AP World ultimate review quizlet
1/483
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
484 Terms
Russian Revolution of 1917
two revolutions, the first of which, in February (March, New Style), overthrew the imperial government and the second of which, in October (November), placed the Bolsheviks in power.
Mexican Revolution
(1910-1920 CE) Fought over a period of almost 10 years form 1910; resulted in ouster of Porfirio Diaz from power; opposition forces led by Pancho Villa and Emiliano Zapata.
Triple Alliance
An alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI.
Triple Entente
Britain, France, Russia
Central Powers
Austria-Hungary, Germany, Ottoman Empire
Allied Powers (WWI)
Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the United States
Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort
Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.
Great Depression
starting with collapse of the US stock market in 1929, period of worldwide economic stagnation and depression. Heavy borrowing by European nations from USA during WW1 contributed to instability in European economies. Sharp declines in income and production as buying and selling slowed down. Widespread unemployment, countries raised tariffs to protect their industries. America stopped investing in Europe. Lead to loss of confidence that economies were self adjusting
Five Year Plan
Stalin's economic policy to rebuild the Soviet economy after WWI. tried to improve heavy industry and improve farm output, but resulted in famine
The New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.
Fascist Corporatist economy
Involved management of sectors of the economy by government or privately controlled organizations
League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations
League of Nations Mandates
A system established after WWI whereby a nation officially administered a territory) mandate_ on behalf of the League of Nations. Thus, France administered Lebanon and Syria as mandates, and Britain administered Iraq and Palestine.
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
Japan offered to liberate Southeast-Asian countries from western colonial rule but instead used them as conquered land for natural resources
Indian National Congress
A movement and political party founded in 1885 to demand greater Indian participation in government. Its membership was middle class, and its demands were modest until World War I. Led after 1920 by Mohandas K. Gandhi, appealing to the poor.
Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans
Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.
Fascism
A political system headed by a dictator that calls for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition
Totaltarian
referring to a form of government in which one person or party holds absolute control
Adolf Hitler
Austrian born Dictator of Germany, implement Fascism and caused WWII and Holocoust.
Joseph Stalin
Bolshevik revolutionary, head of the Soviet Communists after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928 to 1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush opposition
Benito Mussolini
Fascist Dictator of Italy that at first used bullying to gain power, then never had full power.
Atomic Bomb
bomb dropped by an American bomber on Hiroshima and Nagasaki destroying both cities
Fire bombing
Bombs dropped on Germany and Japan with intentions to spread fires and take down cities
Winston Churchill
A noted British statesman who led Britain throughout most of World War II and along with Roosevelt planned many allied campaigns. He predicted an iron curtain that would separate Communist Europe from the rest of the West.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
President of the US during Great Depression and World War II
Genocide
Deliberate extermination of a racial or cultural group
Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.
Armenian Genocide
Assault carried out by mainly Turkish military forces against Armenian population in Anatolia in 1915; over a million Armenians perished and thousands fled to Russia and the Middle East.
Cambodian Genocide
Pol Pot eliminated educated, artists, religious, and minorities
Rwandan Genocide
The killing of more than 500,000 ethnic Tutsis by rival Hutu militias in Rwanda in 1994. The conflict between the dominant Tutsis and the majority Hutus had gone on for centuries, but the suddenness and savagery of the massacres caught the United Nations off-guard. U.N. peacekeepers did not enter the country until after much of the damage had been done.
Ukranian Famine
Joseph stalin took away food from the people of Ukraine, which resulted in the death of millions of people
Bolsheviks
A group of revolutionary Russian Marxists who took control of Russia's government in November 1917
Institutional Revolutionary Party
(PRI) the political party introduced in 1929 in Mexico that helped to introduce democracy and maintain political stability for much of the 20th century
Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria-Hungary assassinated by a Serbian nationalist. A major catalyst for WWI.
Militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
Paris Peace Conference
The peace conference that decided the terms of WWI peace and Treaty of Versailles.
Woodrow Wilson
President of the United States (1913-1921) and the leading figure at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. He was unable to persuade the U.S. Congress to ratify the Treaty of Versailles or join the League of Nations.
Georges Clemenceau
French statesman who played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Versailles (1841-1929)
David Lloyd George
Britain's prime minister at the end of World War I whose goal was to make the Germans pay for the other countries' staggering war losses
Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.
New Economic Policy (NEP)
Lenin's 1921 policy to re-establish limited economic freedom in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration
John Maynard Keynes
British economist who argued that for a nation to recovery fully from a depression, the govt had to spend money to encourage investment and consumption
Totalitarianism
A form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition etc.)
Fransisco Franco
Leader of France, conservative general, lead the Spanish civil war, turns into fascist dictator
Spanish Civil War
In 1936 a rebellion erupted in Spain after a coalition of Republicans, Socialists, and Communists was elected. General Francisco Franco led the rebellion. The revolt quickly became a civil war. The Soviet Union provided arms and advisers to the government forces while Germany and Italy sent tanks, airplanes, and soldiers to help Franco.
Mandate System
Allocation of former German colonies and Ottoman possessions to the victorious powers after World War I; to be administered under League of Nations supervision.
Balfour Declaration
British document that promised land in Palestine as homeland for Jews in exchange for Jews help in WWI
Mao Zedong
Chinese Communist leader from 1949 to 1976.
Chaing Kai-Shek
Leader of the nationalist party in 1928, after Sun Yat-sen's death in 1925, he favored a capitalist state supported by a military dictatorship.
Zionists
Supporters of Jewish nationalism, especially a creation of a Jewish state in Palestine.
Neville Chamberlain
Great British prime minister who advocated peace and a policy of appeasement
Nuremberg Laws
1935 laws defining the status of Jews and withdrawing citizenship from persons of non-German blood.
Nazi Party
the political party founded in Germany in 1919 and brought to power by Hitler in 1933
Appeasement
Accepting demands in order to avoid conflict
Island Hopping
A military strategy used during World War II that involved selectively attacking specific enemy-held islands and bypassing others
D-Day
Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944
Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces against Poland in 1939
Pastoralists
semi-nomadic herders of domesticated animals

Patriarchy
a system of society in which men hold the power

Social Stratifcation
a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy

Metallurgy
the science of working with metals
Monotheism
belief in one god
Polytheism
belief in more than one god
Shamanism
The practice of identifying special individuals (shamans) who will interact with spirits for the benefit of the community.
Animism
The belief that bodies of water, animals, trees, and other natural objects have souls
Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Developed written scriptures and an ethical code (Torah, 10 Commandments) over time.
Vedas
Ancient Sanskrit writings that are the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism.
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms
Monasticism
A way of life in which men and women withdraw from the rest of the world in order to devote themselves to their faith (as monks and nuns)
commodity
valuable product
Legitimacy
the popular acceptance of an authority, like a King or ruler
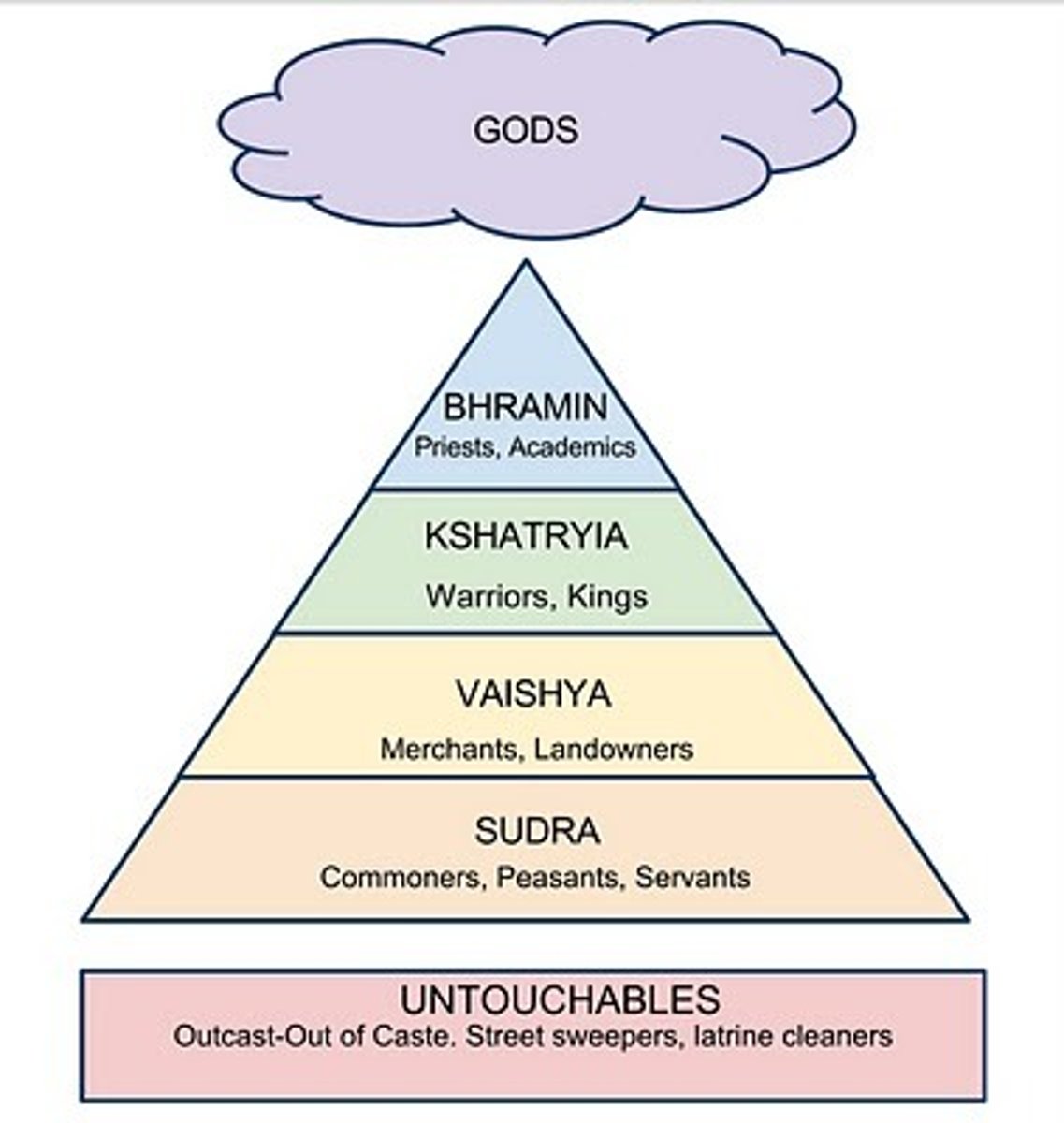
Caste System
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation, but also his or her position in society
Mandate of Heaven
an ancient Chinese belief and philosophical idea that tiān (heaven) granted emperors the right to rule based on their ability to govern well and fairly.

Reincarnation
the rebirth of a soul in a new body.
Eightfold Path
In Buddhism, the path to nirvana. Comprises eight aspects in which an aspirant must become practiced: right views, intention, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, and concentration.
Confucianism
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society and stresses a moral code of conduct.

Buddhism
the teaching of Buddha that emphasizes that life is filled with suffering caused by desire and that suffering ceases when desire ceases. Through right conduct, wisdom and meditation one can end the cycle of rebirth and reach Enlightenment.

Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament, emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.
State
a nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government.
Siddhartha Gautama (The Buddha)
Means "Enlightened One." He is said to have renounced his worldly possessions and taught of a way to overcome suffering.
filial piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.
ancestor veneration
Veneration of the dead or ancestors is based on the beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of the living
syncretic religion
Combines two religious traditions into something distinctly new, while containing traits of both
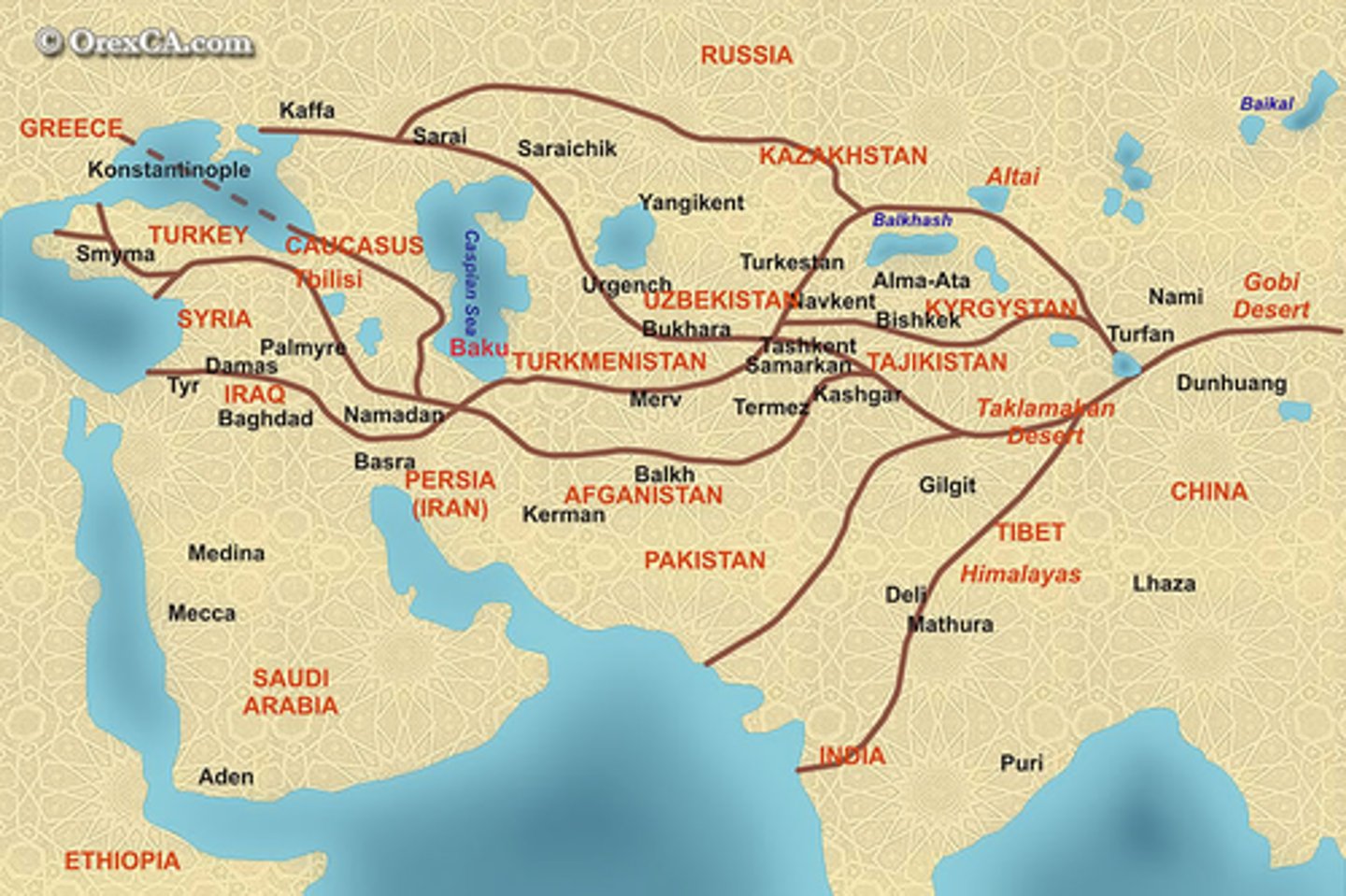
Silk Roads
trade routes stretching from China to the Mediterranean, which allowed for the exchange of goods and ideas from China to the Roman Empire
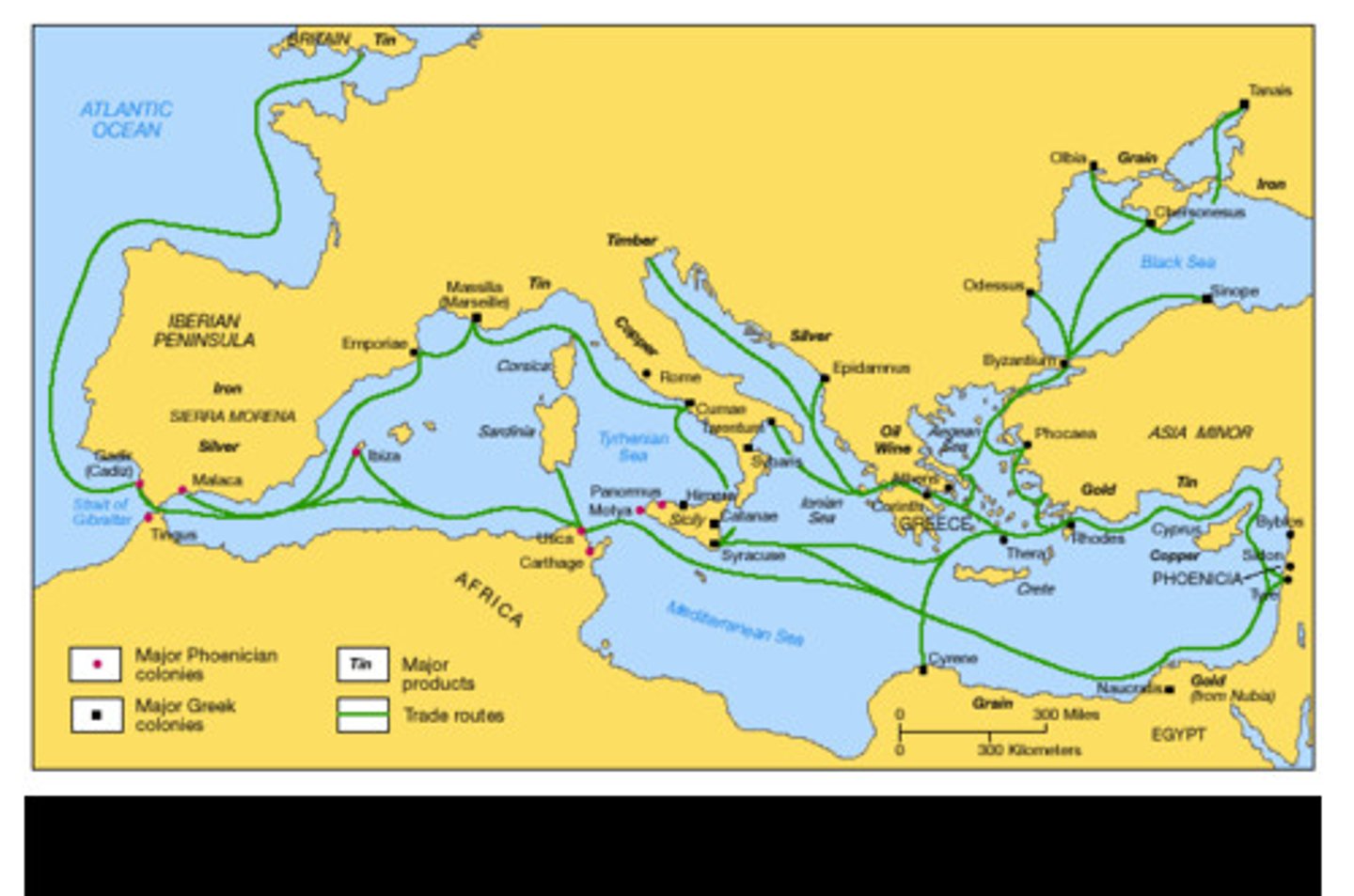
Mediterranean Sea Lanes
Trade routes that connected the Mediterranean civilizations together. The need for a sea rout for trade in the region. Trade increased and diffusion of cultures occurred
tribute system
payment made by one nation to another in acknowledgment of submission, notably used by Chinese dynasties
Bureaucracy
A system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials
commercial exchange
the buying and selling of goods
epidemic
A widespread outbreak of an infectious disease.
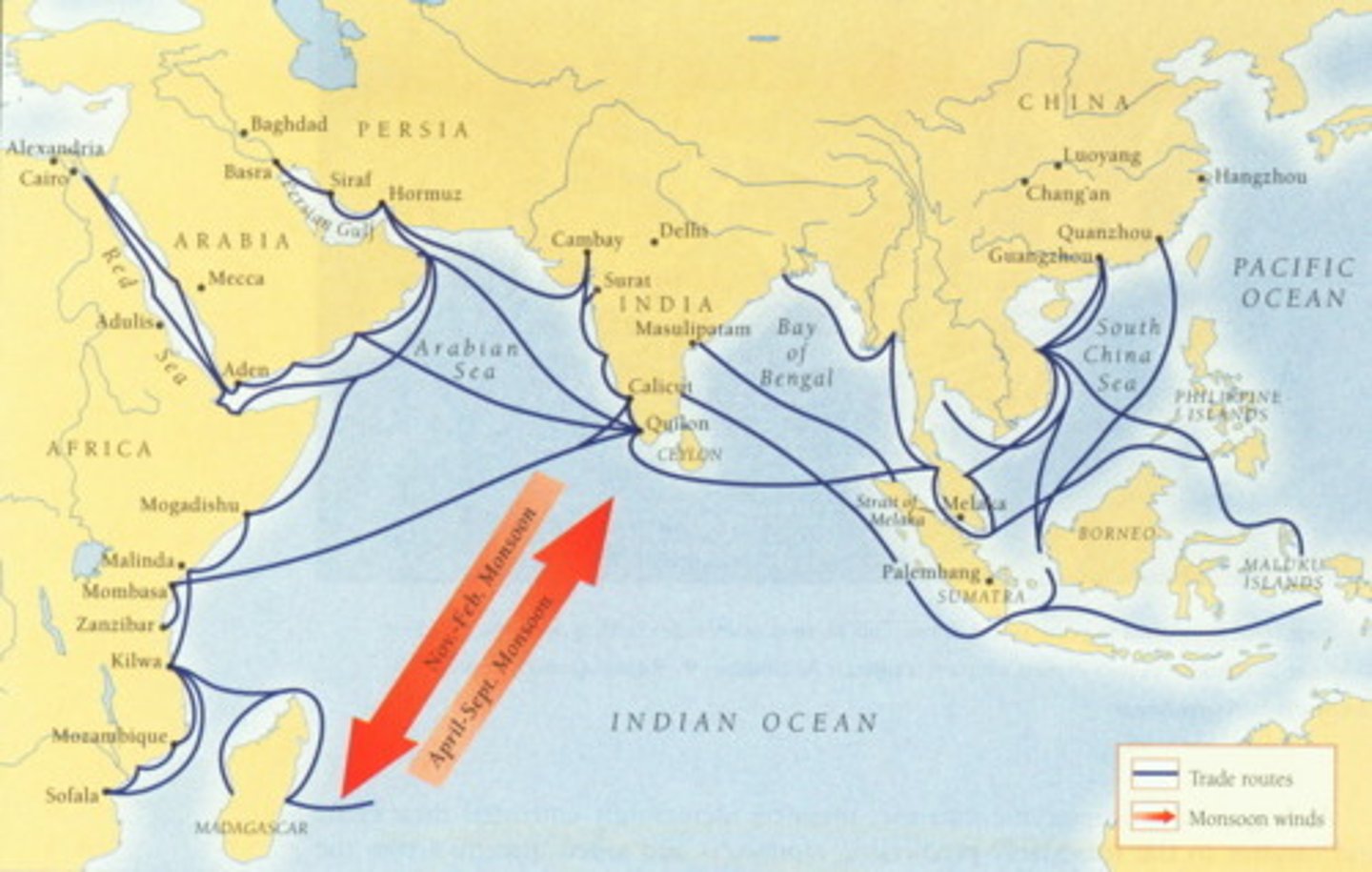
monsoon winds
These seasonal winds carried ships on the Indian Ocean between India and Africa
Missionaries
people who work to spread their religious beliefs
Silk Roads (600-1450)
flourished under the unity of the Mongols, only to lose favor again when the Mongols fell.
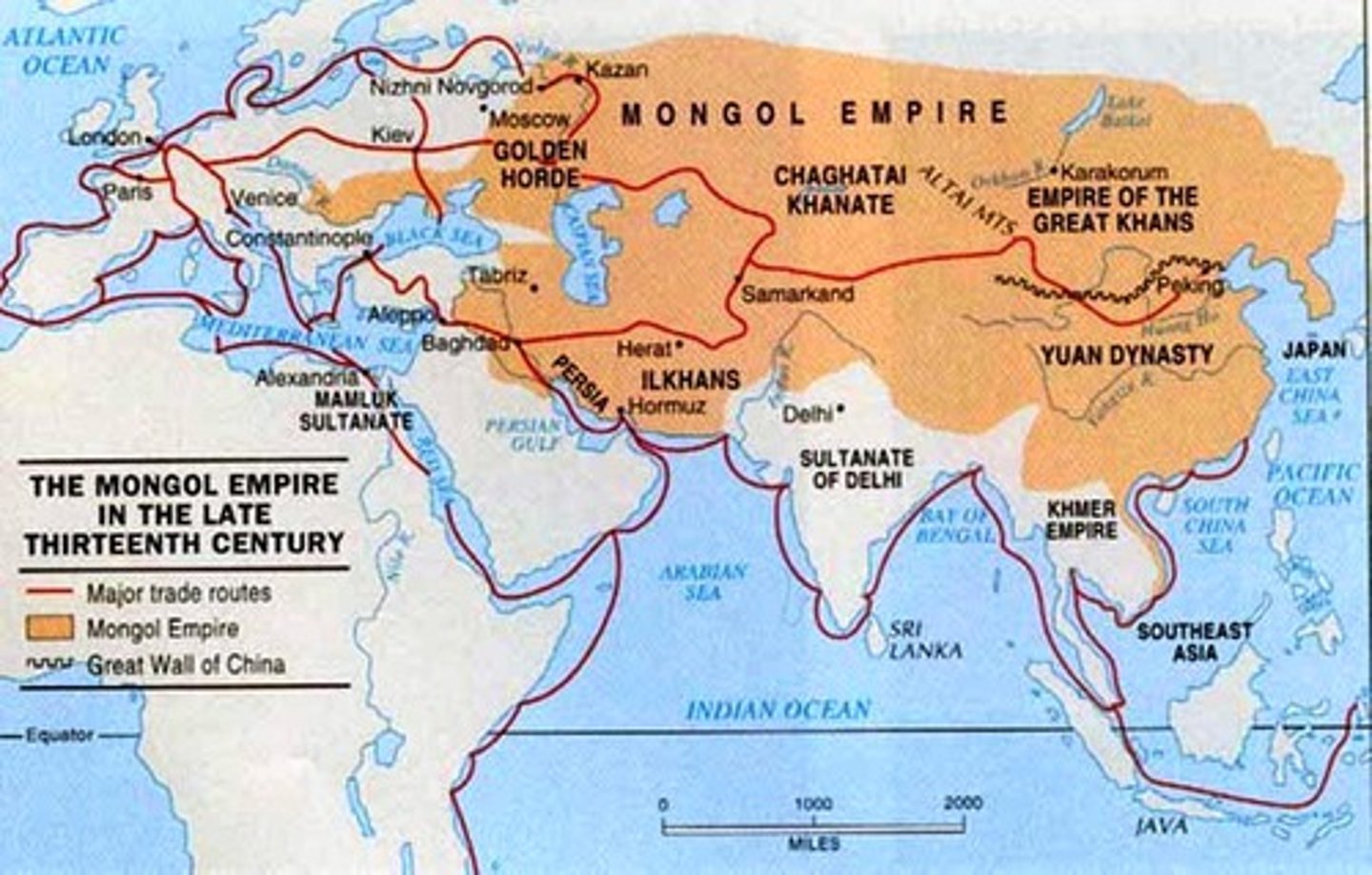
Black Death
The common name for a major outbreak of plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century in part caused by the period of unity along the Silk Road and migration of Mongols.

Indian Ocean trading network
The world's largest sea-based system of comunication and exchange before 1500 C.E., Indian Ocean commerce stretched from southern China to eastern Africa and included not only the exchange of luxury and bulk goods but also the exchange of ideas and crops.
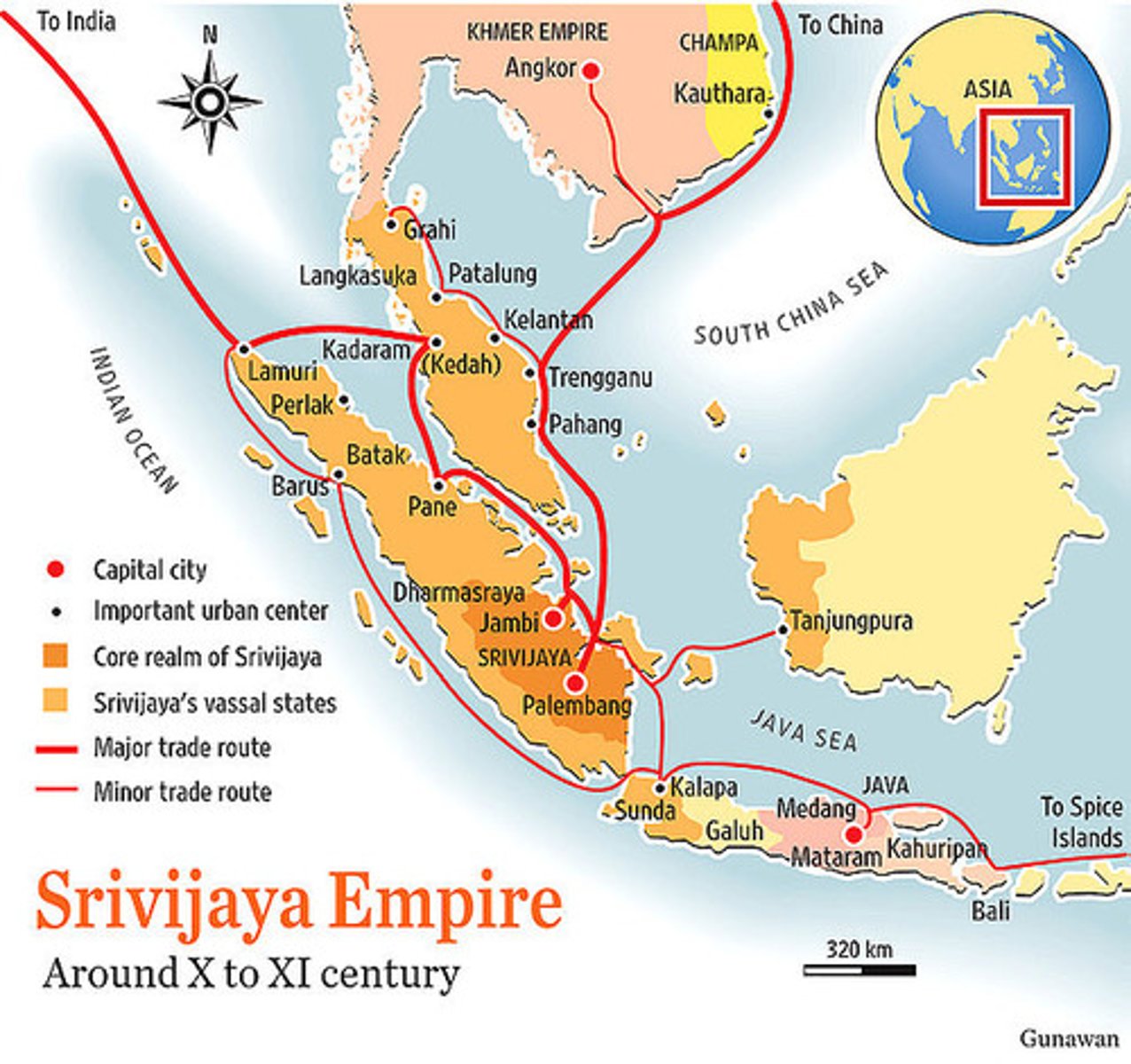
Srivijaya
A Malay kingdom that dominated the Straits of Malacca between 600 and 1075 CE. It amassed wealth and power by a combination of selective adaptation of Indian technologies and concepts, and control of trade routes.
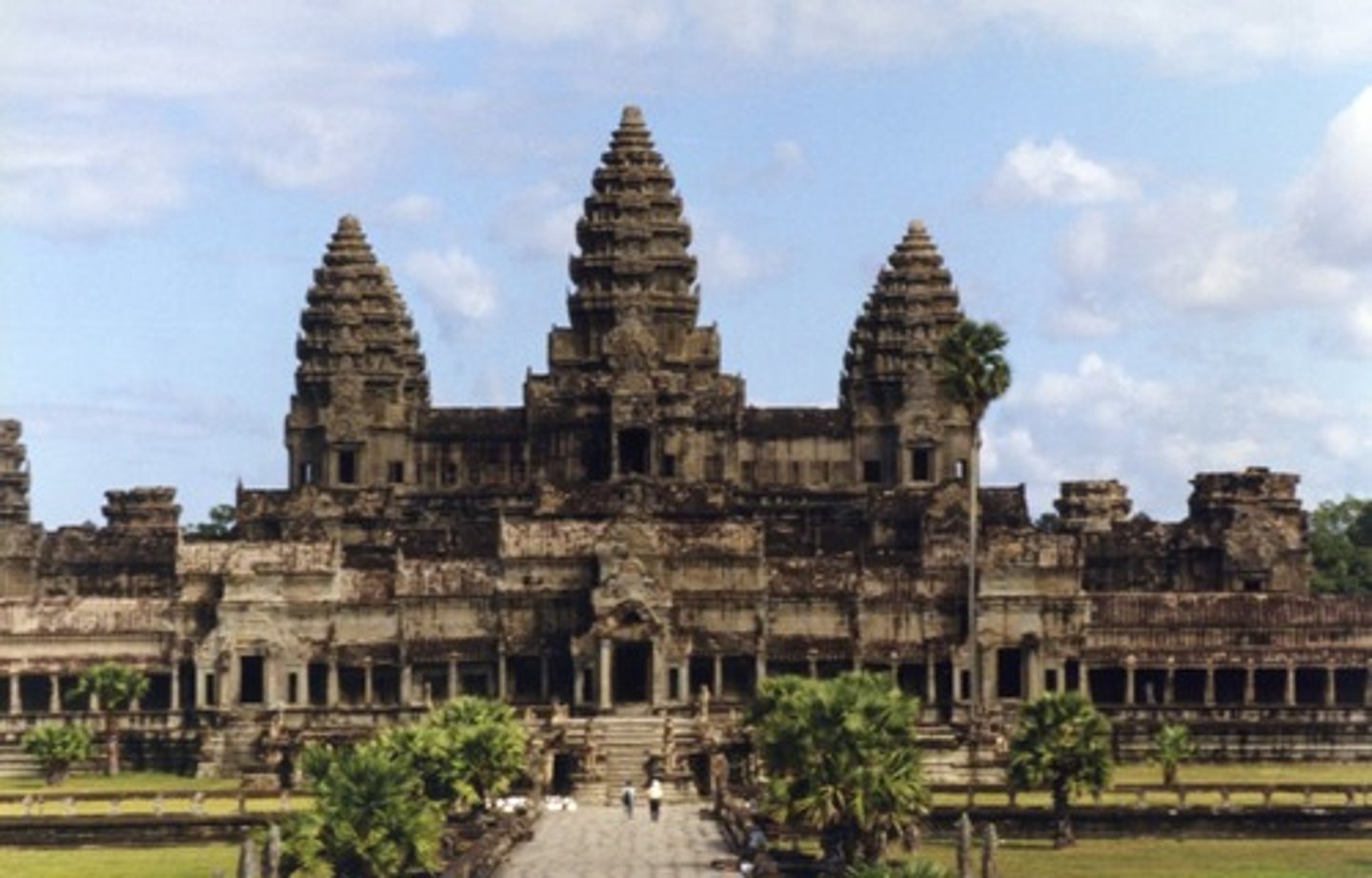
Angkor Wat
This place was first a Hindu (dedicated to the god Vishnu), then subsequently a Buddhist, temple complex in Cambodia and the largest religious monument in the world.
