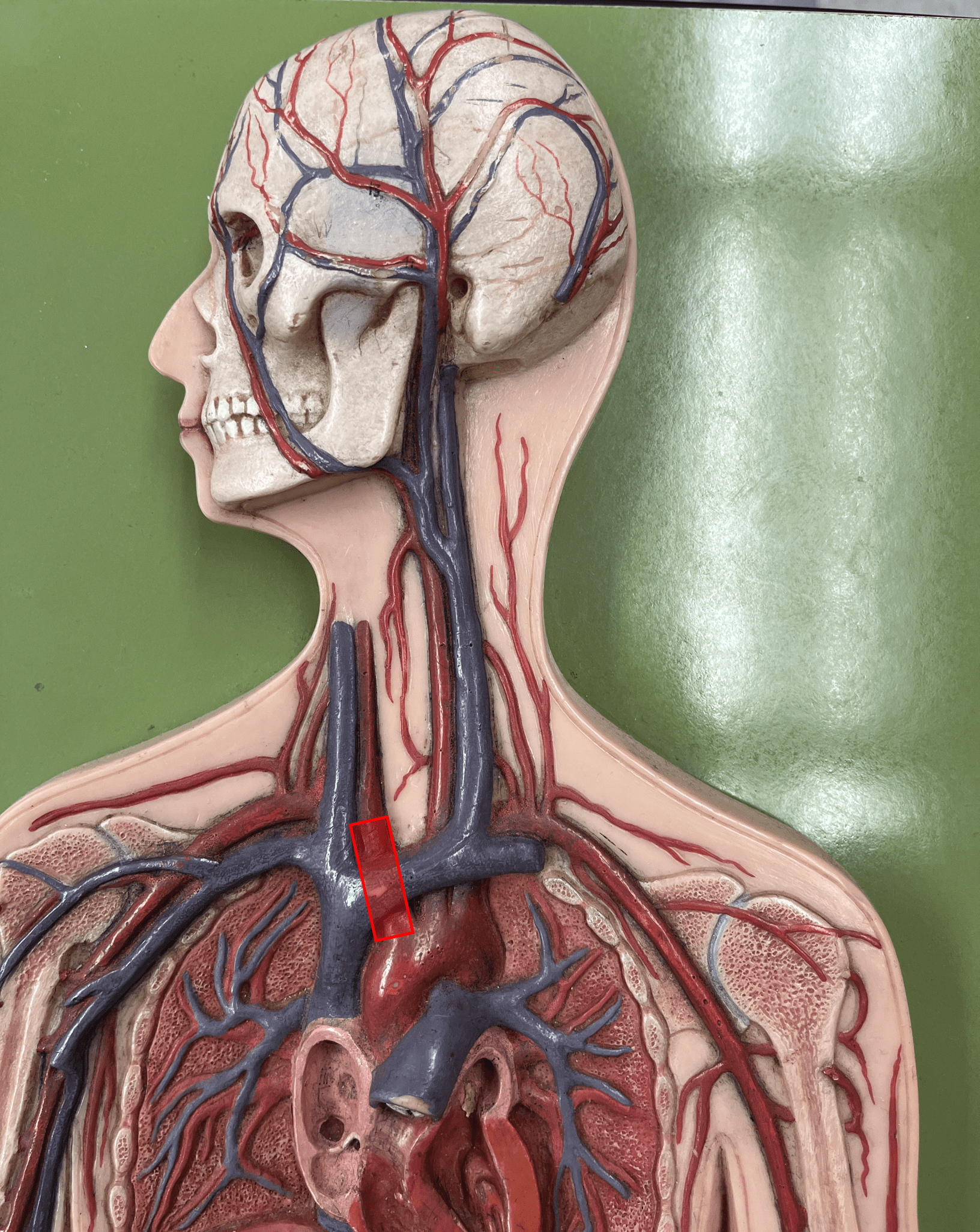
38
New cards
subclavian artery
• An artery of the thorax.
• Originates from the brachiocephalic trunk (R.) or the aortic arch (L.).
• Supplies its branches.
• Originates from the brachiocephalic trunk (R.) or the aortic arch (L.).
• Supplies its branches.
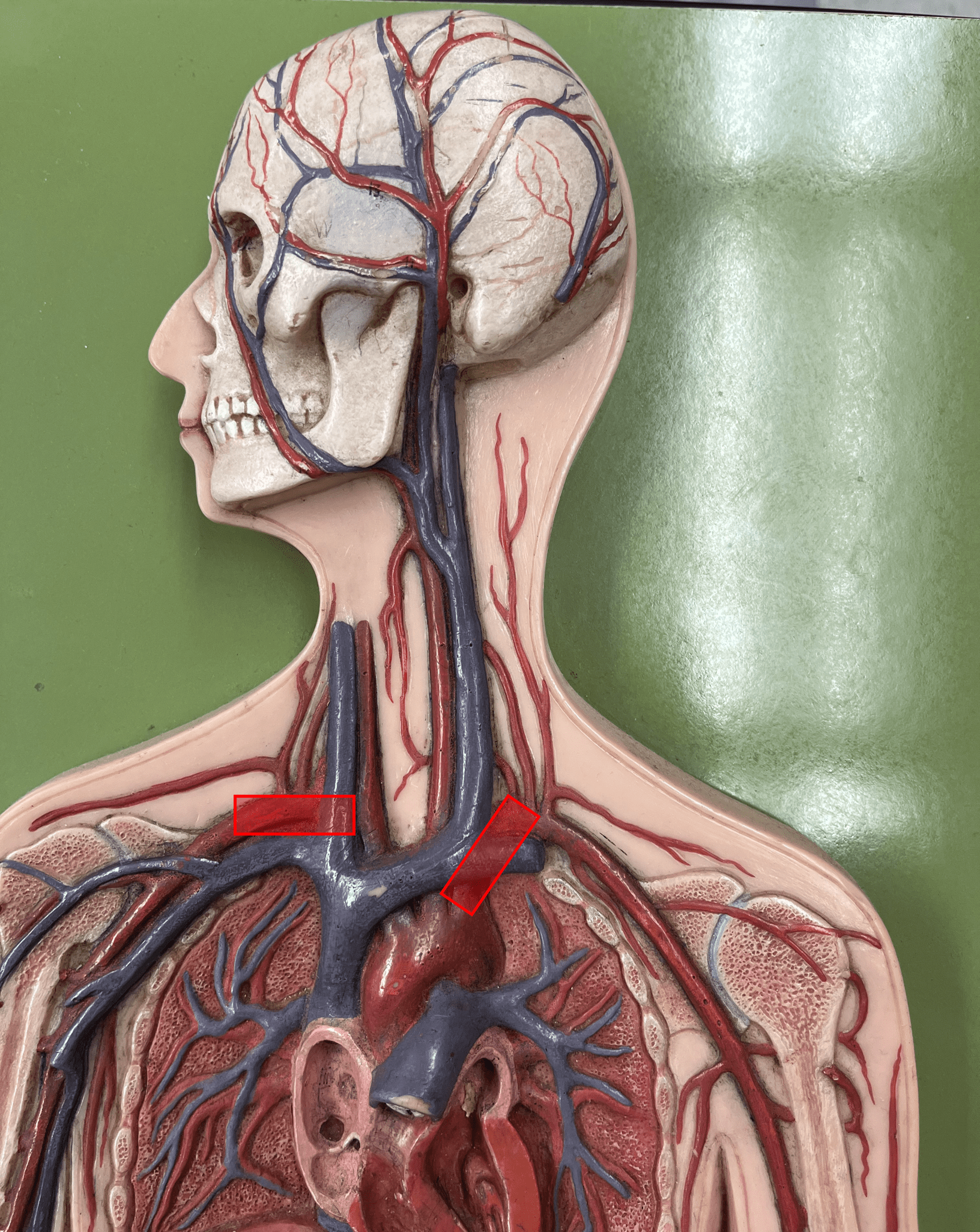
39
New cards
thoracic aorta
• An artery of the thorax.
• Originates as the continuation of the aortic arch.
• Supplies its branches.
• Originates as the continuation of the aortic arch.
• Supplies its branches.
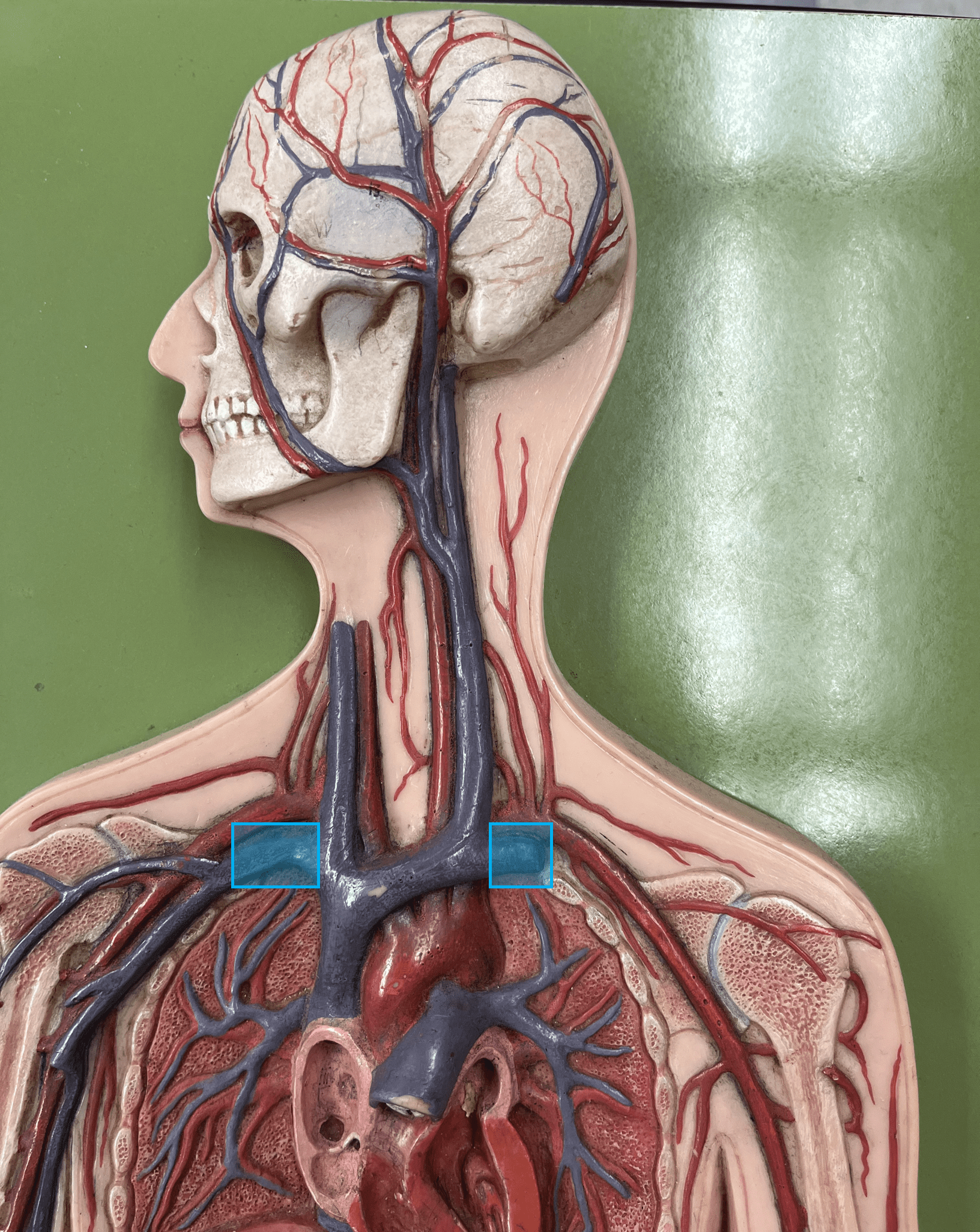
40
New cards
subclavian vein
• A vein of the thorax.
• Drains the axillary vein.
• Empties into the brachiocephalic vein.
• Drains the axillary vein.
• Empties into the brachiocephalic vein.
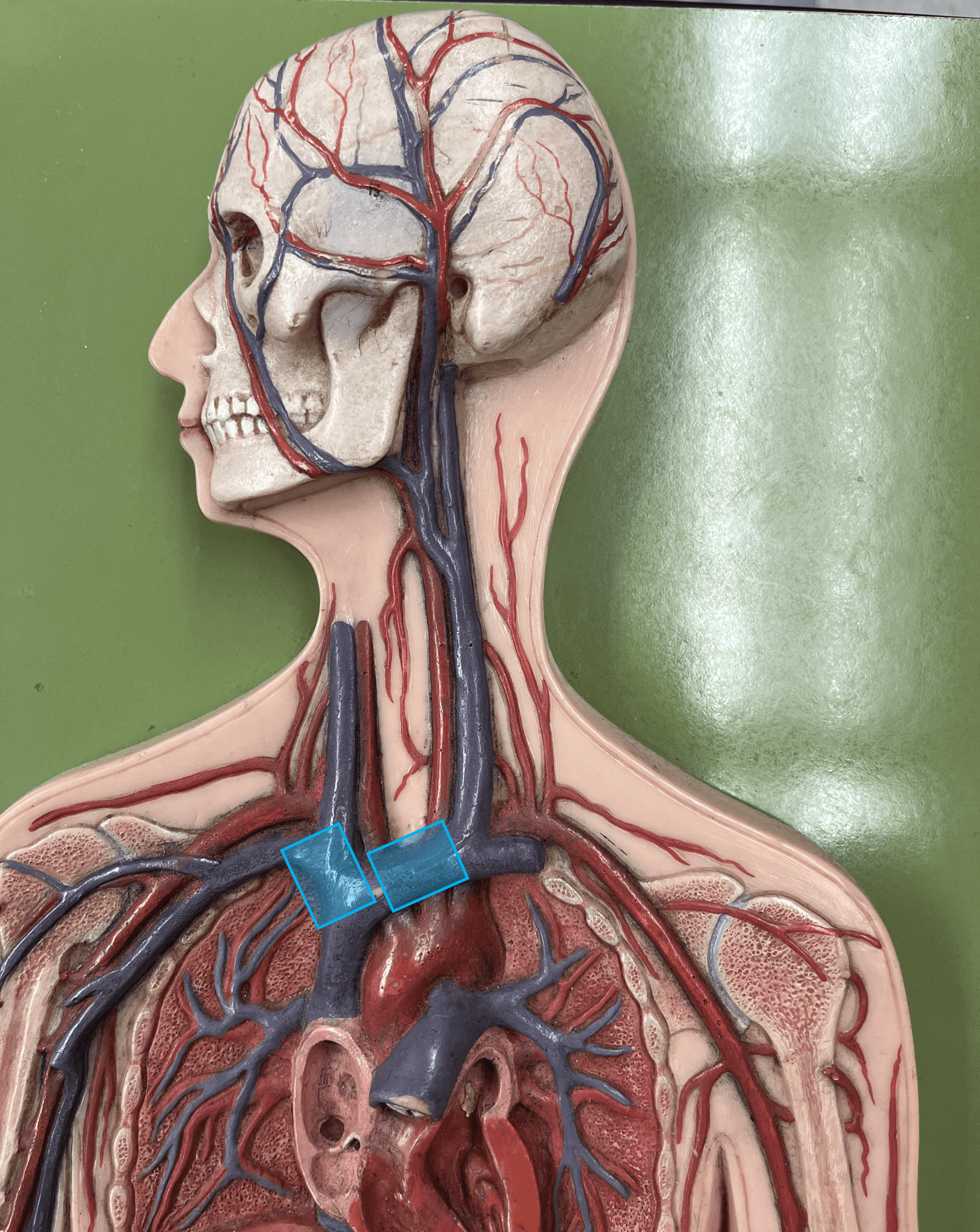
41
New cards
brachiocephalic vein
• A vein of the thorax.
• Drains the subclavian, external jugular, vertebral, internal jugular, and left intercostal (1-3) veins.
• Empties into the superior vena cava.
• Drains the subclavian, external jugular, vertebral, internal jugular, and left intercostal (1-3) veins.
• Empties into the superior vena cava.
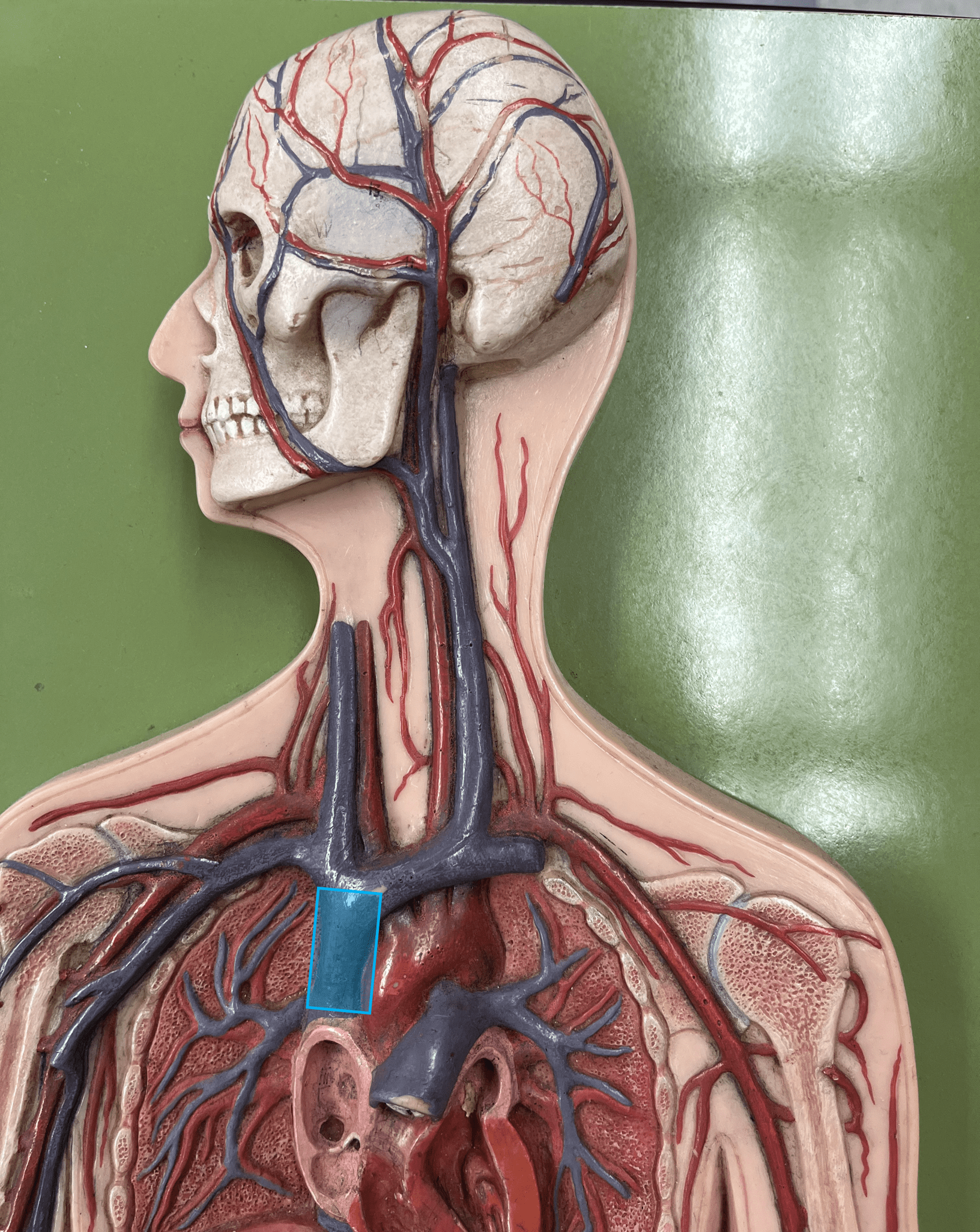
42
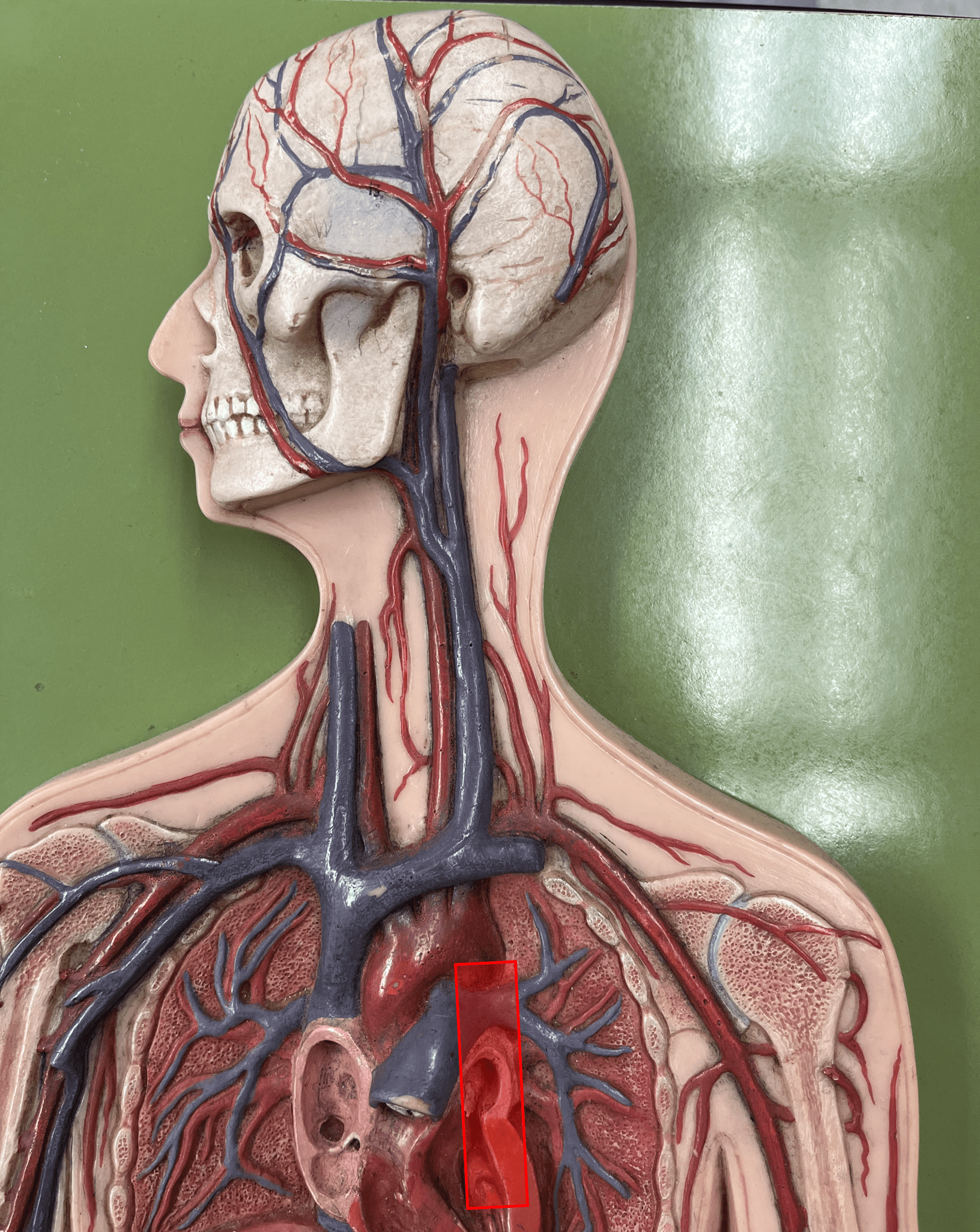
New cards
superior vena cava
• A vein of the thorax.
• Drains the azygos and brachiocephalic veins.
• Empties into the right atrium.
• Drains the azygos and brachiocephalic veins.
• Empties into the right atrium.
43
New cards
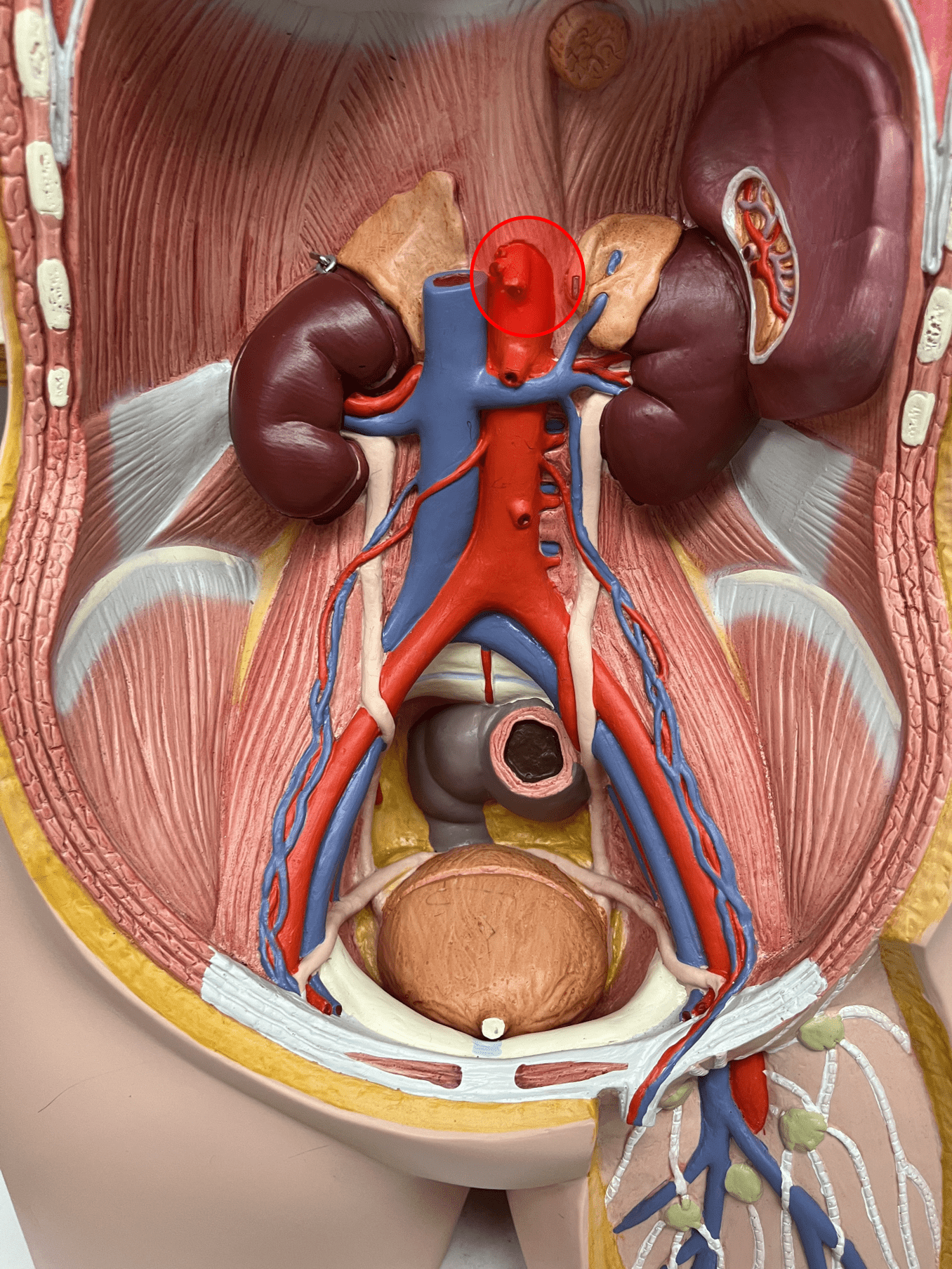
celiac trunk
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the upper abdominal viscera through its branches: the L. gastric, common hepatic, and splenic arteries.
• On the abdominal aorta, the most superior artery.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the upper abdominal viscera through its branches: the L. gastric, common hepatic, and splenic arteries.
• On the abdominal aorta, the most superior artery.
44
New cards
left gastric artery
• An artery of the abdomen (not shown).
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the stomach and inferior esophagus.
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the stomach and inferior esophagus.
45
New cards
common hepatic artery
• An artery of the abdomen (not shown).
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
46
New cards
splenic artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the spleen, pancreas, and stomach.
• Originates from the celiac trunk.
• Supplies the spleen, pancreas, and stomach.
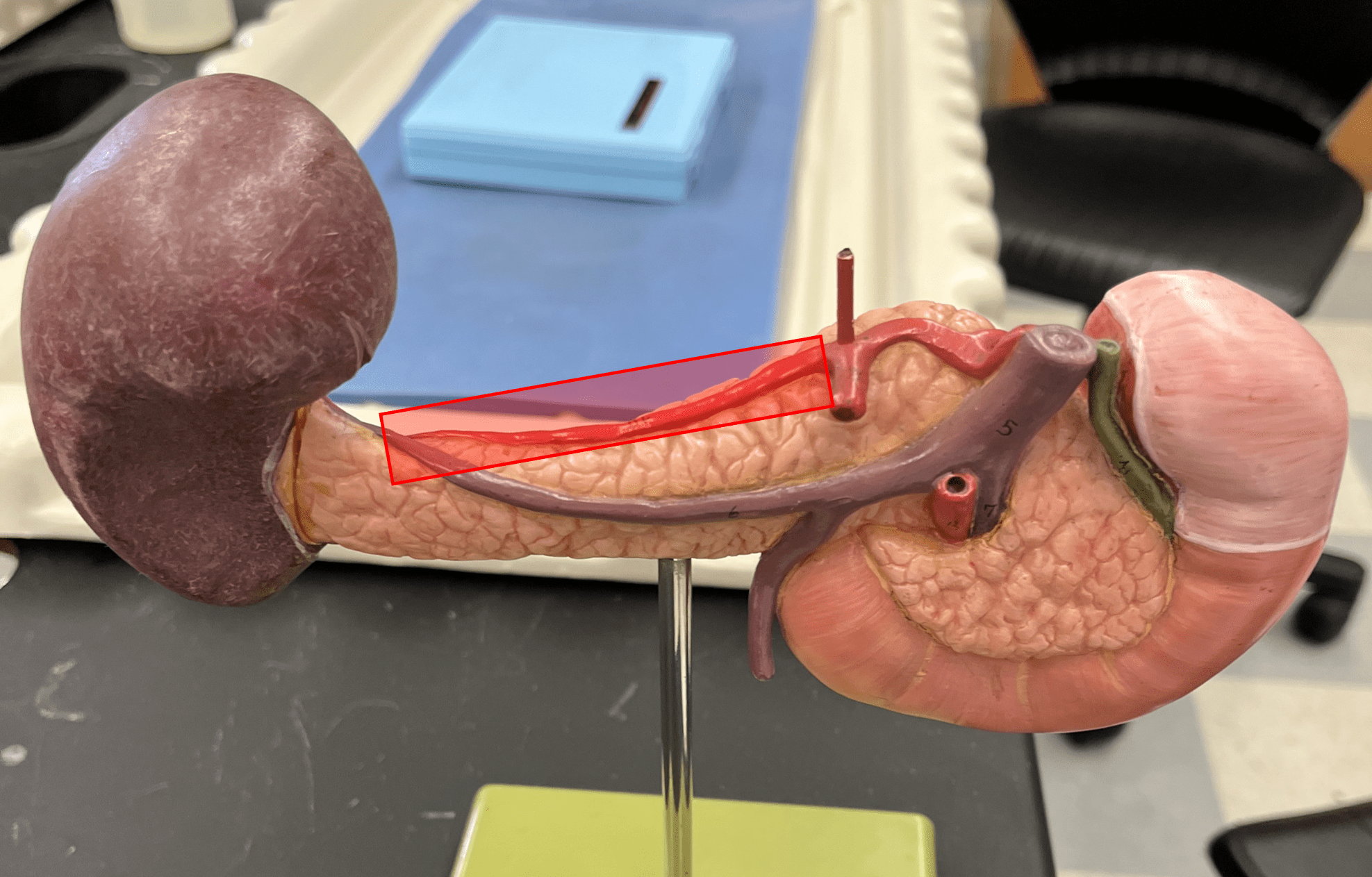
47
New cards
superior mesenteric artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the pancreas, small intestine, and most of the colon.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the celiac trunk and superior to the suprarenal arteries.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the pancreas, small intestine, and most of the colon.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the celiac trunk and superior to the suprarenal arteries.
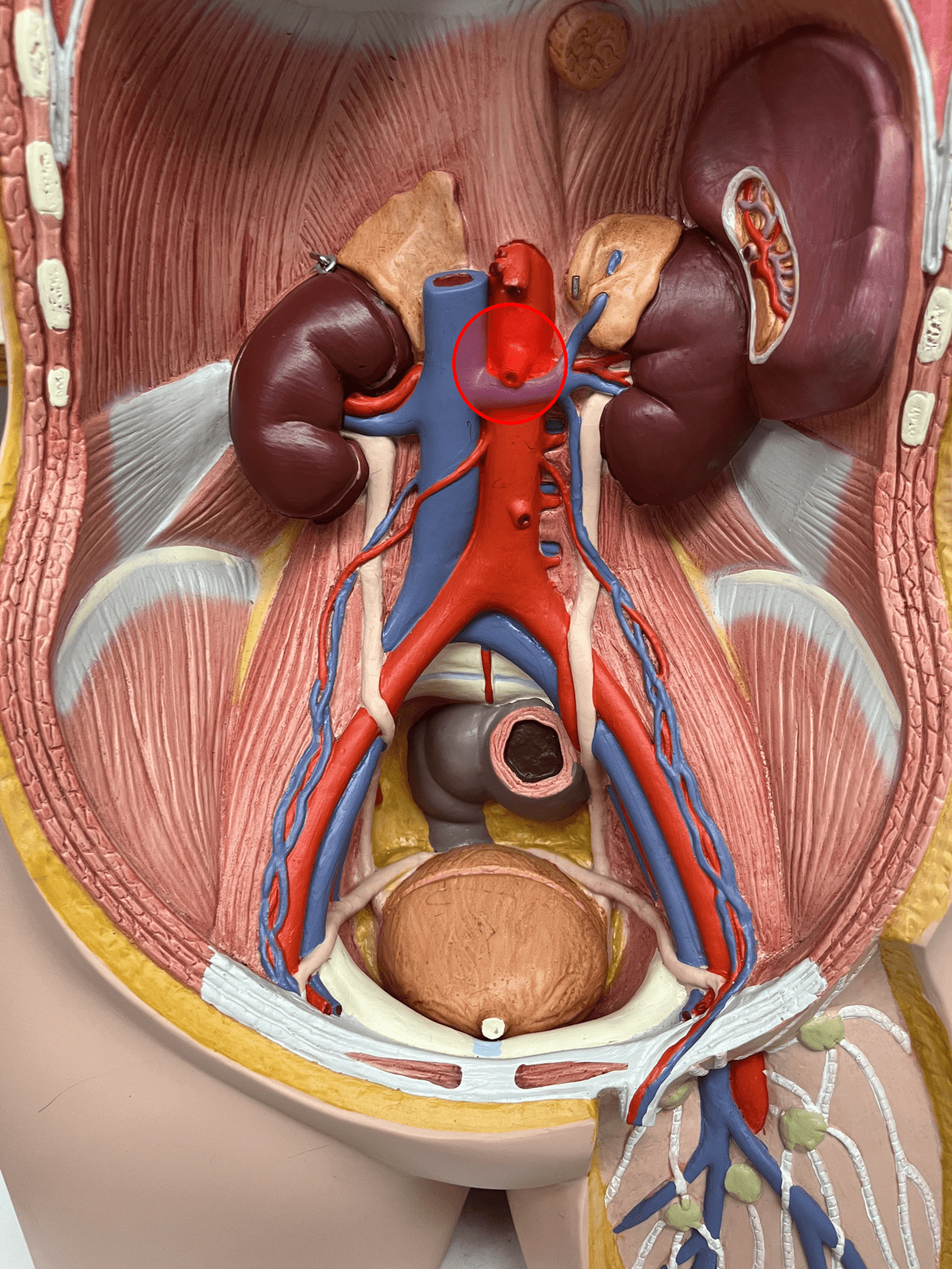
48
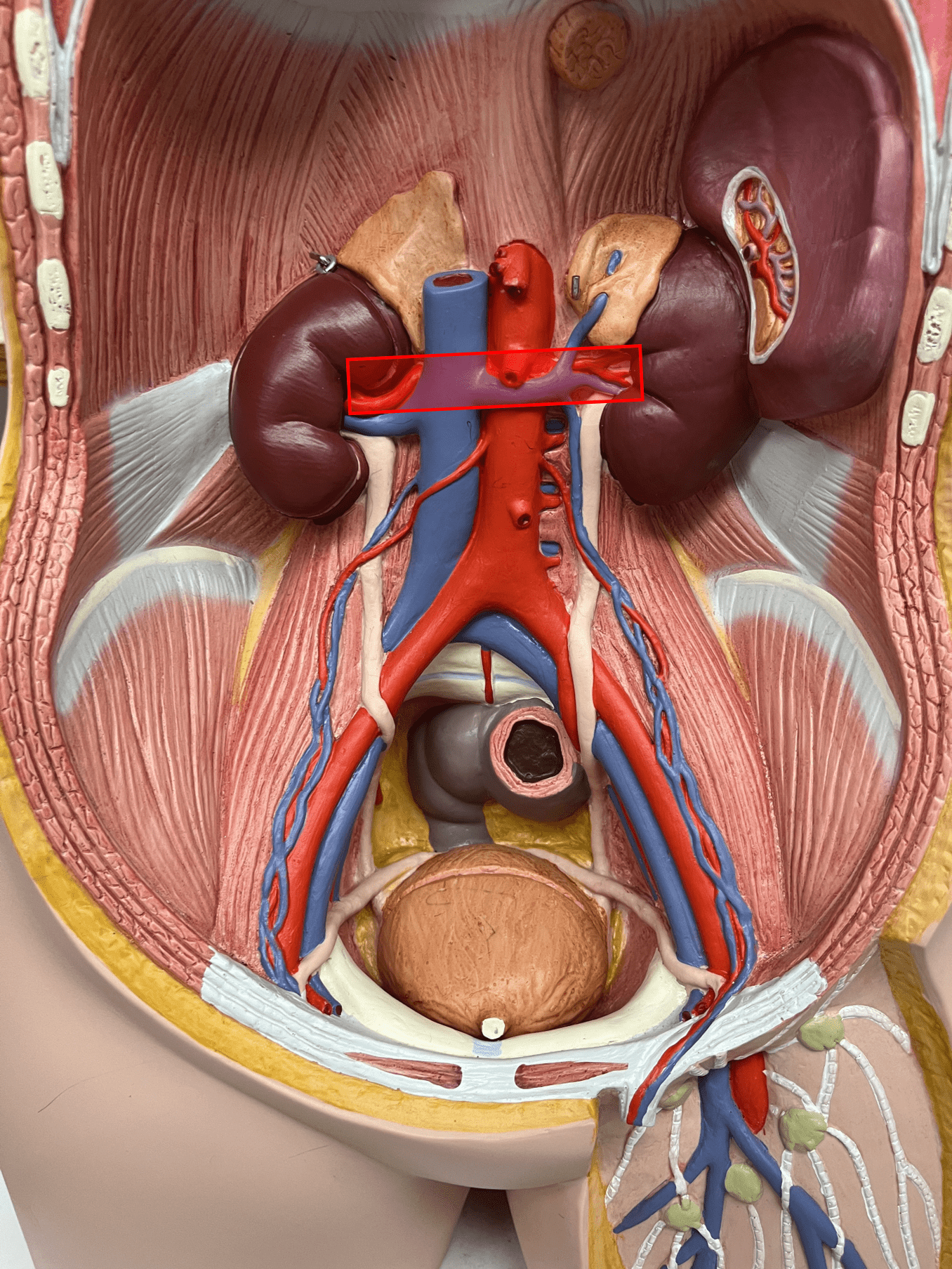
New cards
suprarenal artery
• An artery of the abdomen (not shown).
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the adrenal glands.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the superior mesenteric artery and superior to the renal arteries.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the adrenal glands.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the superior mesenteric artery and superior to the renal arteries.
49
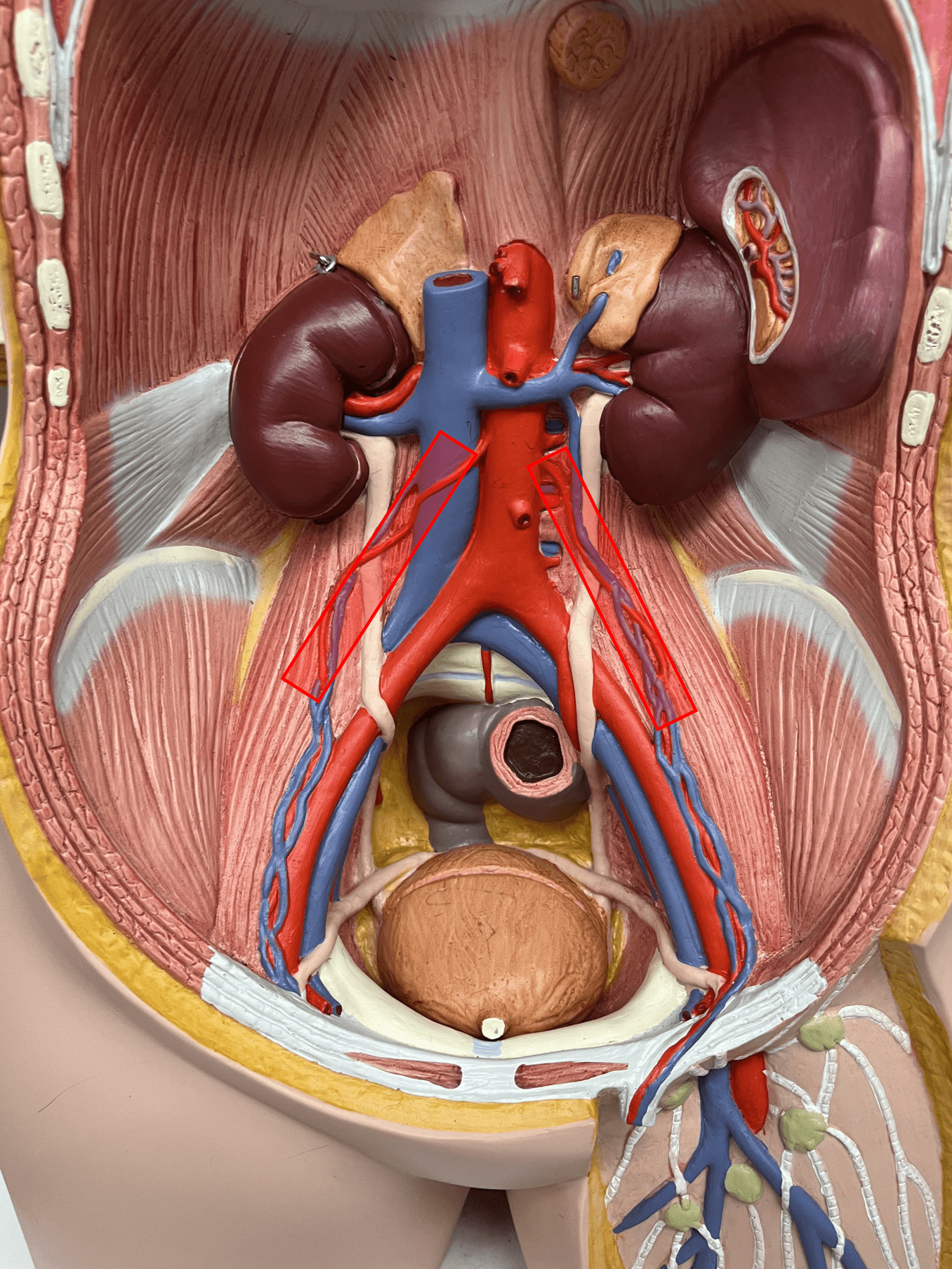
New cards
renal artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the kidneys.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the suprarenal arteries and superior to the gonadal arteries.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the kidneys.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the suprarenal arteries and superior to the gonadal arteries.
50
New cards
gonadal artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the ovaries (female) or testes (male).
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the renal arteries.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the ovaries (female) or testes (male).
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the renal arteries.
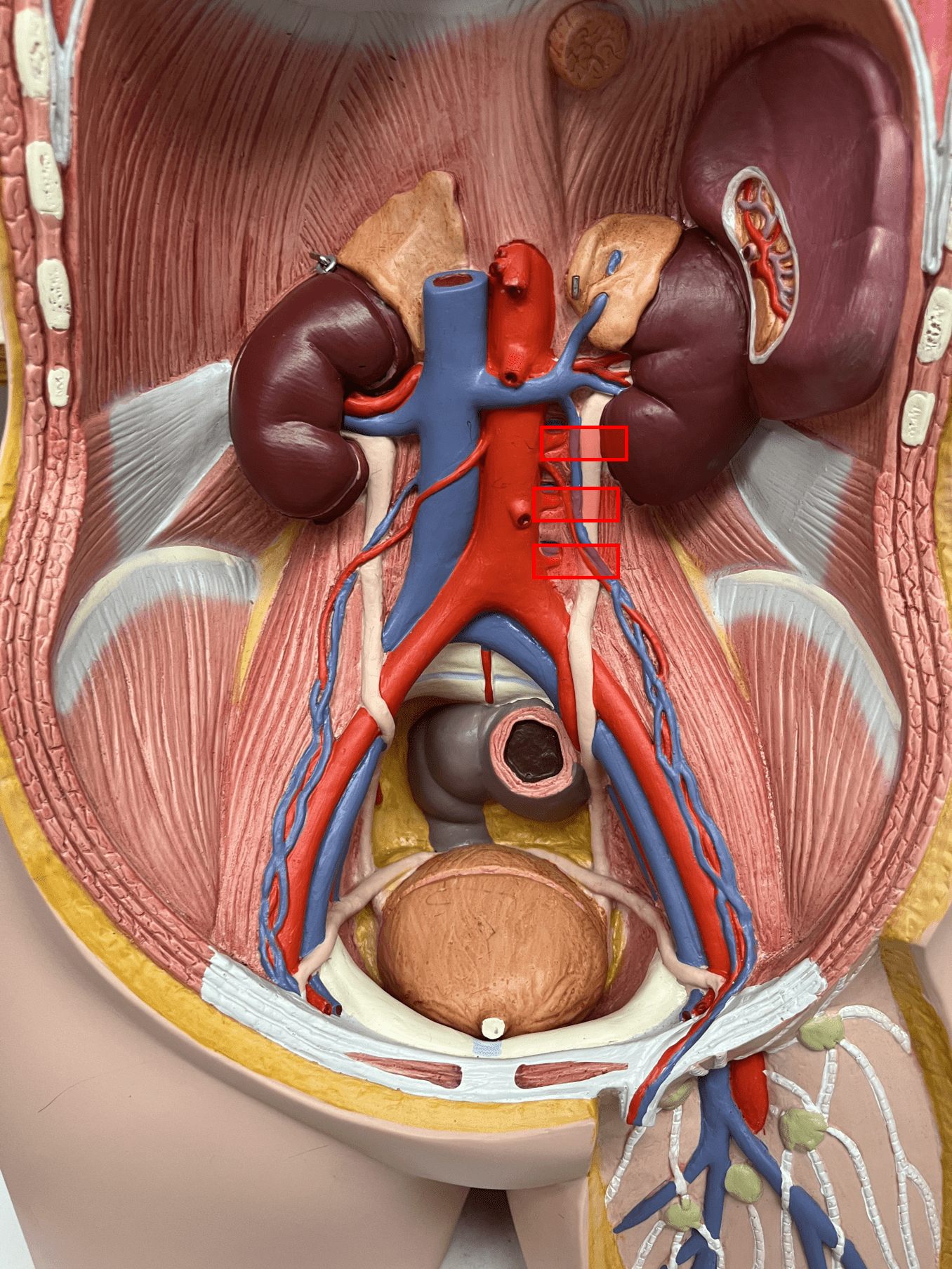
51
New cards
lumbar artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the spinal cord and dorsal abdominal wall.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the spinal cord and dorsal abdominal wall.
52
New cards
inferior mesenteric artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the distal end of the colon and rectum.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the gonadal artery and superior to the common iliac arteries.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the distal end of the colon and rectum.
• On the abdominal aorta, inferior to the gonadal artery and superior to the common iliac arteries.
53
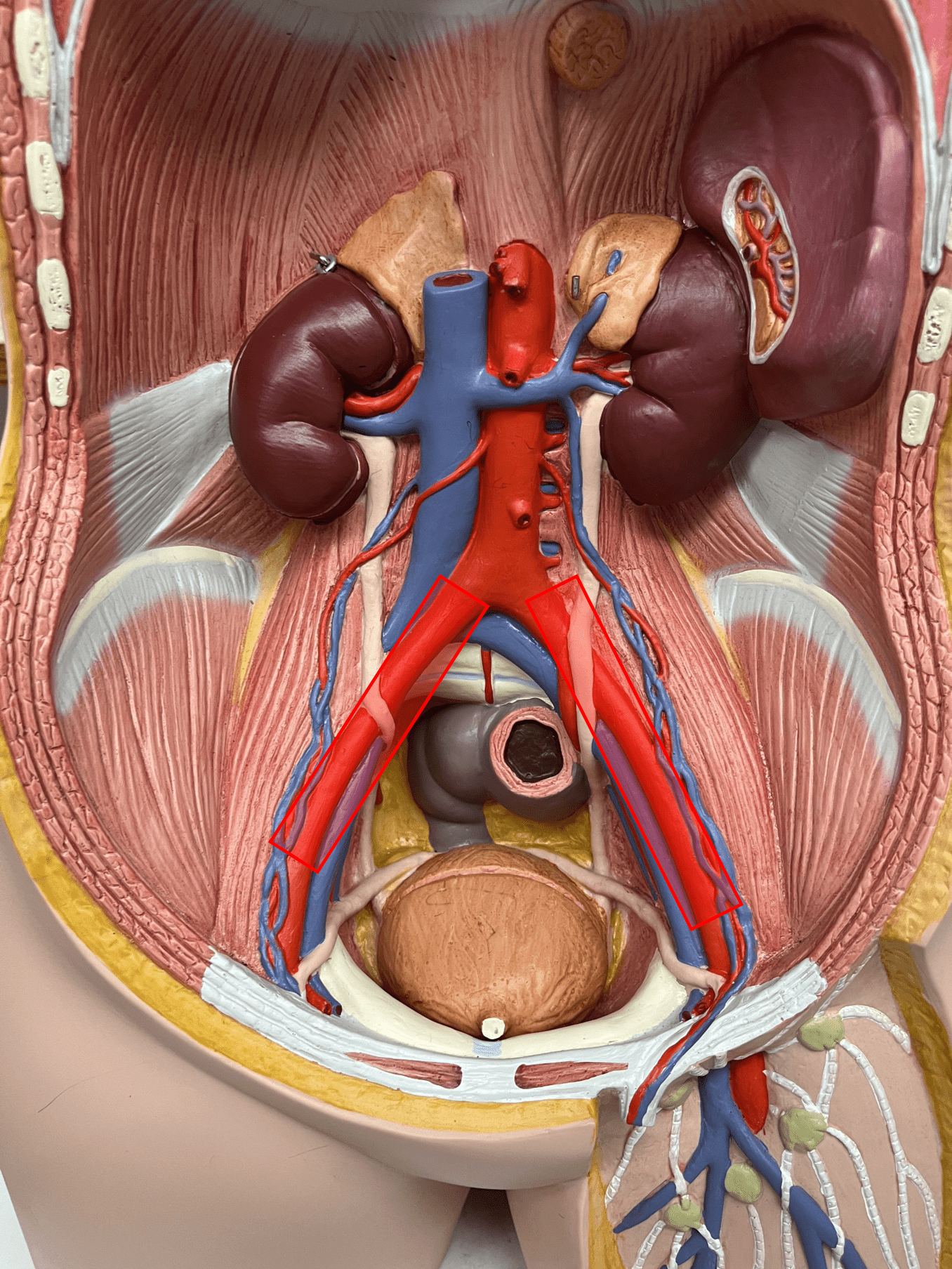
New cards
common iliac artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates as the continuation of the abdominal aorta after it forks.
• Supplies the pelvic structures and lower extremities through its branches.
• Originates as the continuation of the abdominal aorta after it forks.
• Supplies the pelvic structures and lower extremities through its branches.
54
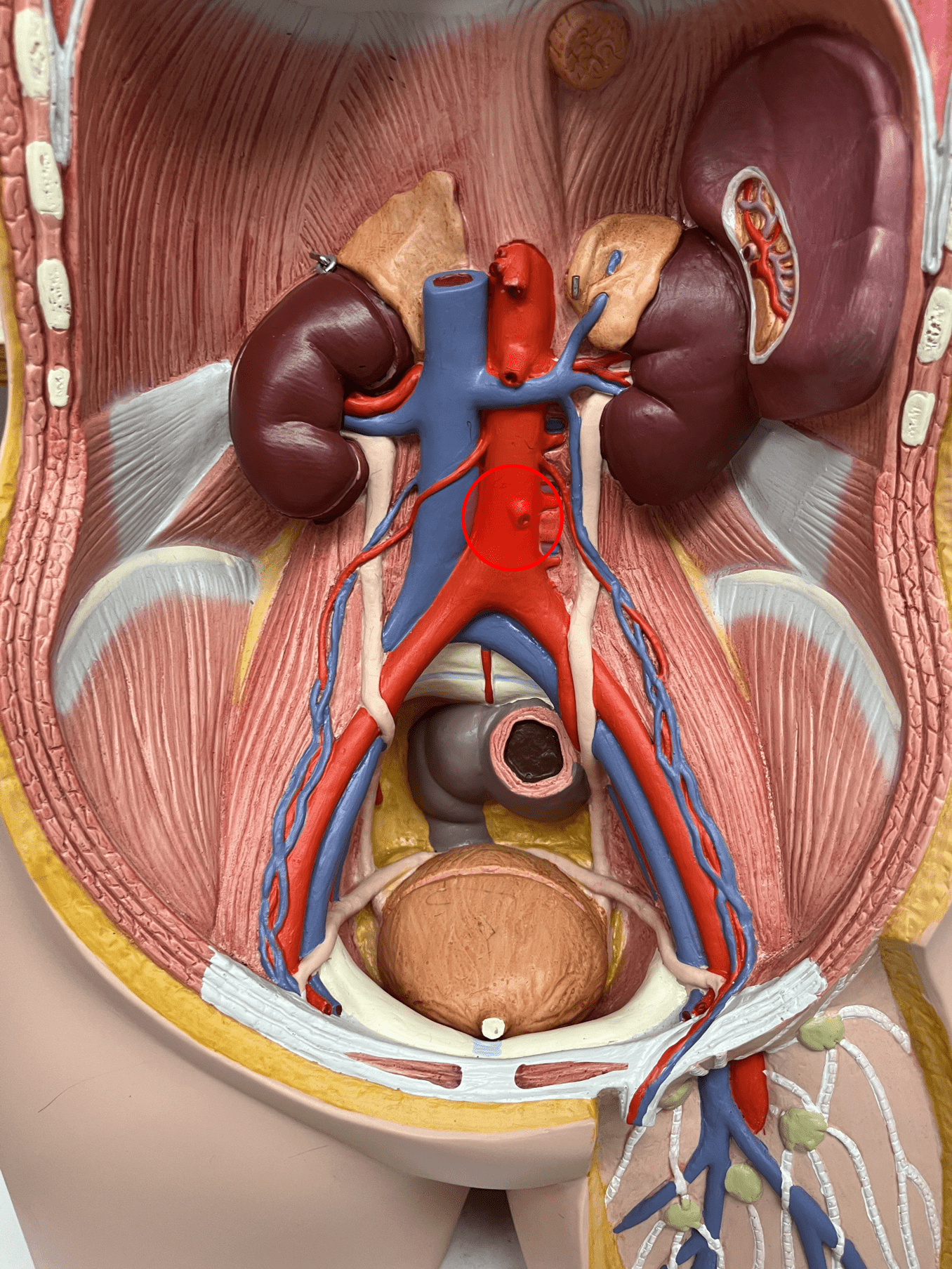
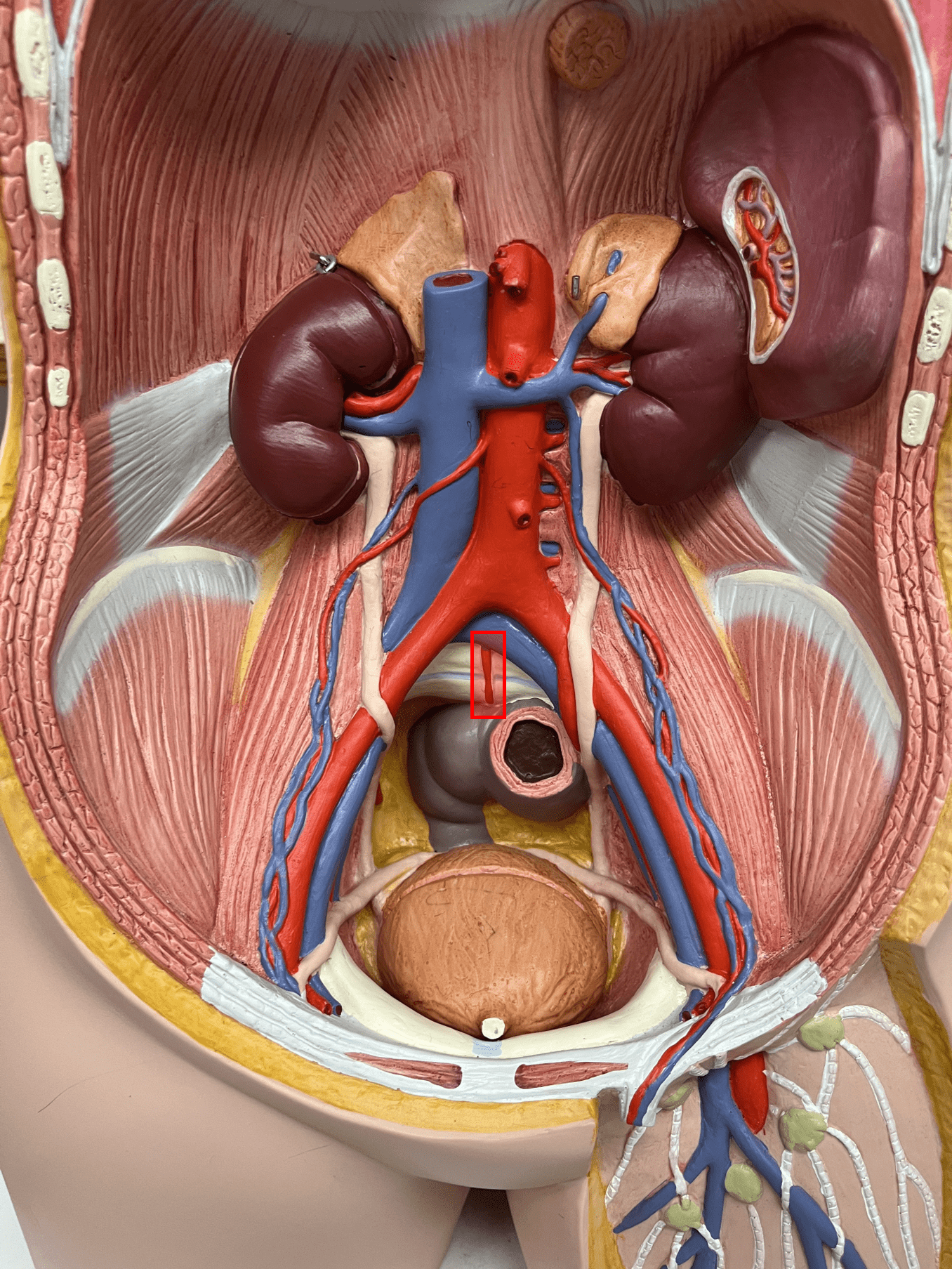
New cards
median sacral artery
• An artery of the abdomen.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the sacrum and coccyx.
• Originates from the abdominal aorta.
• Supplies the sacrum and coccyx.
55
New cards
hepatic vein
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains the liver.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, the most superior veins.
• Drains the liver.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, the most superior veins.
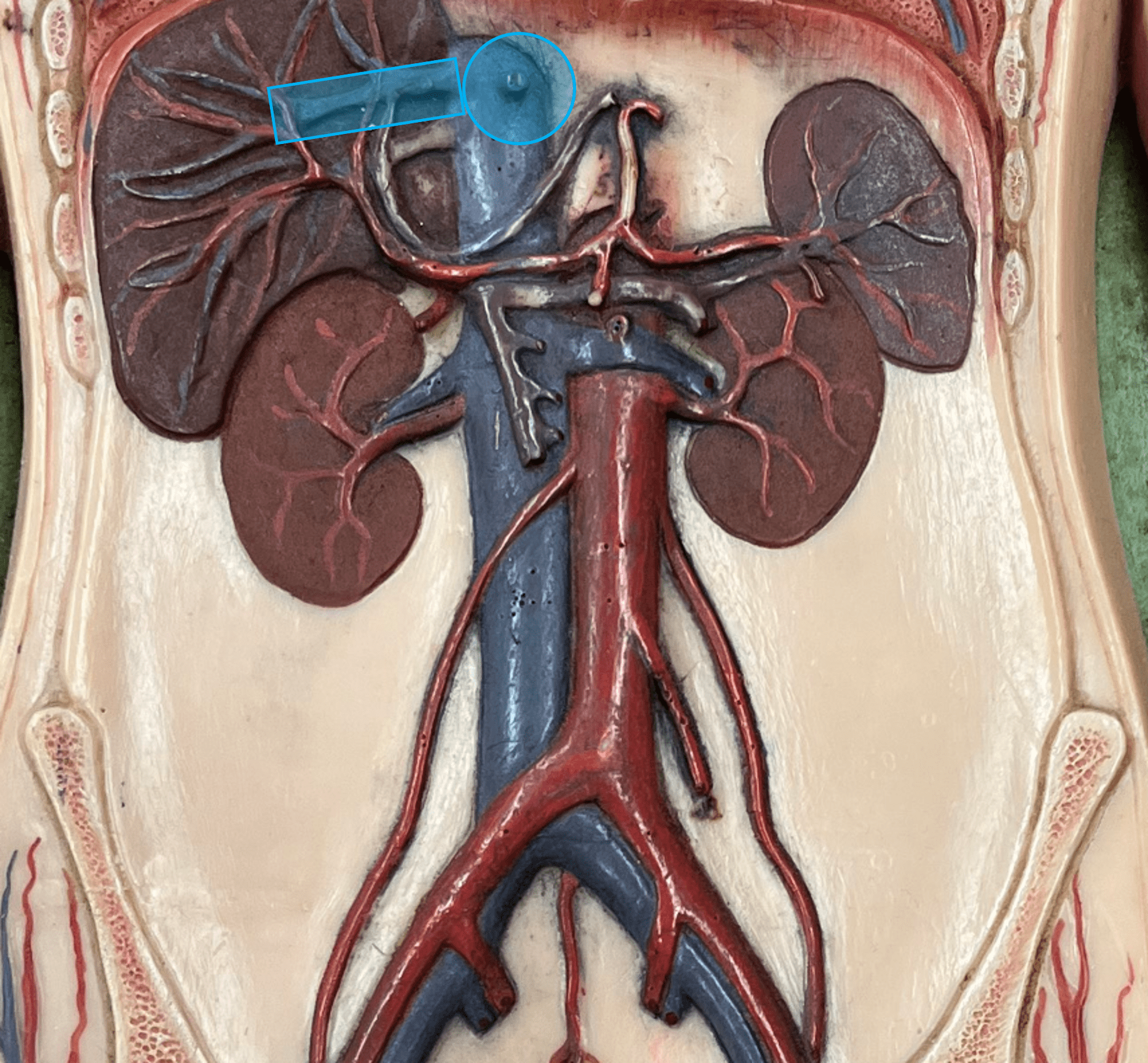
56
New cards
suprarenal vein
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains the adrenal glands.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava (R.) or the L. renal vein (L.).
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the hepatic veins and superior to the renal veins (R.).
• Drains the adrenal glands.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava (R.) or the L. renal vein (L.).
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the hepatic veins and superior to the renal veins (R.).
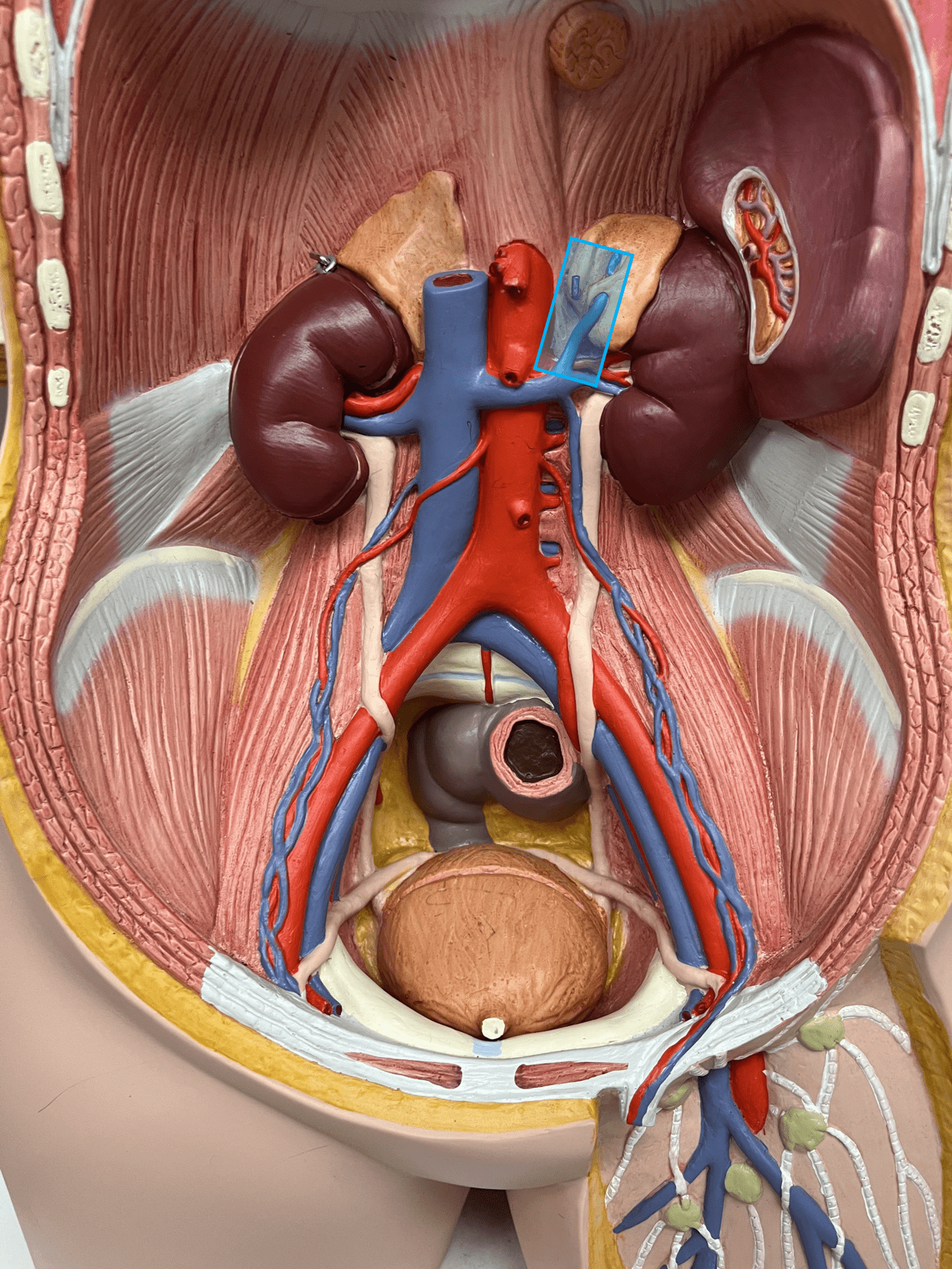
57
New cards
renal vein
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains the kidneys.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the hepatic veins and superior to the gonadal veins.
• Drains the kidneys.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the hepatic veins and superior to the gonadal veins.
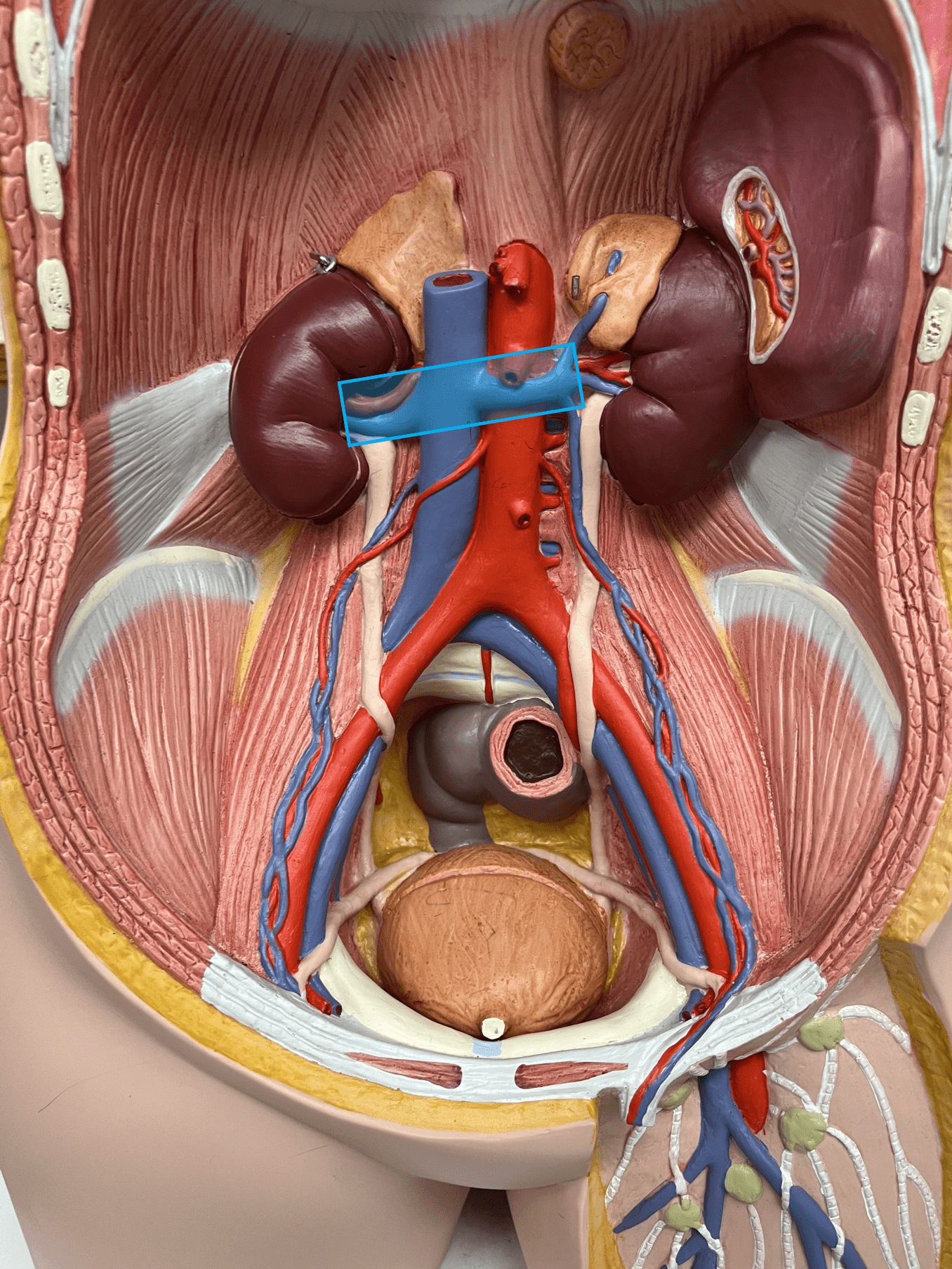
58
New cards
gonadal vein
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains the ovaries (female) or testes (male).
• Empties into the inferior vena cava (R.) or the L. renal vein (L.).
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the renal veins and superior to the lumbar veins (R.).
• Drains the ovaries (female) or testes (male).
• Empties into the inferior vena cava (R.) or the L. renal vein (L.).
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the renal veins and superior to the lumbar veins (R.).
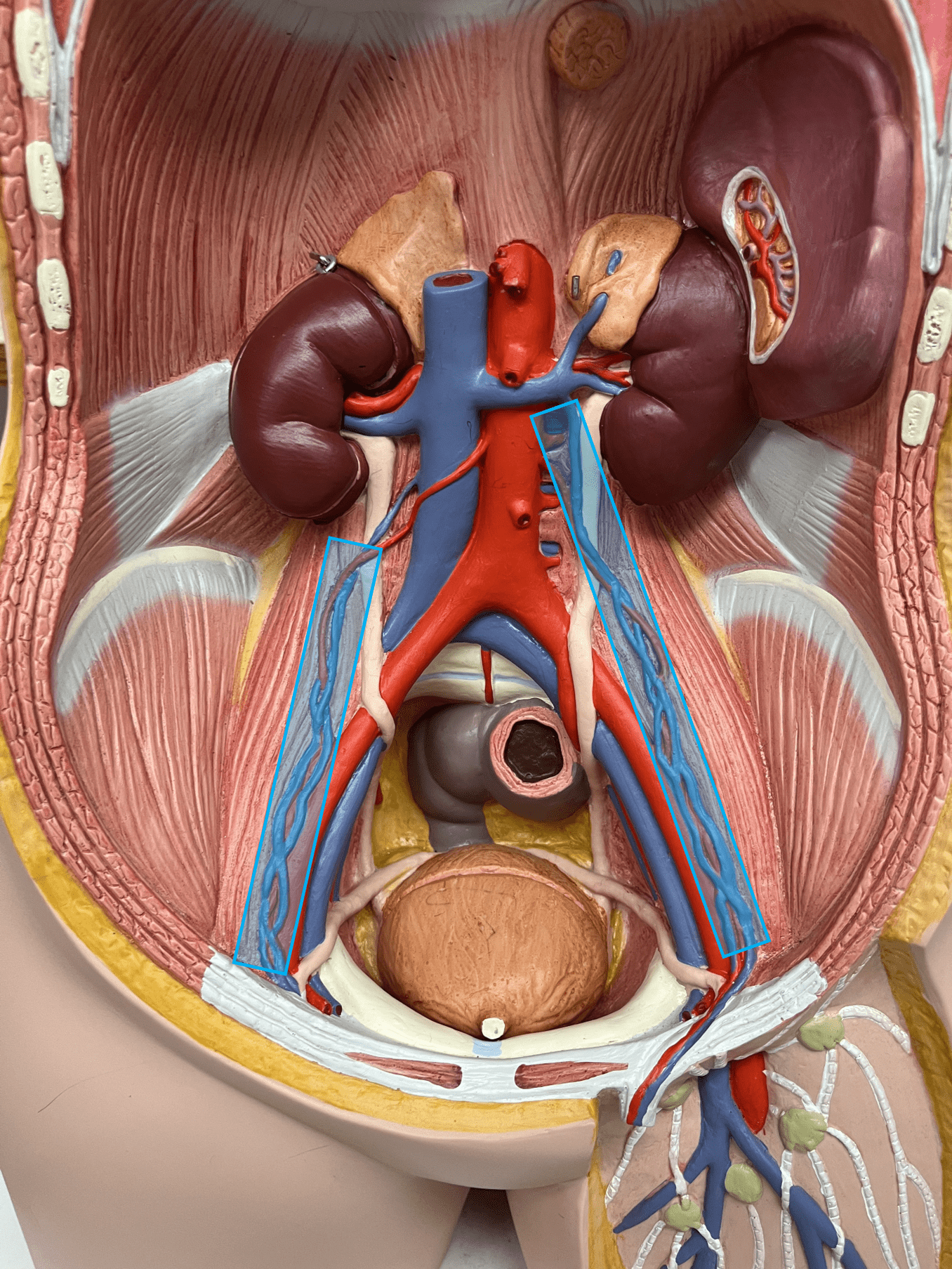
59
New cards
lumbar vein
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains the spinal cord and body wall.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the gonadal veins.
• Drains the spinal cord and body wall.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• On the inferior vena cava, inferior to the gonadal veins.
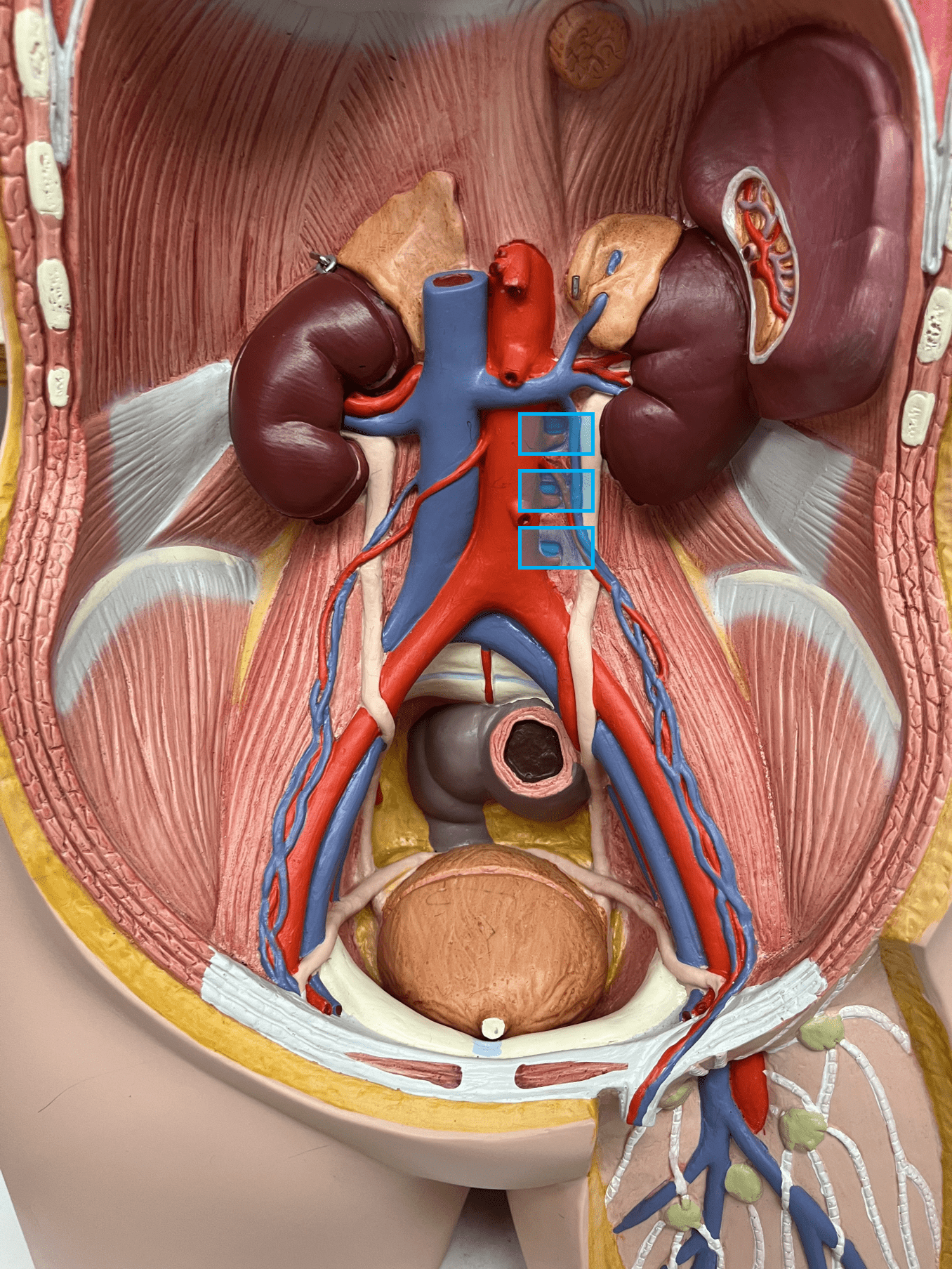
60
New cards
inferior vena cava
• A vein of the abdomen.
• Drains its tributaries: the hepatic, suprarenal, renal, gonadal, lumbar, and common iliac veins.
• Empties into the right atrium of the heart.
• The largest vein in the body.
• Drains its tributaries: the hepatic, suprarenal, renal, gonadal, lumbar, and common iliac veins.
• Empties into the right atrium of the heart.
• The largest vein in the body.
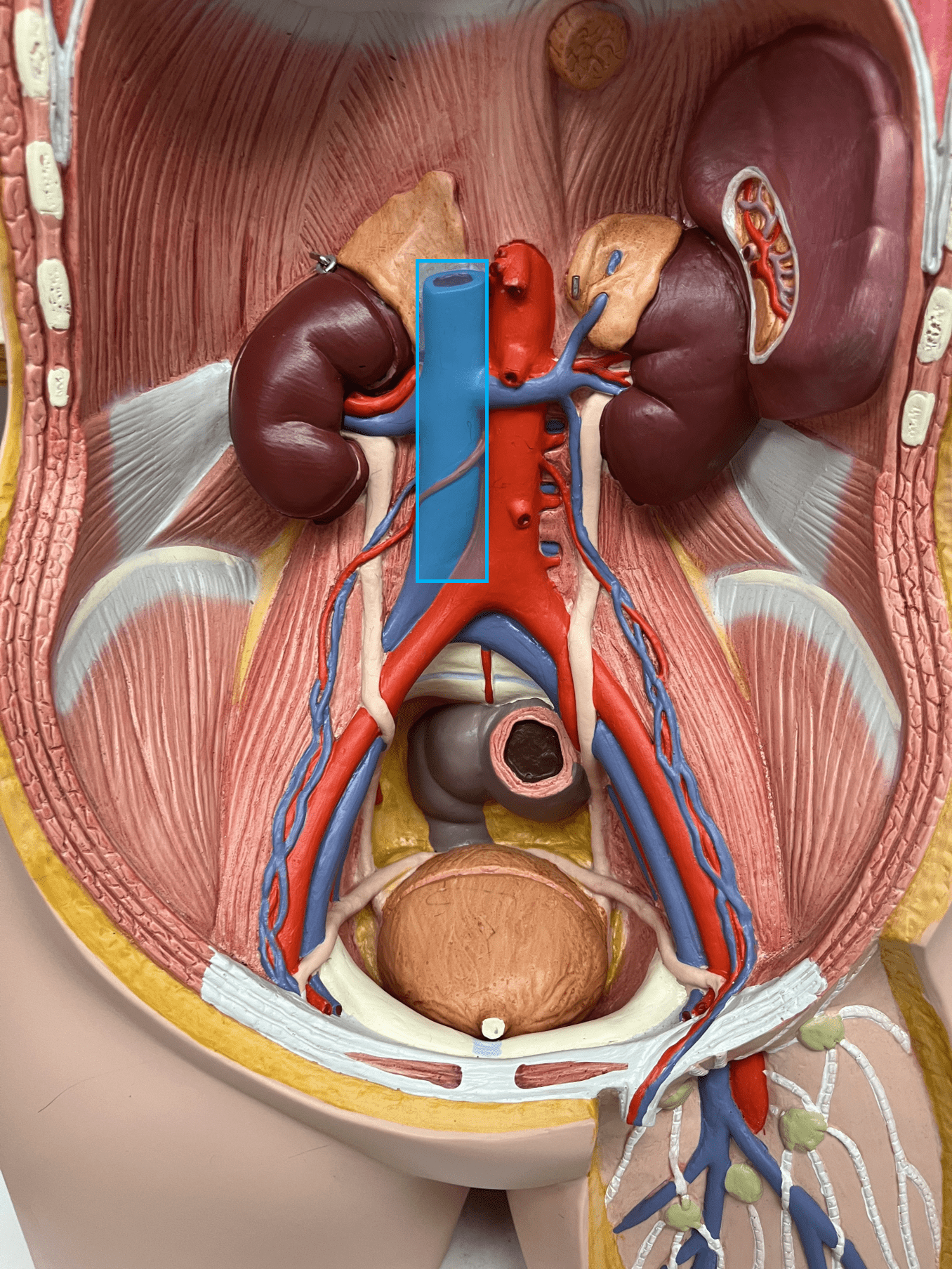
61
New cards
median sacral vein
• A vein of the abdomen (not shown).
• Drains the sacrum and coccyx.
• Empties into the left common iliac vein.
• Drains the sacrum and coccyx.
• Empties into the left common iliac vein.
62
New cards
inferior mesenteric vein
• A vein of the hepatic portal system.
• Drains the rectum and distal colon.
• Empties into the splenic vein.
• Drains the rectum and distal colon.
• Empties into the splenic vein.
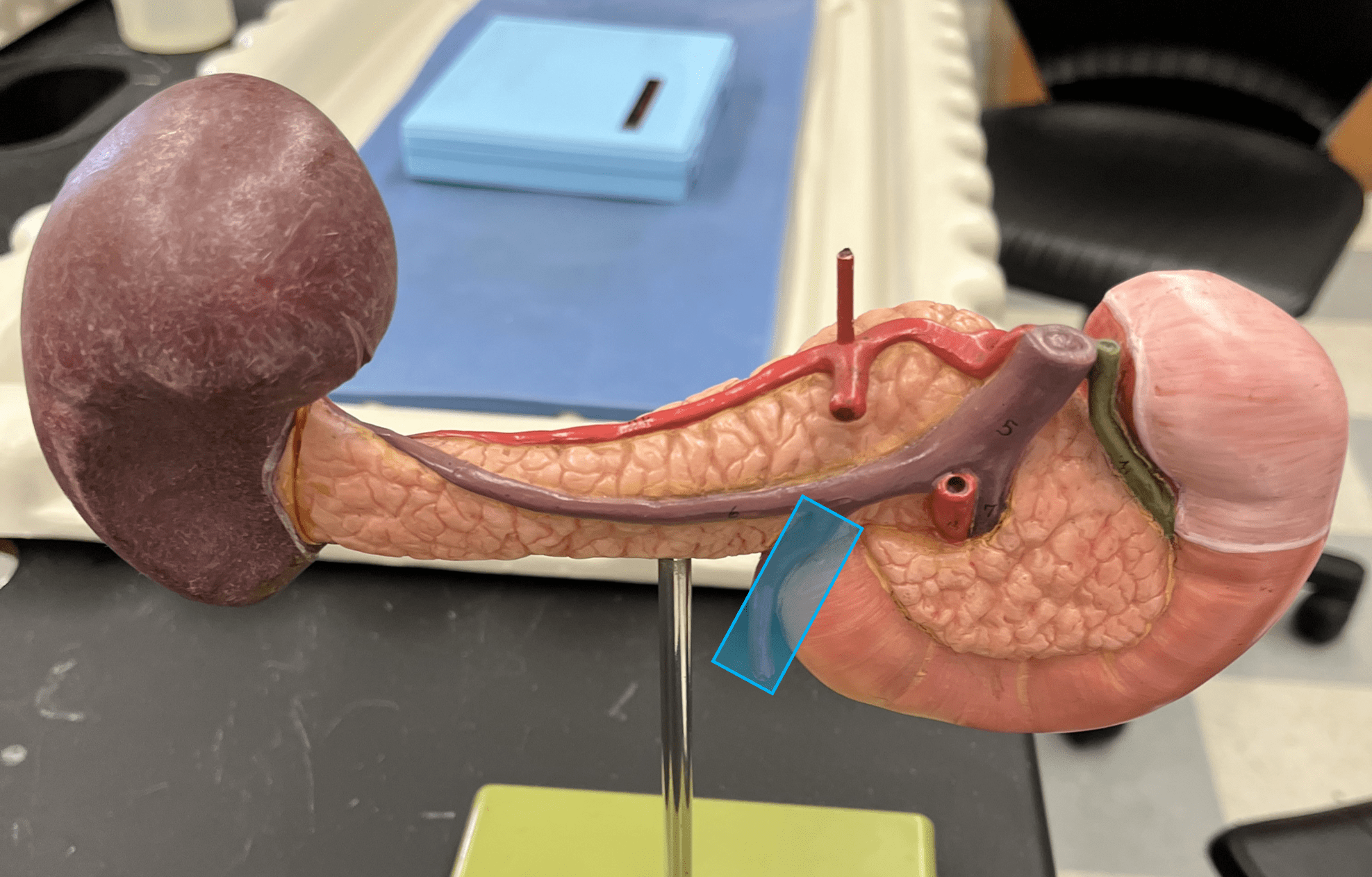
63
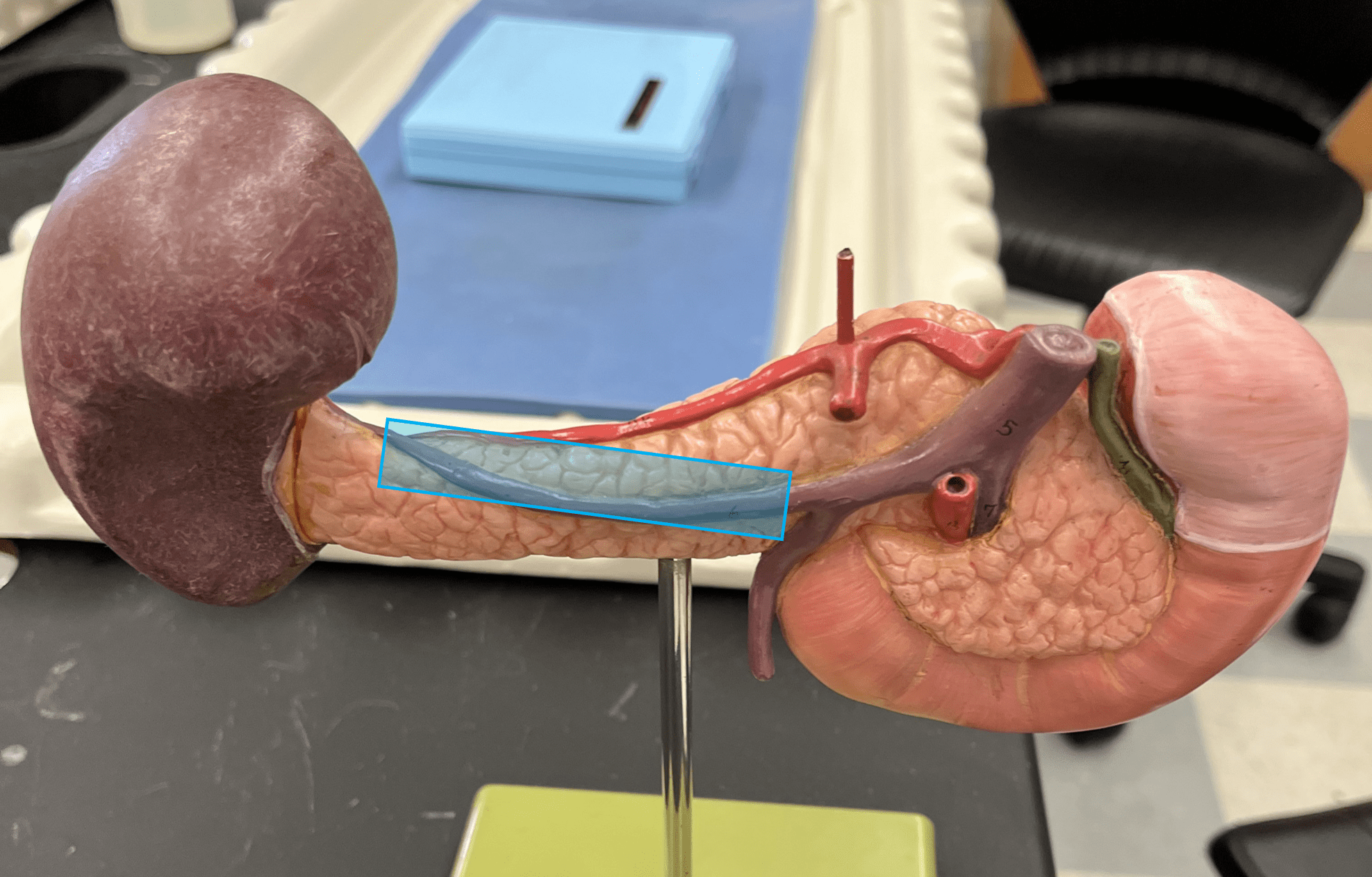
New cards
superior mesenteric vein
• A vein of the hepatic portal system.
• Drains the entire small intestine and parts of the colon and stomach.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
• Drains the entire small intestine and parts of the colon and stomach.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
64
New cards
splenic vein
• A vein of the hepatic portal system.
• Drains the spleen and pancreas.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
• Drains the spleen and pancreas.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
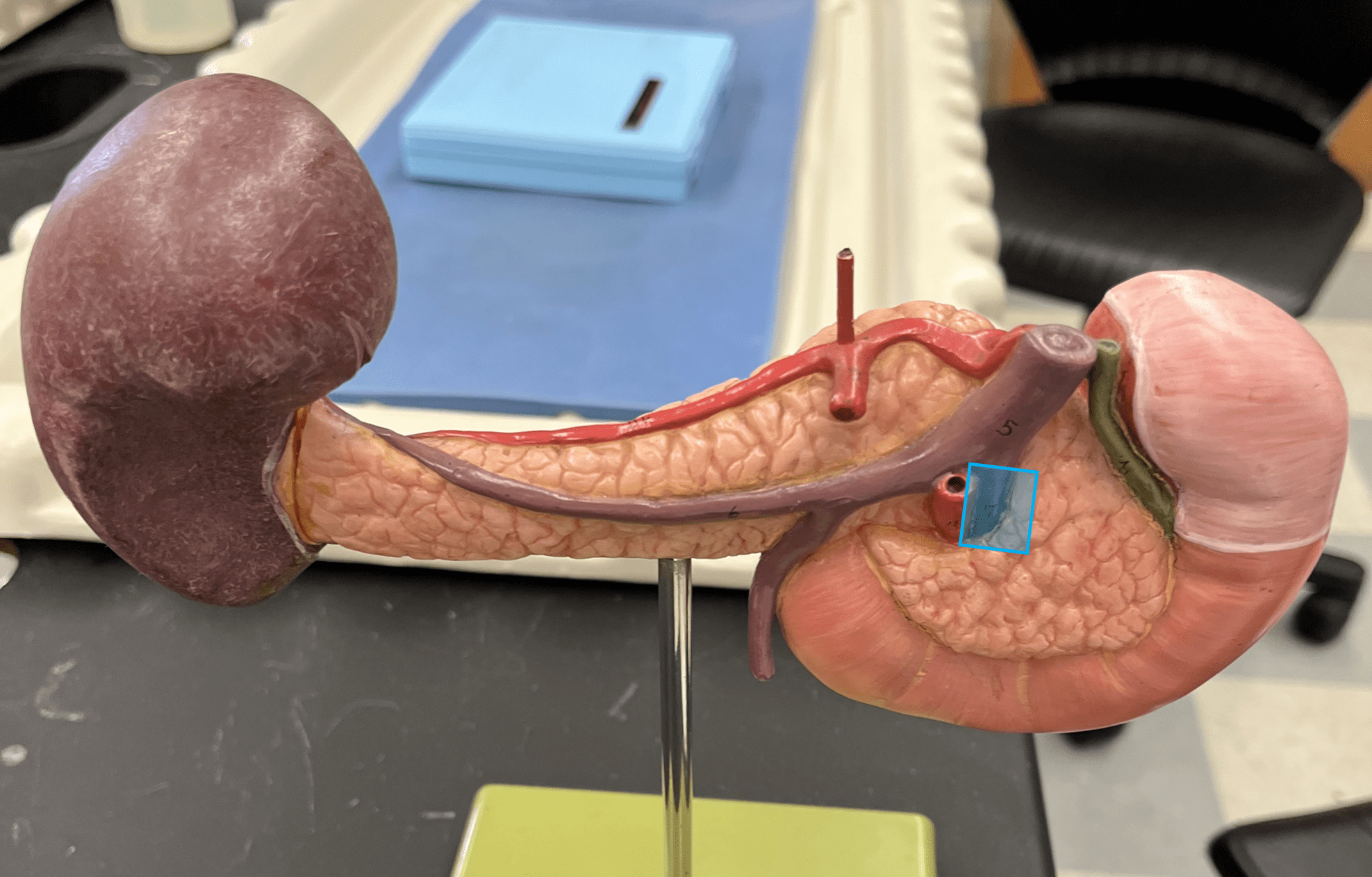
65
New cards
gastric vein
• A vein of the hepatic portal system (not shown).
• Drains the stomach.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
• Drains the stomach.
• Empties into the hepatic portal vein.
66
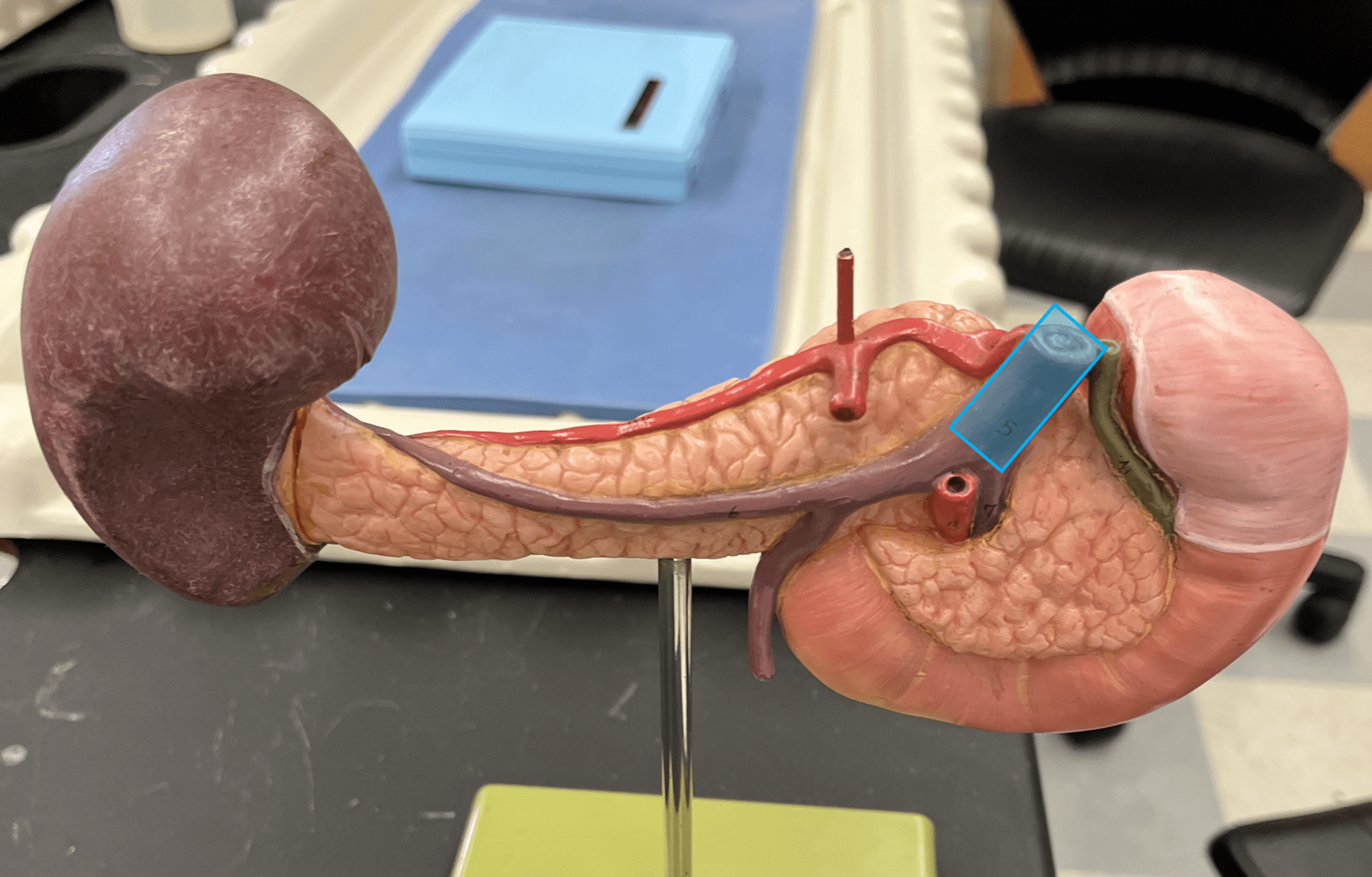
New cards
hepatic portal vein
• A vein of the hepatic portal system.
• Drains the veins of the hepatic portal system: the inferior and superior mesenteric, splenic, and gastric veins.
• Empties into the capillary beds of liver, which drain into the hepatic veins leading back to the inferior vena cava.
• Drains the veins of the hepatic portal system: the inferior and superior mesenteric, splenic, and gastric veins.
• Empties into the capillary beds of liver, which drain into the hepatic veins leading back to the inferior vena cava.
67
New cards
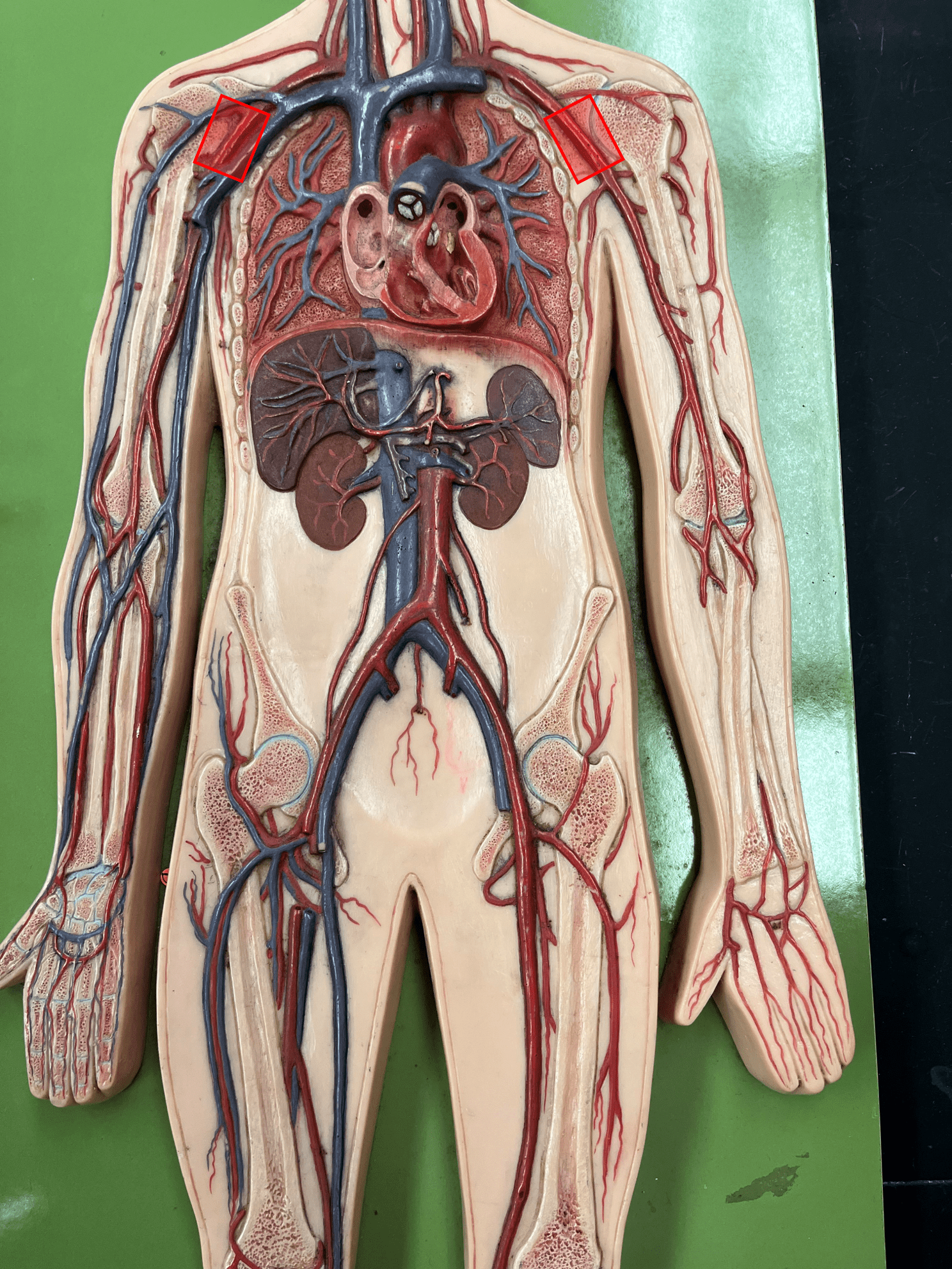
axillary artery
• An artery of the upper limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the subclavian artery.
• Supplies the shoulder.
• Originates as the continuation of the subclavian artery.
• Supplies the shoulder.
68
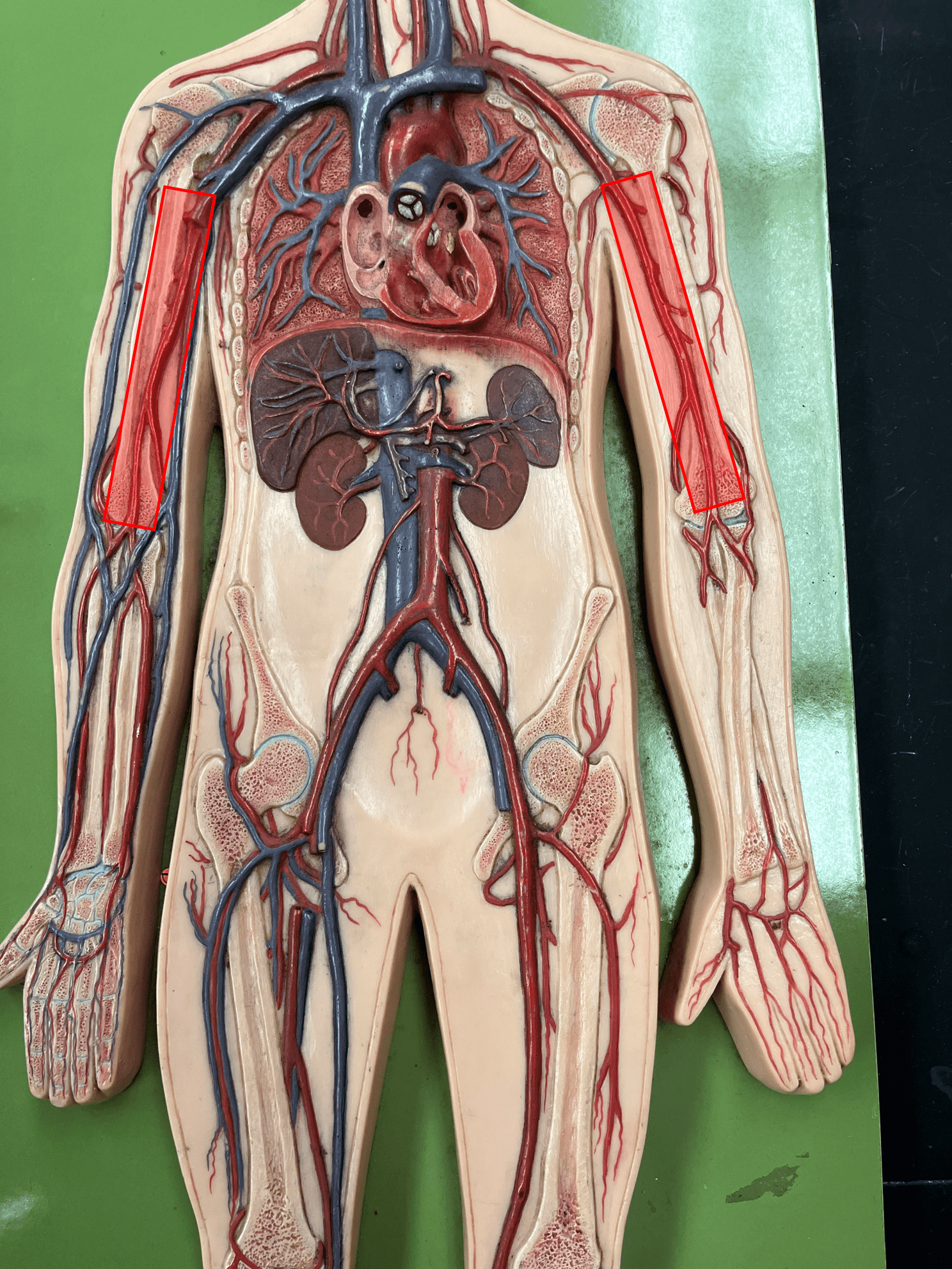
New cards
brachial artery
• An artery of the upper limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the axillary artery.
• Supplies the anterior muscles of the upper arm.
• Originates as the continuation of the axillary artery.
• Supplies the anterior muscles of the upper arm.
69
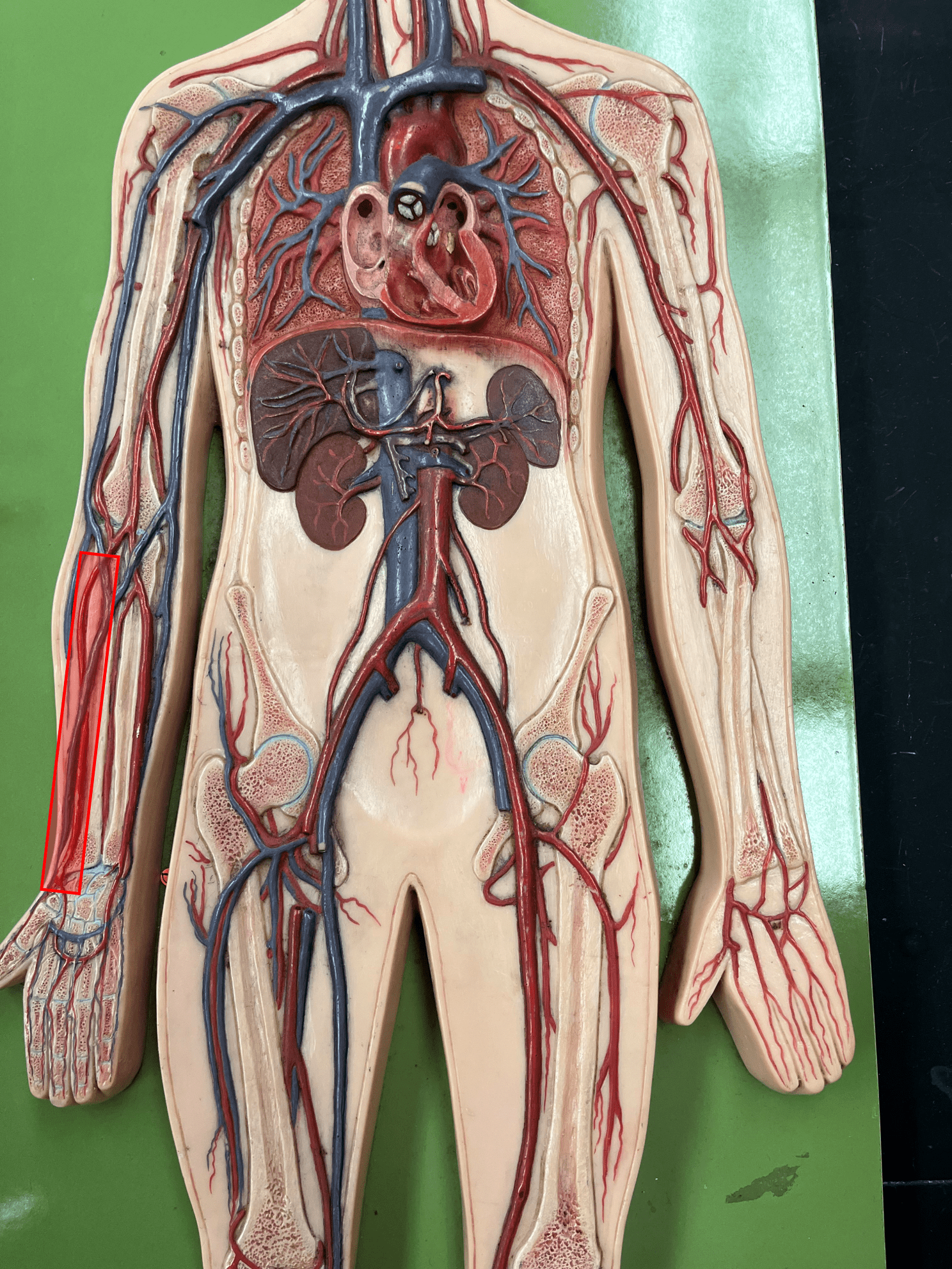
New cards
radial artery
• An artery of the upper limb.
• Originates from the brachial artery.
• Supplies the lateral forearm muscles.
• Originates from the brachial artery.
• Supplies the lateral forearm muscles.
70
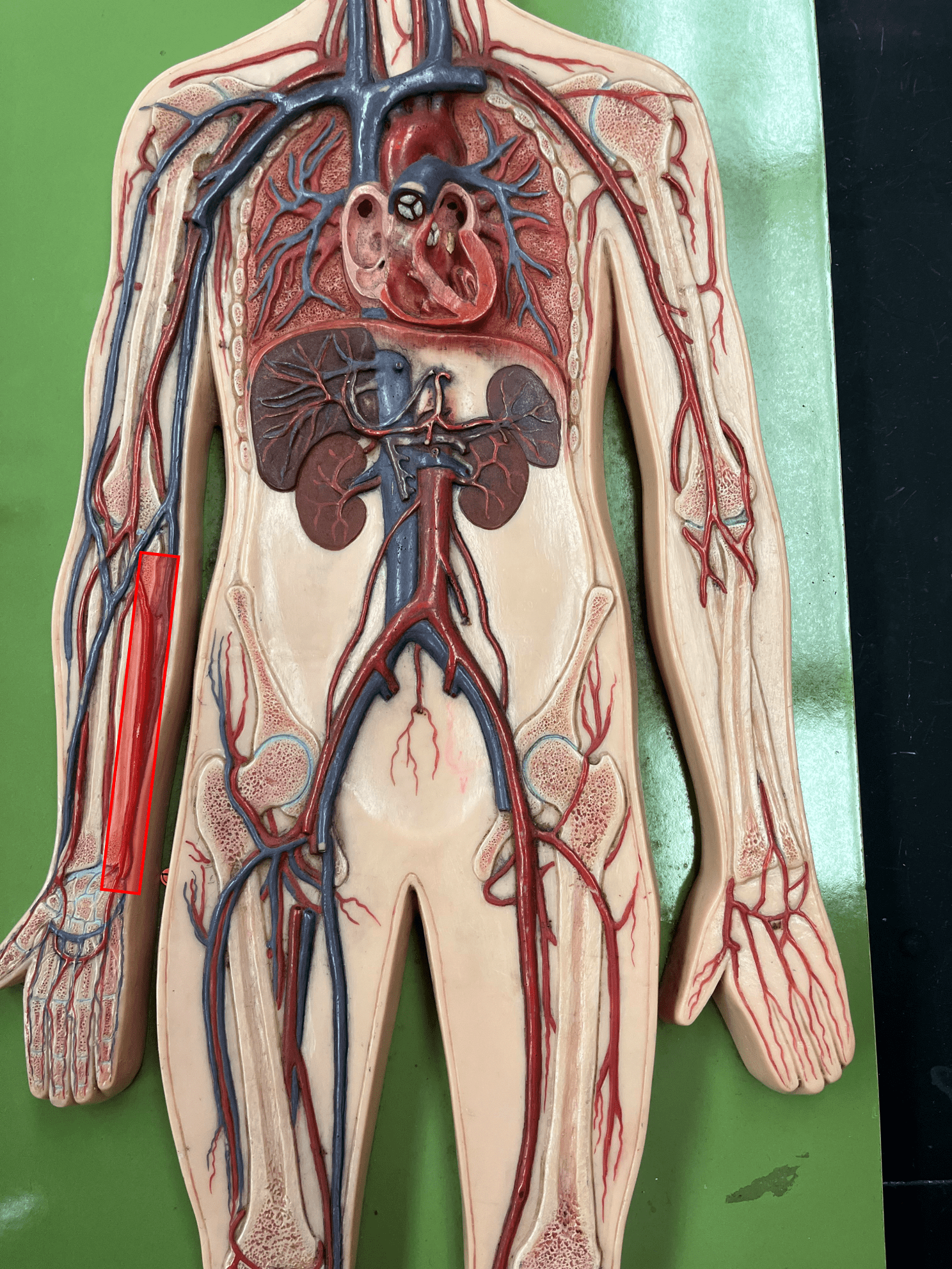
New cards
ulnar artery
• An artery of the upper limb.
• Originates from the brachial artery.
• Supplies the medial forearm muscles.
• Originates from the brachial artery.
• Supplies the medial forearm muscles.
71
New cards
deep palmar arch
• An artery of the upper limb.
• Originates from the convergence of the radial and ulnar arteries.
• Supplies the palm and fingers.
• Originates from the convergence of the radial and ulnar arteries.
• Supplies the palm and fingers.
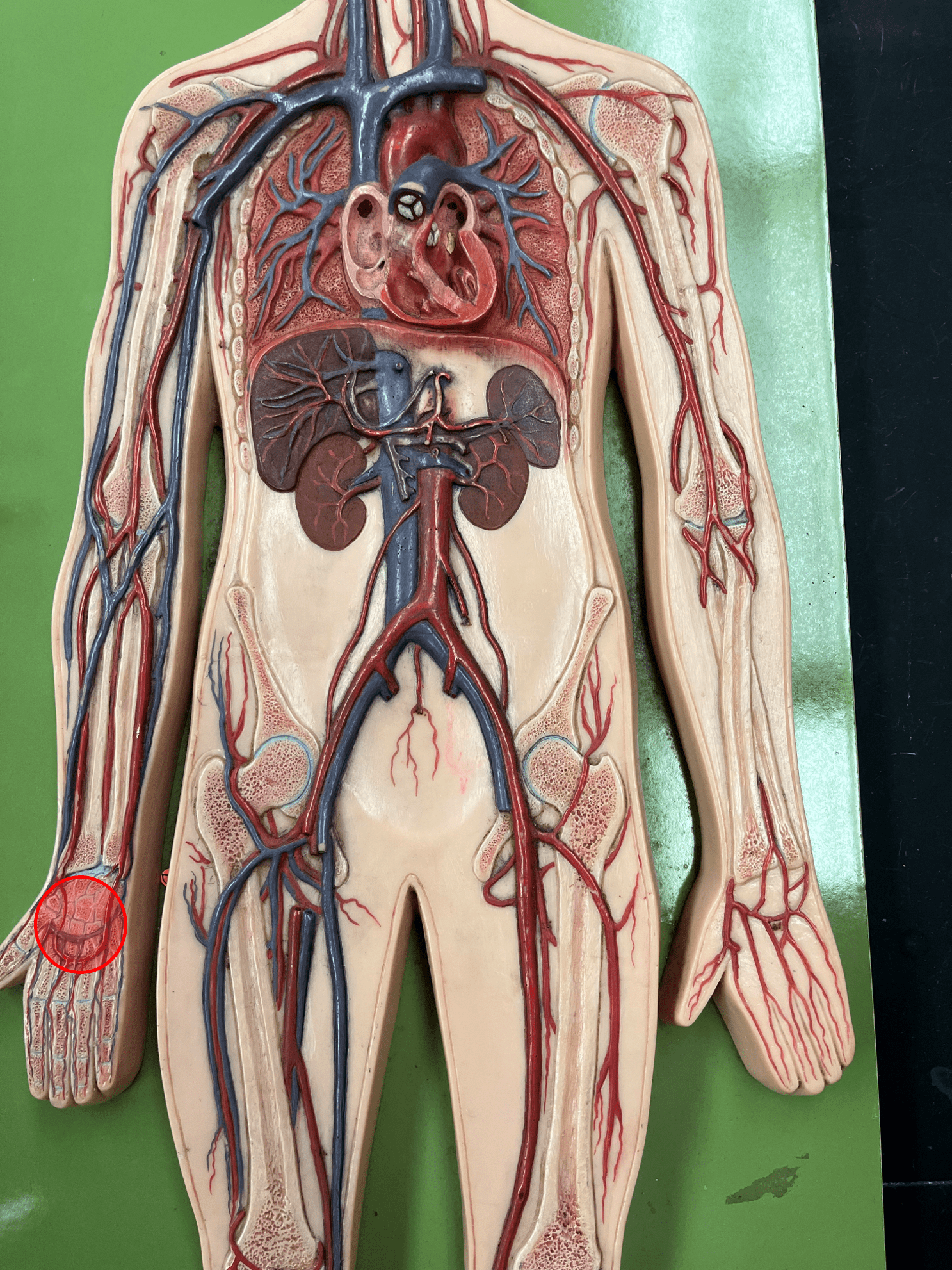
72
New cards
radial vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the lateral hand and forearm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
• Drains the lateral hand and forearm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
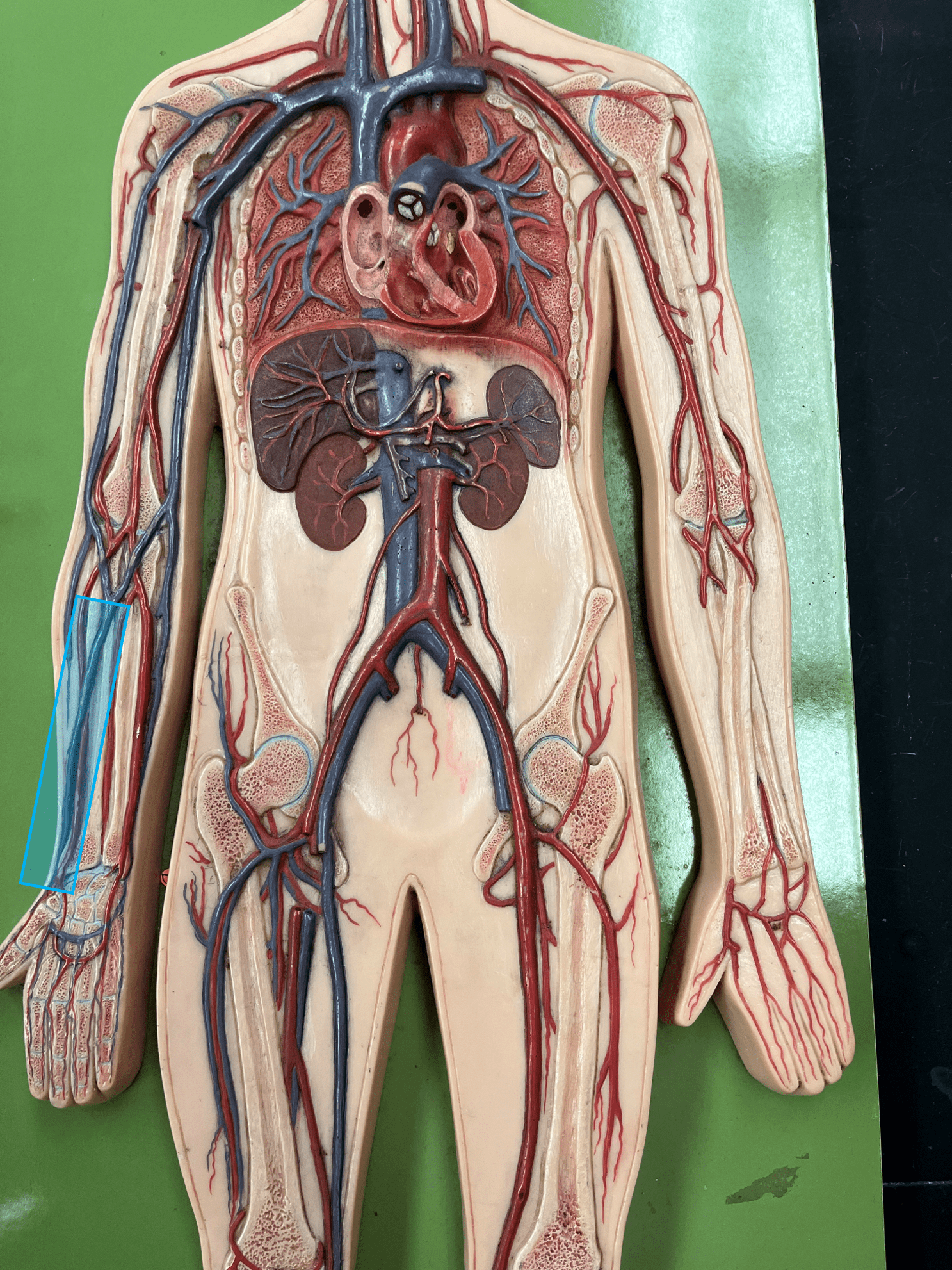
73
New cards
ulnar vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the medial hand and forearm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
• Drains the medial hand and forearm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
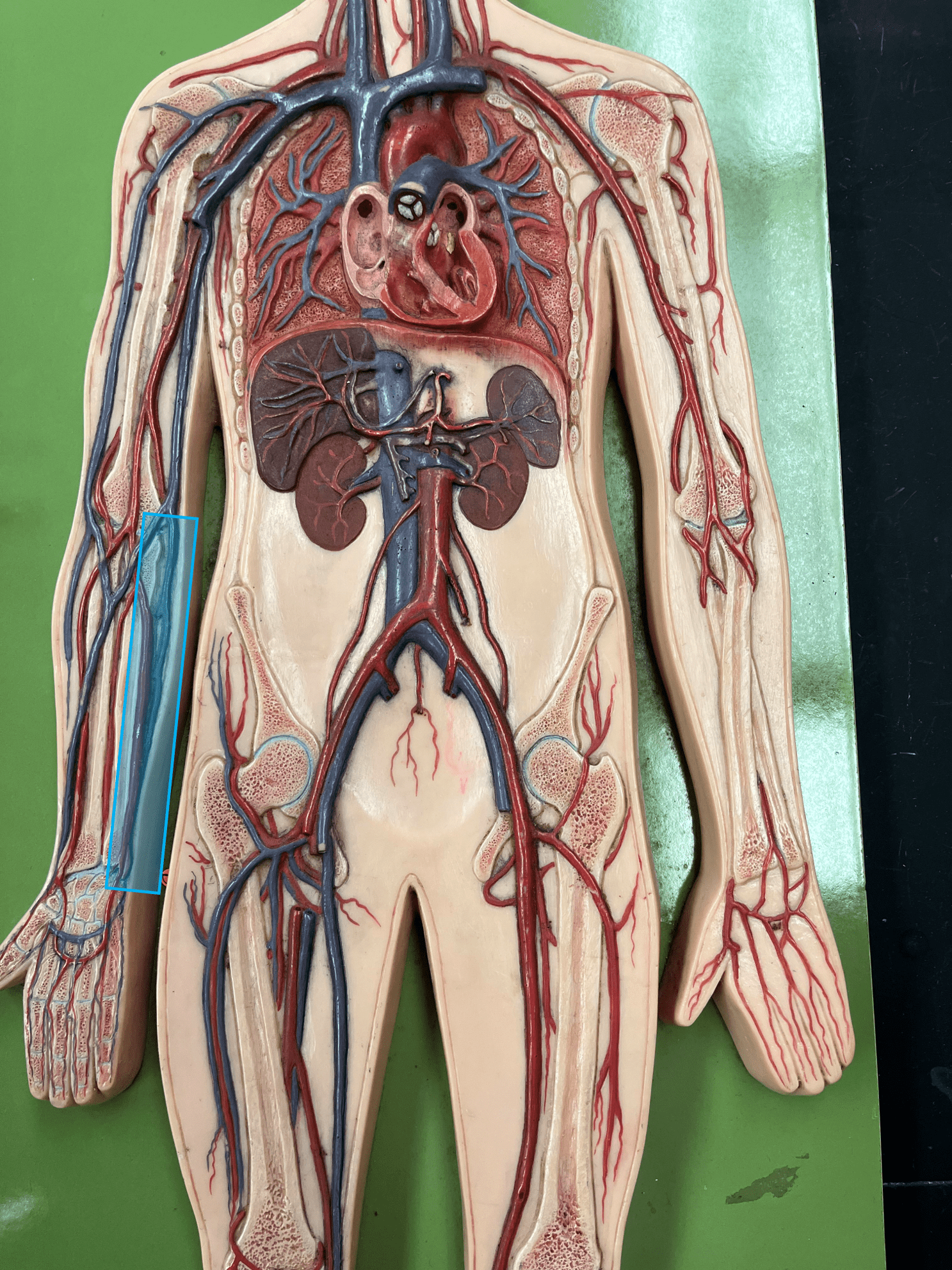
74
New cards
brachial vein
• A vein of the upper limb (not shown).
• Drains the radial and ulnar veins.
• Empties into the axillary vein.
• Drains the radial and ulnar veins.
• Empties into the axillary vein.
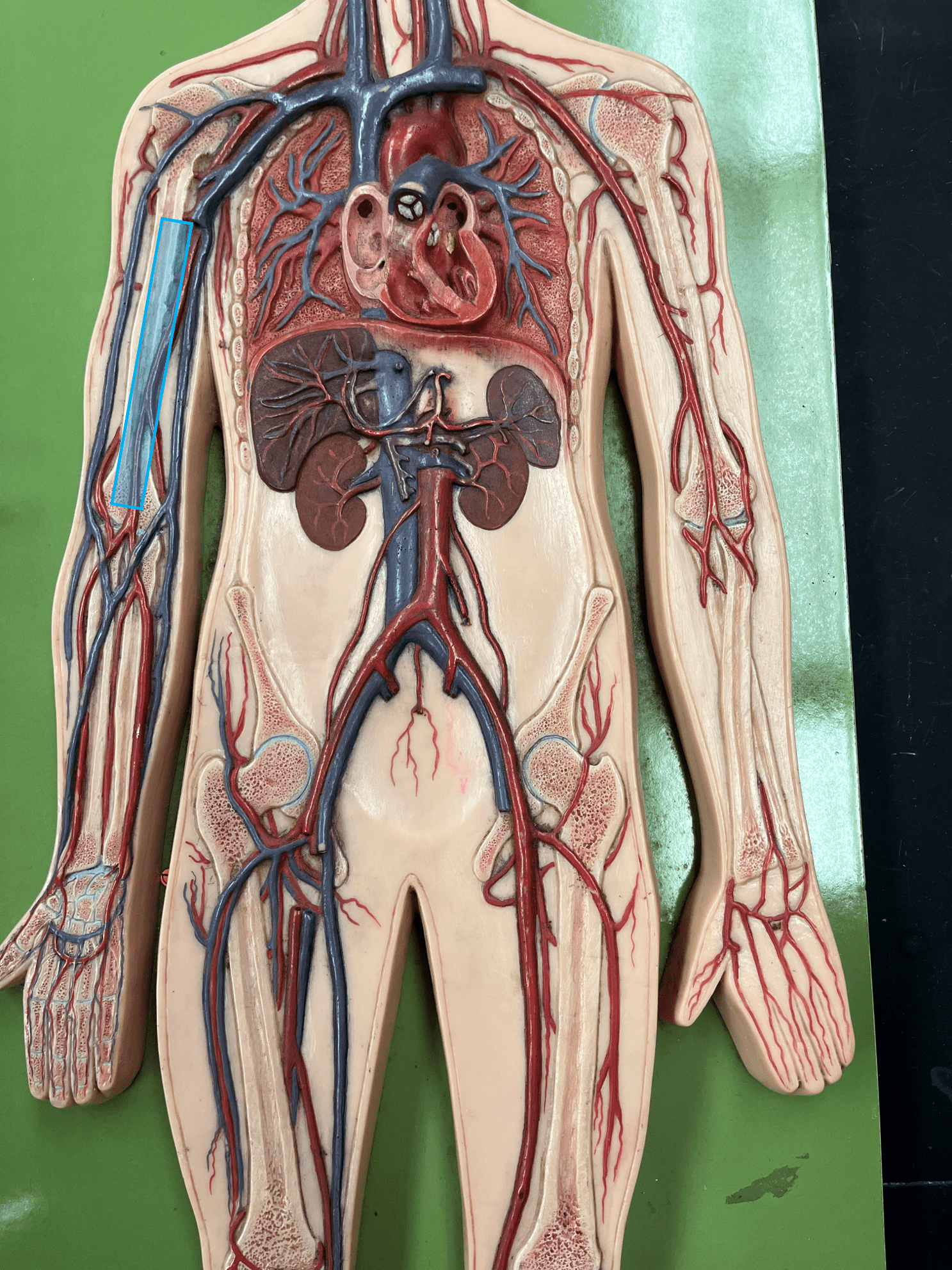
75
New cards
median cubital vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the forearm.
• Connects the basilic and cephalic veins at the antecubital (anterior part of elbow).
• Drains the forearm.
• Connects the basilic and cephalic veins at the antecubital (anterior part of elbow).
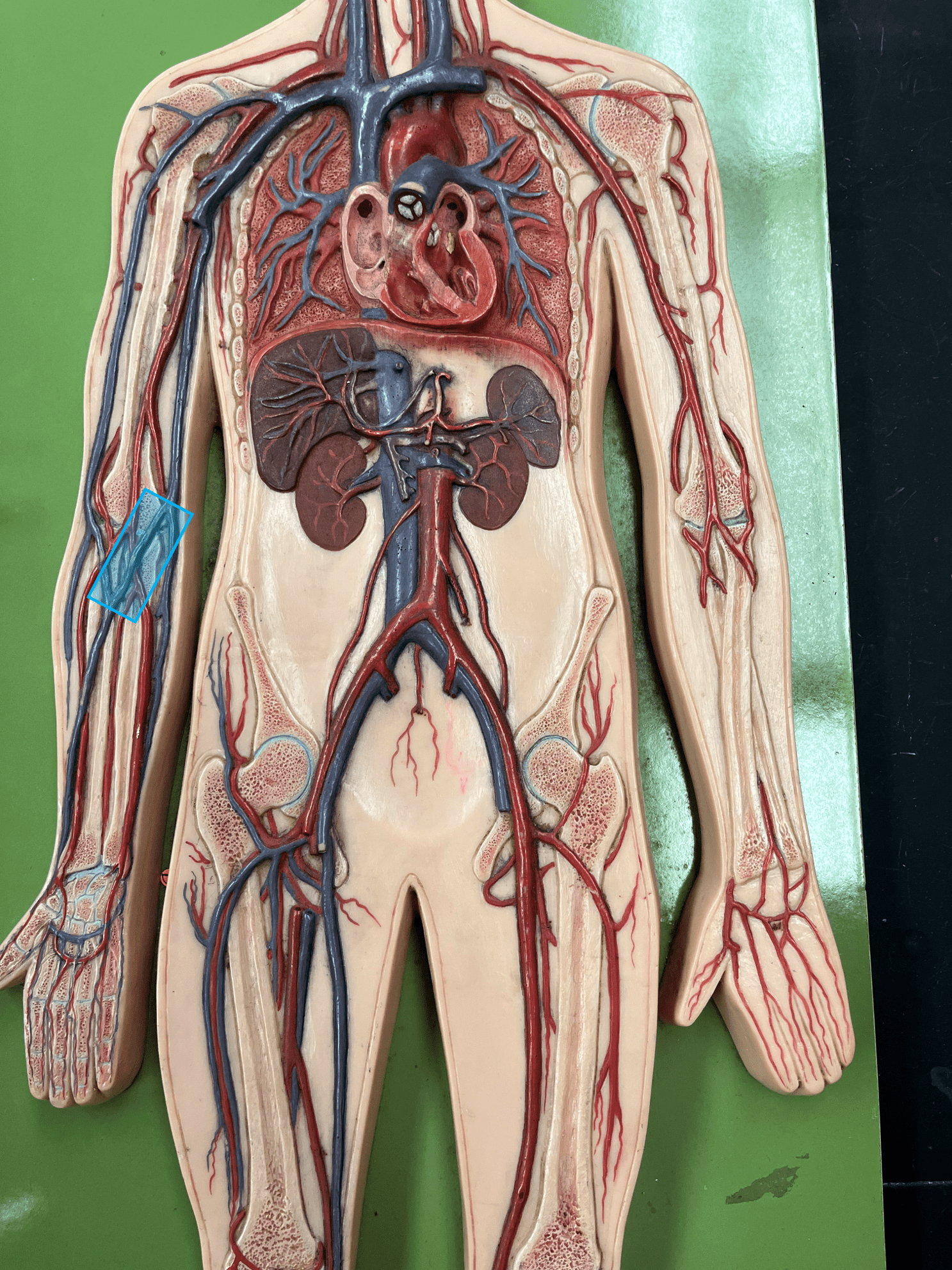
76
New cards
basilic vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the medial arm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
• Drains the medial arm.
• Empties into the brachial vein.
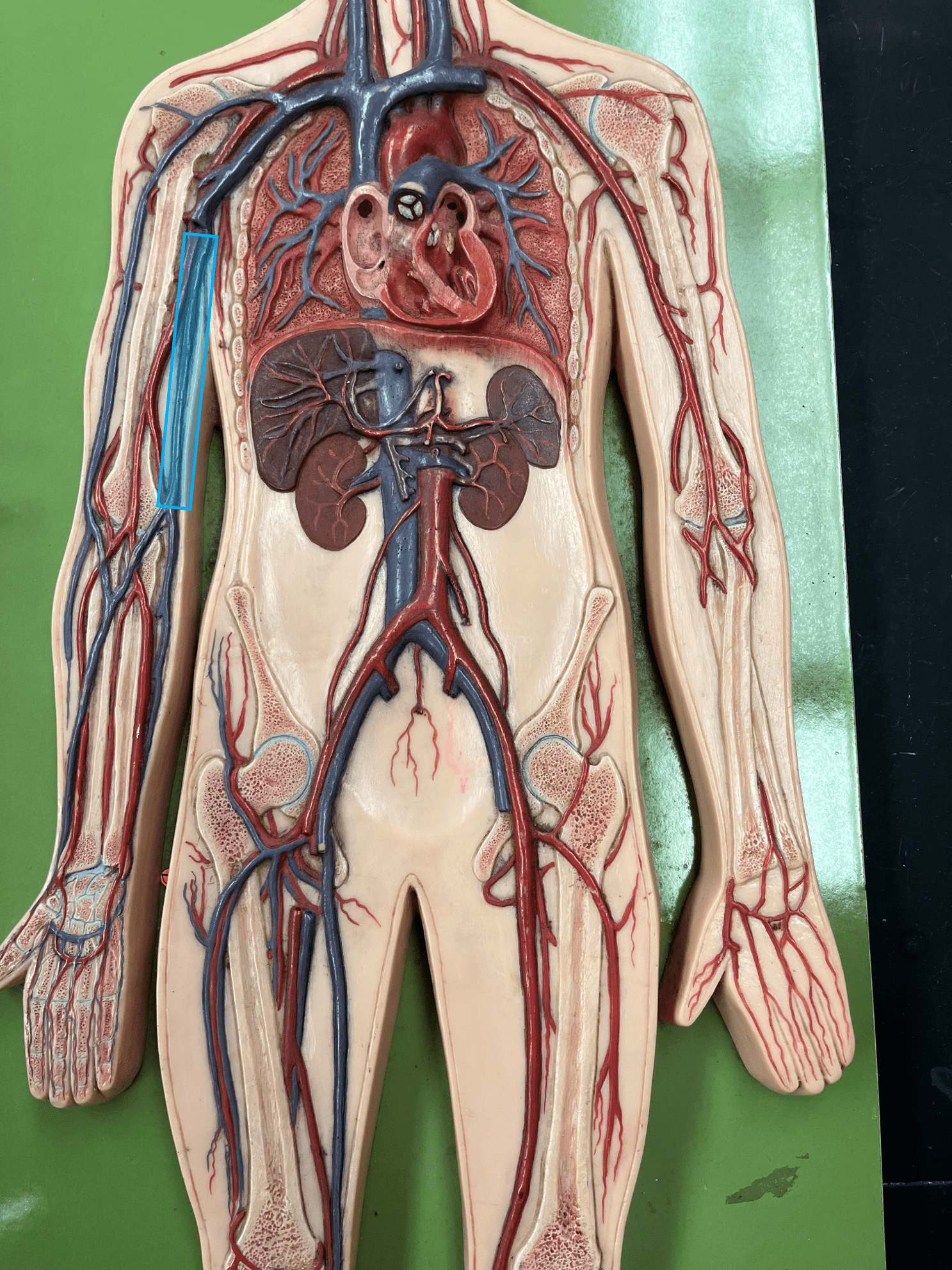
77
New cards
cephalic vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the lateral arm.
• Empties into the axillary vein.
• Drains the lateral arm.
• Empties into the axillary vein.
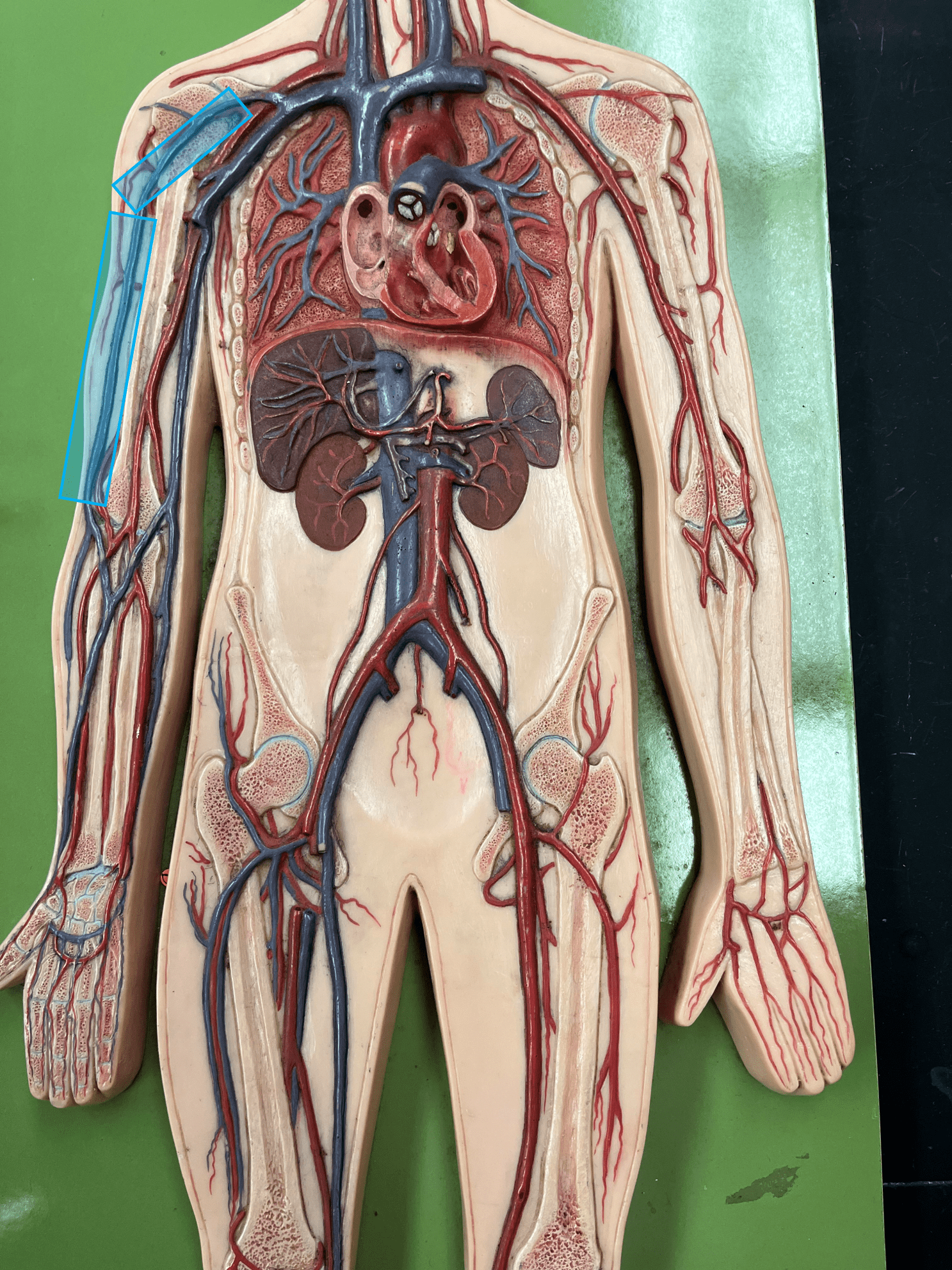
78
New cards
axillary vein
• A vein of the upper limb.
• Drains the brachial and cephalic veins.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
• Drains the brachial and cephalic veins.
• Empties into the subclavian vein.
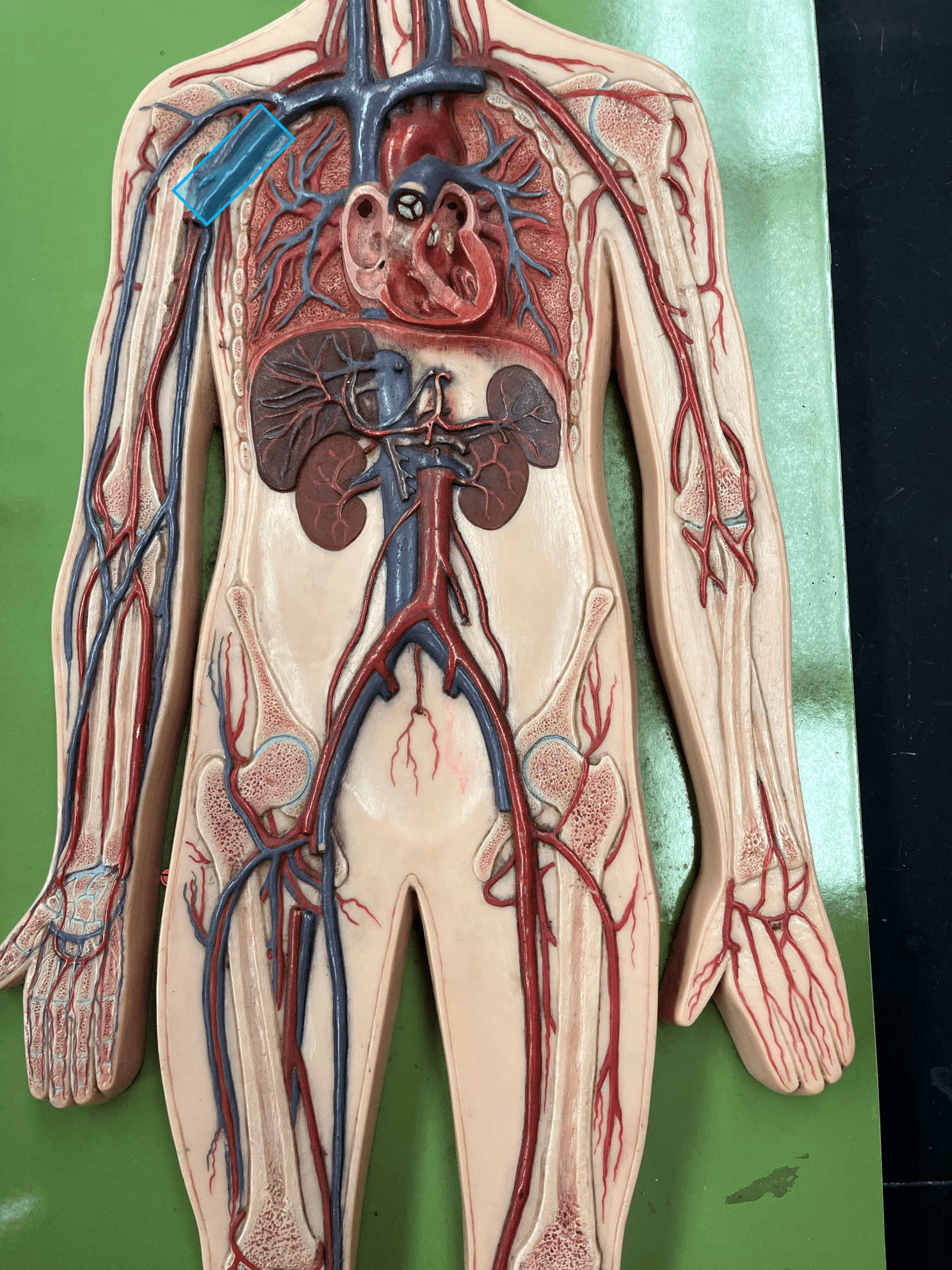
79
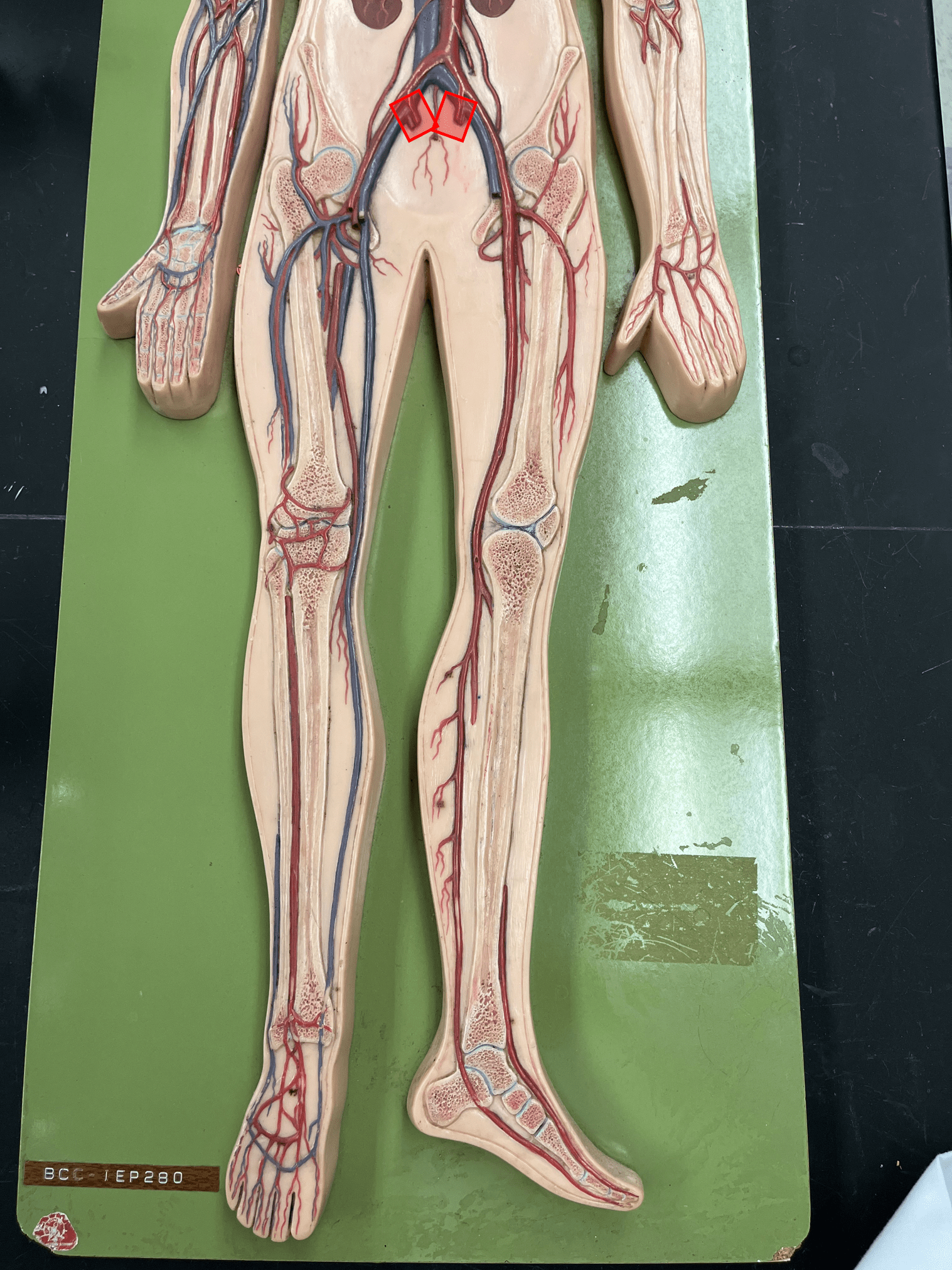
New cards
internal iliac artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates from the common iliac artery.
• Supplies the pelvic wall and viscera.
• Originates from the common iliac artery.
• Supplies the pelvic wall and viscera.
80
New cards
external iliac artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates from the common iliac artery.
• Supplies the lower limb through its branches.
• Originates from the common iliac artery.
• Supplies the lower limb through its branches.
81
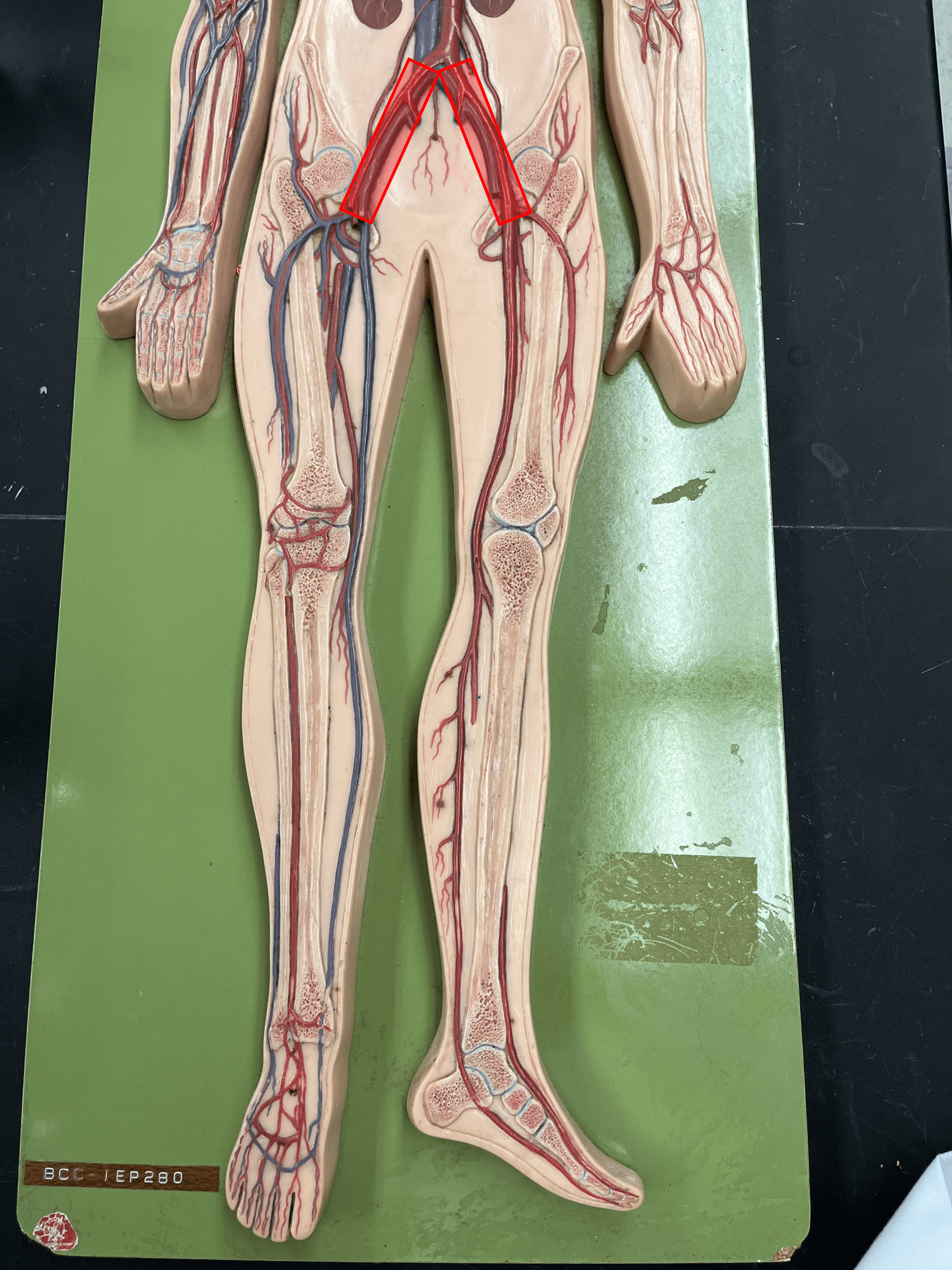
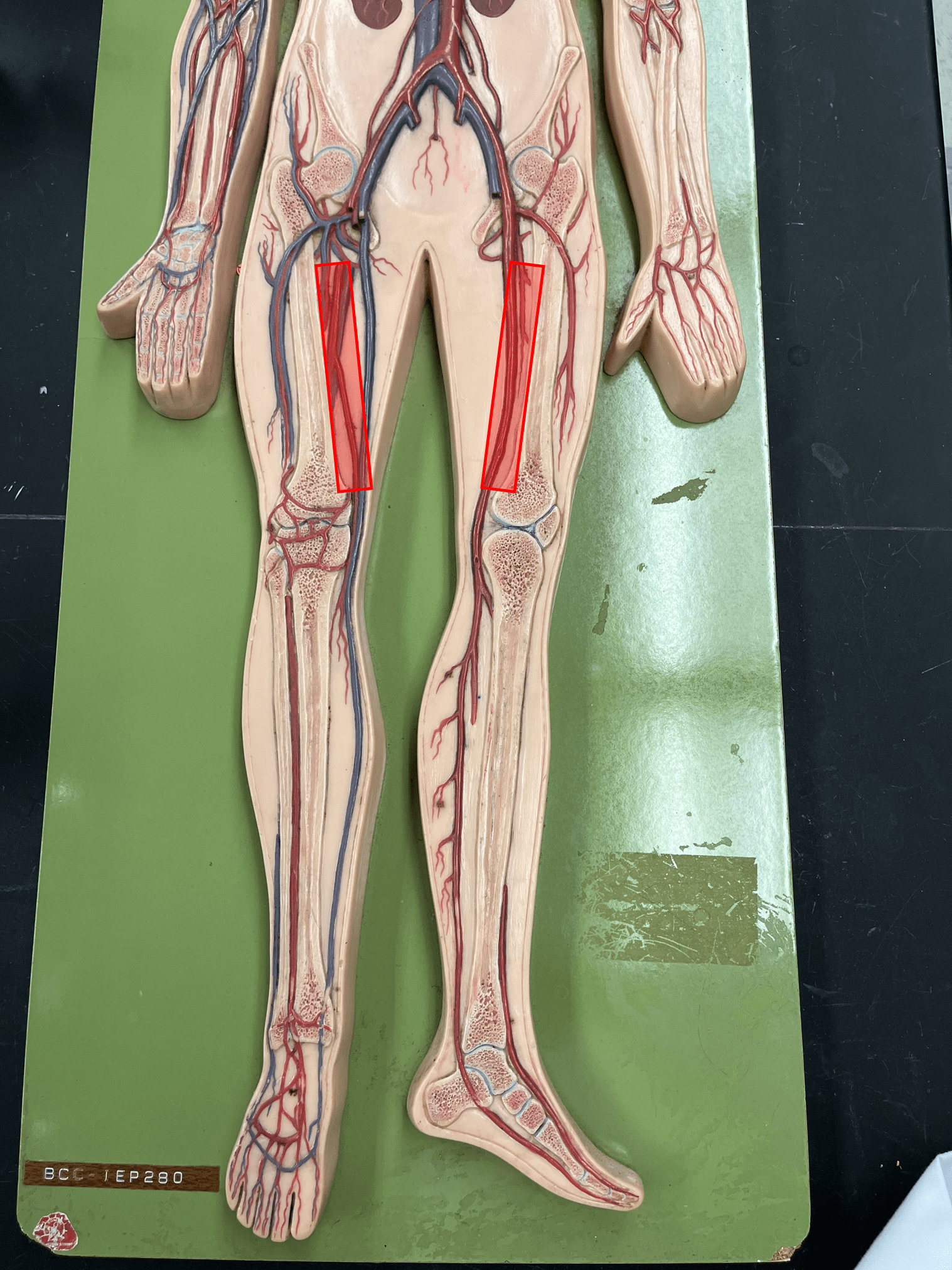
New cards
femoral artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the external iliac artery.
• Supplies the thigh muscles.
• Originates as the continuation of the external iliac artery.
• Supplies the thigh muscles.
82
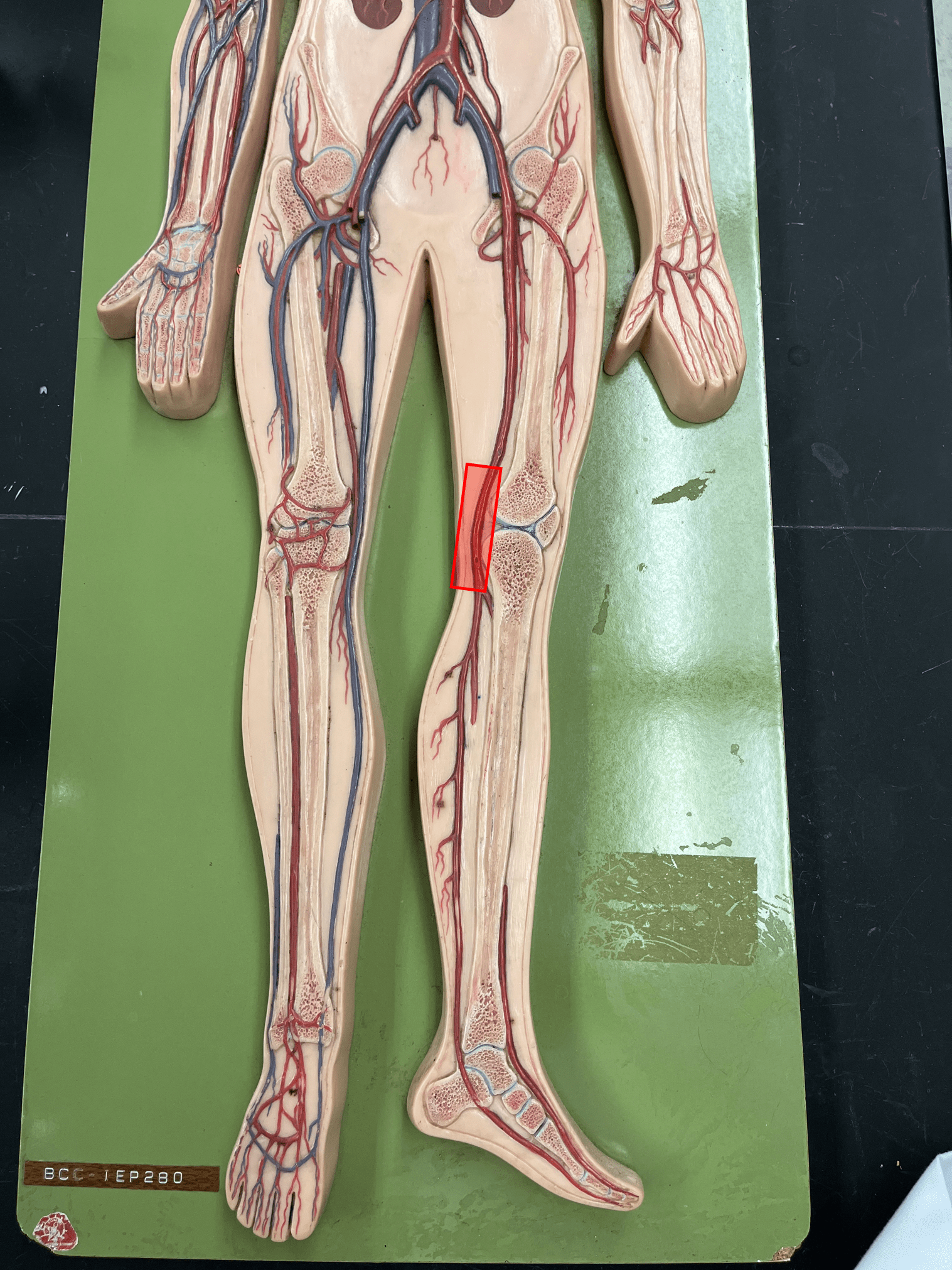
New cards
popliteal artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the femoral artery.
• Supplies the knee.
• Originates as the continuation of the femoral artery.
• Supplies the knee.
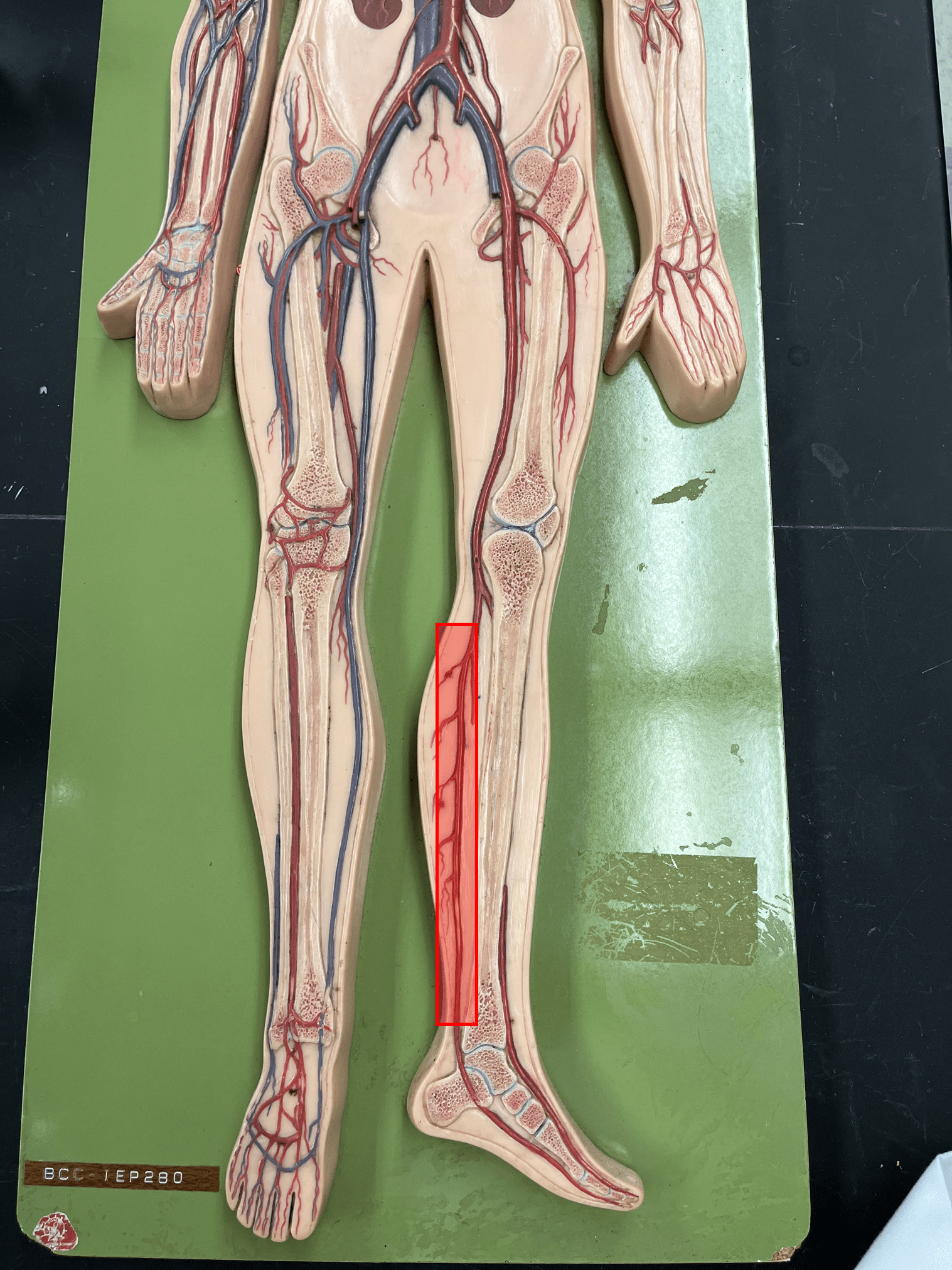
83
New cards
anterior tibial artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates from the popliteal artery.
• Supplies the anterior lower leg muscles.
• Originates from the popliteal artery.
• Supplies the anterior lower leg muscles.
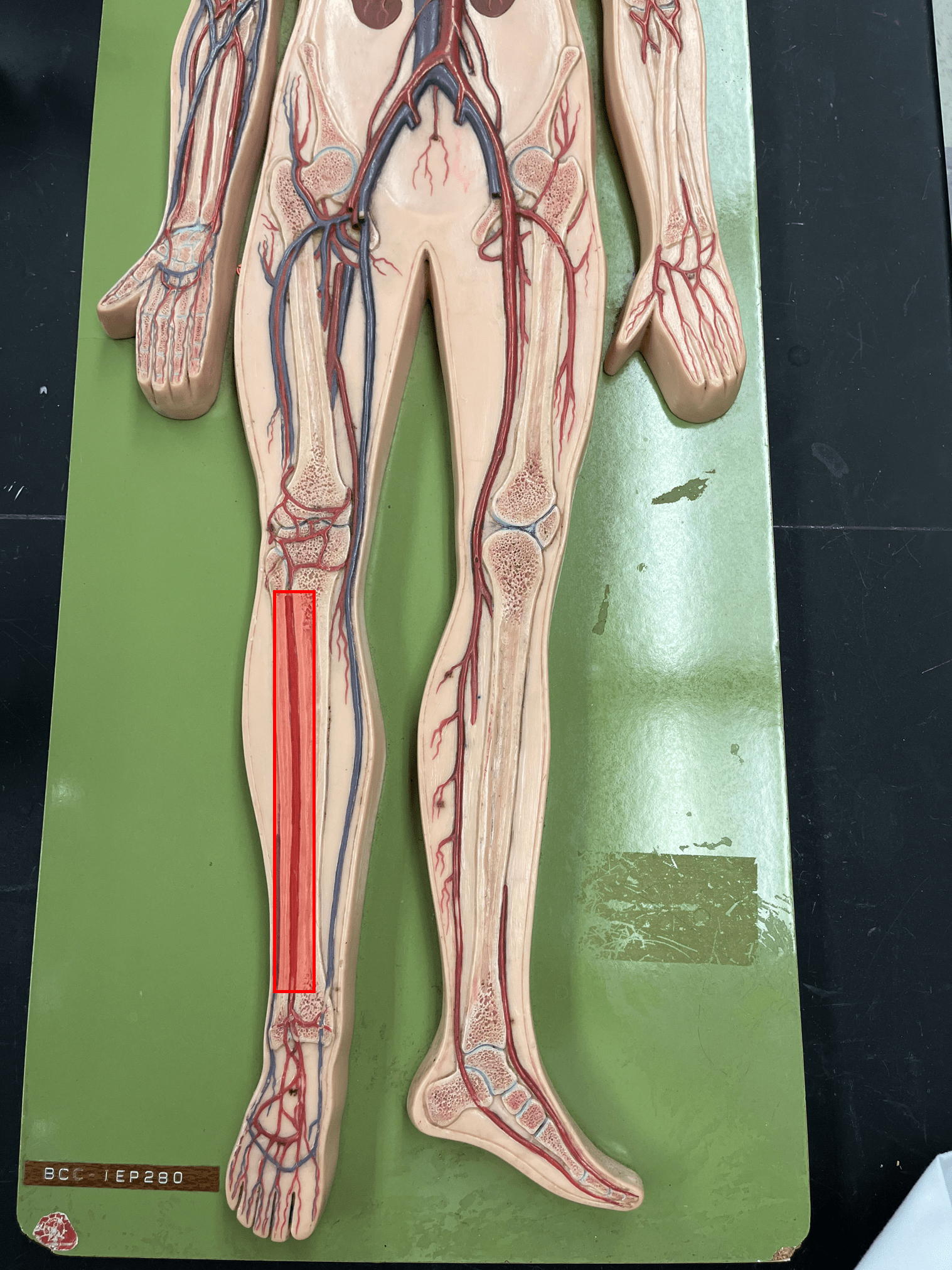
84
New cards
dorsal pedal artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the anterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the ankle and dorsal foot.
• Originates as the continuation of the anterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the ankle and dorsal foot.
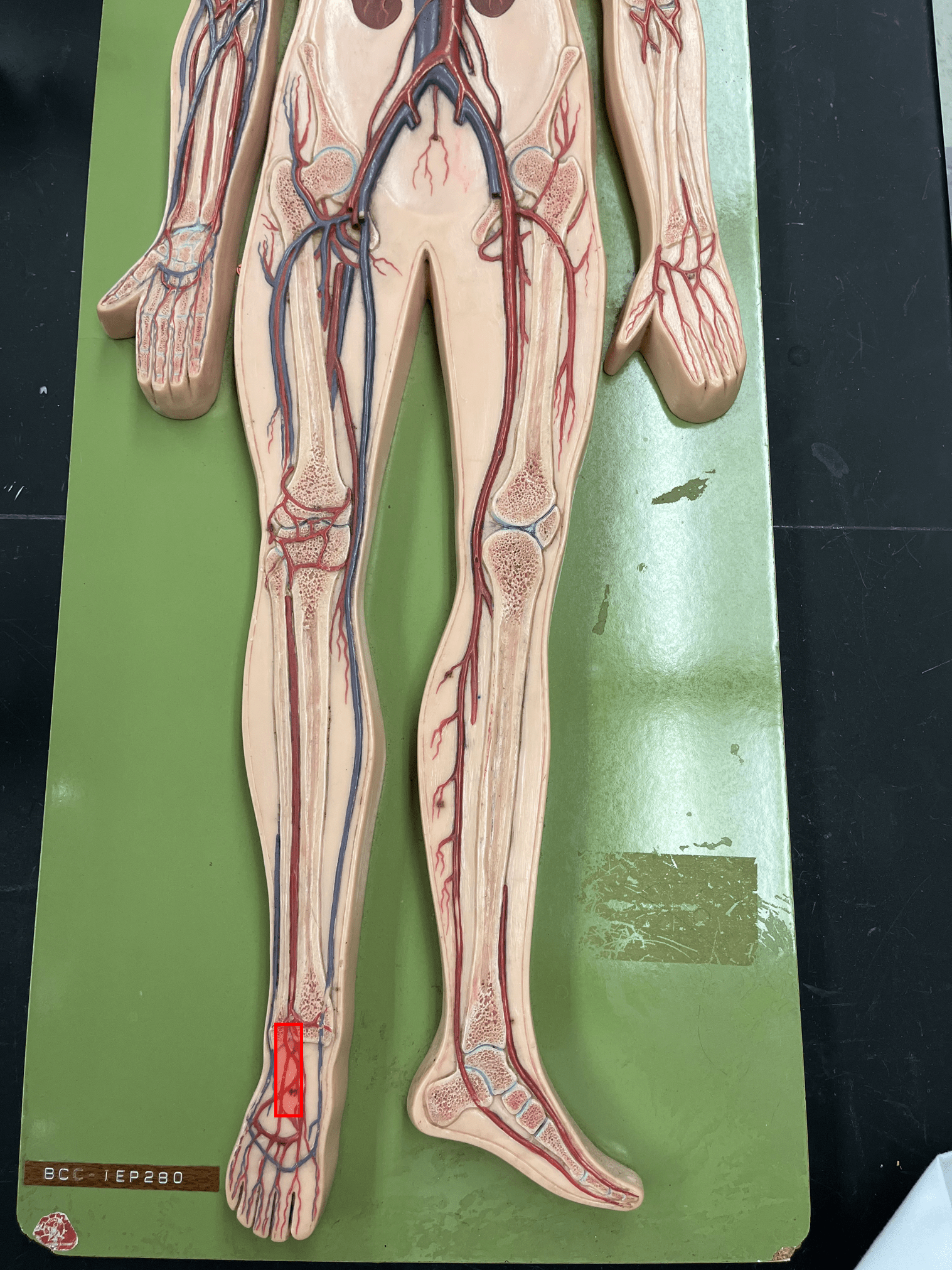
85
New cards
posterior tibial artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates as the continuation of the popliteal artery.
• Supplies the posterior lower leg muscles.
• Originates as the continuation of the popliteal artery.
• Supplies the posterior lower leg muscles.
86
New cards
fibular artery
• An artery of the lower limb (not shown).
• Originates from the posterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the lateral lower leg muscles.
• Originates from the posterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the lateral lower leg muscles.
87
New cards
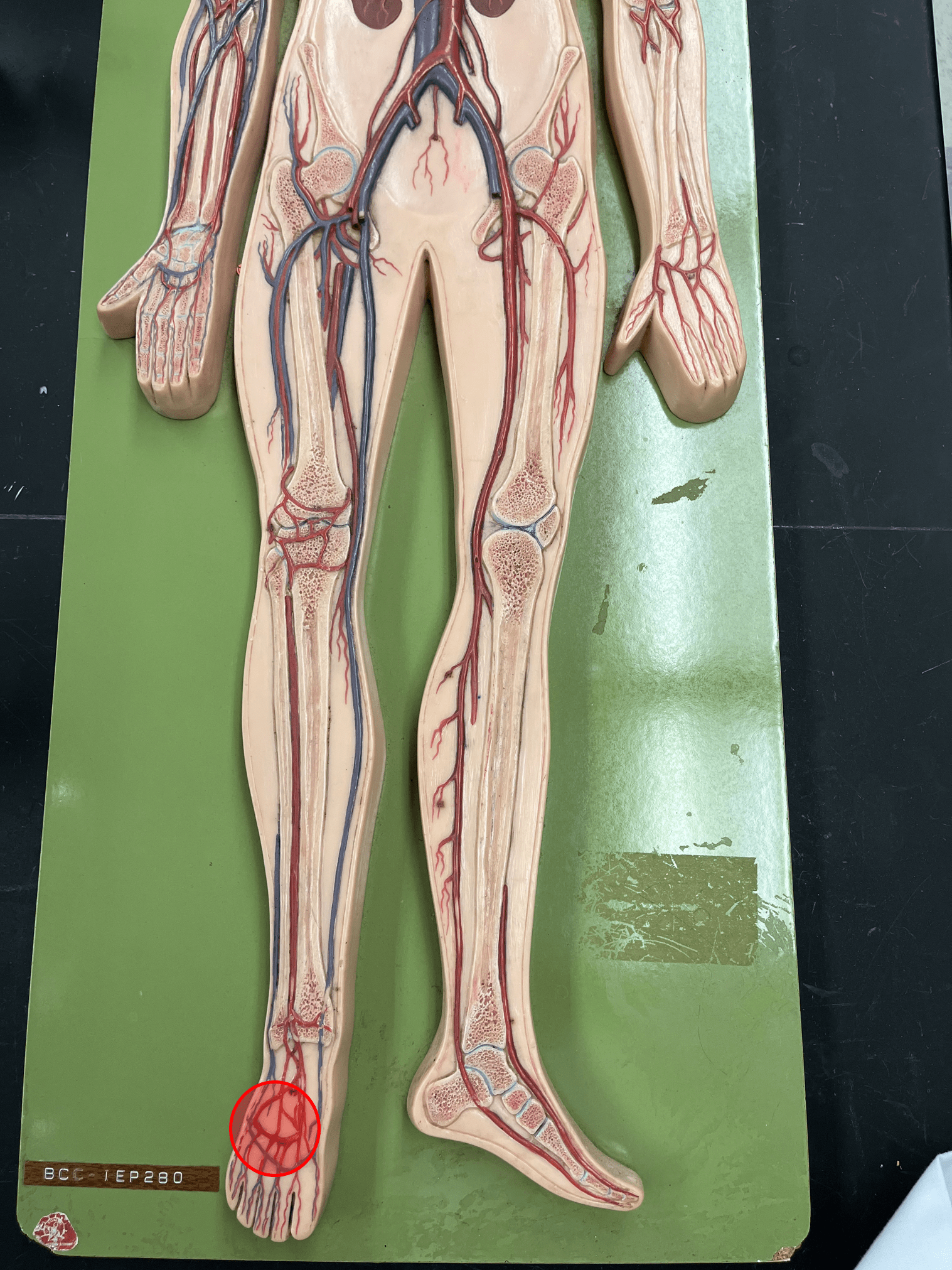
arcuate artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates from the dorsal pedal artery.
• Supplies the foot.
• Originates from the dorsal pedal artery.
• Supplies the foot.
88
New cards
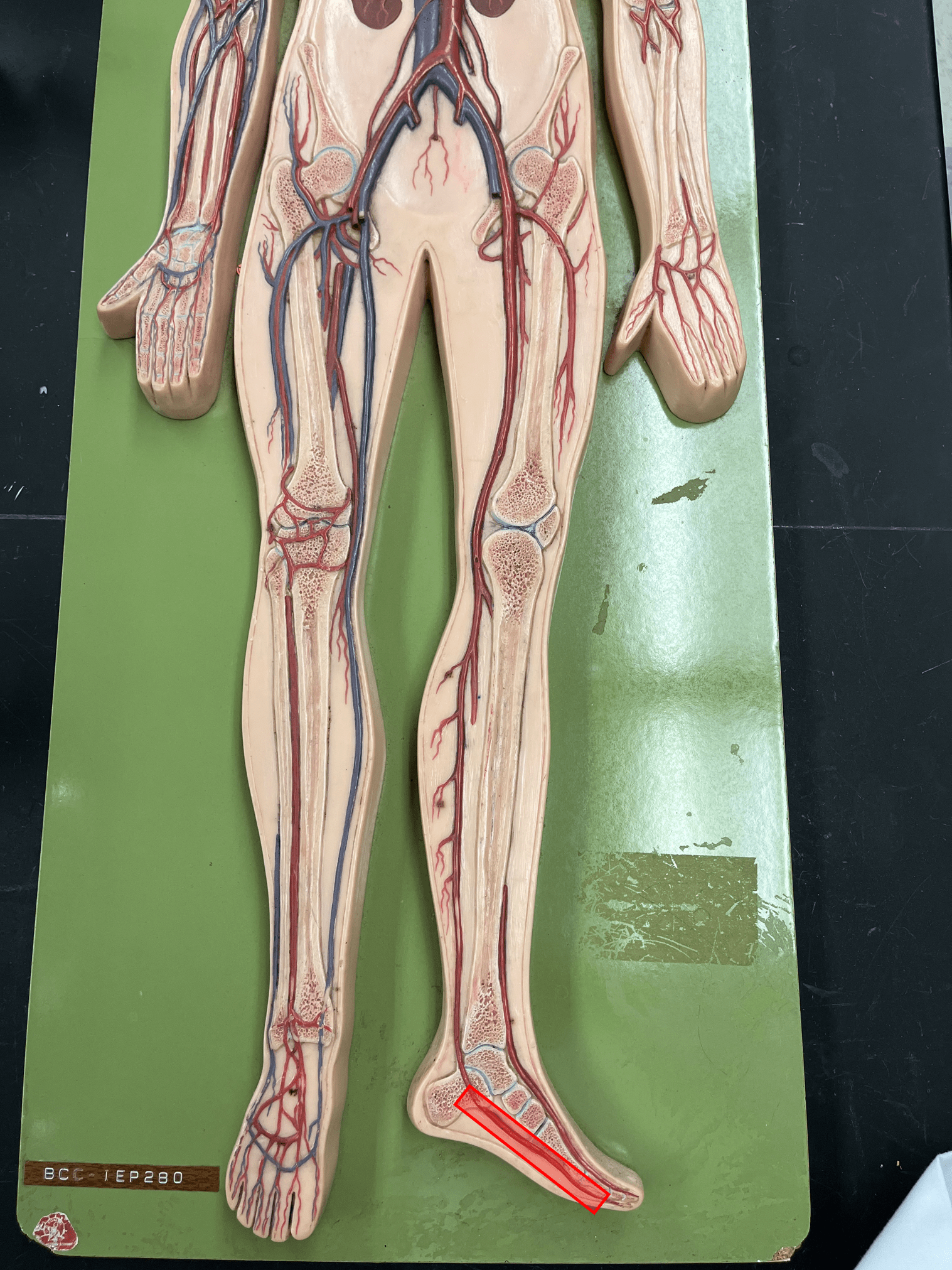
plantar arch artery
• An artery of the lower limb.
• Originates from the posterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the foot.
• Originates from the posterior tibial artery.
• Supplies the foot.
89
New cards
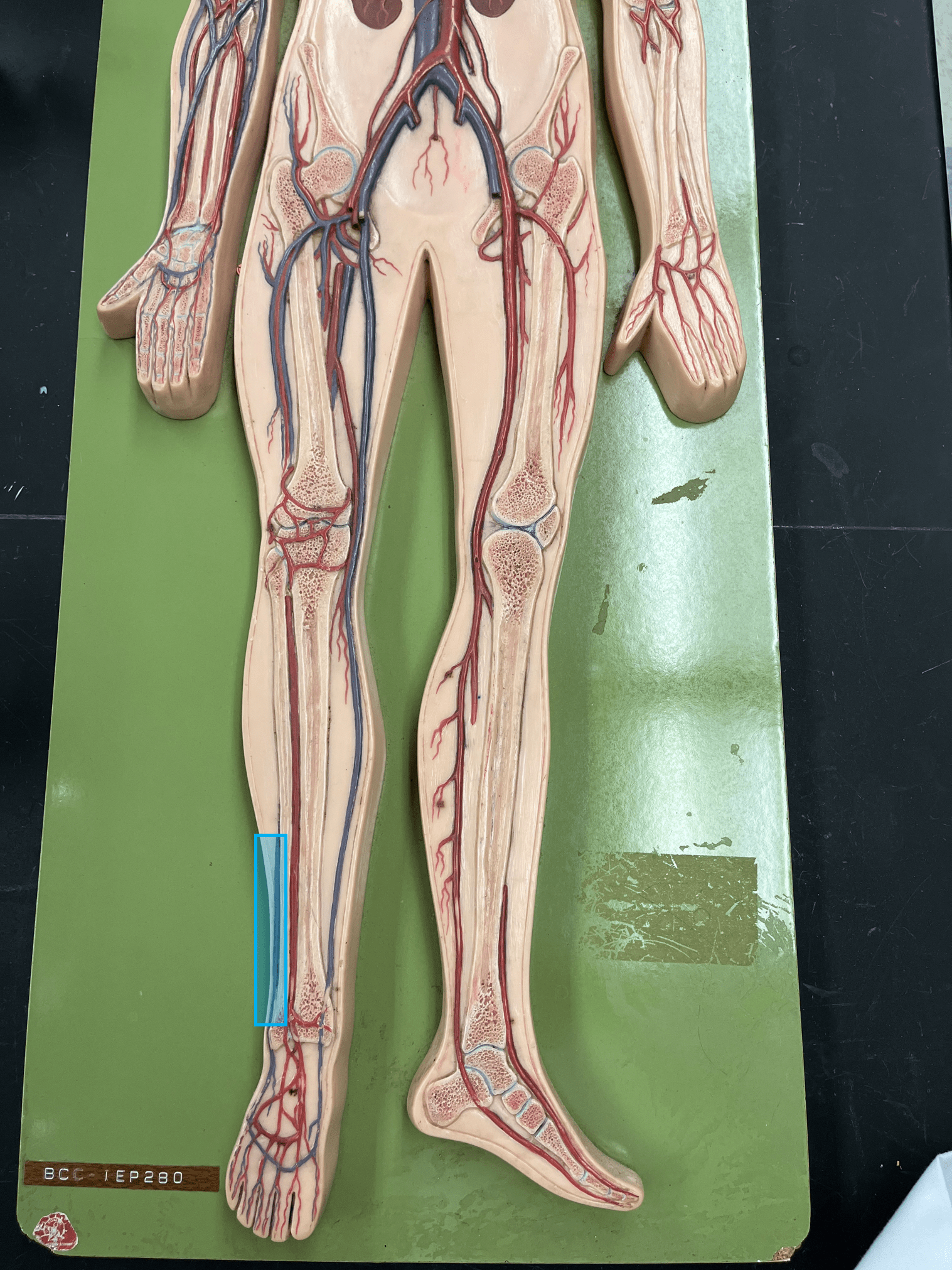
small saphenous vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains the lateral lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
• Drains the lateral lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
90
New cards
posterior tibial vein
• A vein of the lower limb (not shown).
• Drains the posterior lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
• Drains the posterior lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
91
New cards
fibular vein
• A vein of the lower limb (not shown).
• Drains the lateral lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
• Drains the lateral lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
92
New cards
anterior tibial vein
• A vein of the lower limb (not shown).
• Drains the anterior lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
• Drains the anterior lower leg.
• Empties into the popliteal vein.
93
New cards
popliteal vein
• A vein of the lower limb (not shown).
• Drains all of the lower leg veins.
• Empties into the femoral vein.
• Drains all of the lower leg veins.
• Empties into the femoral vein.
94
New cards
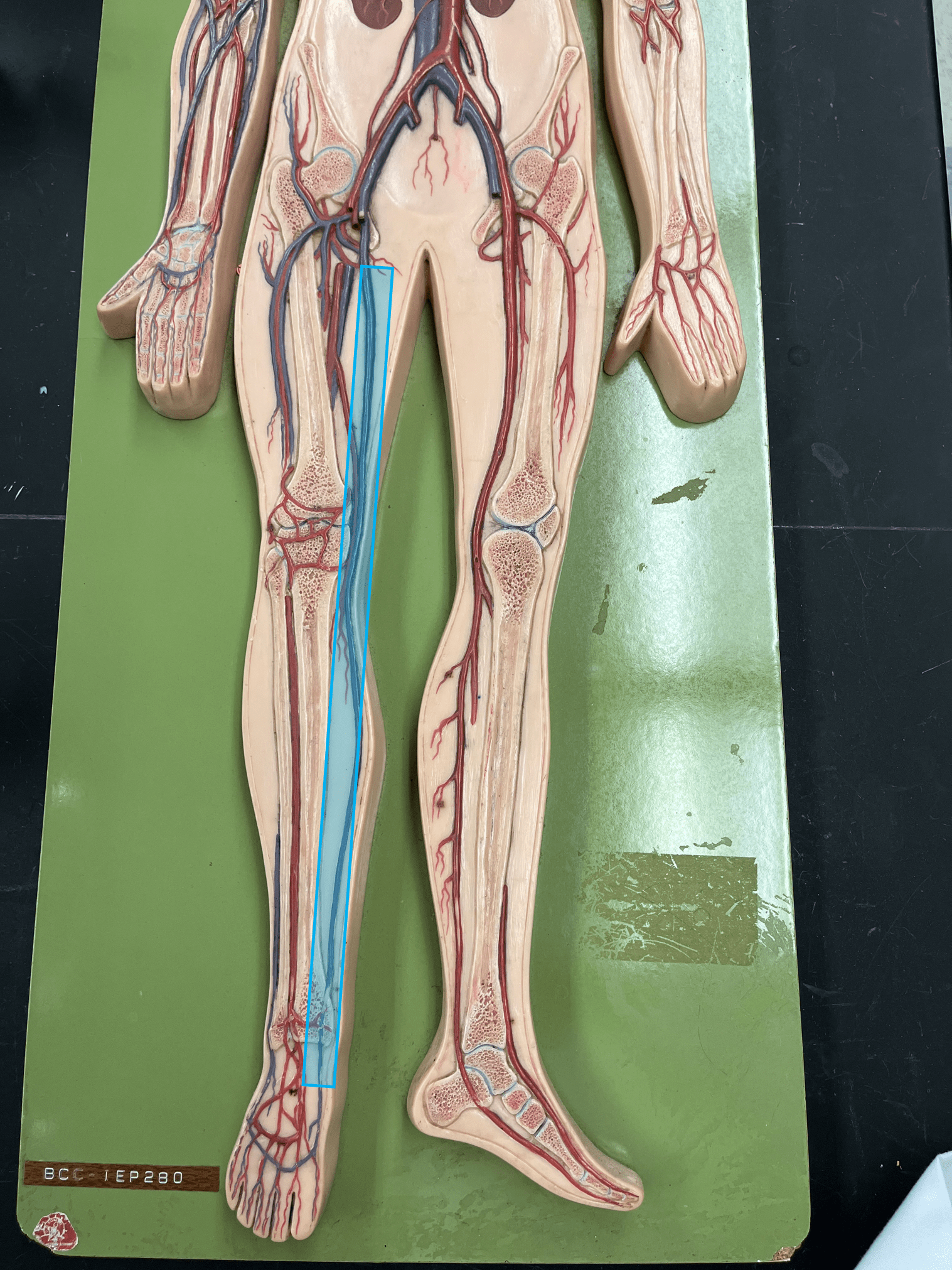
great saphenous vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains the medial lower leg and thigh.
• Empties into the femoral vein.
• Longest vein of the body.
• Drains the medial lower leg and thigh.
• Empties into the femoral vein.
• Longest vein of the body.
95
New cards
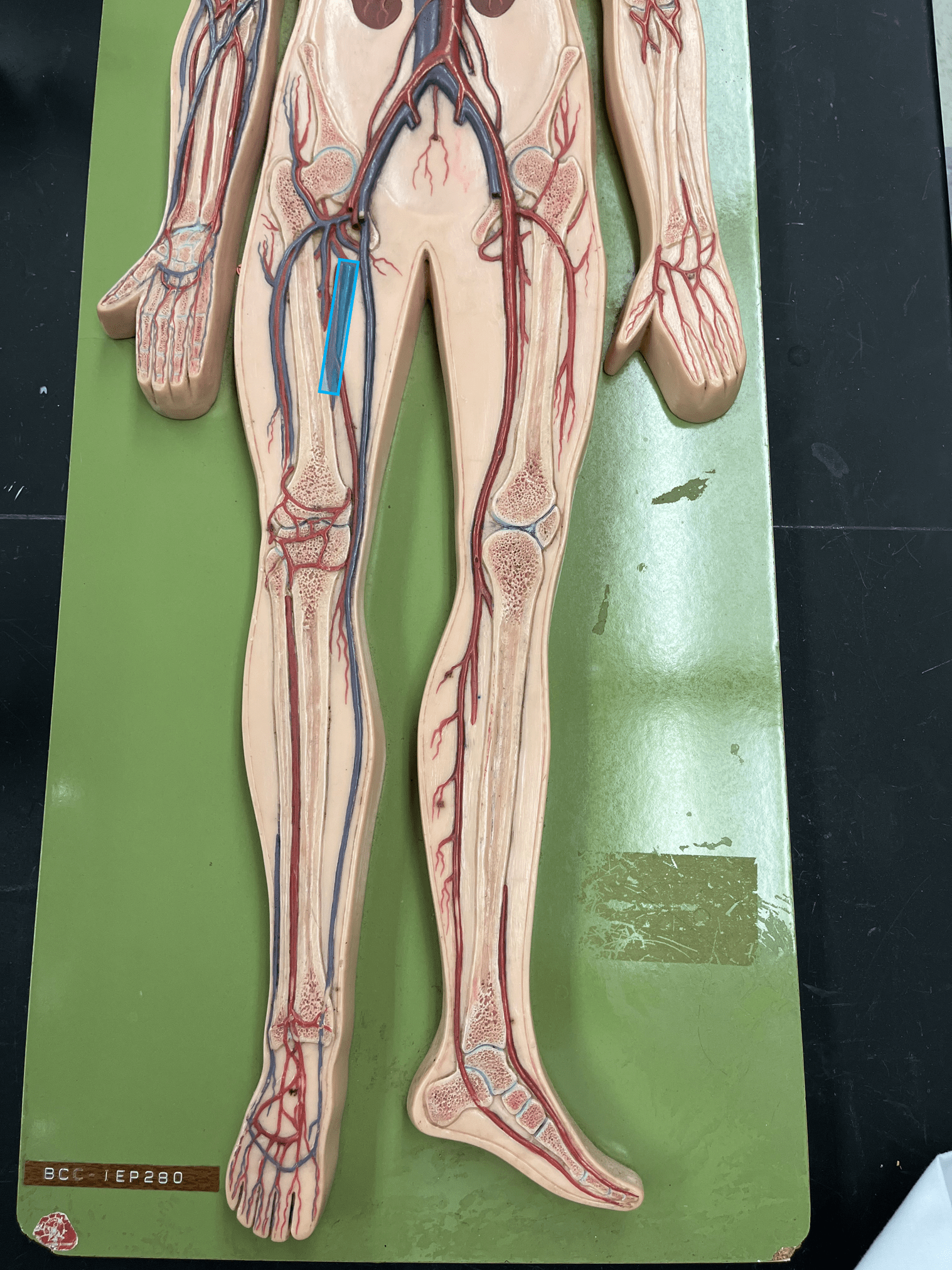
femoral vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains the deep thigh muscles.
• Empties into the external ilaic vein.
• Drains the deep thigh muscles.
• Empties into the external ilaic vein.
96
New cards
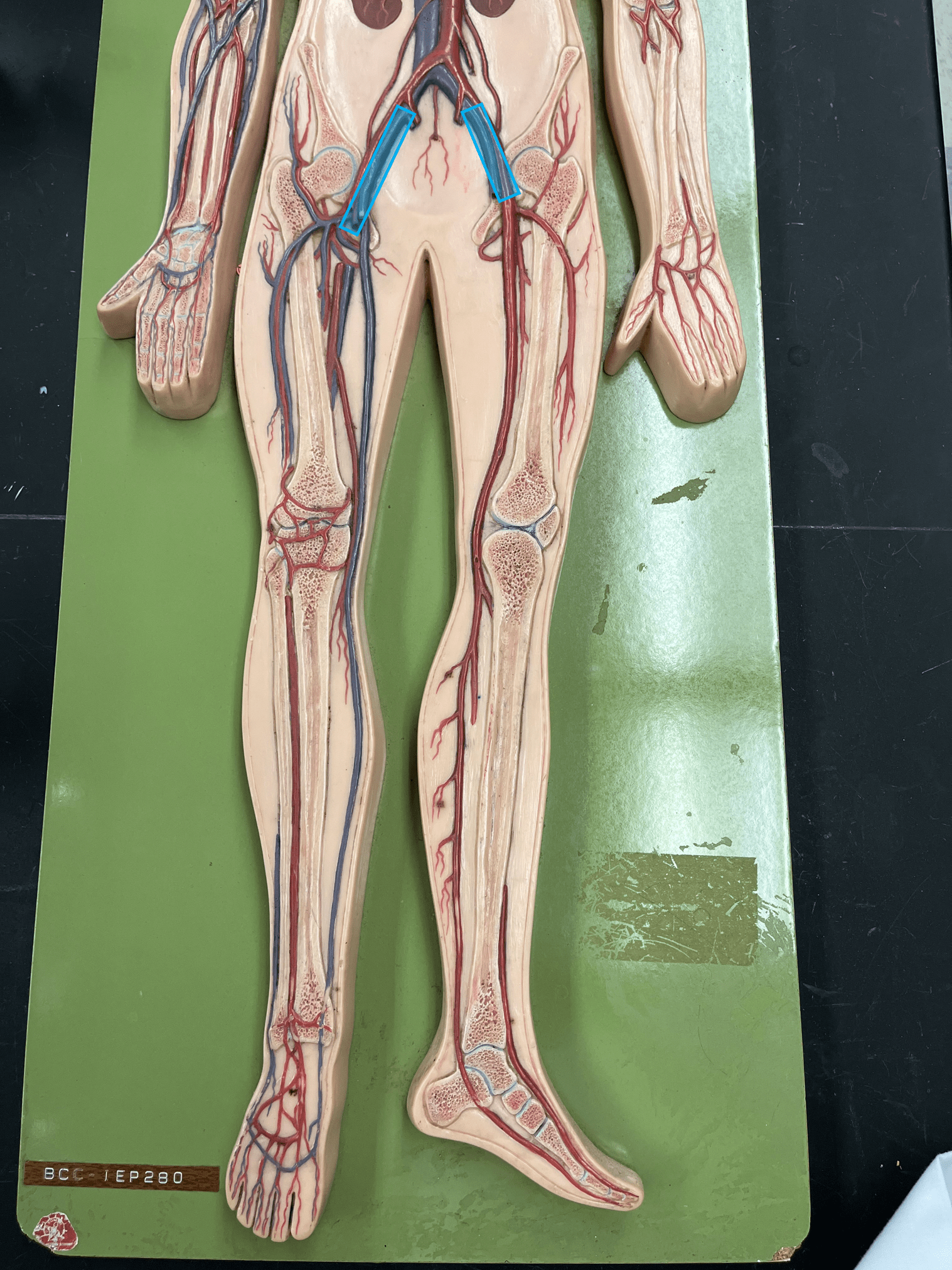
external iliac vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains all of the lower limb veins.
• Empties into the common iliac vein.
• Drains all of the lower limb veins.
• Empties into the common iliac vein.
97
New cards
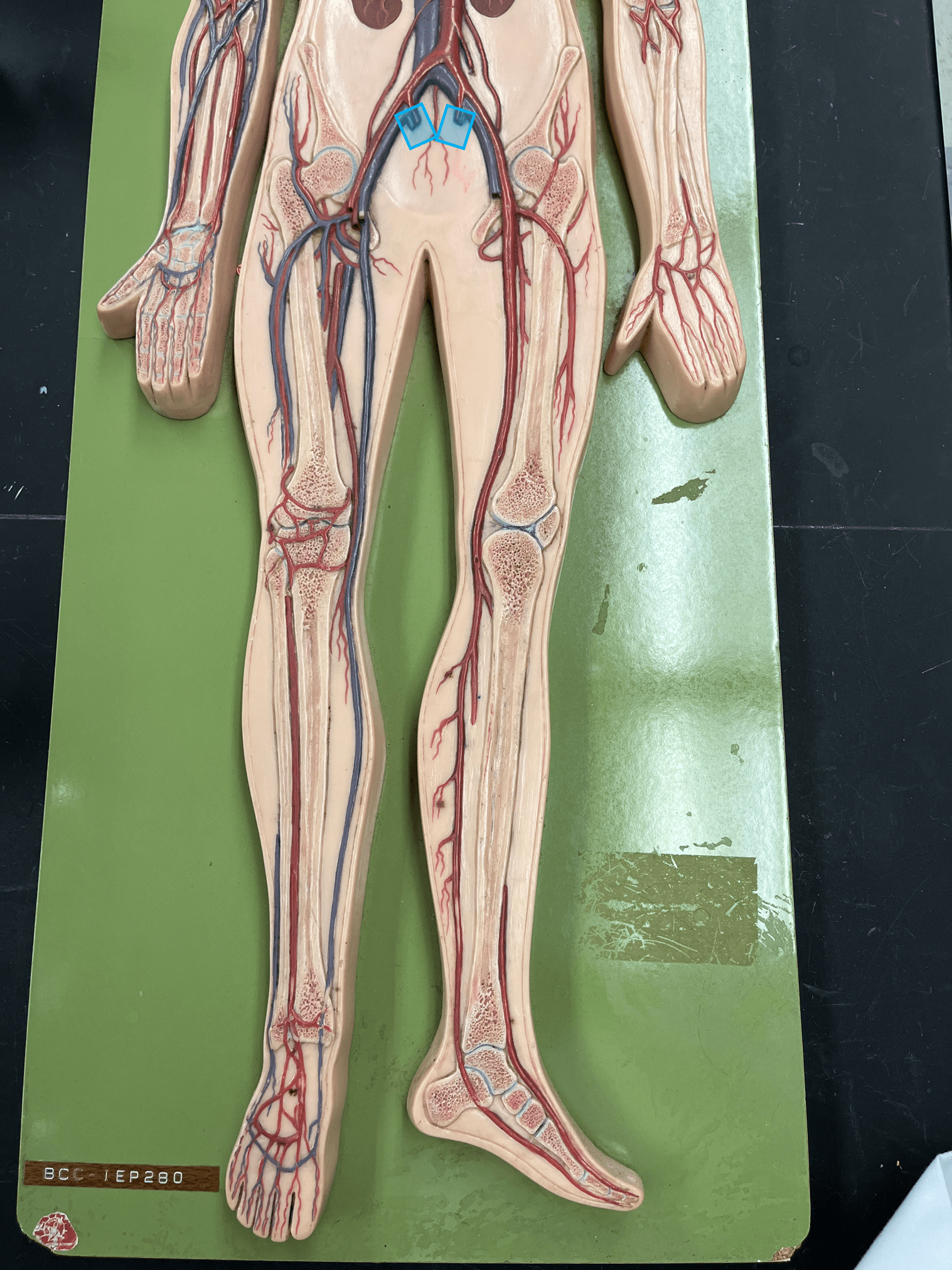
internal iliac vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains the pelvic wall and viscera.
• Empties into the common iliac vein.
• Drains the pelvic wall and viscera.
• Empties into the common iliac vein.
98
New cards
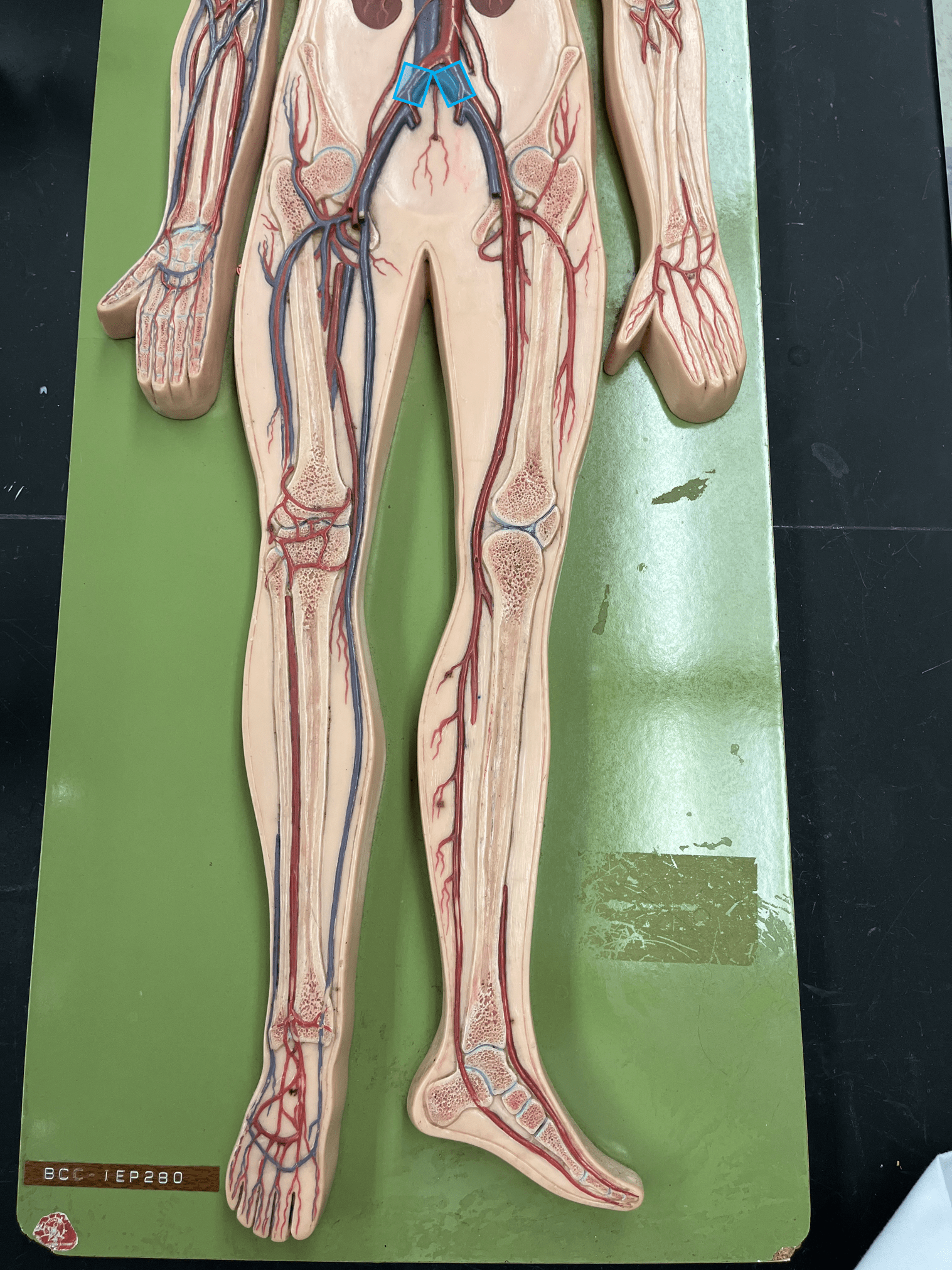
common iliac vein
• A vein of the lower limb.
• Drains the pelvic cavity and leg veins.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
• Drains the pelvic cavity and leg veins.
• Empties into the inferior vena cava.
99
New cards
placenta
• Part of the fetal circulation.
• Contains capillaries from the mother and allows for the exchange of resources between the mother and the fetus.
• Contains capillaries from the mother and allows for the exchange of resources between the mother and the fetus.
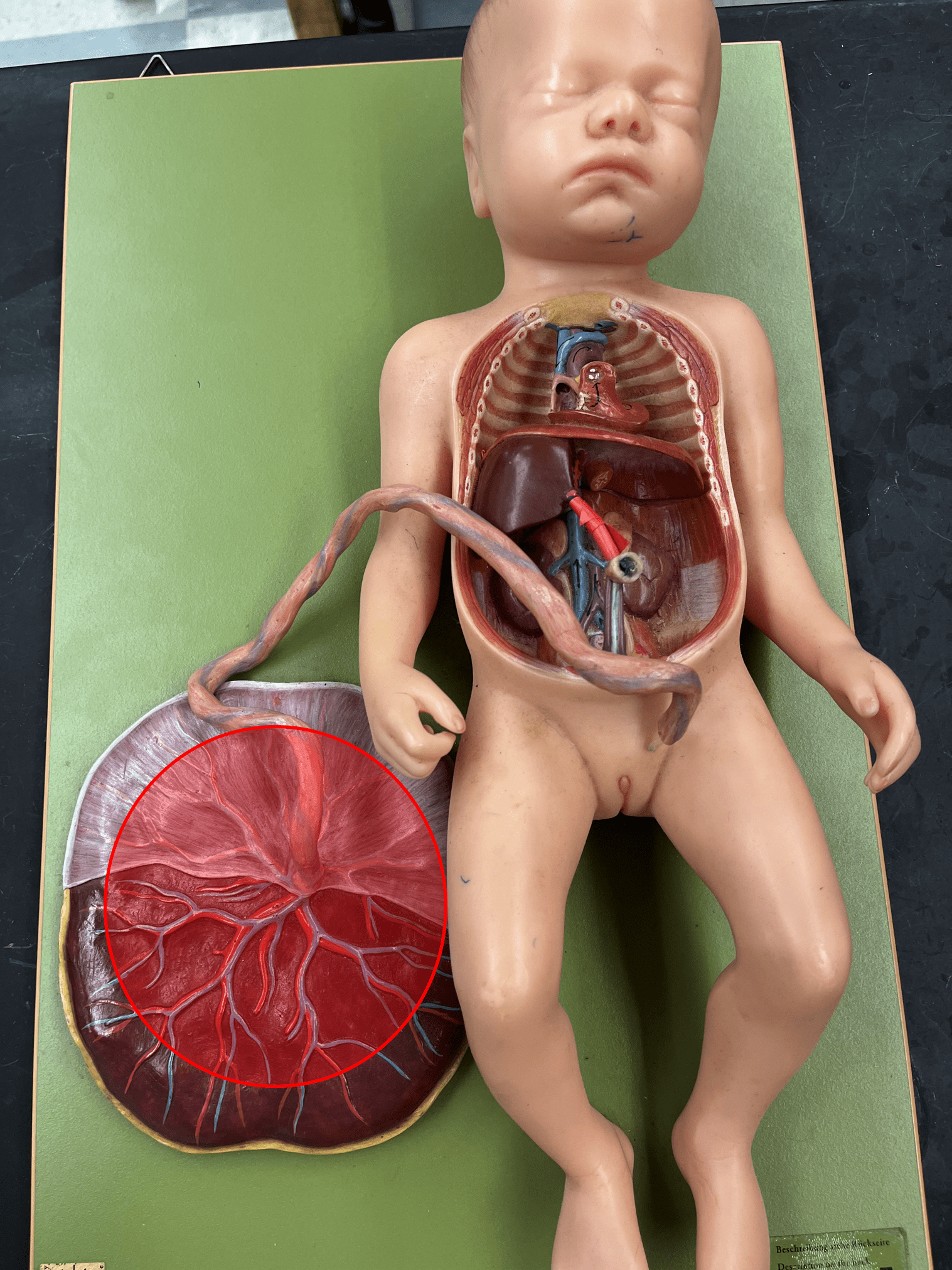
100
New cards
umbilical vein
• Part of the fetal circulation.
• Carries oxygen and nutrients from the placenta through the umbilical cord.
• Carries oxygen and nutrients from the placenta through the umbilical cord.