BIO 203: Principles of Physiology and Thermoregulation
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Physiology
Study of functions in living organisms.
ATP
Energy currency of the cell.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, lower energy than ATP.
Na+
Sodium ion, important for cellular function.
K+
Potassium ion, crucial for nerve impulses.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of stable internal conditions.
Thermoregulation
Process of maintaining body temperature.
Heat Transfer
Movement of thermal energy between systems.
Positive Feedback
Enhances change in a system.
Negative Feedback
Reduces change to maintain stability.
Aerobic Metabolism
Energy production using oxygen.
Anaerobic Metabolism
Energy production without oxygen.
Vital Substances
Essential materials for life processes.
Exchange Systems
Systems facilitating material transfer in organisms.
Respiratory System
Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Digestive System
Processes nutrients and water absorption.
Urinary System
Removes waste and regulates water.
Circulatory System
Distributes blood and nutrients throughout body.
Cellular Level
Basic unit of structure and function.
Tissue Level
Groups of similar cells performing functions.
Organ Level
Different tissues working together for specific tasks.
System Level
Multiple organs cooperating for major functions.
Aquatic Life
All life forms primarily exist in water.
Compartmentalization
Separation of substances into distinct cellular compartments.
Fundamental Problems
Common challenges faced by all living organisms.
Laws of Physics
Natural laws governing biological processes and structures.
Limited Conditions
Organisms can only survive within specific environmental ranges.
Body Fluids Composition
Body fluids resemble seawater in chemical makeup.
Water Percentage in Humans
Water constitutes 75% of human body weight.
Molecular Composition
99% of human molecules are water.
Salts in Body
0.75% of body molecules are inorganic salts.
Biochemical Substances
0.25% of molecules include proteins and nucleic acids.
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Fluid found inside cells.
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Fluid located outside of cells.
Interstitial Fluid
ECF not contained in the circulatory system.
Plasma
Liquid component of blood.
Asymmetric Ion Distribution
Different ion concentrations in ICF and ECF compartments.
Sodium Levels in ECF
Sodium concentration is high in extracellular fluid.
Potassium Levels in ICF
Potassium concentration is high in intracellular fluid.
Physiological Asymmetry
Essential for maintaining cellular functions.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Main energy currency used in cellular processes.
Metabolic Rate (MR)
Energy expenditure measured over time.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Index for exchange efficiency in organisms.
Size Principle
Relationship between animal size and heat exchange.
Large Animal Heat Exchange
Low heat exchange per unit volume.
Small Animal Heat Exchange
High heat exchange per unit volume.
Heat Retention
Ability to maintain temperature within body.
Good Heat Retention
Characteristic of large animals.
Poor Heat Retention
Characteristic of small animals.
Cell-to-Cell Communication
Necessary for maintaining homeostasis.
Feedback System Components
Sensor, integrator, and effector are essential.
Sensor
Measures aspect of internal environment (e.g., temperature).
Integrator
Compares sensor measurement to reference value.
Effector
Changes internal environment based on sensor input.
Set Point
Desired value for a physiological parameter.
Thermostat Example
Illustrates negative feedback in temperature regulation.
Physiological Ecology
Study of organism's relationship to environment.
Heat Definition
Kinetic energy from molecular motion.
Temperature Definition
Measure of heat intensity in an object.
Water and Ion Balance
Context for physiological ecology and homeostasis.
Body Temperature Regulation
Mechanisms to maintain optimal body temperature.
Temperature
Index of molecular motion and kinetic energy.
Thermal Budget
Balance of heat gained and lost.
Conduction
Heat transfer through physical contact.
Convection
Heat transfer via moving fluids or gases.
Evaporation
Liquid water transforms to vapor, cooling body.
Radiation
Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves.
Heat Gain
Heat obtained from external environment.
Heat Loss
Heat lost to external environment.
Endogenous Heat Production
Heat generated internally via metabolism.
Temperature Gradient
Difference in temperature driving heat flow.
Thermal Conductivity (K)
Material's ability to conduct heat (W x m-1 x K-1).
Surface Area (A)
Area of contact influencing heat transfer rate.
Length (l)
Distance between objects affecting heat movement.
Differential Equations
Mathematical equations describing heat transfer rates.
Free Convection
Natural movement of fluid due to temperature differences.
Forced Convection
Fluid movement induced by external forces.
Boundary Layers
Thin layers affecting heat exchange efficiency.
Evaporative Cooling
Cooling effect from water vaporization.
Heat of Vaporization
Energy required to convert liquid to vapor.
Infrared Electromagnetic Radiation
Longer wavelengths with lower energy.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to increase heat loss.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels to reduce heat loss.
Core Body Temperature
Average temperature for physiological function.
Counter-Current Exchange Mechanism
Heat transfer between arterial and venous blood.
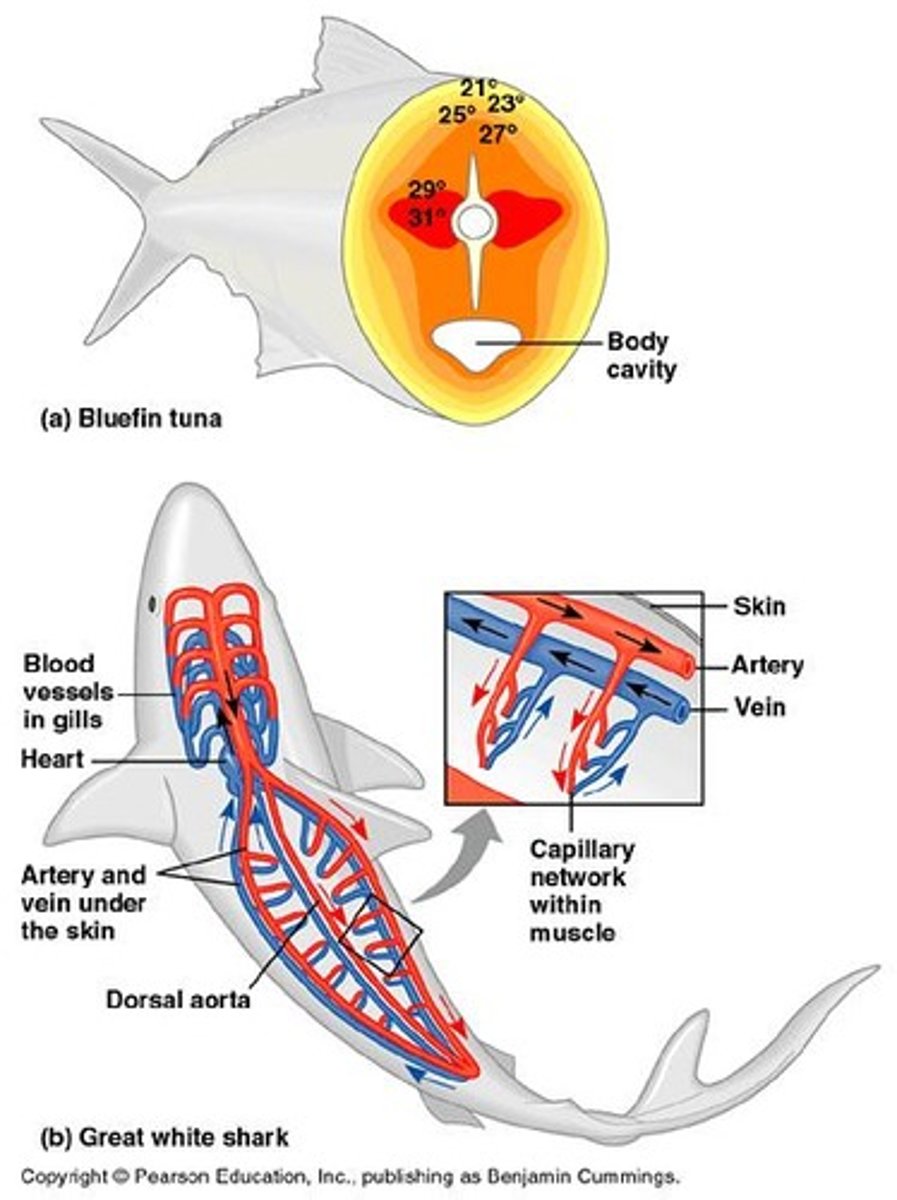
Ectothermy
Thermoregulation using external heat sources.
Endothermy
Thermoregulation using internal metabolic heat.
Heterothermy
Combination of internal and external heat regulation.
Ambient Temperature (Tamb)
Temperature of the surrounding environment.
Poikilotherms
Organisms with variable body temperature.
Homeotherms
Organisms maintaining constant body temperature.
Thermoregulation Strategies
Methods organisms use to control body temperature.
Physiological Thermoregulation
Internal mechanisms for temperature control.
Behavioral Thermoregulation
Actions taken to regulate body temperature.
Thermal Acclimation
Physiological adjustments to temperature changes.
Hibernation
Extended state of inactivity during cold periods.
Torpor
Short-term hibernation-like state for energy conservation.
Estivation
Dormancy during hot, dry periods.
Fever Generation
Increased body temperature response to infection.
Hypothalamus Role
Regulates body temperature and fever response.