Ch 1 - Welcome to Economics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:23 AM on 6/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
Economics
**The study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity.** These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions
2
New cards
Scarcity
Human wants (infinite) for goods, services and resources exceed what is available (finite).
\
Ex: homeless people, but all experience scarcity like time
\
Ex: homeless people, but all experience scarcity like time
3
New cards
Economics & Information
Economics is greatly impacted by how well information travels through society (Social Media)
People use information to make decisions: can be wrong: **Imperfect Information**
Need data like from FRED to describe & measure issues
People use information to make decisions: can be wrong: **Imperfect Information**
Need data like from FRED to describe & measure issues
4
New cards
Assumption #1
People are rational and base decisions on imperfect information
5
New cards
Adam Smith
Introduced the idea of dividing labor into discrete tasks, in his famous 1776 book, titled *The Wealth of Nations*.
6
New cards
**Division of labor**
The way in which different workers divide required tasks to produce a good or service. Produces greater quantity of goods/services.
\
Ex: Workers in an assembly line
\
Ex: Workers in an assembly line
7
New cards
Specialization
* When workers or firms focus on particular tasks for which they are well-suited within the overall production process.
* Do not need to hunt, farm, or build own house
\
* Do not need to hunt, farm, or build own house
\
8
New cards
Benefits of Specialization
1) Allows workers to focus on part of production w/ advantage
2) Learn to produce quicker & better over time
3) Economies of Scale: For many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines
2) Learn to produce quicker & better over time
3) Economies of Scale: For many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines
9
New cards
Specialization Requires
Trade to purchase goods/services with pay from specialized job
Consume all goods and produce what specialized at
Consume all goods and produce what specialized at
10
New cards
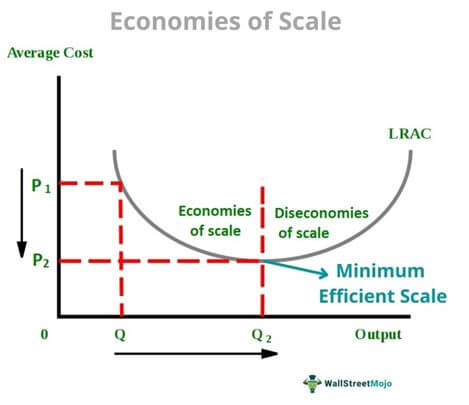
Economies of Scale Graph
* Cost on y-axis
* Quantity on x-axis
* Long-run average total cost
* Minimum Efficiency of Scale: Get unit price to lowest point
* Diseconomies of scale: after MES, making too much quantity requires more resources, increasing unit cost
* Quantity on x-axis
* Long-run average total cost
* Minimum Efficiency of Scale: Get unit price to lowest point
* Diseconomies of scale: after MES, making too much quantity requires more resources, increasing unit cost
11
New cards
Why Study Economics
* Tool to solve major issues with data
* Ex: Model how small changes affect poverty/education
* Make informed decisions like voting intelligently
* Well-rounded thinker
* Ex: Model how small changes affect poverty/education
* Make informed decisions like voting intelligently
* Well-rounded thinker
12
New cards
Economics Subject
Concerned with the well-being of *all* people, including those with jobs and those without jobs, as well as those with high incomes and those with low incomes
13
New cards
Microeconomics
Focuses on the actions of individual agents within the economy, like households, workers, and businesses
\
Theory Consumer Behavior: Budgets, choices, work, saving, borrowing
Theory of the Firm: Product and quantity choices, prices, production, # workers
\
Theory Consumer Behavior: Budgets, choices, work, saving, borrowing
Theory of the Firm: Product and quantity choices, prices, production, # workers
14
New cards
Macroeconomics
Focuses on broad issues such as growth, unemployment, inflation, deficits, and trade balance
Main Goals:
* Improve standard of living
* Decrease unemployment
* Decrease inflation
Main Goals:
* Improve standard of living
* Decrease unemployment
* Decrease inflation
15
New cards
Monetary policy
* Nation’s Central Bank (Federal Reserve)
* Policy that involves
* Altering the level of interest rates
* The availability of credit in the economy
* The extent of borrowing.
* Policy that involves
* Altering the level of interest rates
* The availability of credit in the economy
* The extent of borrowing.

16
New cards
Fiscal Policy
* Nation’s Legislative Body (Congress)
* Economic policies that involve
* Government spending
* Taxes
* Economic policies that involve
* Government spending
* Taxes

17
New cards
Classical vs. Keynesian Economics
Keynesian: Govt. should be involved because the market takes too long to correct itself (John Keynes)
Classical (laissez-faire): Let the free market decide
Classical (laissez-faire): Let the free market decide
18
New cards
Theory
* A simplified representation of how two or more variables interact with each other
* Simple enough to understand, while complex enough to capture the key features of the object or situation you are studying
* Simple enough to understand, while complex enough to capture the key features of the object or situation you are studying
19
New cards
Model v. Theory
Economists use **models** to test theories, but for this course we will use the terms model and theory interchangeably
\
y= B0 + B1 \* X1 + B2 \* X2 + e (everything else)
\
y= B0 + B1 \* X1 + B2 \* X2 + e (everything else)
20
New cards
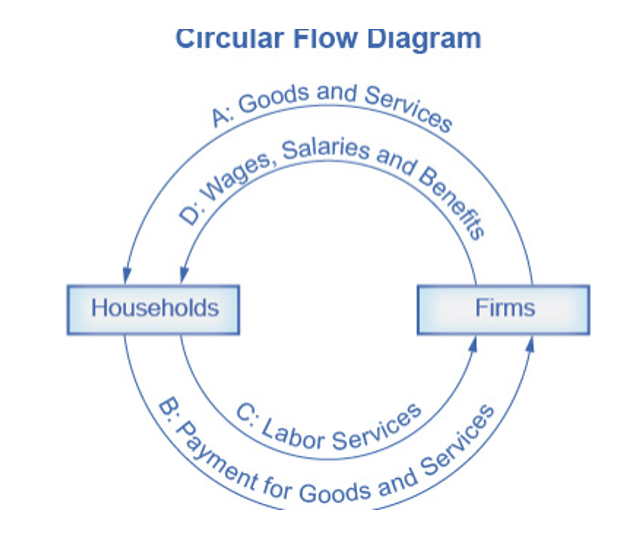
Circular Flow Diagram
* The **circular flow diagram** shows how households and firms interact in the goods and services market, and in the labor market.
* In the **goods and services market**, households receive goods and services and pay firms for them.
* In the **labor market**, households provide labor and receive payment from firms through wages, salaries, and benefits.
21
New cards
1) Traditional Economy
* Typically an agricultural economy where things are done the same as they have always been done
* Oldest economic system
* Used in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America
* Occupations tend to stay in the family
* What you produce is what you consume
* Little economic progress or development
* Oldest economic system
* Used in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America
* Occupations tend to stay in the family
* What you produce is what you consume
* Little economic progress or development
22
New cards
2) Command Economy
* An economy where economic decisions are passed down from government authority and where the government owns the resources.
* Very little trade between countries
* Government decides what goods and services will be produced and what prices it will charge for them.
* The government decides what methods of production to use and sets wages for workers.
* The government provides many necessities like healthcare and education for free
* Former USSR & communism, Current Cuba, N Korea
* Very little trade between countries
* Government decides what goods and services will be produced and what prices it will charge for them.
* The government decides what methods of production to use and sets wages for workers.
* The government provides many necessities like healthcare and education for free
* Former USSR & communism, Current Cuba, N Korea
23
New cards
3) Market Economy
* An economy where economic decisions are decentralized, private individuals own resources, and businesses supply goods and services based on demand.
* Income from what society values
* Income from what society values
24
New cards
Market
Interaction between potential buyers and sellers; a combination of demand and supply.
Ex: NYSE, NBA Signings
Ex: NYSE, NBA Signings
25
New cards
Private enterprise
System where private individuals or groups of private individuals own and operate the means of production (resources and businesses)
26
New cards
Reality of Economies
* Most economies in the real world are __mixed__. They combine elements of command, traditional, and market systems
* The U.S. economy is toward the market-oriented end
* Many European/S American market-oriented with more govt. involvement than US
* China & Russia more command, but have some market-oriented aspects
* The U.S. economy is toward the market-oriented end
* Many European/S American market-oriented with more govt. involvement than US
* China & Russia more command, but have some market-oriented aspects
27
New cards
Regulations
* There is no such thing as an absolutely free market
* Regulations always define the “rules of the game” in the economy
* Economies that are primarily market-oriented have fewer regulations
* Just enough to maintain an even playing field for participants (balance market freedom & govt. rules)
* Safeguard theft, outlaw violence, uphold contracts, collect taxes
28
New cards
Underground Economies
Markets where the buyers and sellers make transactions without the government’s approval where there are heavily regulated economies
29
New cards
Globalization
* The trend in which buying and selling in markets have increasingly crossed national borders
* Expanding cultural, political, and economies interactions
* Expanding cultural, political, and economies interactions
30
New cards
Exports
The goods and services that a nation produces domestically and sells abroad
31
New cards
Imports
The goods and services that are produced abroad and then sold domestically
32
New cards
**GDP**
Gross Domestic Product: measures the size of total production in an economy within country’s borders
33
New cards
Reasons for Globalization
* Cargo ships / planes
* Computing for long-distance communication
* Information
* Software / music
* International agreements
* Computing for long-distance communication
* Information
* Software / music
* International agreements
34
New cards
Exports / GDP
Production sold abroad
35
New cards
Net Export
Export - Import