Erosion processes & landforms
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LA5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
4 main types of wave action
Corrasion/abrasion, Attrition, Solution/corrosion, Hydraulic action
CASH!
Corrosion/abrasion
The wearing of the coastal rocks of cliff faces by materials e.g. sand, pebbles and boulders carried and hurled against the coast by waves = cutting and breaking rocks
Attrition
The mutual wearing down of the materials e.g. sand, pebbles and boulders which are transported by waves = become smoother, rounder in shape and smaller in size
Solution/corrosion
The dissolving of soluble minerals in coastal rocks by sea water or waves.
The dissolved minerals may crystallise from evaporating sea water spray, and this helps detach mineral grains from coastal rocks.
The dissolved minerals may also be removed by sea water in solution.
The remaining rocks become weakened and are more susceptible to wave erosion by abrasion and hydraulic action.
Hydraulic action
The wearing away of coastal rocks when waves striking the cliff faces compresses air in cracks on the cliff face. This puts tremendous pressure on the surrounding rock. The air then expands explosively when the waves retreat resulting in a sudden releases of pressure. This process shatters the rocks, opens up and enlarges the cracks.
Wave erosion is accelerated by: (8)
exposure to strong prevailing winds
great wind velocity
stormy weather conditions
long fetch
large wave size
steep coastal slope/deep waters right up to the coast
weak coastal rocks which are less resistant to wave attack
large quantity of rock materials carried by waves
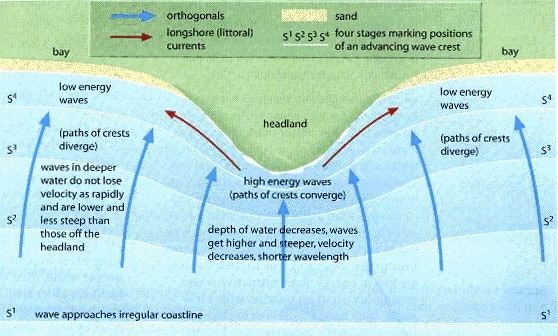
Wave refraction
The bending of wave fronts as they approach a shore so as to break almost parallel to the shore.
Shallow water at headland, deeper water at bays. Water slows down more near headlands but less near bays. Water “wraps” around headlands, wave energy concentrates on headlands. This causes more erosion at the headland.
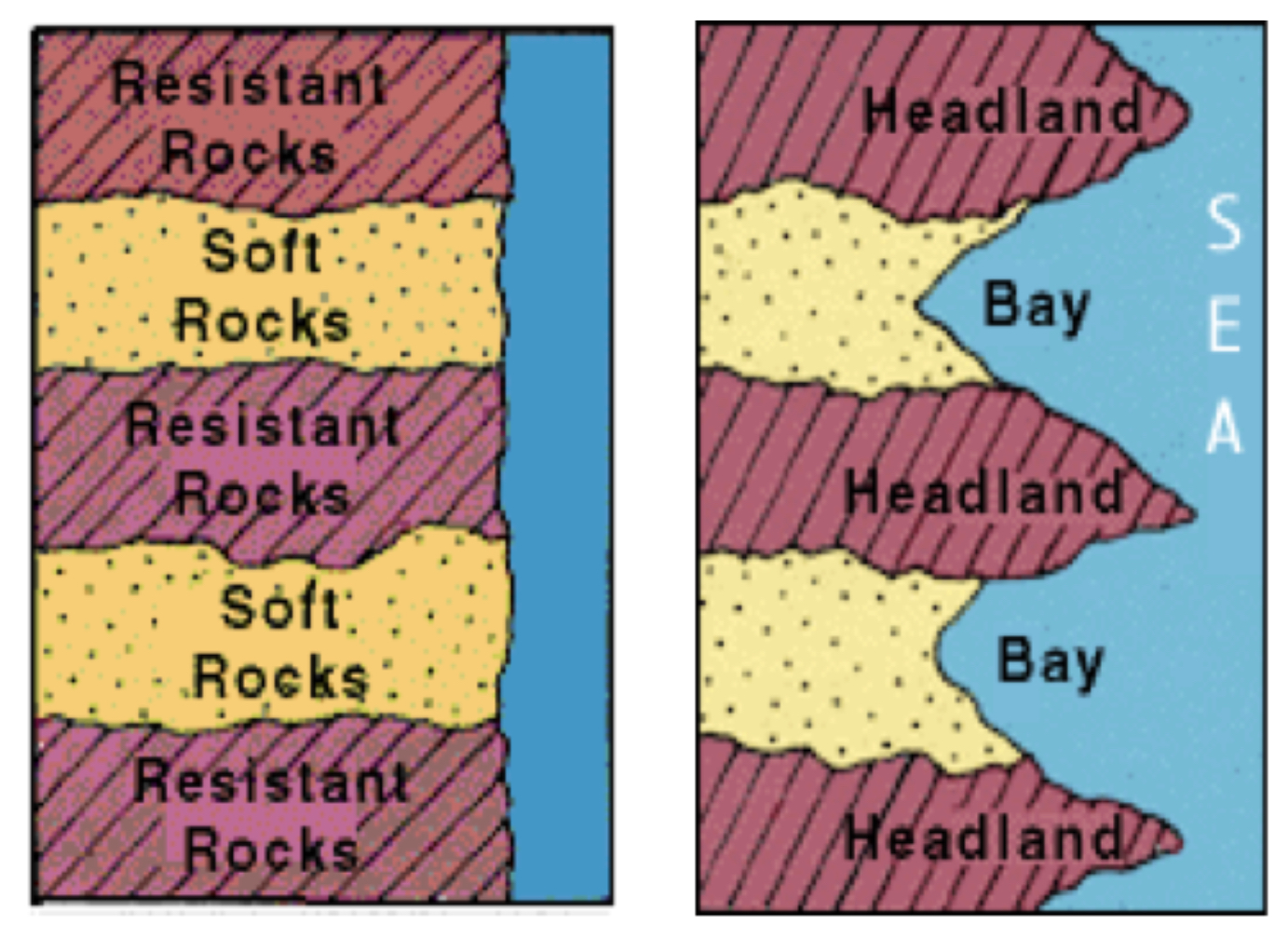
Formation of headlands and bays
Resistant & less resistant rocks lie at right angles to coast, results in rocks being eroded unevenly
Less resistant rocks erode to form bays.
More resistant rocks form coiffed headlands which protrudes into the sea.
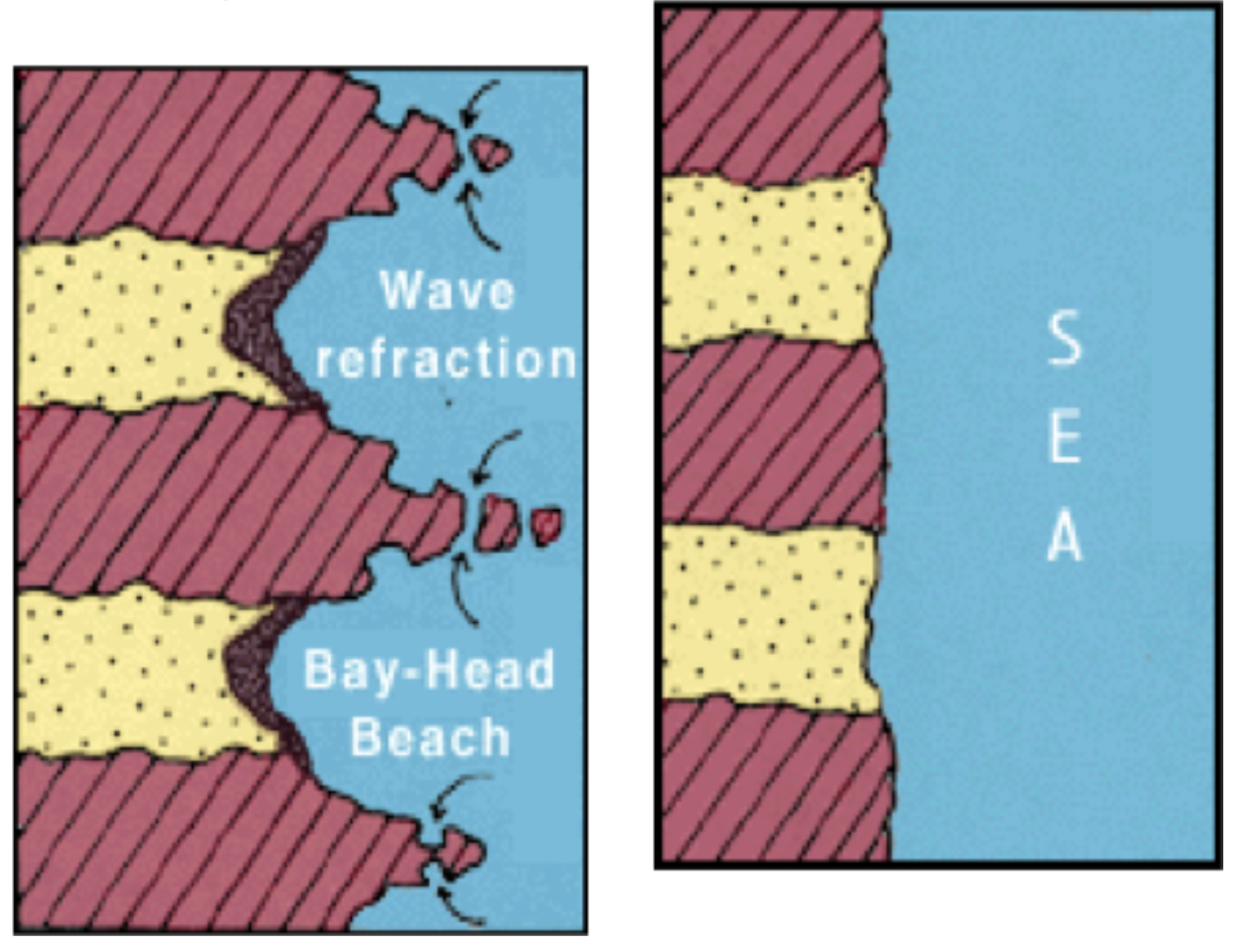
How do headlands and bays go back to a straight coastline?
Wave refraction causes waves to curve in on headlands
Energy concentrates on headland - erosion
Waves curves out in the bay, energy dissipates - deposition
This results in straighter coastline
Bays
A wide inwards curve of the coastline which surrounds the sea
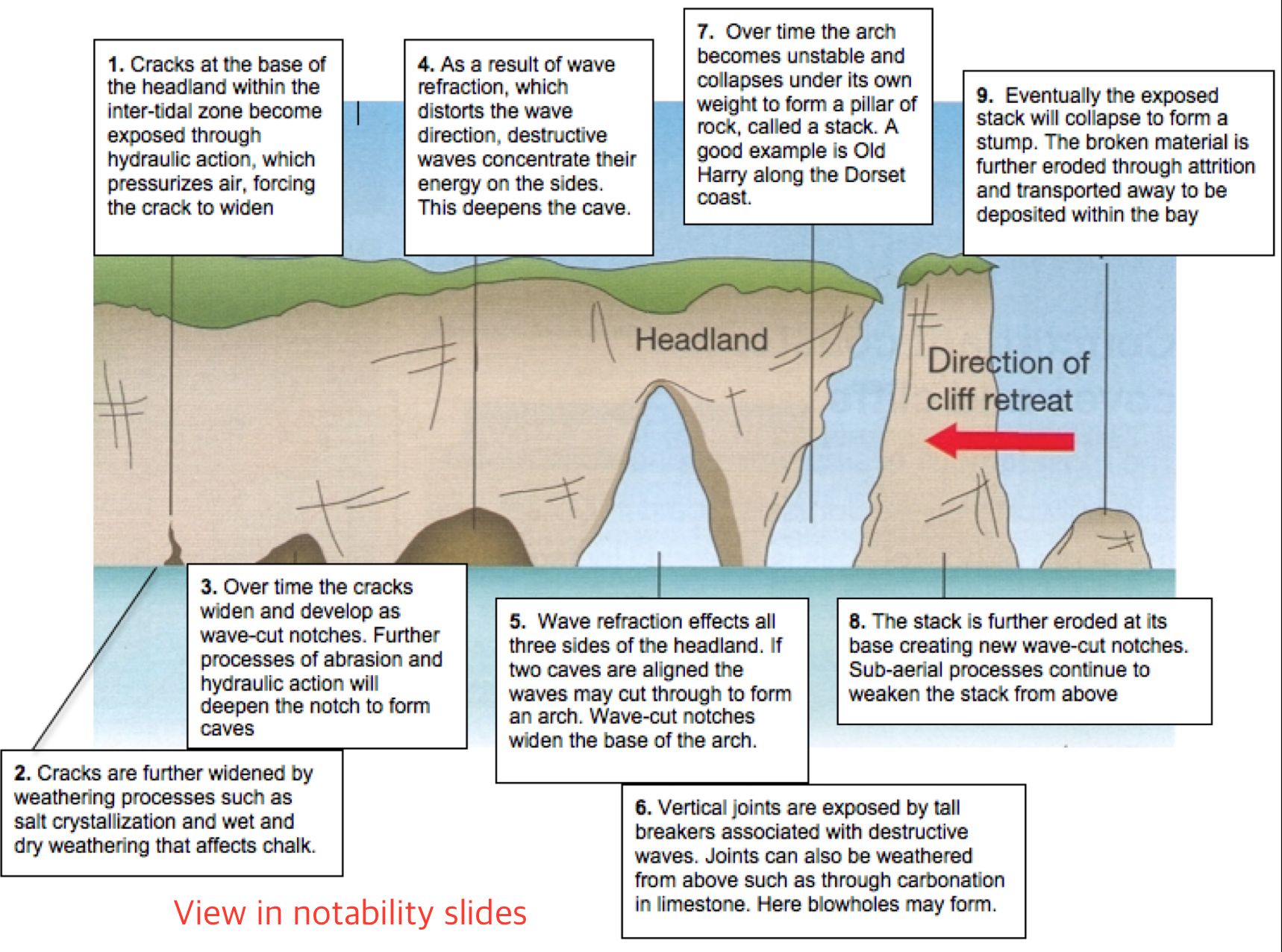
How are caves formed?
Some rocks may be less resistant to erosion (weaker). These rocks are eroded more quickly (esp by hydraulic action and abrasion).
Waves attack lines of weakness (joints and faults) at the base of the headland and undercut it.
The continuous action of waves forms a cave at the area that is hollowed by wave action.
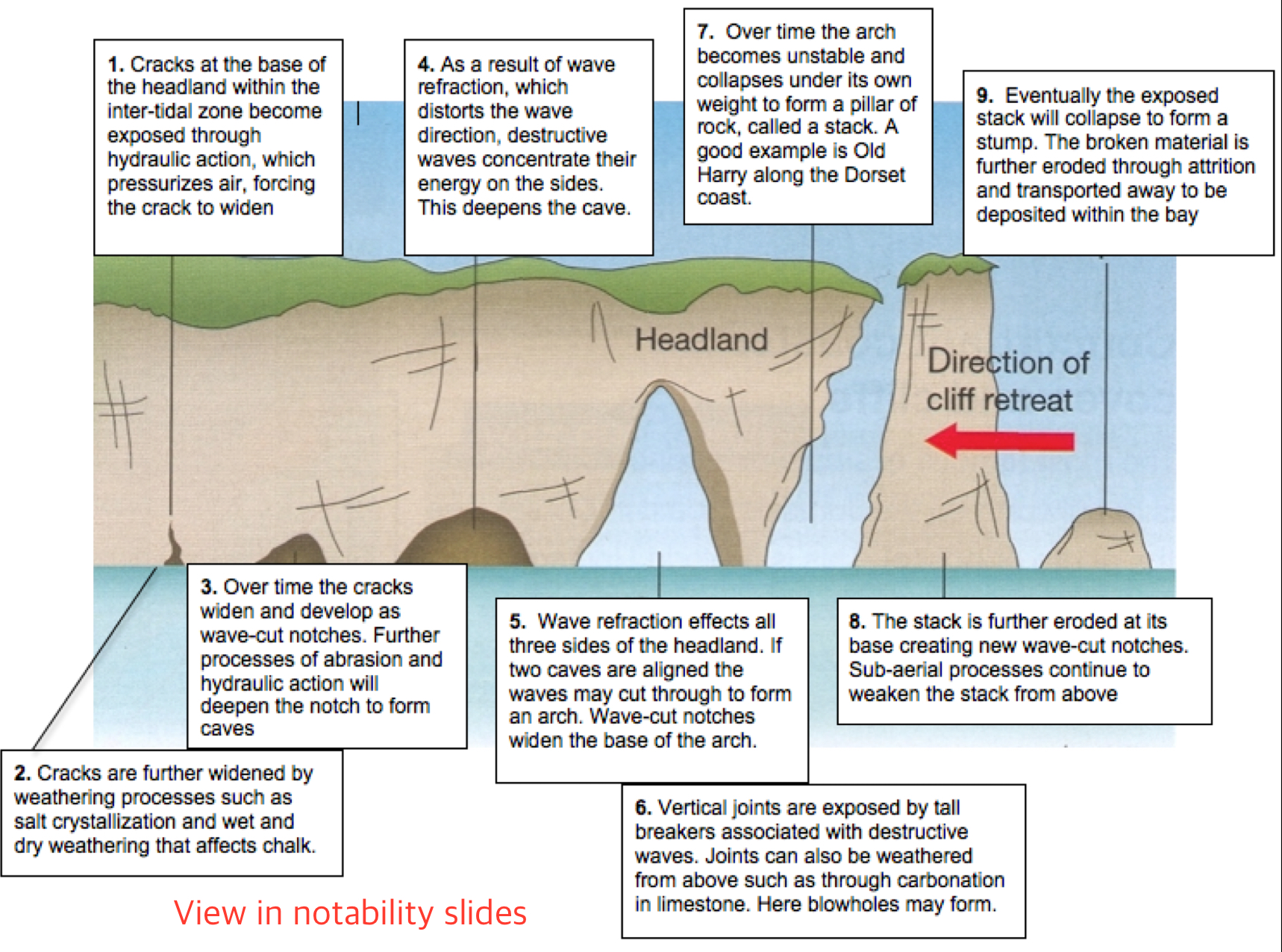
How are arches formed?
As the cave is attacked and eroded repeatedly by waves, it widens and depend to eventually become an arch.
OR
Caves may develop on each side of the headland.
Erosion may eventually join caves together, leaving an arch above the opening
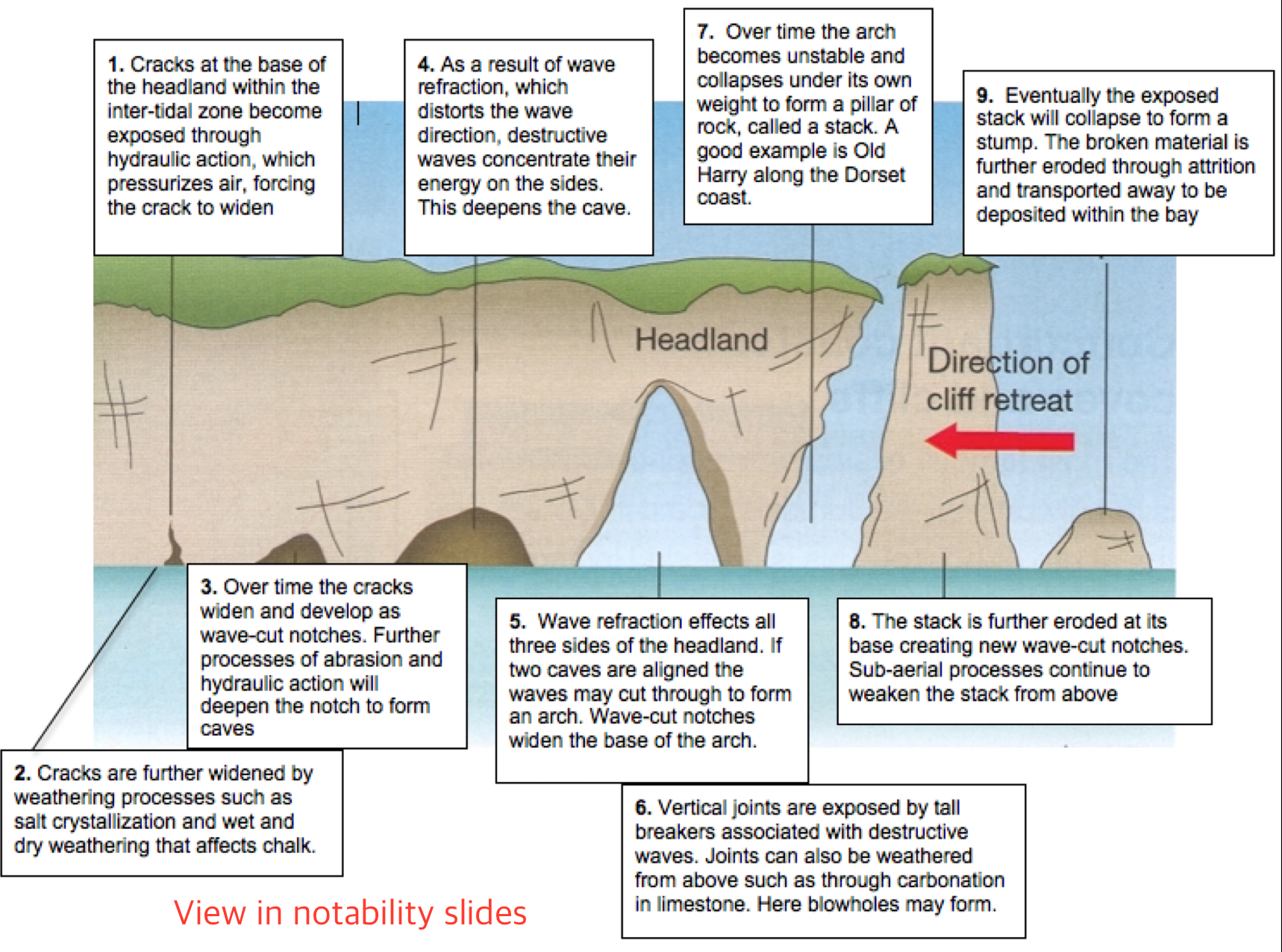
Stack
A pillar of rock in the sea left behind after an arch collapsed
How is a stack formed?
As the arch becomes wider, the roof becomes thinner, and when the roof becomes too weak and unstable, the roof of the arch collapses to form a stack.
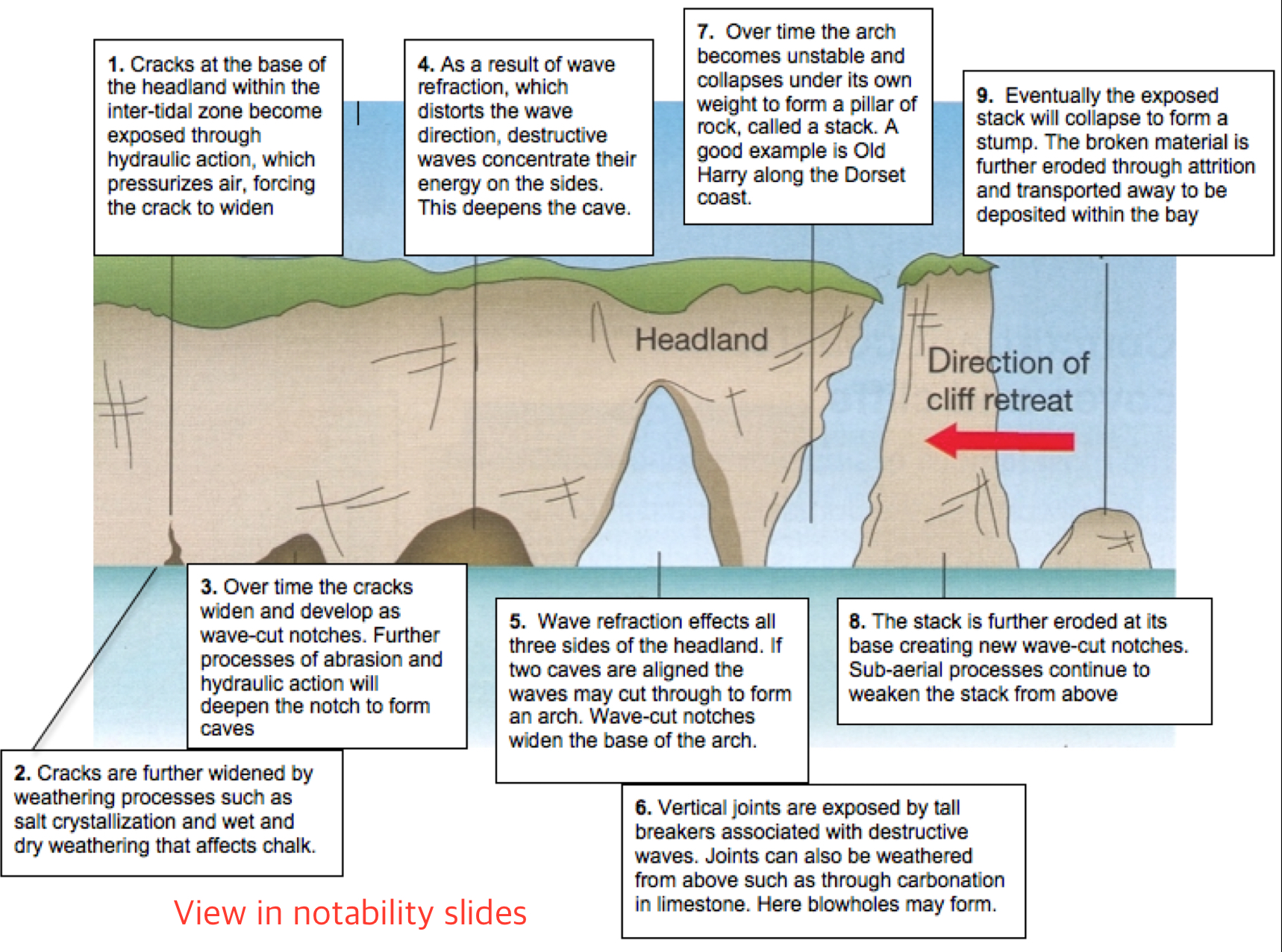
How is a stump formed?
When the stack is further eroded by waves.
Cliff
A steep and near-vertical rock face found along coasts.
It is produced by the action of waves undercutting a steep, rocky coast.
How are cliffs formed?
When high energy waves reach land with steep slopes, they erode the weaker parts of the steep slopes to produce a wave cut-notch (near high tide). (Corrasion, solution, hydraulic action)
This notch is further enlarged and deepened to form a cave.
Continued erosion and undercutting causes the roof of the cave to collapse, forming a steep rock face called a cliff.
How are wave-cut platforms formed?
Erosion at the base of the cliff, together with the removal of eroded materials by waves, causes the cliff to retreat landwards.
A flat surface is exposed at the foot of the cliff - a wave-cut platform
When does the erosion of wave-cut platform cease?
After some time, cliff becomes steeper & retreats landwards, wave-cut platform becomes wider.
The wave-cut platforms is buried by deposits, causing a belt of shallow water which reduces the wave energy.
Erosion of wave-cut platform ceases.
Offshore terrace
When the eroded cliff materials are transported away are deposited in the offshore zone.